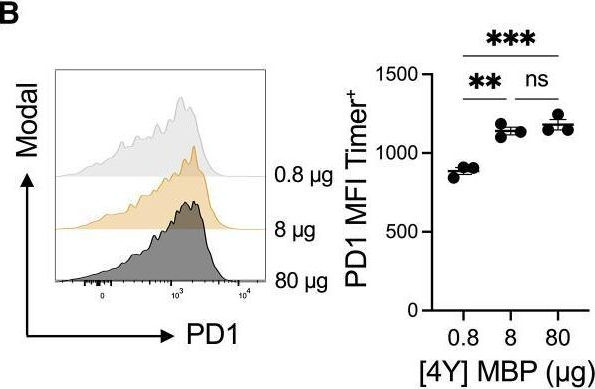
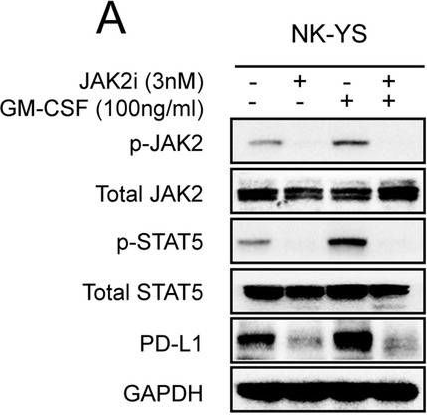
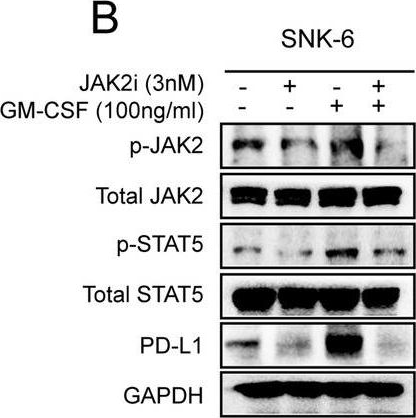
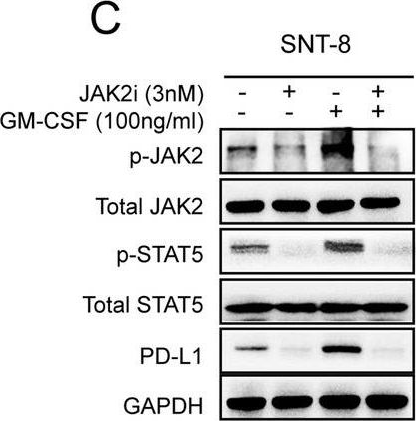
InVivoMAb anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Recombinant PD-1-Ig fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling in vitro PD-1 neutralization Immunohistochemistry (frozen) Immunofluorescence Western blot Flow cytometry in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_2687796 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip
Lidström T, Cumming J, Gaur R, Frängsmyr L, Pateras IS, Mickert MJ, Franklin O, Forsell MNE, Arnberg N, Dongre M, Patthey C, Öhlund D (2023). "Extracellular Galectin 4 Drives Immune Evasion and Promotes T-cell Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancer I
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is characterized by rich deposits of extracellular matrix (ECM), affecting the pathophysiology of the disease. Here, we identified galectin 4 (gal 4) as a cancer cell-produced protein that was deposited into the ECM of PDAC tumors and detected high-circulating levels of gal 4 in patients with PDAC. In orthotopic transplantation experiments, we observed increased infiltration of T cells and prolonged survival in immunocompetent mice transplanted with cancer cells with reduced expression of gal 4. Increased survival was not observed in immunodeficient RAG1-/- mice, demonstrating that the effect was mediated by the adaptive immune system. By performing single-cell RNA-sequencing, we found that the myeloid compartment and cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) subtypes were altered in the transplanted tumors. Reduced gal 4 expression associated with a higher proportion of myofibroblastic CAFs and reduced numbers of inflammatory CAFs. We also found higher proportions of M1 macrophages, T cells, and antigen-presenting dendritic cells in tumors with reduced gal 4 expression. Using a coculture system, we observed that extracellular gal 4 induced apoptosis in T cells by binding N-glycosylation residues on CD3ε/δ. Hence, we show that gal 4 is involved in immune evasion and identify gal 4 as a promising drug target for overcoming immunosuppression in PDAC.
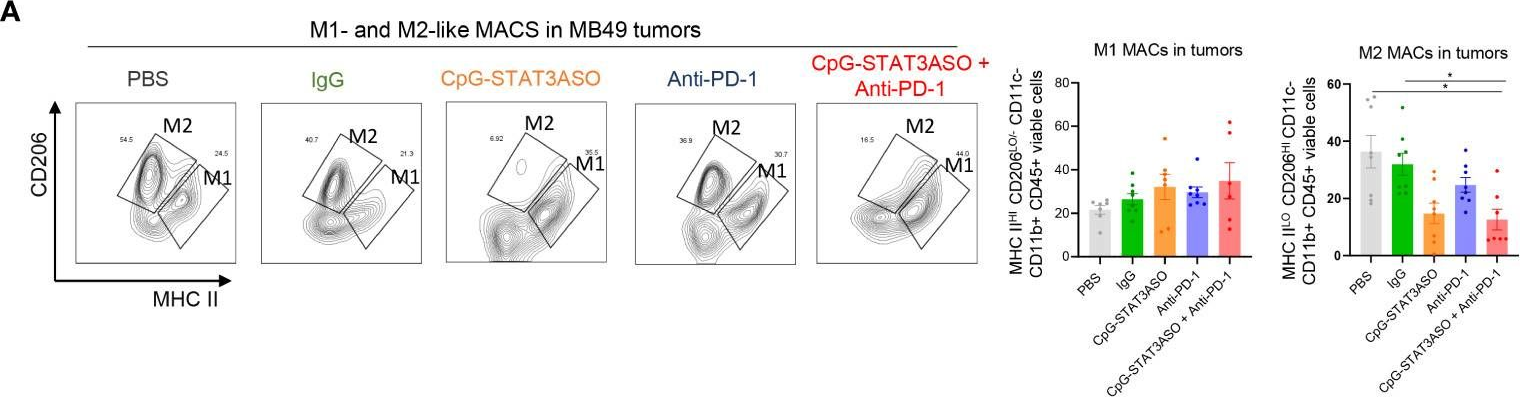
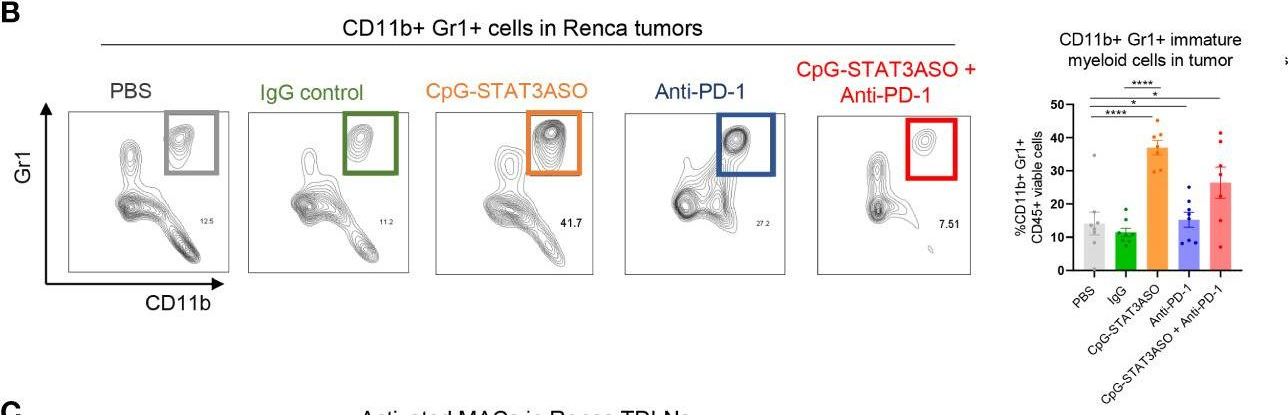
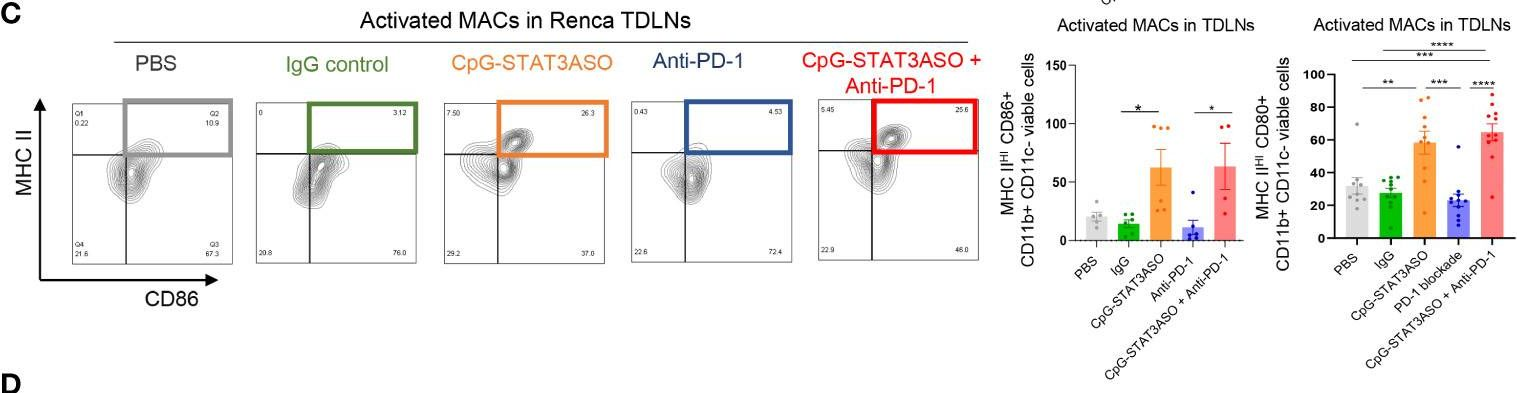
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Wang, W., et al (2018). "RIP1 Kinase Drives Macrophage-Mediated Adaptive Immune Tolerance in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancer Cell 34(5): 757-774 e757.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is characterized by immune tolerance and immunotherapeutic resistance. We discovered upregulation of receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1 (RIP1) in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in PDA. To study its role in oncogenic progression, we developed a selective small-molecule RIP1 inhibitor with high in vivo exposure. Targeting RIP1 reprogrammed TAMs toward an MHCII(hi)TNFalpha(+)IFNgamma(+) immunogenic phenotype in a STAT1-dependent manner. RIP1 inhibition in TAMs resulted in cytotoxic T cell activation and T helper cell differentiation toward a mixed Th1/Th17 phenotype, leading to tumor immunity in mice and in organotypic models of human PDA. Targeting RIP1 synergized with PD1-and inducible co-stimulator-based immunotherapies. Tumor-promoting effects of RIP1 were independent of its co-association with RIP3. Collectively, our work describes RIP1 as a checkpoint kinase governing tumor immunity.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Wang, W., et al (2018). "RIP1 Kinase Drives Macrophage-Mediated Adaptive Immune Tolerance in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancer Cell 34(5): 757-774 e757.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is characterized by immune tolerance and immunotherapeutic resistance. We discovered upregulation of receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1 (RIP1) in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in PDA. To study its role in oncogenic progression, we developed a selective small-molecule RIP1 inhibitor with high in vivo exposure. Targeting RIP1 reprogrammed TAMs toward an MHCII(hi)TNFalpha(+)IFNgamma(+) immunogenic phenotype in a STAT1-dependent manner. RIP1 inhibition in TAMs resulted in cytotoxic T cell activation and T helper cell differentiation toward a mixed Th1/Th17 phenotype, leading to tumor immunity in mice and in organotypic models of human PDA. Targeting RIP1 synergized with PD1-and inducible co-stimulator-based immunotherapies. Tumor-promoting effects of RIP1 were independent of its co-association with RIP3. Collectively, our work describes RIP1 as a checkpoint kinase governing tumor immunity.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Gordon, S. R., et al (2017). "PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity" Nature 545(7655): 495-499.
PubMed
