InVivoMAb polyclonal Syrian hamster IgG
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Syrian hamster IgG |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107782 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
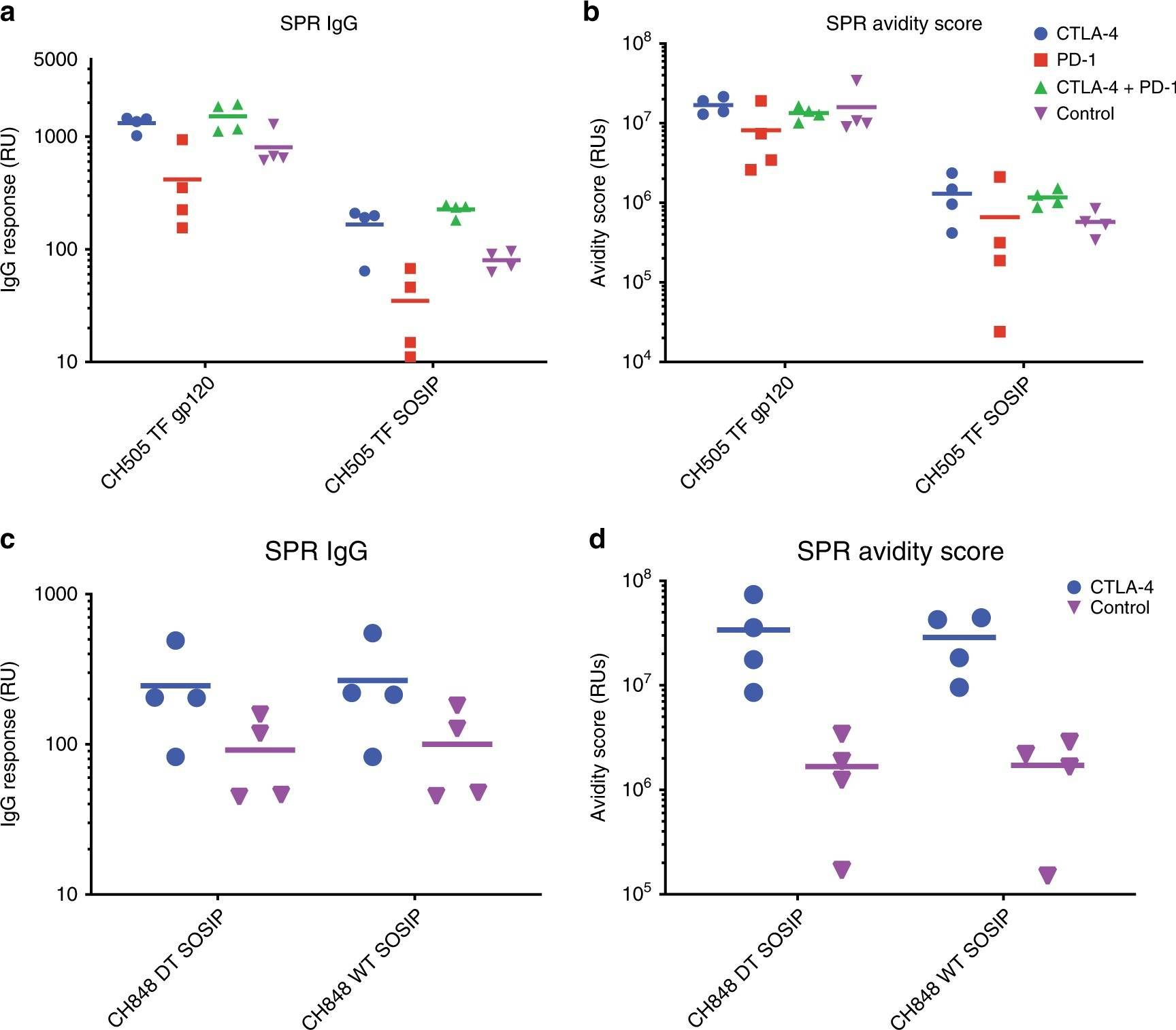
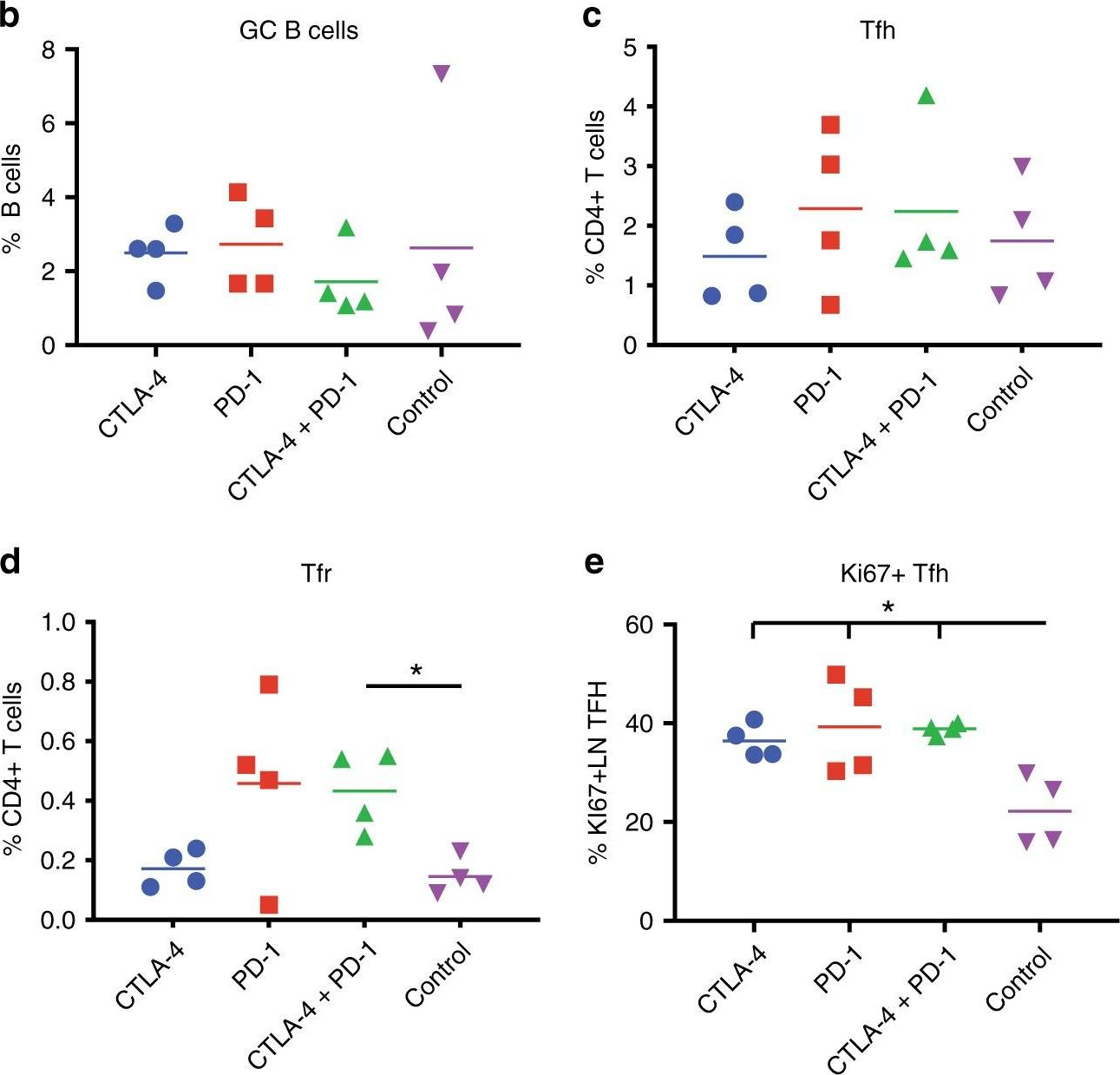
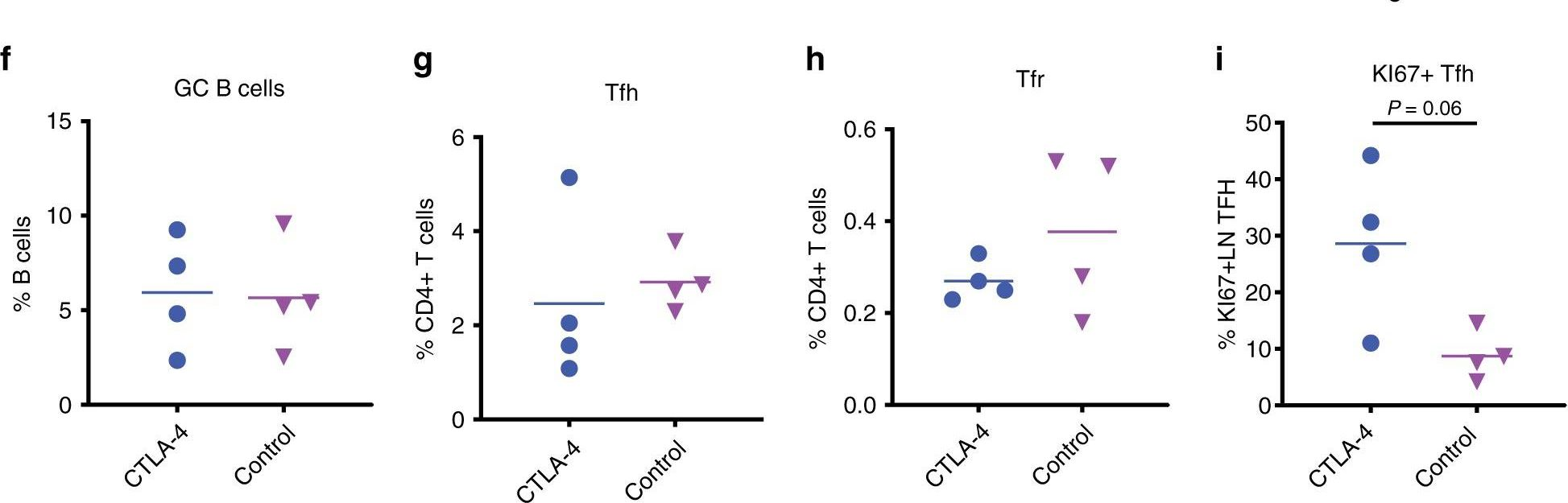
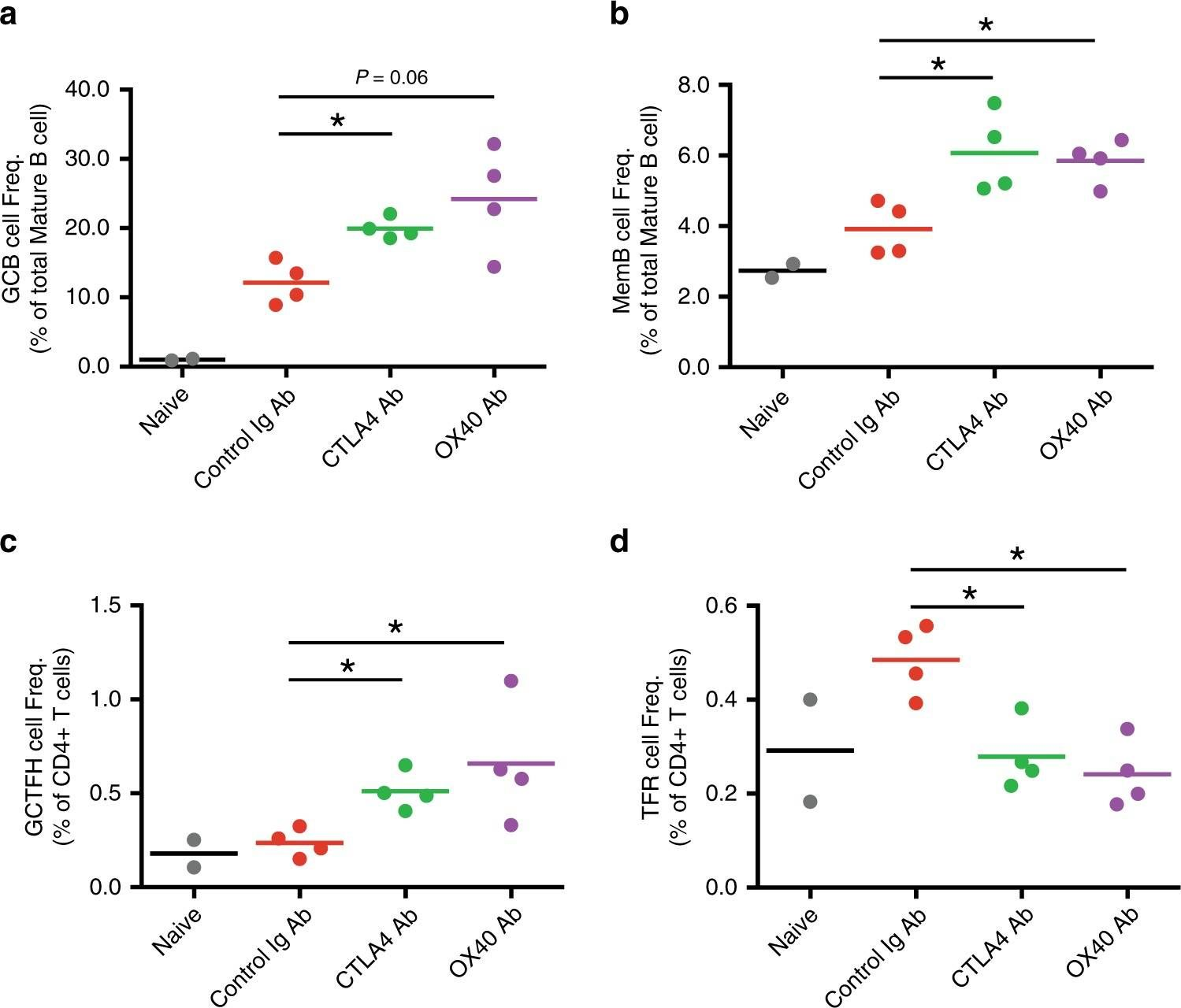
Bradley, T., et al (2020). "Immune checkpoint modulation enhances HIV-1 antibody induction" Nat Commun 11(1): 948.
PubMed
Eliciting protective titers of HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) is a goal of HIV-1 vaccine development, but current vaccine strategies have yet to induce bnAbs in humans. Many bnAbs isolated from HIV-1-infected individuals are encoded by immunoglobulin gene rearrangments with infrequent naive B cell precursors and with unusual genetic features that may be subject to host regulatory control. Here, we administer antibodies targeting immune cell regulatory receptors CTLA-4, PD-1 or OX40 along with HIV envelope (Env) vaccines to rhesus macaques and bnAb immunoglobulin knock-in (KI) mice expressing diverse precursors of CD4 binding site HIV-1 bnAbs. CTLA-4 blockade augments HIV-1 Env antibody responses in macaques, and in a bnAb-precursor mouse model, CTLA-4 blocking or OX40 agonist antibodies increase germinal center B and T follicular helper cells and plasma neutralizing antibodies. Thus, modulation of CTLA-4 or OX40 immune checkpoints during vaccination can promote germinal center activity and enhance HIV-1 Env antibody responses.
Klepsch, V., et al (2020). "Targeting the orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 in T cells primes tumors for immune checkpoint therapy" Cell Commun Signal 18(1): 8.
