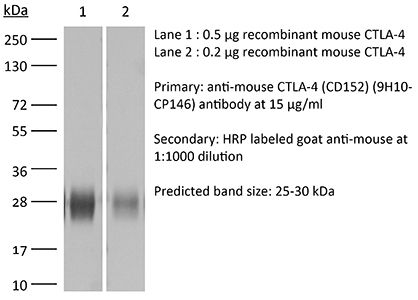
RecombiMAb anti-mouse CTLA-4 (CD152)
(switched from Syrian hamster IgG)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb mouse IgG1 isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CTLA-4-human IgG1 fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization* in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization* Western blot *Reported for the original Syrian hamster IgG 9H10 antibody |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from CHO cell supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2927521 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
Fc-optimized anti-CTLA-4 antibodies increase tumor-associated high endothelial venules and sensitize refractory tumors to PD-1 blockade.
In Cell Rep Med on 17 June 2025 by Blanchard, L., Vina, E., et al.
PubMed
The lack of T cells in tumors is a major hurdle to successful immune checkpoint therapy (ICT). Therefore, therapeutic strategies promoting T cell recruitment into tumors are warranted to improve the treatment efficacy. Here, we report that Fc-optimized anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) antibodies are potent remodelers of tumor vasculature that increase tumor-associated high endothelial venules (TA-HEVs), specialized blood vessels supporting lymphocyte entry into tumors. Mechanistically, this effect is dependent on the Fc domain of anti-CTLA-4 antibodies and CD4+ T cells and involves interferon gamma (IFNγ). Unexpectedly, we find that the human anti-CTLA-4 antibody ipilimumab fails to increase TA-HEVs in a humanized mouse model. However, increasing its Fc effector function rescues the modulation of TA-HEVs, promotes CD4+ and CD8+ T cell infiltration into tumors, and sensitizes recalcitrant tumors to programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade. Our findings suggest that Fc-optimized anti-CTLA-4 antibodies could be used to reprogram tumor vasculature in poorly immunogenic cold tumors and improve the efficacy of ICT.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
High PD-1 and CTLA-4 expression correlates with host immune suppression in patients and a mouse model infected with Echinococcus multilocularis.
In Parasit Vectors on 25 October 2024 by Sun, T., Yang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE), a fatal disease caused by Echinococcus multilocularis, often affects the liver, with tumor-like growth. However, the mechanism by which E. multilocularis evades host immune surveillance remains unclear.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Proteolysis-targeting vaccines (PROTAVs) for robust combination immunotherapy of melanoma
In bioRxiv on 3 October 2024 by Wang, Q., Su, T., et al.
-