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is an immune checkpoint receptor that is upregulated on activated T cells for the induction of immune tolerance. Tumour cells frequently overexpress the ligand for PD-1, programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), facilitating their escape from the immune system. Monoclonal antibodies that block the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1, by binding to either the ligand or receptor, have shown notable clinical efficacy in patients with a variety of cancers, including melanoma, colorectal cancer, non-small-cell lung cancer and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Although it is well established that PD-1-PD-L1 blockade activates T cells, little is known about the role that this pathway may have in tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs). Here we show that both mouse and human TAMs express PD-1. TAM PD-1 expression increases over time in mouse models of cancer and with increasing disease stage in primary human cancers. TAM PD-1 expression correlates negatively with phagocytic potency against tumour cells, and blockade of PD-1-PD-L1 in vivo increases macrophage phagocytosis, reduces tumour growth and lengthens the survival of mice in mouse models of cancer in a macrophage-dependent fashion. This suggests that PD-1-PD-L1 therapies may also function through a direct effect on macrophages, with substantial implications for the treatment of cancer with these agents.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Gordon, S. R., et al (2017). "PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity" Nature 545(7655): 495-499.
PubMed
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is an immune checkpoint receptor that is upregulated on activated T cells for the induction of immune tolerance. Tumour cells frequently overexpress the ligand for PD-1, programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), facilitating their escape from the immune system. Monoclonal antibodies that block the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1, by binding to either the ligand or receptor, have shown notable clinical efficacy in patients with a variety of cancers, including melanoma, colorectal cancer, non-small-cell lung cancer and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Although it is well established that PD-1-PD-L1 blockade activates T cells, little is known about the role that this pathway may have in tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs). Here we show that both mouse and human TAMs express PD-1. TAM PD-1 expression increases over time in mouse models of cancer and with increasing disease stage in primary human cancers. TAM PD-1 expression correlates negatively with phagocytic potency against tumour cells, and blockade of PD-1-PD-L1 in vivo increases macrophage phagocytosis, reduces tumour growth and lengthens the survival of mice in mouse models of cancer in a macrophage-dependent fashion. This suggests that PD-1-PD-L1 therapies may also function through a direct effect on macrophages, with substantial implications for the treatment of cancer with these agents.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Koyama, S., et al (2016). "STK11/LKB1 Deficiency Promotes Neutrophil Recruitment and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production to Suppress T-cell Activity in the Lung Tumor Microenvironment" Cancer Res 76(5): 999-1008.
PubMed
STK11/LKB1 is among the most commonly inactivated tumor suppressors in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), especially in tumors harboring KRAS mutations. Many oncogenes promote immune escape, undermining the effectiveness of immunotherapies, but it is unclear whether the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, such as STK11/LKB1, exerts similar effects. In this study, we investigated the consequences of STK11/LKB1 loss on the immune microenvironment in a mouse model of KRAS-driven NSCLC. Genetic ablation of STK11/LKB1 resulted in accumulation of neutrophils with T-cell-suppressive effects, along with a corresponding increase in the expression of T-cell exhaustion markers and tumor-promoting cytokines. The number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was also reduced in LKB1-deficient mouse and human tumors. Furthermore, STK11/LKB1-inactivating mutations were associated with reduced expression of PD-1 ligand PD-L1 in mouse and patient tumors as well as in tumor-derived cell lines. Consistent with these results, PD-1-targeting antibodies were ineffective against Lkb1-deficient tumors. In contrast, treating Lkb1-deficient mice with an IL6-neutralizing antibody or a neutrophil-depleting antibody yielded therapeutic benefits associated with reduced neutrophil accumulation and proinflammatory cytokine expression. Our findings illustrate how tumor suppressor mutations can modulate the immune milieu of the tumor microenvironment, and they offer specific implications for addressing STK11/LKB1-mutated tumors with PD-1-targeting antibody therapies.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Flow Cytometry
Koyama, S., et al (2016). "Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints" Nat Commun 7: 10501.