PubMed
BACKGROUND: NR2F6 has been proposed as an alternative cancer immune checkpoint in the effector T cell compartment. However, a realistic assessment of the in vivo therapeutic potential of NR2F6 requires acute depletion. METHODS: Employing primary T cells isolated from Cas9-transgenic mice for electroporation of chemically synthesized sgRNA, we established a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated acute knockout protocol of Nr2f6 in primary mouse T cells. RESULTS: Analyzing these Nr2f6(CRISPR/Cas9 knockout) T cells, we reproducibly observed a hyper-reactive effector phenotype upon CD3/CD28 stimulation in vitro, highly reminiscent to Nr2f6(-/-) T cells. Importantly, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Nr2f6 ablation prior to adoptive cell therapy (ACT) of autologous polyclonal T cells into wild-type tumor-bearing recipient mice in combination with PD-L1 or CTLA-4 tumor immune checkpoint blockade significantly delayed MC38 tumor progression and induced superior survival, thus further validating a T cell-inhibitory function of NR2F6 during tumor progression. CONCLUSIONS: These findings indicate that Nr2f6(CRISPR/Cas9 knockout) T cells are comparable to germline Nr2f6(-/-) T cells, a result providing an independent confirmation of the immune checkpoint function of lymphatic NR2F6. Taken together, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated acute Nr2f6 gene ablation in primary mouse T cells prior to ACT appeared feasible for potentiating established PD-L1 and CTLA-4 blockade therapies, thereby pioneering NR2F6 inhibition as a sensitizing target for augmented tumor regression. Video abstract.
Wang, Q., et al (2019). "Single-cell profiling guided combinatorial immunotherapy for fast-evolving CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant HER2-positive breast cancer" Nat Commun 10(1): 3817.
PubMed
Acquired resistance to targeted cancer therapy is a significant clinical challenge. In parallel with clinical trials combining CDK4/6 inhibitors to treat HER2+ breast cancer, we sought to prospectively model tumor evolution in response to this regimen in vivo and identify a clinically actionable strategy to combat drug resistance. Despite a promising initial response, acquired resistance emerges rapidly to the combination of anti-HER2/neu antibody and CDK4/6 inhibitor Palbociclib. Using high-throughput single-cell profiling over the course of treatments, we reveal a distinct immunosuppressive immature myeloid cell (IMC) population to infiltrate the resistant tumors. Guided by single-cell transcriptome analysis, we demonstrate that combination of IMC-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor cabozantinib and immune checkpoint blockade enhances anti-tumor immunity, and overcomes the resistance. Furthermore, sequential combinatorial immunotherapy enables a sustained control of the fast-evolving CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant tumors. Our study demonstrates a translational framework for treating rapidly evolving tumors through preclinical modeling and single-cell analyses.
Binnewies, M., et al (2019). "Unleashing Type-2 Dendritic Cells to Drive Protective Antitumor CD4(+) T Cell Immunity" Cell 177(3): 556-571.e516.
PubMed
Differentiation of proinflammatory CD4(+) conventional T cells (T(conv)) is critical for productive antitumor responses yet their elicitation remains poorly understood. We comprehensively characterized myeloid cells in tumor draining lymph nodes (tdLN) of mice and identified two subsets of conventional type-2 dendritic cells (cDC2) that traffic from tumor to tdLN and present tumor-derived antigens to CD4(+) T(conv), but then fail to support antitumor CD4(+) T(conv) differentiation. Regulatory T cell (T(reg)) depletion enhanced their capacity to elicit strong CD4(+) T(conv) responses and ensuing antitumor protection. Analogous cDC2 populations were identified in patients, and as in mice, their abundance relative to T(reg) predicts protective ICOS(+) PD-1(lo) CD4(+) T(conv) phenotypes and survival. Further, in melanoma patients with low T(reg) abundance, intratumoral cDC2 density alone correlates with abundant CD4(+) T(conv) and with responsiveness to anti-PD-1 therapy. Together, this highlights a pathway that restrains cDC2 and whose reversal enhances CD4(+) T(conv) abundance and controls tumor growth.
Su, W., et al (2019). "The Polycomb Repressor Complex 1 Drives Double-Negative Prostate Cancer Metastasis by Coordinating Stemness and Immune Suppression" Cancer Cell 36(2): 139-155.e110.
PubMed
The mechanisms that enable immune evasion at metastatic sites are poorly understood. We show that the Polycomb Repressor Complex 1 (PRC1) drives colonization of the bones and visceral organs in double-negative prostate cancer (DNPC). In vivo genetic screening identifies CCL2 as the top prometastatic gene induced by PRC1. CCL2 governs self-renewal and induces the recruitment of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages and regulatory T cells, thus coordinating metastasis initiation with immune suppression and neoangiogenesis. A catalytic inhibitor of PRC1 cooperates with immune checkpoint therapy to reverse these processes and suppress metastasis in genetically engineered mouse transplantation models of DNPC. These results reveal that PRC1 coordinates stemness with immune evasion and neoangiogenesis and point to the potential clinical utility of targeting PRC1 in DNPC.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Combination LIGHT overexpression and checkpoint blockade disrupts the tumor immune environment impacting colorectal liver metastases.
In Sci Adv on 10 October 2025 by Keenan, B. P., Qiao, G., et al.
