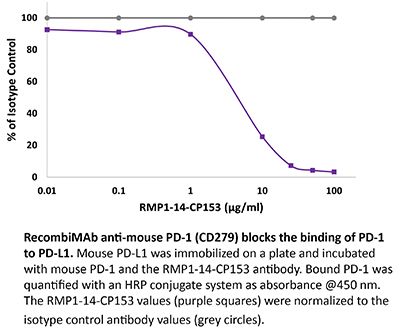
RecombiMAb anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279) (LALA-PG)
(switched from rat IgG2a)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb mouse IgG2a (LALA-PG) isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Mutations | LALA-PG |
| Immunogen | Syrian Hamster BKH cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling* *Reported for the original rat IgG2a RMP1-14 antibody |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
<1EU/mg (<0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from CHO cell supernatant in an animal free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Combination of HDAC inhibition and cytokine enhances therapeutic HPV vaccine therapy.
In J Immunother Cancer on 2 May 2025 by Poppe, L. K., Roller, N., et al.
PubMed
Human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated malignancies continue to present a major health concern despite the development of prophylactic vaccines. Standard therapies offer limited benefit to patients with advanced-stage disease. Despite improved outcomes with programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) targeted therapies, treatment resistance and modest response rates highlight a significant unmet need to develop novel therapies for these patients. PDS0101 (designated HPV vaccine) is a liposomal nanoparticle HPV16-specific therapeutic vaccine that has been shown to generate strong HPV-specific responses in preclinical and clinical studies. Here we assess the efficacy of this HPV vaccine in combination with the tumor-targeting immunocytokine NHS-IL12 (PDS01ADC), plus either αPD-1 or the class I histone deacetylase inhibitor Entinostat.
-