PubMed
Despite compelling antitumour activity of antibodies targeting the programmed death 1 (PD-1): programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) immune checkpoint in lung cancer, resistance to these therapies has increasingly been observed. In this study, to elucidate mechanisms of adaptive resistance, we analyse the tumour immune microenvironment in the context of anti-PD-1 therapy in two fully immunocompetent mouse models of lung adenocarcinoma. In tumours progressing following response to anti-PD-1 therapy, we observe upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints, notably T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 (TIM-3), in PD-1 antibody bound T cells and demonstrate a survival advantage with addition of a TIM-3 blocking antibody following failure of PD-1 blockade. Two patients who developed adaptive resistance to anti-PD-1 treatment also show a similar TIM-3 upregulation in blocking antibody-bound T cells at treatment failure. These data suggest that upregulation of TIM-3 and other immune checkpoints may be targetable biomarkers associated with adaptive resistance to PD-1 blockade.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Flow Cytometry
Koyama, S., et al (2016). "Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints" Nat Commun 7: 10501.
PubMed
Despite compelling antitumour activity of antibodies targeting the programmed death 1 (PD-1): programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) immune checkpoint in lung cancer, resistance to these therapies has increasingly been observed. In this study, to elucidate mechanisms of adaptive resistance, we analyse the tumour immune microenvironment in the context of anti-PD-1 therapy in two fully immunocompetent mouse models of lung adenocarcinoma. In tumours progressing following response to anti-PD-1 therapy, we observe upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints, notably T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 (TIM-3), in PD-1 antibody bound T cells and demonstrate a survival advantage with addition of a TIM-3 blocking antibody following failure of PD-1 blockade. Two patients who developed adaptive resistance to anti-PD-1 treatment also show a similar TIM-3 upregulation in blocking antibody-bound T cells at treatment failure. These data suggest that upregulation of TIM-3 and other immune checkpoints may be targetable biomarkers associated with adaptive resistance to PD-1 blockade.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Koyama, S., et al (2016). "STK11/LKB1 Deficiency Promotes Neutrophil Recruitment and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production to Suppress T-cell Activity in the Lung Tumor Microenvironment" Cancer Res 76(5): 999-1008.
PubMed
STK11/LKB1 is among the most commonly inactivated tumor suppressors in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), especially in tumors harboring KRAS mutations. Many oncogenes promote immune escape, undermining the effectiveness of immunotherapies, but it is unclear whether the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, such as STK11/LKB1, exerts similar effects. In this study, we investigated the consequences of STK11/LKB1 loss on the immune microenvironment in a mouse model of KRAS-driven NSCLC. Genetic ablation of STK11/LKB1 resulted in accumulation of neutrophils with T-cell-suppressive effects, along with a corresponding increase in the expression of T-cell exhaustion markers and tumor-promoting cytokines. The number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was also reduced in LKB1-deficient mouse and human tumors. Furthermore, STK11/LKB1-inactivating mutations were associated with reduced expression of PD-1 ligand PD-L1 in mouse and patient tumors as well as in tumor-derived cell lines. Consistent with these results, PD-1-targeting antibodies were ineffective against Lkb1-deficient tumors. In contrast, treating Lkb1-deficient mice with an IL6-neutralizing antibody or a neutrophil-depleting antibody yielded therapeutic benefits associated with reduced neutrophil accumulation and proinflammatory cytokine expression. Our findings illustrate how tumor suppressor mutations can modulate the immune milieu of the tumor microenvironment, and they offer specific implications for addressing STK11/LKB1-mutated tumors with PD-1-targeting antibody therapies.
in vitro PD-1 neutralization
Park, S. J., et al (2014). "Negative role of inducible PD-1 on survival of activated dendritic cells" J Leukoc Biol 95(4): 621-629.
PubMed
PD-1 is a well-established negative regulator of T cell responses by inhibiting proliferation and cytokine production of T cells via interaction with its ligands, B7-H1 (PD-L1) and B7-DC (PD-L2), expressed on non-T cells. Recently, PD-1 was found to be expressed in innate cells, including activated DCs, and plays roles in suppressing production of inflammatory cytokines. In this study, we demonstrate that PD-1 KO DCs exhibited prolonged longevity compared with WT DCs in the dLNs after transfer of DCs into hind footpads. Interestingly, upon LPS stimulation, WT DCs increased the expression of PD-1 and started to undergo apoptosis. DCs, in spleen of LPS-injected PD-1 KO mice, were more resistant to LPS-mediated apoptosis in vivo than WT controls. Moreover, treatment of blocking anti-PD-1 mAb during DC maturation resulted in enhanced DC survival, suggesting that PD-1:PD-L interactions are involved in DC apoptosis. As a result, PD-1-deficient DCs augmented T cell responses in terms of antigen-specific IFN-gamma production and proliferation of CD4 and CD8 T cells to a greater degree than WT DCs. Moreover, PD-1 KO DCs exhibited increased MAPK1 and CD40-CD40L signaling, suggesting a possible mechanism for enhanced DC survival in the absence of PD-1 expression. Taken together, our findings further extend the function of PD-1, which plays an important role in apoptosis of activated DCs and provides important implications for PD-1-mediated immune regulation.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Cooper, Z. A., et al (2014). "Response to BRAF inhibition in melanoma is enhanced when combined with immune checkpoint blockade" Cancer Immunol Res 2(7): 643-654.
PubMed
BRAF-targeted therapy results in objective responses in the majority of patients; however, the responses are short lived ( approximately 6 months). In contrast, treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors results in a lower response rate, but the responses tend to be more durable. BRAF inhibition results in a more favorable tumor microenvironment in patients, with an increase in CD8(+) T-cell infiltrate and a decrease in immunosuppressive cytokines. There is also increased expression of the immunomodulatory molecule PDL1, which may contribute to the resistance. On the basis of these findings, we hypothesized that BRAF-targeted therapy may synergize with the PD1 pathway blockade to enhance antitumor immunity. To test this hypothesis, we developed a BRAF(V600E)/Pten(-/-) syngeneic tumor graft immunocompetent mouse model in which BRAF inhibition leads to a significant increase in the intratumoral CD8(+) T-cell density and cytokine production, similar to the effects of BRAF inhibition in patients. In this model, CD8(+) T cells were found to play a critical role in the therapeutic effect of BRAF inhibition. Administration of anti-PD1 or anti-PDL1 together with a BRAF inhibitor led to an enhanced response, significantly prolonging survival and slowing tumor growth, as well as significantly increasing the number and activity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. These results demonstrate synergy between combined BRAF-targeted therapy and immune checkpoint blockade. Although clinical trials combining these two strategies are ongoing, important questions still remain unanswered. Further studies using this new melanoma mouse model may provide therapeutic insights, including optimal timing and sequence of therapy.
in vitro PD-1 neutralization
Park, S. J., et al (2014). "Negative role of inducible PD-1 on survival of activated dendritic cells" J Leukoc Biol 95(4): 621-629.
PubMed
PD-1 is a well-established negative regulator of T cell responses by inhibiting proliferation and cytokine production of T cells via interaction with its ligands, B7-H1 (PD-L1) and B7-DC (PD-L2), expressed on non-T cells. Recently, PD-1 was found to be expressed in innate cells, including activated DCs, and plays roles in suppressing production of inflammatory cytokines. In this study, we demonstrate that PD-1 KO DCs exhibited prolonged longevity compared with WT DCs in the dLNs after transfer of DCs into hind footpads. Interestingly, upon LPS stimulation, WT DCs increased the expression of PD-1 and started to undergo apoptosis. DCs, in spleen of LPS-injected PD-1 KO mice, were more resistant to LPS-mediated apoptosis in vivo than WT controls. Moreover, treatment of blocking anti-PD-1 mAb during DC maturation resulted in enhanced DC survival, suggesting that PD-1:PD-L interactions are involved in DC apoptosis. As a result, PD-1-deficient DCs augmented T cell responses in terms of antigen-specific IFN-gamma production and proliferation of CD4 and CD8 T cells to a greater degree than WT DCs. Moreover, PD-1 KO DCs exhibited increased MAPK1 and CD40-CD40L signaling, suggesting a possible mechanism for enhanced DC survival in the absence of PD-1 expression. Taken together, our findings further extend the function of PD-1, which plays an important role in apoptosis of activated DCs and provides important implications for PD-1-mediated immune regulation.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Cooper, Z. A., et al (2014). "Response to BRAF inhibition in melanoma is enhanced when combined with immune checkpoint blockade" Cancer Immunol Res 2(7): 643-654.