PubMed
Colorectal cancer and liver metastases are a leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Overexpression of the immunostimulatory cytokine TNFSF14/LIGHT associates with improved survival and correlates with increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients and a clinically relevant model of colorectal liver metastases. We demonstrate that LIGHT monotherapy activates T cells, but also induces T cell exhaustion and the recruitment of immunosuppressive elements. As colorectal liver metastases exhibit high levels of CTLA-4 expression, we combined LIGHT overexpression with anti-CTLA-4, leading to complete tumor control. The combination functions by homing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, inducing tumor antigen-specific T cells, and reversing T cell exhaustion. Whereas both LIGHT overexpression and anti-CTLA-4 increase tumor-promoting macrophages, the combination eliminates this population. The ability of LIGHT overexpression combined with CTLA-4 inhibition to reverse T cell exhaustion and myeloid cell suppression is supported by analysis of complementary patient cohorts and has strong clinical relevance, especially given that liver metastases contribute to immunotherapy resistance across various cancer types.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Genetics
-
Cancer Research
Engineered exosomes with KrasG12D specific siRNA in pancreatic cancer: a phase I study with immunological correlates.
In Nat Commun on 30 September 2025 by LeBleu, V. S., Smaglo, B., et al.
PubMed
Oncogenic KRAS is amongst the key genetic drivers for initiation and maintenance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Here, we show that engineered exosomes with KrasG12D specific siRNA (iExoKrasG12D) reveal a biodistribution in pancreas with negligible toxicity in preclinical studies in mice and Rhesus macaques. Clinical testing of iExoKrasG12D in the iEXPLORE (iExoKrasG12D in Pancreatic Cancer) Phase I study employed a non-randomized single-arm classical 3 + 3 dose escalation design (Phase Ia), followed by an accelerated titration design (Phase Ib) (NCT03608631). The primary outcomes included safety, tolerability and target engagement, and the secondary outcomes aimed to assess disease control. Patients with advanced metastatic disease were enrolled after failure of multiple lines of therapy. iExoKrasG12D therapy was well-tolerated: the primary outcomes were met with iExoKrasG12D showing no dose-limiting toxicity. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached even at the highest dose. In some cases, iExoKrasG12D therapy was associated with stable disease response (secondary outcome). Downregulation of KRASG12D DNA and suppression of phospho-Erk was documented together with an increase in intratumoral CD8+ T cells following treatment. The CD8+ T cell recruitment priming by iExoKrasG12D informed on potential efficacy of immune checkpoint therapy and lead to validation testing in preclinical PDAC models. Combination therapy of iExoKrasG12D and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies, but not anti-PD1, revealed robust pre-clinical anti-tumor efficacy via FAS mediated CD8+ T cell anti-tumor activity. This first-in-human, precision medicine clinical trial and supporting preclinical functional studies offer new insights into priming of immunotherapy by oncogenic Kras inhibitor for future opportunistic combination therapy for PDAC patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Identification of anti-TIM-3 based checkpoint inhibitor combinations with activity in immunotherapy refractory melanoma models.
In J Immunother Cancer on 18 August 2025 by Phadke, M. S., Li, J., et al.
PubMed
A significant percentage of melanomas are refractory to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) monotherapies and combinations. As there are currently no effective second-line therapies available for ICI-resistant patients, we sought to identify novel checkpoint inhibitor combinations for future clinical evaluation.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Different tumour-resident memory T-cell subsets regulate responses to anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 cancer immunotherapies.
In Nat Commun on 1 July 2025 by Damei, I., Caidi, A., et al.
PubMed
The involvement of tumour-resident memory T (TRM) cells in responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors remains unclear. Here, we show that while CD103+CD8 TRM cells are involved in response to PD-1 blockade, CD49a+CD4 TRM cells are required for the response to anti-CTLA-4. Using preclinical mouse models, we demonstrate that the benefits of anti-PD-1 treatment are compromised in animals challenged with anti-CD8 and anti-CD103 blocking antibodies. By contrast, the benefits of anti-CTLA-4 are decreased by anti-CD4 and anti-CD49a neutralizing antibodies. Single-cell RNA sequencing on tumour-infiltrating T-lymphocytes (TIL) reveals a CD49a+CD4 TRM signature, enriched in Ctla-4 transcripts, exacerbated upon anti-CTLA-4. CTLA-4 blockade expands CD49a+CD4 TRM cells and increases tumour-specific CD4-TIL-mediated cytotoxicity. A CD49a+CD4 TRM signature enriched in CTLA-4 and cytotoxicity-linked transcripts is also identified in human TILs. Multiplex immunohistochemistry in a cohort of anti-CTLA-4-plus-anti-PD-1-treated melanomas reveals an increase in CD49a+CD4 T-cell density in pre-treatment tumours, which correlates with higher rates of patient progression-free survival. Thus, CD49a+CD4 TRM cells may correspond to a predictive biomarker of response to combined immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Fc-optimized anti-CTLA-4 antibodies increase tumor-associated high endothelial venules and sensitize refractory tumors to PD-1 blockade.
In Cell Rep Med on 17 June 2025 by Blanchard, L., Vina, E., et al.
