InVivoMAb human IgG2 isotype control
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Human IgG2, λ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
<2EU/mg (<0.002EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from human myeloma serum |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2715459 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Human Pathogen Test Results |
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen: Negative Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 antibodies: Negative Human Immunodeficiency Virus 2 antibodies: Negative Hepatitis C Virus antibodies: Negative * These tests cannot guarantee the absence of infective agents |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
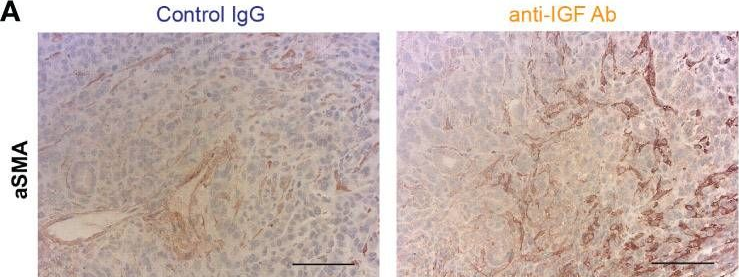
Inhibition of insulin-like growth factors increases production of CXCL9/10 by macrophages and fibroblasts and facilitates CD8+ cytotoxic T cell recruitment to pancreatic tumours.
In Front Immunol on 21 August 2024 by Freeman, P., Bellomo, G., et al.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly lethal malignancy with an urgent unmet clinical need for new therapies. Using a combination of in vitro assays and in vivo preclinical