PubMed
BRAF-targeted therapy results in objective responses in the majority of patients; however, the responses are short lived ( approximately 6 months). In contrast, treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors results in a lower response rate, but the responses tend to be more durable. BRAF inhibition results in a more favorable tumor microenvironment in patients, with an increase in CD8(+) T-cell infiltrate and a decrease in immunosuppressive cytokines. There is also increased expression of the immunomodulatory molecule PDL1, which may contribute to the resistance. On the basis of these findings, we hypothesized that BRAF-targeted therapy may synergize with the PD1 pathway blockade to enhance antitumor immunity. To test this hypothesis, we developed a BRAF(V600E)/Pten(-/-) syngeneic tumor graft immunocompetent mouse model in which BRAF inhibition leads to a significant increase in the intratumoral CD8(+) T-cell density and cytokine production, similar to the effects of BRAF inhibition in patients. In this model, CD8(+) T cells were found to play a critical role in the therapeutic effect of BRAF inhibition. Administration of anti-PD1 or anti-PDL1 together with a BRAF inhibitor led to an enhanced response, significantly prolonging survival and slowing tumor growth, as well as significantly increasing the number and activity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. These results demonstrate synergy between combined BRAF-targeted therapy and immune checkpoint blockade. Although clinical trials combining these two strategies are ongoing, important questions still remain unanswered. Further studies using this new melanoma mouse model may provide therapeutic insights, including optimal timing and sequence of therapy.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vitro PD-1 neutralization
Duraiswamy, J., et al (2013). "Dual blockade of PD-1 and CTLA-4 combined with tumor vaccine effectively restores T-cell rejection function in tumors" Cancer Res 73(12): 3591-3603.
PubMed
Tumor progression is facilitated by regulatory T cells (Treg) and restricted by effector T cells. In this study, we document parallel regulation of CD8(+) T cells and Foxp3(+) Tregs by programmed death-1 (PD-1, PDCD1). In addition, we identify an additional role of CTL antigen-4 (CTLA-4) inhibitory receptor in further promoting dysfunction of CD8(+) T effector cells in tumor models (CT26 colon carcinoma and ID8-VEGF ovarian carcinoma). Two thirds of CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) expressed PD-1, whereas one third to half of CD8(+) TIL coexpressed PD-1 and CTLA-4. Double-positive (PD-1(+)CTLA-4(+)) CD8(+) TIL had characteristics of more severe dysfunction than single-positive (PD-1(+) or CTLA-4(+)) TIL, including an inability to proliferate and secrete effector cytokines. Blockade of both PD-1 and CTLA-4 resulted in reversal of CD8(+) TIL dysfunction and led to tumor rejection in two thirds of mice. Double blockade was associated with increased proliferation of antigen-specific effector CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells, antigen-specific cytokine release, inhibition of suppressive functions of Tregs, and upregulation of key signaling molecules critical for T-cell function. When used in combination with GVAX vaccination (consisting of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-expressing irradiated tumor cells), inhibitory pathway blockade induced rejection of CT26 tumors in 100% of mice and ID8-VEGF tumors in 75% of mice. Our study indicates that PD-1 signaling in tumors is required for both suppressing effector T cells and maintaining tumor Tregs, and that PD-1/PD-L1 pathway (CD274) blockade augments tumor inhibition by increasing effector T-cell activity, thereby attenuating Treg suppression.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
in vitro PD-1 neutralization
Duraiswamy, J., et al (2013). "Dual blockade of PD-1 and CTLA-4 combined with tumor vaccine effectively restores T-cell rejection function in tumors" Cancer Res 73(12): 3591-3603.
PubMed
Tumor progression is facilitated by regulatory T cells (Treg) and restricted by effector T cells. In this study, we document parallel regulation of CD8(+) T cells and Foxp3(+) Tregs by programmed death-1 (PD-1, PDCD1). In addition, we identify an additional role of CTL antigen-4 (CTLA-4) inhibitory receptor in further promoting dysfunction of CD8(+) T effector cells in tumor models (CT26 colon carcinoma and ID8-VEGF ovarian carcinoma). Two thirds of CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) expressed PD-1, whereas one third to half of CD8(+) TIL coexpressed PD-1 and CTLA-4. Double-positive (PD-1(+)CTLA-4(+)) CD8(+) TIL had characteristics of more severe dysfunction than single-positive (PD-1(+) or CTLA-4(+)) TIL, including an inability to proliferate and secrete effector cytokines. Blockade of both PD-1 and CTLA-4 resulted in reversal of CD8(+) TIL dysfunction and led to tumor rejection in two thirds of mice. Double blockade was associated with increased proliferation of antigen-specific effector CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells, antigen-specific cytokine release, inhibition of suppressive functions of Tregs, and upregulation of key signaling molecules critical for T-cell function. When used in combination with GVAX vaccination (consisting of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-expressing irradiated tumor cells), inhibitory pathway blockade induced rejection of CT26 tumors in 100% of mice and ID8-VEGF tumors in 75% of mice. Our study indicates that PD-1 signaling in tumors is required for both suppressing effector T cells and maintaining tumor Tregs, and that PD-1/PD-L1 pathway (CD274) blockade augments tumor inhibition by increasing effector T-cell activity, thereby attenuating Treg suppression.
Flow Cytometry
Good-Jacobson, K. L., et al (2012). "CD80 expression on B cells regulates murine T follicular helper development, germinal center B cell survival, and plasma cell generation" J Immunol 188(9): 4217-4225.
PubMed
Germinal center (GC) B cells and T follicular helper (T(FH)) cells interact in the production of high-affinity long-lived plasma cells (PCs) and memory B cells, although the mechanisms regulating the formation of these long-lived populations remain unclear. Because CD80 is one of the few markers shared by human and murine memory B cells, we investigated its role in the development of GCs, memory cells, and PCs. In CD80-deficient mice, fewer long-lived PCs were generated upon immunization compared with that in B6 controls. In concert, the absence of CD80 resulted in an increase in apoptotic GC B cells during the contraction phase of the GC. CD80(-/-) mice had fewer T(FH) cells compared with that of B6, and residual T(FH) cells failed to mature, with decreased ICOS and PD-1 expression and decreased synthesis of IL-21 mRNA. Mixed bone marrow chimeras demonstrated a B cell-intrinsic requirement for CD80 expression for normal T(FH) cell and PC development. Therefore, B cell expression of CD80 plays a critical role in regulating B-T interactions in both early and late GC responses. This, in turn, results in impaired ability to produce long-lived PCs. These data provide new insights into the development of GCs and Ab-forming cells and the functions of CD80 in humoral immunity.
Flow Cytometry
Good-Jacobson, K. L., et al (2012). "CD80 expression on B cells regulates murine T follicular helper development, germinal center B cell survival, and plasma cell generation" J Immunol 188(9): 4217-4225.
PubMed
Germinal center (GC) B cells and T follicular helper (T(FH)) cells interact in the production of high-affinity long-lived plasma cells (PCs) and memory B cells, although the mechanisms regulating the formation of these long-lived populations remain unclear. Because CD80 is one of the few markers shared by human and murine memory B cells, we investigated its role in the development of GCs, memory cells, and PCs. In CD80-deficient mice, fewer long-lived PCs were generated upon immunization compared with that in B6 controls. In concert, the absence of CD80 resulted in an increase in apoptotic GC B cells during the contraction phase of the GC. CD80(-/-) mice had fewer T(FH) cells compared with that of B6, and residual T(FH) cells failed to mature, with decreased ICOS and PD-1 expression and decreased synthesis of IL-21 mRNA. Mixed bone marrow chimeras demonstrated a B cell-intrinsic requirement for CD80 expression for normal T(FH) cell and PC development. Therefore, B cell expression of CD80 plays a critical role in regulating B-T interactions in both early and late GC responses. This, in turn, results in impaired ability to produce long-lived PCs. These data provide new insights into the development of GCs and Ab-forming cells and the functions of CD80 in humoral immunity.