PubMed
The lack of T cells in tumors is a major hurdle to successful immune checkpoint therapy (ICT). Therefore, therapeutic strategies promoting T cell recruitment into tumors are warranted to improve the treatment efficacy. Here, we report that Fc-optimized anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) antibodies are potent remodelers of tumor vasculature that increase tumor-associated high endothelial venules (TA-HEVs), specialized blood vessels supporting lymphocyte entry into tumors. Mechanistically, this effect is dependent on the Fc domain of anti-CTLA-4 antibodies and CD4+ T cells and involves interferon gamma (IFNγ). Unexpectedly, we find that the human anti-CTLA-4 antibody ipilimumab fails to increase TA-HEVs in a humanized mouse model. However, increasing its Fc effector function rescues the modulation of TA-HEVs, promotes CD4+ and CD8+ T cell infiltration into tumors, and sensitizes recalcitrant tumors to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade. Our findings suggest that Fc-optimized anti-CTLA-4 antibodies could be used to reprogram tumor vasculature in poorly immunogenic cold tumors and improve the efficacy of ICT.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Defining CDK12 as a tumor suppressor and therapeutic target in mouse models of tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma.
In Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A on 17 June 2025 by Tien, J. C., Zhai, Y., et al.
PubMed
Ovarian cancer is the sixth leading cause of cancer death among American women, with most fatalities attributable to tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC). This malignancy usually develops resistance to conventional chemotherapy, underscoring the need for robust preclinical models to guide the development of novel therapies. Here, we introduce an HGSC mouse model generated via Ovgp1-driven Cre recombinase effecting CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of Trp53, Rb1, and Nf1 tumor suppressors in mouse oviductal epithelium (m-sgPRN model). Cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12) inactivation-frequently observed in human HGSC-is associated with poorer outcomes, DNA damage accumulation (including tandem duplications), and increased tumor immunogenicity. In our system, coablation of Cdk12 (m-sgPRN;Cdk12KO) recapitulated hallmark features of HGSC, while accelerating tumor progression and reducing survival. In a conventional (Cre-lox-mediated) Trp53/Nf1/Rb1 triple knockout model with concurrent Cdk12 ablation (PRN;Cdk12KO mice), we observed T cell-rich immune infiltrates mirroring those seen clinically. We established both models as subcutaneous or intraperitoneal syngeneic allografts of CDK12-inactivated HGSC that exhibited sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Furthermore, a CRISPR/Cas9 synthetic lethality screen in PRN;Cdk12KO-derived cell lines identified CDK13-an essential paralog of CDK12-as the most depleted candidate, confirming a previously reported synthetic lethal interaction. Pharmacologic CDK13/12 degradation (employing YJ1206) demonstrated enhanced efficacy in cell lines derived from both m-sgPRN;Cdk12KO and PRN;Cdk12KO models. Our results define CDK12 as a key tumor suppressor in tubo-ovarian HGSC and highlight CDK13 targeting as a promising therapeutic approach in CDK12-inactive disease. Additionally, we have established valuable in vivo resources to facilitate further investigation and drug development in this challenging malignancy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Characterisation of an autochthonous mouse ccRCC model of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy resistance.
In Sci Rep on 5 June 2025 by Peighambari, A., Huang, H., et al.
PubMed
Many metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCC) are resistant to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies, however the mechanisms underlying sensitivity or resistance remain incompletely characterised. We demonstrate that ccRCCs in the Vhl/Trp53/Rb1 mutant mouse model are resistant to combined anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4 therapy alone and in combination with additional therapeutic agents that reflect current ccRCC clinical trials. However, in some animals in vivo checkpoint therapy allowed isolated splenic T cells to recognise cultured ccRCC cells from the same animal, implicating the tumour microenvironment in suppression of T cell activation. We identified putative immunosuppressive myeloid cell populations with features similar to myeloid cells in the microenvironment of human ccRCC. The expression patterns of immune checkpoint ligands in both the mouse model and in human ccRCC suggests that several checkpoint systems other than PD-1 and CTLA-4 are likely to represent the dominant T cell suppressive forces in ccRCC. Our findings characterise an autochthonous mouse ccRCC model of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy resistance and pave the way for a systematic functional dissection of the identified potential molecular barriers to effective immune therapy of ccRCC.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Antigen-presenting cancer-associated fibroblasts in murine pancreatic tumors differentially control regulatory T cell phenotype and function via CXCL9 and CCL22
In bioRxiv on 1 April 2025 by Maru, S. Y., Wetzel, M., et al.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
KRASG12D-Specific Targeting with Engineered Exosomes Reprograms the Immune Microenvironment to Enable Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Therapy in PDAC Patients
In medRxiv on 6 March 2025 by LeBleu, V. S., Smaglo, B. G., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Inhibitors of oncogenic Kras specifically prime CTLA4 blockade to transcriptionally reprogram Tregs and overcome resistance to suppress pancreas cancer
In bioRxiv on 4 March 2025 by Mahadevan, K. K., Maldonado, A. S., et al.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Molecular control of PDPNhi macrophage subset induction by ADAP as a host defense in sepsis.
In JCI Insight on 4 February 2025 by Zhang, P., Wang, X., et al.