models we demonstrate that therapeutic inhibition of the IGF signalling axis promotes the accumulation of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells within the tumour microenvironment of PDAC tumours. Mechanistically, we show that IGF blockade promotes macrophage and fibroblast production of the chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 to facilitate CD8+ T cell recruitment and trafficking towards the PDAC tumour. Exploring this pathway further, we show that IGF inhibition leads to increased STAT1 transcriptional activity, correlating with a downregulation of the AKT/STAT3 signalling axis, in turn promoting Cxcl9 and Cxcl10 gene transcription. Using patient derived tumour explants, we also demonstrate that our findings translate into the human setting. PDAC tumours are frequently described as "immunologically cold", therefore bolstering CD8+ T cell recruitment to PDAC tumours through IGF inhibition may serve to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors which rely on the presence of CD8+ T cells in tumours.
-
-
-
In vitro experiments
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
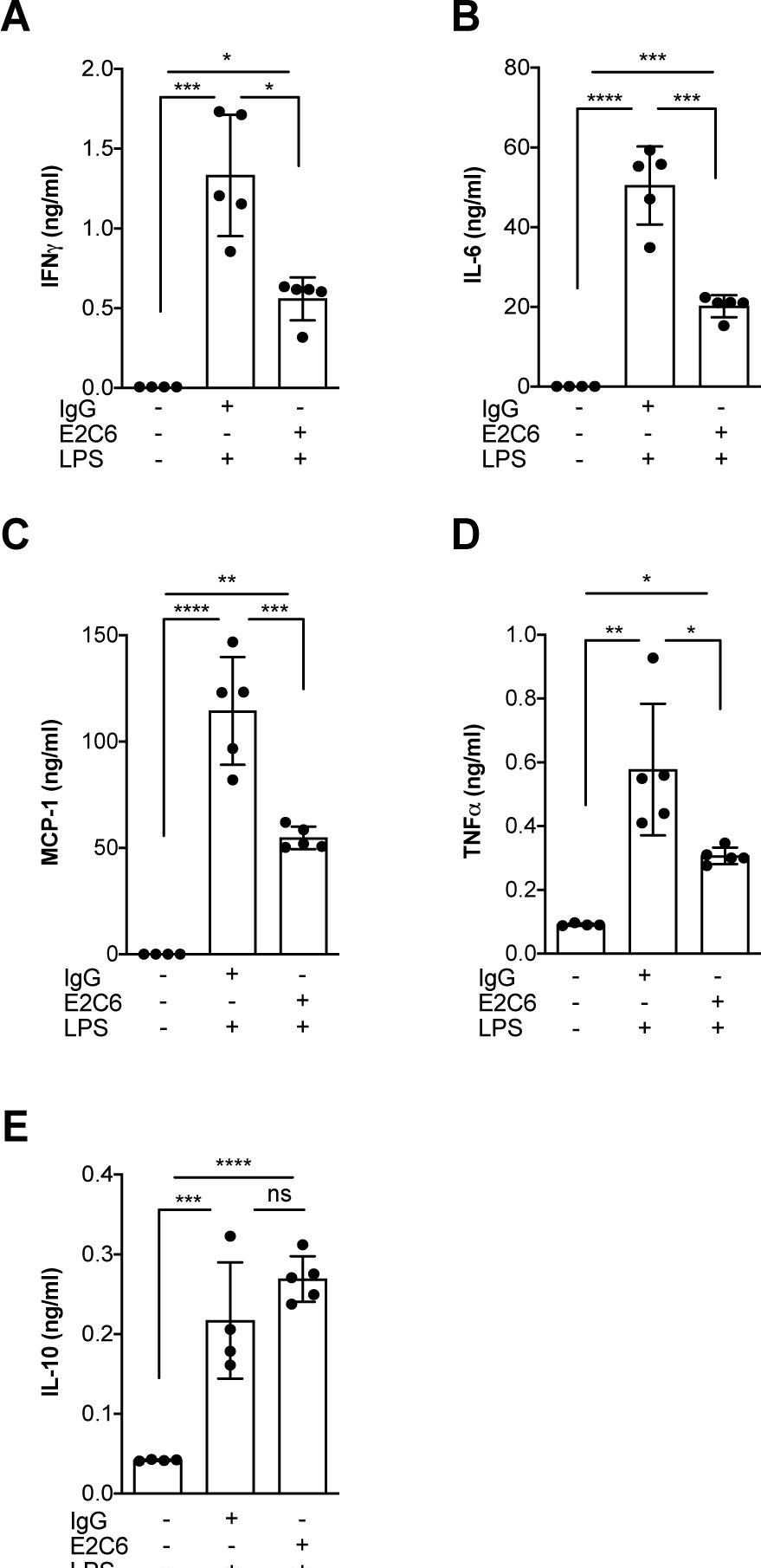
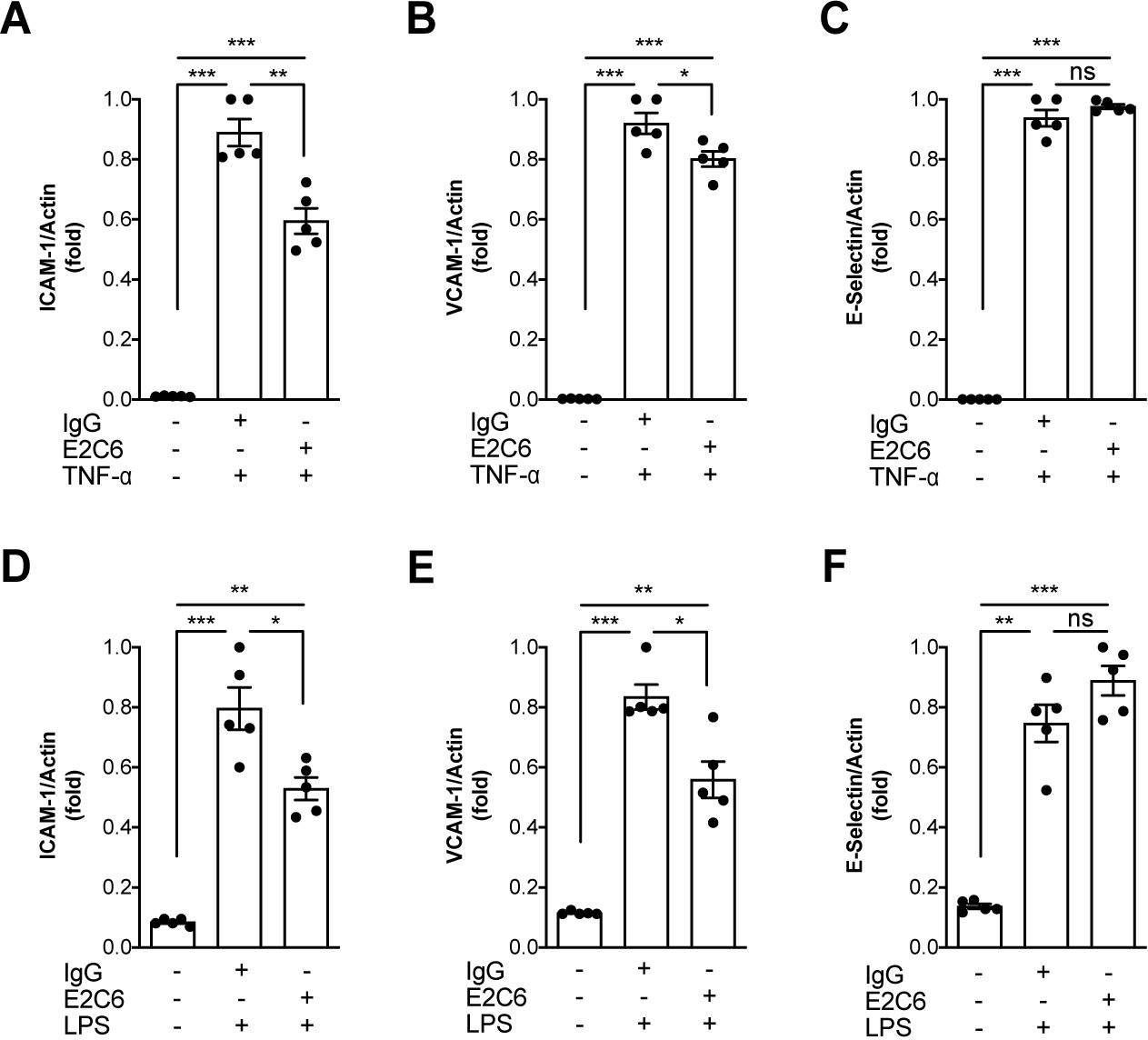