Immunofluorescence
Western Blot
Chen, L., et al (2009). "Role of the immune modulator programmed cell death-1 during development and apoptosis of mouse retinal ganglion cells" Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(10): 4941-4948.
PubMed
PURPOSE: Mammalian programmed cell death (PD)-1 is a membrane-associated receptor regulating the balance between T-cell activation, tolerance, and immunopathology; however, its role in neurons has not yet been defined. The hypothesis that PD-1 signaling actively promotes retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death within the developing mouse retina was investigated. METHODS: Mature retinal cell types expressing PD-1 were identified by immunofluorescence staining of vertical retina sections; developmental expression was localized by immunostaining and quantified by Western blot analysis. PD-1 involvement in developmental RGC survival was assessed in vitro using retinal explants and in vivo using PD-1 knockout mice. PD-1 ligand gene expression was detected by RT-PCR. RESULTS: PD-1 is expressed in most adult RGCs and undergoes dynamic upregulation during the early postnatal window of retinal cell maturation and physiological programmed cell death (PCD). In vitro blockade of PD-1 signaling during this time selectively increases the survival of RGCs. Furthermore, PD-1-deficient mice show a selective increase in RGC number in the neonatal retina at the peak of developmental RGC death. Lastly, gene expression of the immune PD-1 ligand genes Pdcd1lg1 and Pdcd1lg2 was found throughout postnatal retina maturation. CONCLUSIONS: These findings collectively support a novel role for a PD-1-mediated signaling pathway in developmental PCD during postnatal RGC maturation.
Immunofluorescence
Western Blot
Chen, L., et al (2009). "Role of the immune modulator programmed cell death-1 during development and apoptosis of mouse retinal ganglion cells" Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(10): 4941-4948.
PubMed
PURPOSE: Mammalian programmed cell death (PD)-1 is a membrane-associated receptor regulating the balance between T-cell activation, tolerance, and immunopathology; however, its role in neurons has not yet been defined. The hypothesis that PD-1 signaling actively promotes retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death within the developing mouse retina was investigated. METHODS: Mature retinal cell types expressing PD-1 were identified by immunofluorescence staining of vertical retina sections; developmental expression was localized by immunostaining and quantified by Western blot analysis. PD-1 involvement in developmental RGC survival was assessed in vitro using retinal explants and in vivo using PD-1 knockout mice. PD-1 ligand gene expression was detected by RT-PCR. RESULTS: PD-1 is expressed in most adult RGCs and undergoes dynamic upregulation during the early postnatal window of retinal cell maturation and physiological programmed cell death (PCD). In vitro blockade of PD-1 signaling during this time selectively increases the survival of RGCs. Furthermore, PD-1-deficient mice show a selective increase in RGC number in the neonatal retina at the peak of developmental RGC death. Lastly, gene expression of the immune PD-1 ligand genes Pdcd1lg1 and Pdcd1lg2 was found throughout postnatal retina maturation. CONCLUSIONS: These findings collectively support a novel role for a PD-1-mediated signaling pathway in developmental PCD during postnatal RGC maturation.
Immunohistochemistry (frozen)
Menke, J., et al (2007). "Programmed death 1 ligand (PD-L) 1 and PD-L2 limit autoimmune kidney disease: distinct roles" J Immunol 179(11): 7466-7477.
PubMed
The programmed death 1/programmed death 1 ligand (PD-L) pathway is instrumental in peripheral tolerance. Blocking this pathway exacerbates experimental autoimmune diseases, but its role in autoimmune kidney disease has not been explored. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that the programmed death 1 ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2), provide a protective barrier during T cell- and macrophage (Mphi)-dependent autoimmune kidney disease. For this purpose, we compared nephrotoxic serum nephritis (NSN) in mice lacking PD-L1 (PD-L1(-/-)), PD-L2 (PD-L2(-/-)), or both (PD-L1/L2(-/-)) to wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice. Kidney pathology, loss of renal function, and intrarenal leukocyte infiltrates were increased in each PD-L(-/-) strain as compared with WT mice. Although the magnitude of renal pathology was similar in PD-L1(-/-) and PD-L2(-/-) mice, our findings suggest that kidney disease in each strain is regulated by distinct mechanisms. Specifically, we detected increased CD68(+) cells along with elevated circulating IgG and IgG deposits in glomeruli in PD-L2(-/-) mice, but not PD-L1(-/-) mice. In contrast, we detected a rise in activated CD8(+) T cells in PD-L1(-/-) mice, but not PD-L2(-/-) mice. Furthermore, since PD-L1 is expressed by parenchymal and hemopoietic cells in WT kidneys, we explored the differential impact of PD-L1 expression on these cell types by inducing NSN in bone marrow chimeric mice. Our results indicate that PD-L1 expression on hemopoietic cells, and not parenchymal cells, is primarily responsible for limiting leukocyte infiltration during NSN. Taken together, our findings indicate that PD-L1 and PD-L2 provide distinct negative regulatory checkpoints poised to suppress autoimmune renal disease.
Immunohistochemistry (frozen)
Menke, J., et al (2007). "Programmed death 1 ligand (PD-L) 1 and PD-L2 limit autoimmune kidney disease: distinct roles" J Immunol 179(11): 7466-7477.
PubMed
The programmed death 1/programmed death 1 ligand (PD-L) pathway is instrumental in peripheral tolerance. Blocking this pathway exacerbates experimental autoimmune diseases, but its role in autoimmune kidney disease has not been explored. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that the programmed death 1 ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2), provide a protective barrier during T cell- and macrophage (Mphi)-dependent autoimmune kidney disease. For this purpose, we compared nephrotoxic serum nephritis (NSN) in mice lacking PD-L1 (PD-L1(-/-)), PD-L2 (PD-L2(-/-)), or both (PD-L1/L2(-/-)) to wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice. Kidney pathology, loss of renal function, and intrarenal leukocyte infiltrates were increased in each PD-L(-/-) strain as compared with WT mice. Although the magnitude of renal pathology was similar in PD-L1(-/-) and PD-L2(-/-) mice, our findings suggest that kidney disease in each strain is regulated by distinct mechanisms. Specifically, we detected increased CD68(+) cells along with elevated circulating IgG and IgG deposits in glomeruli in PD-L2(-/-) mice, but not PD-L1(-/-) mice. In contrast, we detected a rise in activated CD8(+) T cells in PD-L1(-/-) mice, but not PD-L2(-/-) mice. Furthermore, since PD-L1 is expressed by parenchymal and hemopoietic cells in WT kidneys, we explored the differential impact of PD-L1 expression on these cell types by inducing NSN in bone marrow chimeric mice. Our results indicate that PD-L1 expression on hemopoietic cells, and not parenchymal cells, is primarily responsible for limiting leukocyte infiltration during NSN. Taken together, our findings indicate that PD-L1 and PD-L2 provide distinct negative regulatory checkpoints poised to suppress autoimmune renal disease.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Barber, D. L., et al (2006). "Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection" Nature 439(7077): 682-687.
PubMed
Functional impairment of antigen-specific T cells is a defining characteristic of many chronic infections, but the underlying mechanisms of T-cell dysfunction are not well understood. To address this question, we analysed genes expressed in functionally impaired virus-specific CD8 T cells present in mice chronically infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), and compared these with the gene profile of functional memory CD8 T cells. Here we report that PD-1 (programmed death 1; also known as Pdcd1) was selectively upregulated by the exhausted T cells, and that in vivo administration of antibodies that blocked the interaction of this inhibitory receptor with its ligand, PD-L1 (also known as B7-H1), enhanced T-cell responses. Notably, we found that even in persistently infected mice that were lacking CD4 T-cell help, blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathway had a beneficial effect on the ‘helpless’ CD8 T cells, restoring their ability to undergo proliferation, secrete cytokines, kill infected cells and decrease viral load. Blockade of the CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4) inhibitory pathway had no effect on either T-cell function or viral control. These studies identify a specific mechanism of T-cell exhaustion and define a potentially effective immunological strategy for the treatment of chronic viral infections.
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling
Barber, D. L., et al (2006). "Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection" Nature 439(7077): 682-687.