PubMed
Induction of podoplanin (PDPN) expression is a critical response of macrophages to LPS stimulation or bacterial infection in sepsis, but how this key process of TLR4-stimulated PDPN upregulation is regulated and the effect of PDPN expression on macrophage function remain elusive. Here, we determined how this process is regulated in vitro and in vivo. PDPN failed to be upregulated in TLR4-stimulated macrophages deficient in adhesion and degranulation-promoting adapter protein (ADAP), which could be rescued by the reconstitution of ADAP. A distinct PDPNhi peritoneal macrophage (PM) subset, which exhibited an M2-like phenotype and enhanced phagocytic activity, was generated in WT but not in ADAP-deficient septic mice. The blockade of PDPNhi PMs mimicked the effect of ADAP deficiency, which exacerbated sepsis. Mechanistically, Bruton's tyrosine kinase-mediated (BTK-mediated) tyrosine phosphorylation of ADAP at Y571 worked together with mTOR to converge on STAT3 activation for the transactivation of the PDPN promoter. Moreover, agonist activation of STAT3 profoundly potentiated the PDPNhi PM subset generation and alleviated sepsis severity in mice. Together, our findings reveal a mechanism whereby ADAP resets macrophage function by controlling the TLR4-induced upregulation of PDPN as a host innate immune defense during sepsis.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
CDK8 remodels the tumor microenvironment to resist the therapeutic efficacy of targeted KRASG12Dinhibition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
In bioRxiv on 2 February 2025 by McAndrews, K. M., Mahadevan, K. K., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Development of Syngeneic Murine Glioma Models with Somatic Mismatch Repair Deficiency to Study Therapeutic Responses to Alkylating Agents and Immunotherapy.
In Curr Protoc on 1 February 2025 by Bhatt, D., Sundaram, R. K., et al.
PubMed
Glioblastoma (GBM) carries a dismal prognosis, with a median survival of less than 15 months. Temozolomide (TMZ), the standard frontline chemotherapeutic for GBM, is an alkylating agent that generates DNA O6-methylguanine (O6MeG) lesions. Without O6MeG-methyltransferase (MGMT), this lesion triggers the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway and leads to cytotoxicity via futile cycling. TMZ resistance frequently arises via the somatic acquisition of MMR deficiency (MMRd). Moreover, DNA-damaging agents have been shown capable of increasing tumor immunogenicity and improving response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), which has had limited success in glioma. The study of how alkylating chemotherapy such as TMZ impacts antitumor immunity in glioma has been hindered by a lack of immunocompetent models that incorporate relevant DNA repair genotypes. Here, we used CRISPR/Cas9 to generate models isogenic for knockout (KO) of Mlh1 in the syngeneic SB28 murine glioma cell line. MMR KO models readily formed intracranial tumors and exhibited in vitro and in vivo resistance to TMZ. In contrast, MMR KO cells maintained sensitivity to KL-50, a newly developed alkylating compound that exerts MGMT-dependent, MMR-independent cytotoxicity. Lastly, MMR KO tumors remained resistant to ICB, mirroring the lack of response seen in patients with somatic MMRd GBM. The development of syngeneic, immunologically cold glioma models with somatic loss of MMR will facilitate future studies on the immunomodulatory effects of alkylating agents in relevant DNA repair contexts, which will be vital for optimizing combinations with ICB. © 2025 Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Validation of mismatch repair knockouts and in vitro sensitivity to alkylating agents Basic Protocol 2: Stereotaxic injection of isogenic SB28 cells in female C57BL/6J mice and in vivo treatment.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome abrogates cardiotoxicity of immune checkpoint blockers.
In J Immunother Cancer on 7 January 2025 by Lu, Y., Gao, J., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized the treatment of many malignant tumors. However, ICI-induced hyper-immune activation causes cardiotoxicity. Traditional treatments such as glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants have limited effectiveness and may even accelerate tumor growth. This study aimed to identify approaches that effectively reduce cardiotoxicity and simultaneously preserve or enhance the antitumor immunity of ICI therapy.
-
-
CTLA4 blockade abrogates KEAP1/STK11-related resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibitors.
In Nature on 1 November 2024 by Skoulidis, F., Araújo, H. A., et al.
PubMed
For patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), dual immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) with CTLA4 inhibitors and PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors (hereafter, PD-(L)1 inhibitors) is associated with higher rates of anti-tumour activity and immune-related toxicities, when compared with treatment with PD-(L)1 inhibitors alone. However, there are currently no validated biomarkers to identify which patients will benefit from dual ICB1,2. Here we show that patients with NSCLC who have mutations in the STK11 and/or KEAP1 tumour suppressor genes derived clinical benefit from dual ICB with the PD-L1 inhibitor durvalumab and the CTLA4 inhibitor tremelimumab, but not from durvalumab alone, when added to chemotherapy in the randomized phase III POSEIDON trial3. Unbiased genetic screens identified loss of both of these tumour suppressor genes as independent drivers of resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition, and showed that loss of Keap1 was the strongest genomic predictor of dual ICB efficacy-a finding that was confirmed in several mouse models of Kras-driven NSCLC. In both mouse models and patients, KEAP1 and STK11 alterations were associated with an adverse tumour microenvironment, which was characterized by a preponderance of suppressive myeloid cells and the depletion of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, but relative sparing of CD4+ effector subsets. Dual ICB potently engaged CD4+ effector cells and reprogrammed the tumour myeloid cell compartment towards inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-expressing tumoricidal phenotypes that-together with CD4+ and CD8+ T cells-contributed to anti-tumour efficacy. These data support the use of chemo-immunotherapy with dual ICB to mitigate resistance to PD-(L)1 inhibition in patients with NSCLC who have STK11 and/or KEAP1 alterations.
-
-
Cancer Research
Modeling NK-cell lymphoma in mice reveals its cell-of-origin and microenvironmental changes and identifies therapeutic targets.
In Nat Commun on 22 October 2024 by Koya, J., Tanigawa, T., et al.