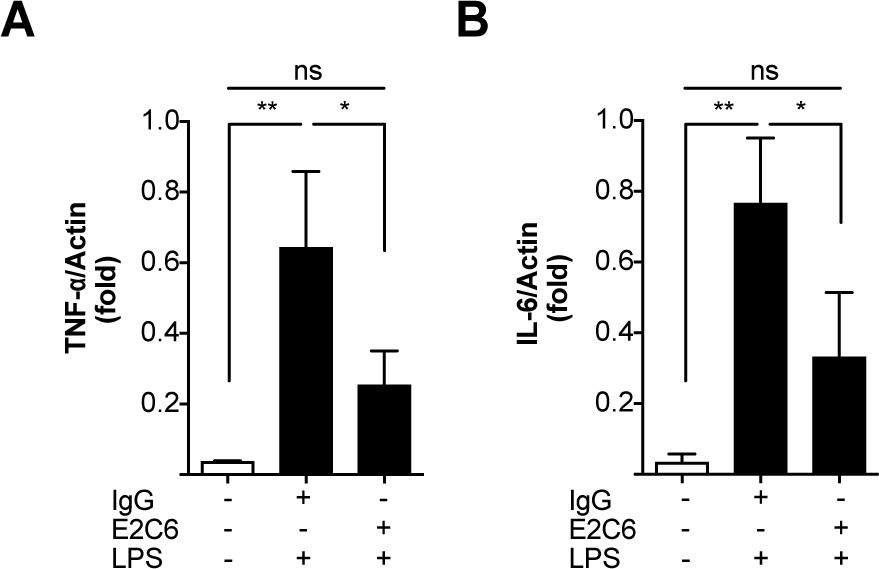
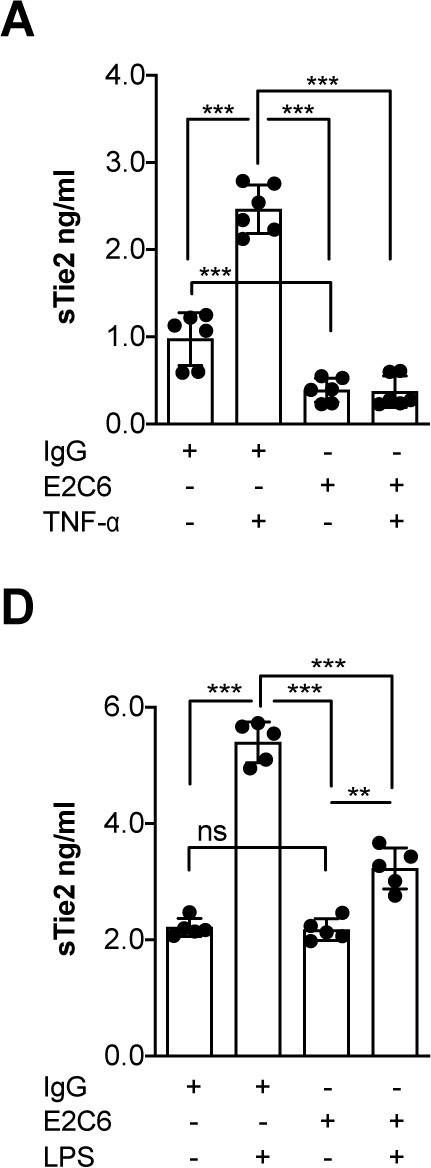
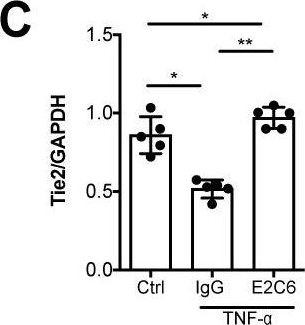
Identification of specific Tie2 cleavage sites and therapeutic modulation in experimental sepsis.
In Elife on 24 August 2020 by Idowu, T. O., Etzrodt, V., et al.
PubMed
Endothelial Tie2 signaling plays a pivotal role in vascular barrier maintenance at baseline and after injury. We previously demonstrated that a sharp drop in Tie2 expression observed across various murine models of critical illnesses is associated with increased vascular permeability and mortality. Matrix metalloprotease (MMP)-14-mediated Tie2 ectodomain shedding has recently been recognized as a possible mechanism for Tie2 downregulation in sepsis. Here, we identified the exact MMP14-mediated Tie2 ectodomain cleavage sites and could show that pharmacological MMP14 blockade in experimental murine sepsis exerts barrier protective and anti-inflammatory effects predominantly through the attenuation of Tie2 cleavage to improve survival both in a pre-treatment and rescue approach. Overall, we show that protecting Tie2 shedding might offer a new therapeutic opportunity for the treatment of septic vascular leakage.
-