PubMed
Functional impairment of antigen-specific T cells is a defining characteristic of many chronic infections, but the underlying mechanisms of T-cell dysfunction are not well understood. To address this question, we analysed genes expressed in functionally impaired virus-specific CD8 T cells present in mice chronically infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), and compared these with the gene profile of functional memory CD8 T cells. Here we report that PD-1 (programmed death 1; also known as Pdcd1) was selectively upregulated by the exhausted T cells, and that in vivo administration of antibodies that blocked the interaction of this inhibitory receptor with its ligand, PD-L1 (also known as B7-H1), enhanced T-cell responses. Notably, we found that even in persistently infected mice that were lacking CD4 T-cell help, blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathway had a beneficial effect on the ‘helpless’ CD8 T cells, restoring their ability to undergo proliferation, secrete cytokines, kill infected cells and decrease viral load. Blockade of the CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4) inhibitory pathway had no effect on either T-cell function or viral control. These studies identify a specific mechanism of T-cell exhaustion and define a potentially effective immunological strategy for the treatment of chronic viral infections.
Immunohistochemistry (frozen)
Liang, S. C., et al (2003). "Regulation of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 expression during normal and autoimmune responses" Eur J Immunol 33(10): 2706-2716.
PubMed
Newer members of the B7-CD28 superfamily include the receptor PD-1 and its two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. Here, we characterize the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in tissues of naive miceand in target organs from two models of autoimmunity, the pancreas from non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice and brain from mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). In naive mice, proteiexpression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 was detected in the thymus, while PD-1 and PD-L1 were detected in the spleen. PD-L1, but not PD-L2, was also detected at low levels on cardiac endothelium, pancreatic islets, and syncyciotrophoblasts in the placenta. In pre-diabetic NOD mice, PD-1 and PD-L1 were expressed on infiltrating cells in the pancreatic islets. Furthermore, PD-L1 was markedly up-regulated on islet cells. In brains from mice with EAE, PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 were expressed on infiltrating inflammatory cells, and PD-L1 was up-regulated on endothelium within EAE brain. The distinct expression patterns of PD-L1 and PD-L2 led us to compare their transcriptional regulation in STAT4(-/-), STAT6(-/-), or NF-kappaB p50(-/-)p65(+/-) dendritic cells (DC).PD-L2, but not PD-L1, expression was dramatically reduced in p50(-/-)p65(+/-) DC. Thus, PD-L1 and PD-L2 exhibit distinct expression patterns and are differentially regulated on the transcriptional level.
Immunohistochemistry (frozen)
Liang, S. C., et al (2003). "Regulation of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 expression during normal and autoimmune responses" Eur J Immunol 33(10): 2706-2716.
PubMed
Newer members of the B7-CD28 superfamily include the receptor PD-1 and its two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. Here, we characterize the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in tissues of naive miceand in target organs from two models of autoimmunity, the pancreas from non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice and brain from mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). In naive mice, proteiexpression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 was detected in the thymus, while PD-1 and PD-L1 were detected in the spleen. PD-L1, but not PD-L2, was also detected at low levels on cardiac endothelium, pancreatic islets, and syncyciotrophoblasts in the placenta. In pre-diabetic NOD mice, PD-1 and PD-L1 were expressed on infiltrating cells in the pancreatic islets. Furthermore, PD-L1 was markedly up-regulated on islet cells. In brains from mice with EAE, PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 were expressed on infiltrating inflammatory cells, and PD-L1 was up-regulated on endothelium within EAE brain. The distinct expression patterns of PD-L1 and PD-L2 led us to compare their transcriptional regulation in STAT4(-/-), STAT6(-/-), or NF-kappaB p50(-/-)p65(+/-) dendritic cells (DC).PD-L2, but not PD-L1, expression was dramatically reduced in p50(-/-)p65(+/-) DC. Thus, PD-L1 and PD-L2 exhibit distinct expression patterns and are differentially regulated on the transcriptional level.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Targeting the atypical chemokine receptor 2 (Ackr2) improves the benefit of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma mouse model.
In Oncoimmunology on 1 December 2025 by Noman, M. Z., Szpakowska, M., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies, such as anti-PD-1, have transformed cancer treatment, but many patients do not respond due to a non-inflammatory tumor microenvironment (TME). Here, we investigated the impact of targeting Atypical Chemokine Receptor 2 (ACKR2), which scavenges key chemokines involved in immune cell recruitment, on the improvement of anti-PD-1-based therapy. In a melanoma mouse model, we demonstrated that Ackr2 inhibition increases the release of proinflammatory chemokines CCL5 and CXCL10 and enhances the infiltration of NK cells, activated CD8+ and CD4+ effector T cells while reducing regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the TME. Targeting Ackr2 led to tumor growth inhibition, improved survival, and enhanced response to anti-PD-1 therapy. In BRAF- and NRAS-mutant melanoma patients, low ACKR2 expression or high CCL5/CXCL10 levels correlated with improved survival and higher CD8+ T cell markers. Targeting ACKR2 represents a promising approach for developing combination therapies, particularly for 'cold' ICB resistant tumors.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling of HNSCC identifies AMIGO2 as a therapeutic target modulating tumor microenvironment.
In NPJ Precis Oncol on 18 November 2025 by Liu, G., Yao, X., et al.
PubMed
Extensive studies have demonstrated the relationship between metabolic reprogramming and the tumor microenvironment. Here, we characterized the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) evolutionary landscape using spatial metabolomics/transcriptomics, single-cell transcriptomics, and bulk multi-omics. Metabolic heterogeneity during HNSCC malignant transformation was identified, with significant enrichment in the purine metabolism. Integrating single-cell and bulk data, we developed a robust ligand-receptor-based signature (LRS) linked to NT5E, a key upstream regulator of purine metabolism, which served as an independent prognostic indicator. The low LRS subtype was associated with a high proportion of immune cell infiltration and improved response to immunotherapy. Notably, in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that AMIGO2, a core molecule within the LRS, regulates tumor-associated purine metabolism, and that its downregulation suppresses tumor cell invasion and migration, inhibits myofibroblast differentiation, and promotes immune effector cell infiltration. Moreover, combining AMIGO2 targeting with anti-PD-1 therapy yielded superior efficacy. Consistent validation was also obtained in a clinical cohort of HNSCC and premalignancy patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
An immunometabolic prodrug strategy overcomes DHODH inhibitor resistance in refractory melanoma.
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 14 November 2025 by Hai, Y., Wang, W., et al.
PubMed
Metabolic reprogramming, particularly upregulated de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis, drives cancer progression and immune evasion. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a key enzyme in this pathway, is a promising therapeutic target, but its inhibitors often face resistance in immune-refractory melanoma, linked to low basal stimulator of interferon genes (STING) expression.
-
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Brain tumors induce widespread disruption of calvarial bone and alteration of skull marrow immune landscape.
In Nat Neurosci on 1 November 2025 by Dubey, A., Yamashita, E., et al.
PubMed
The skull marrow niche has recently been identified as a reservoir that supplies the brain with monocytes and neutrophils in the context of disease and injury, but its role in brain cancers remains unknown. Here we show that glioblastoma, the most malignant type of brain tumor, induces calvarial bone abnormalities in murine models and patients with glioblastoma, altering osteoclast activities and increasing the number of skull channels in mice. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed glioblastoma-mediated alterations in the immune landscape of skull marrow and femoral bone marrow, including expansion of neutrophils and deterioration of various B cell subsets. In vivo inhibition of bone resorption reduced bone abnormalities, but promoted tumor progression in mesenchymal subtype tumors. This also abolished the survival benefit of the checkpoint inhibitor anti-PD-L1, by reducing activated T cell and increasing inflammatory neutrophil numbers. Together, these data provide insight into how brain tumors affect skull bone and the immune environment.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
TRIM32 promotes tumor immune evasion and impedes Anti-PD-1 treatment by inducing immunosuppressive macrophages in gastric cancer.
In J Transl Med on 29 October 2025 by Wang, C., Zhu, X., et al.