PubMed
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTCL) is an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-related neoplasm preferentially involving the upper aerodigestive tract. Here we show that NK-cell-specific Trp53 disruption in mice leads to the development of NK-cell lymphomas after long latency, which involve not only the hematopoietic system but also the salivary glands. Before tumor onset, Trp53 knockout causes extensive gene expression changes, resulting in immature NK-cell expansion, exclusively in the salivary glands. Both human and murine NK-cell lymphomas express tissue-resident markers, suggesting tissue-resident NK cells as their cell-of-origin. Murine NK-cell lymphomas show recurrent Myc amplifications and upregulation of MYC target gene signatures. EBV-encoded latent membrane protein 1 expression accelerates NK-cell lymphomagenesis and causes diverse microenvironmental changes, particularly myeloid propagation, through interferon-γ signaling. In turn, myeloid cells support tumor cells via CXCL16-CXCR6 signaling and its inhibition is effective against NK-cell tumors in vivo. Remarkably, KLRG1-expressing cells expand in the tumor and are capable of repopulating tumors in secondary recipients. Furthermore, targeting KLRG1 alone or combined with MYC inhibition using an eIF4 inhibitor is effective against NK-cell tumors. Therefore, our observations provide insights into the pathogenesis and highlight potential therapeutic targets, including CXCL16, KLRG1, and MYC, in ENKTCL, which can help improve its diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
CDK12 loss drives prostate cancer progression, transcription-replication conflicts, and synthetic lethality with paralog CDK13.
In Cell Rep Med on 15 October 2024 by Tien, J. C., Luo, J., et al.
PubMed
Biallelic loss of cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12) defines a metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) subtype. It remains unclear, however, whether CDK12 loss drives prostate cancer (PCa) development or uncovers pharmacologic vulnerabilities. Here, we show Cdk12 ablation in murine prostate epithelium is sufficient to induce preneoplastic lesions with lymphocytic infiltration. In allograft-based CRISPR screening, Cdk12 loss associates positively with Trp53 inactivation but negatively with Pten inactivation. Moreover, concurrent Cdk12/Trp53 ablation promotes proliferation of prostate-derived organoids, while Cdk12 knockout in Pten-null mice abrogates prostate tumor growth. In syngeneic systems, Cdk12/Trp53-null allografts exhibit luminal morphology and immune checkpoint blockade sensitivity. Mechanistically, Cdk12 inactivation mediates genomic instability by inducing transcription-replication conflicts. Strikingly, CDK12-mutant organoids and patient-derived xenografts are sensitive to inhibition or degradation of the paralog kinase, CDK13. We therein establish CDK12 as a bona fide tumor suppressor, mechanistically define how CDK12 inactivation causes genomic instability, and advance a therapeutic strategy for CDK12-mutant mCRPC.
-
-
TCF-1 and TOX regulate the memory formation of intestinal group 2 innate lymphoid cells in asthma.
In Nat Commun on 8 September 2024 by Bao, K., Gu, X., et al.
PubMed
Immune memory has been expanded to group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), but the cellular and molecular bases remain incompletely understood. Based on house dust mite (HDM)-induced mice asthma models and human samples, we applied flow cytometry, parabiosis, in vivo imaging and adoptive transplantation to confirm the persistence, migration and function of CD45+lineage-CD90.2+NK1.1-NKp46-ST2-KLRG1+IL-17RB+ memory-like ILC2s (ml-ILC2s). Regulated by CCR9/CCL25 and S1P signaling, ml-ILC2s reside in the lamina propria of small intestines (siLP) in asthma remission, and subsequently move to airway upon re-encountering antigens or alarmins. Furthermore, ml-ILC2s possess properties of longevity, potential of rapid proliferation and producing IL-13, and display transcriptional characteristics with up-regulation of Tox and Tcf-7. ml-ILC2s transplantation restore the asthmatic changes abrogated by Tox and Tcf7 knockdown. Our data identify siLP ml-ILC2s as a memory-like subset, which promotes asthma relapse. Targeting TCF-1 and TOX might be promising for preventing asthma recurrence.
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Type I conventional dendritic cells facilitate immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer.
In Science on 28 June 2024 by Mahadevan, K. K., Dyevoich, A. M., et al.
PubMed
Inflammation and tissue damage associated with pancreatitis can precede or occur concurrently with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We demonstrate that in PDAC coupled with pancreatitis (ptPDAC), antigen-presenting type I conventional dendritic cells (cDC1s) are specifically activated. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy (iCBT) leads to cytotoxic CD8+ T cell activation and elimination of ptPDAC with restoration of life span even upon PDAC rechallenge. Using PDAC antigen-loaded cDC1s as a vaccine, immunotherapy-resistant PDAC was rendered sensitive to iCBT with elimination of tumors. cDC1 vaccination coupled with iCBT identified specific CDR3 sequences in the tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells with potential therapeutic importance. This study identifies a fundamental difference in the immune microenvironment in PDAC concurrent with, or without, pancreatitis and provides a rationale for combining cDC1 vaccination with iCBT as a potential treatment option.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Transcriptomic, clonal, and functional analyses reveal Liver tissue-imprinted immuno-profile of circulating autoreactive CD4 T cells in autoimmune liver diseases
In bioRxiv on 29 March 2024 by Cardon, A., Guinebretière, T., et al.
-