PubMed
The tumor microenvironment (TME) in gastric cancer (GC) exhibits immunosuppressive features that facilitate tumor advancement and obstruct the effectiveness of immunotherapy. The role of tripartite motif 32 (TRIM32) in the TME has not been extensively studied.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Molecular glue degrader function of SPOP enhances STING-dependent immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma models.
In J Clin Invest on 28 October 2025 by Zhu, Z., Zhou, X., et al.
PubMed
The E3 ligase SPOP plays a context-dependent role in cancer by targeting specific cellular proteins for degradation, thereby influencing cell behavior. However, its role in tumor immunity remains largely unexplored. In this study, we revealed that SPOP targeted the innate immune sensor STING for degradation in a CK1γ phosphorylation-dependent manner to promote melanoma growth. Stabilization of STING by escaping SPOP-mediated degradation enhanced anti-tumor immunity by increasing IFNβ production and ISG expression. Notably, small-molecule SPOP inhibitors not only blocked STING recognition by SPOP, but also acted as molecular glues, redirecting SPOP to target neo-substrates such as CBX4 for degradation. This CBX4 degradation led to increased DNA damage, which in turn activated STING and amplified innate immune responses. In a xenografted melanoma B16 tumor model, single-cell RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that SPOP inhibition induced the infiltration of immune cells associated with anti-PD1 responses. Consequently, SPOP inhibitors synergized with immune checkpoint blockade to suppress B16 tumor growth in syngeneic murine models and enhanced the efficacy of CD19-CAR-T therapy. Our findings highlight a molecular glue degrader property of SPOP inhibitors, with potential implications for other E3 ligase-targeting small molecules designed to disrupt protein-protein interactions.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
FASN inhibits ferroptosis in breast cancer via USP5 palmitoylation-dependent regulation of GPX4 deubiquitination.
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 14 October 2025 by Qian, Z., Jiang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Increasing studies have reported that dysregulated lipid metabolism is an independent risk factor for breast cancer (BC); it would be, therefore, enlightening to investigate the relationship between metabolic reprogramming and the tumor microenvironment in the future. Ferroptosis, a novel form of programmed cell death, is characterized by glutathione (GSH) depletion and inactivation of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), the central regulator of the antioxidant system. While the close association between fatty acid metabolism and ferroptosis has been studied in various diseases, the interplay between the key fatty acid metabolic enzyme fatty acid synthase (FASN) and ferroptosis in BC remains unexplored. At the beginning of the current study, we demonstrated that FASN expression positively correlates with an immune-cold tumor microenvironment in BC. Subsequent findings revealed that FASN knockdown promotes GPX4 degradation-induced ferroptosis, thereby enhancing the efficacy of anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) immunotherapy. Co-immunoprecipitation coupled with mass spectrometry (IP/MS) and co-IP experiments demonstrated that ubiquitin specific protease 5 (USP5) stabilizes GPX4 by binding to and deubiquitinating it. Furthermore, knockdown of FASN inhibited the palmitoylation of USP5, reducing its interaction with GPX4 and consequently increasing GPX4 ubiquitination and degradation. Our results demonstrate that FASN suppresses ferroptosis in BC by stabilizing GPX4 via USP5-mediated mechanisms, highlighting FASN inhibition as a potential therapeutic approach to enhance immunotherapy response.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Enhancing anti-tumor immunity by targeting BATF and the STAT1/PD-L1 pathway in cervical carcinoma.
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 11 October 2025 by Peng, X., Zhu, Y., et al.
PubMed
Cervical carcinoma remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women worldwide, with poor prognosis often linked to immune evasion mechanisms. The Basic Leucine Zipper Activating Transcription Factor (BATF) has emerged as a critical regulator of T-cell functionality, yet its role in cervical cancer progression and immune modulation remains poorly understood. This study investigates the role of BATF in cervical carcinoma, focusing on its effects on tumor progression, immune modulation, and immune checkpoint regulation, to identify BATF as a therapeutic target to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
RTP4 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Progression via MHC-I-Mediated CD8+ T Cell Infiltration and Enhances Immunotherapy Response.
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 October 2025 by Yu, C., Li, Y., et al.
PubMed
While RTP4 is known to regulate odorant receptor trafficking, its role in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear. This study investigates the clinical relevance and functional mechanisms of RTP4 in CRC. Comprehensive analyses revealed significant downregulation of RTP4 expression in CRC tissues, correlating with poor patient prognosis. RTP4 expression showed strong associations with immune-related genes, biological processes and anti-tumour immune cell infiltration. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that RTP4 upregulates MHC-I expression, which enhances CD8+ T cell recruitment and strengthens anti-tumour immunity in both cellular and animal models. Furthermore, RTP4 overexpression markedly improved the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. All in all, our findings establish RTP4 as a dual-functional biomarker for prognosis prediction and a potential target to enhance immunotherapy responsiveness in CRC.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Targeting IGF1R Overcomes Armored and Cold Tumor Microenvironment and Boosts Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 October 2025 by Wan, M., Mei, J., et al.
PubMed
In the previous study, patients with tumors based on collagen deposition and immunoreactivity are classified and identified the armored & cold subtype as the most treatment-refractory tumor type. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most lethal tumor type globally, making it critical to overcome the armored and cold tumor microenvironment (TME) for effective treatment of these patients. In this study, the transcriptomic collagen activity and immune profiles of cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) are analyzed, and found that intratumoral collagen is associated with an unfavorable immunotherapeutic response and T cell exhaustion. Additionally, collagen is shown to regulate IGF1R expression at both transcriptional and post-translational levels via SOX4 and DDR1, respectively. It is also found that IGF1R promotes tumor cell migration and invasion, as well as T cell exhaustion, with these effects mediated through collagen. Moreover, in vivo inhibition of IGF1R reversed the armored & cold TME, thereby enhancing anti-PD-1 therapy. In conclusion, this study identified IGF1R as a novel therapeutic target for the immuno-collagenic subtype, and combining IGF1R inhibition with anti-PD-1 therapy provides a promising foundation for a novel combination immunotherapy regimen for TNBC.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Nuclear glycine decarboxylase suppresses STAT1-dependent MHC-I and promotes cancer immune evasion.
In EMBO J on 1 October 2025 by Liu, R., Li, H. F., et al.
PubMed
Inadequate antigen presentation by MHC-I in tumor microenvironment (TME) is a common immune escape mechanism. Here, we show that glycine decarboxylase (GLDC), a key enzyme in glycine metabolism, functions as an inhibitor of MHC-I expression in EGFR-activated tumor cells to induce immune escape by a mechanism independent of its enzymatic activity. Upon EGFR activation, GLDC is phosphorylated by SRC and subsequently translocated to the nucleus in human NSCLC cells. Nuclear GLDC sequesters STAT1 co-activator SMARCE1, inhibiting STAT1-dependent transcription of the inflammatory genes IRF1 and NLRC5. Further, GLDC recruits DNMT1 to the IRF1/NLRC5 promoter inducing DNA hypermethylation, suppressing transcription of downstream MHC-I genes. Inhibition of GLDC restores MHC-I levels in tumor cells, improves tumor-specific CD8+ T cells functions in the TME, and rescues anti-tumor effects of PD-1 blockade therapy in mice. Our findings reveal a non-enzymatic nuclear function for GLDC in the suppression of MHC-I antigen presentation, suggesting new strategies for ICB-based combination immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
CD137L promotes immune surveillance in melanoma via HLTF regulation.
In Nat Commun on 26 September 2025 by Liang, L., Zhu, L., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) have demonstrated substantial efficacy across various malignancies, yet the benefits of ICBs are limited to a subset of patients. Therefore, it is essential to identify novel therapeutic targets. By integrating multi-omics data from cohorts of patients with melanoma treated with ICBs, a positive correlation is observed between tumor CD137L expression and the efficacy of PD-1 blockade. Functionally, CD137L induction in cancer cells significantly enhances anti-tumor immunity by promoting CD8+ T cell survival, both in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, helicase-like transcription factor (HLTF) is identified as a pivotal transcriptional regulator of CD137L, controlling its expression through phosphorylation of serine at position 398. Therapeutically, the AMPK agonist AICAR (acadesine) as an inducer of CD137L, exhibiting synergistic effects with PD-1 or CTLA-4 blockade. In summary, our findings elucidate a mechanism controlling CD137L expression and highlight a promising combination therapy to enhance the efficacy of ICBs in melanoma. One Sentence Summary: Inducing co-stimulatory immune checkpoint CD137L expression in melanoma cells enhances T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
In vivo neutrophils hitchhiking for tumor targeting and microenvironment regulation boosts oncolytic virus therapy.
In Cell Rep Med on 16 September 2025 by Zhao, X., Huang, H., et al.
PubMed
Neutrophils constitute a substantial proportion of the immune cell population infiltrating tumors, where they play a pivotal role in establishing an immunosuppressive microenvironment to facilitate tumor growth. Our clinical investigation has unveiled that, following oncolytic virus (OV) treatment, immunosuppressive neutrophils could lead to T cell exhaustion and compromised antitumor efficacy. In this study, we devise a dual-functional conjugation strategy that enables OVs to selectively bind with circulating neutrophils and initiate their death. Prior to dysfunction, neutrophils can harbor OVs and facilitate their infiltration into tumors, leading to a 5.38-fold increase in OV levels within tumors compared to direct intravenous injection. Additionally, infiltrated neutrophils undergo dying after 8 h, which promotes T cell priming, reduces T cell exhaustion, and remodels the tumor immune microenvironment. Our findings illuminate the determinants influencing the efficacy of OVs and propose targeted solutions, thereby offering insights for the clinical translation of these therapeutic agents.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
NanoPDLIM2-Based Combination Therapy for Lung Cancer Treatment in Mouse Preclinical Studies.
In Bio Protoc on 5 September 2025 by Le, T. H., Sun, F., et al.
PubMed
This protocol describes the preparation, administration, and analysis of a nanoparticle-based therapeutic strategy (nanoPDLIM2) in combination with PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy and chemotherapy for the treatment of lung cancer in mouse preclinical studies. NanoPDLIM2 uses a polyethyleneimine (PEI)-based delivery system that encapsulates PDLIM2 expression plasmids for reconstituting PDLIM2 that is repressed in tumors. This approach induces tumor immunogenicity, suppresses drug resistance, and improves treatment efficacy when used in combination with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and anti-PD-1 antibodies. The protocol describes steps for mouse lung tumor induction, nanoPDLIM2 and other therapeutic reagents' preparation and administration, and subsequent analysis of tumor burden, immune response, and toxicity, providing a reproducible approach for investigators. Key features • Comprehensive workflow for preparation and delivery of nanoPDLIM2. • Combination of nanoPDLIM2 with PD-1 blockade and chemotherapeutics for superior efficacy in lung cancer treatment. • Detailed protocols for therapeutic reagents preparation, administration, tumor examination, immune analysis, health monitoring, and toxicity evaluation in a preclinical lung cancer model.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
PTf-SRiApt Targeting SCAF4-POLR2A Interaction Suppresses Tumor Growth and Promotes Antitumor Immunity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 September 2025 by Fei, L., Pan, Y., et al.
PubMed
The interaction between SCAF4 and RNA polymerase II (POLR2A) is crucial for proper mRNA termination, with its dysregulation leading to truncated mRNAs and nonfunctional proteins, impairing cellular growth. Despite its potential relevance, the role of this interaction in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains unexplored due to the lack of effective molecular tools. To address this, we employed SRiApt, an aptamer generated through the recently established Blocker-SELEX pipeline. Its biological stability is improved by phosphorothioate modifications to form PTf-SRiApt. Using this aptamer, the critical role of the SCAF4-POLR2A interaction in driving TNBC tumor growth and immune regulation is uncovered. PTf-SRiApt effectively inhibits tumor growth and induces cell cycle arrest in TNBC cells with elevated SCAF4 and POLR2A expression. Additionally, PTf-SRiApt promotes premature mRNA termination, boosting antigen presentation and promoting T-cell infiltration. Analysis of patient samples further confirmed the negative correlation between SCAF4-POLR2A interaction and the effectiveness of immunotherapy, highlighting the potential of PTf-SRiApt in improving immune efficacy. Together, the work provides a powerful tool not only for dissecting previously "undruggable" protein-protein interactions but also for enhancing tumor immunogenicity and reshaping the tumor microenvironment.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Harnessing an integrated glyco-nanovaccine technology for enhanced cancer immunotherapy.
In Commun Med (Lond) on 29 August 2025 by Niimura, M., Sakamoto, Y., et al.
PubMed
Cancer immunotherapy, particularly using immune checkpoint inhibitors, has revolutionized cancer treatment; however, its efficacy remains limited to a subset of patients. Nanoparticles have potential in cancer treatment because they offer advantages such as biocompatibility, greater stability, and precise targeting capabilities.
-
-
Enhancing Antitumor Nanovaccine Efficacy via Integrated Cholesterol Modulation In Situ
In Research Square on 30 July 2025 by Jin, H., Deng, Z., et al.
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Estrogens determine the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy in obese males with melanoma.
In JCI Insight on 22 July 2025 by Dupuychaffray, E., Poinot, H., et al.
PubMed
Although obesity is a major risk factor for cancer, it may also improve the response to cancer therapy. Here we investigated the impact of obesity on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI). In male mice, obesity promoted tumor growth but enhanced the response to ICI. This was associated with higher expression of immune-related genes within the tumor and enhanced infiltration of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells. Further, obesity in mice was associated with higher estrogen levels and enrichment of estrogen response genes in the tumor, and anti-programmed cell death 1 (anti-PD-1) efficacy was reduced upon administration of the aromatase inhibitor letrozole, which blocks the production of estrogens. Mechanistically, adipocyte-derived estrogens increased antigen presentation by dendritic cells and tumor-specific CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. Last, overweight and obese men with melanoma responded better to ICI, with high estrogen levels being associated with improved response and survival. Our results suggest that estrogens may serve as a predictive factor of response to ICI in men with melanoma.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Augment proteasome inhibitor efficacy activates CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity in breast cancer.
In Cell Rep Med on 15 July 2025 by Tang, D., Lin, S., et al.
PubMed
Although three proteasome inhibitors are used for liquid tumor treatment, their effectiveness against solid tumors remains inadequate. To address this issue, we employ a drug combination strategy and discover that ammonium tetrathiomolybdate (TM) and AMD3100 can sensitize solid cancer cell lines to proteasome inhibitors. Mechanistically, we find that TM and AMD3100 reduce proteasome activity by decreasing the protein level of PSMB5. This reduction occurs through the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation. Notably, our in vivo studies reveal that drug combinations retard tumor growth dependent on CD8+ T cells. The combination of bortezomib with TM or AMD3100 induces cancer cell antigen presentation and the production of CCL5, which together stimulate the recruitment and generation of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. This study identifies synergistic lethal pairs that enhance the effectiveness of bortezomib-centered therapy for breast cancer treatment in a way relied on intact immune system.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Polymerised superparamagnetic antigen presenting cell lymphocyte capture for enriching tumour reactive T-cells and neoantigen identification.
In Nat Commun on 2 June 2025 by Hsu, C. Y., Tsai, P. C., et al.
PubMed
Ultrasensitive antigen recognition between T lymphocytes and cognate targets via immunological synapse (IS) formation enables live cell-based antigen-specific T cell detection. However, unpredictable antigen processing and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) turnover limit specificity. Here, intracellularly polymerized antigen-presenting cells (pAPCs) are developed for modular, persistent antigen display via kinetically driven loading. Although inanimate, pAPCs mimic cellular interactions, inducing IS hallmarks such as supramolecular activation cluster formation, cytoskeletal contraction, and trogocytosis. Incorporation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles allows label-free magnetic isolation of antigen-specific T cells, surpassing MHC-conjugated beads in sensitivity and specificity. In tumor-bearing hosts, pAPCs enrich tumor-reactive lymphocytes, enhancing adoptive T cell therapy and neoantigen-specific T cell identification. Additionally, pAPCs from engineered cells expressing monovalent human MHC enrich virus- and tumor-specific CD8 T cells from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and human leukocyte antigen-transgenic mice, demonstrating the potential of this cell-gel hybrid platform for precise antigen-specific T cell capture.
-