InVivoSIM anti-human CTLA-4 (Ipilimumab Biosimilar)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Human IgG1 |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb human IgG1 isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Human CTLA-4 |
| Reported Applications |
in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization Flow Cytometry ELISA Western Blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
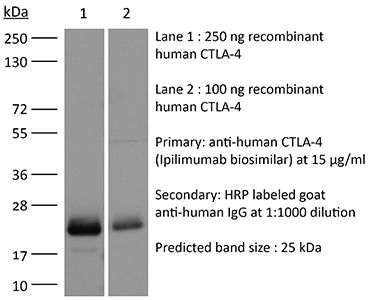
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2894725 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Watanabe T, Ishino T, Ueda Y, Nagasaki J, Sadahira T, Dansako H, Araki M, Togashi Y (2023). "Activated CTLA-4-independent immunosuppression of Treg cells disturbs CTLA-4 blockade-mediated antitumor immunity" Cancer Sci 114(5):1859-1870.
PubMed
Combination therapy with anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) has dramatically improved the prognosis of patients with multiple types of cancer, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, more than half of RCC patients fail to respond to this therapy. Regulatory T cells (Treg cells) are a subset of highly immunosuppressive CD4+ T cells that promote the immune escape of tumors by suppressing effector T cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) through various mechanisms. CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed in Treg cells and is regarded as a key molecule for Treg-cell-mediated immunosuppressive functions, suppressing antigen-presenting cells by binding to CD80/CD86. Reducing Treg cells in the TME with an anti-CTLA-4 mAb with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity is considered an essential mechanism to achieve tumor regression. In contrast, we demonstrated that CTLA-4 blockade without ADCC activity enhanced CD28 costimulatory signaling pathways in Treg cells and promoted Treg-cell proliferation in mouse models. CTLA-4 blockade also augmented CTLA-4-independent immunosuppressive functions, including cytokine production, leading to insufficient antitumor effects. Similar results were also observed in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from patients with RCC. Our findings highlight the importance of Treg-cell depletion to achieve tumor regression in response to CTLA-4 blockade therapies.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Crupi MJF, Taha Z, Janssen TJA, Petryk J, Boulton S, Alluqmani N, Jirovec A, Kassas O, Khan ST, Vallati S, Lee E, Huang BZ, Huh M, Pikor L, He X, Marius R, Austin B, Duong J, Pelin A, Neault S, Azad T, Breitbach CJ, Stojdl DF, Burgess MF, McComb S, A
PubMed
Colorectal cancer is the third most diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, highlighting an urgent need for new therapeutic options and combination strategies for patients. The orchestration of potent T cell responses against human cancers is necessary for effective antitumour immunity. However, regression of a limited number of cancers has been induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors, T cell engagers (TCEs) and/or oncolytic viruses. Although one TCE has been FDA-approved for the treatment of hematological malignancies, many challenges exist for the treatment of solid cancers. Here, we show that TCEs targeting CEACAM5 and CD3 stimulate robust activation of CD4 and CD8-positive T cells in in vitro co-culture models with colorectal cancer cells, but in vivo efficacy is hindered by a lack of TCE retention in the tumour microenvironment and short TCE half-life, as demonstrated by HiBiT bioluminescent TCE-tagging technology. To overcome these limitations, we engineered Bispecific Engager Viruses, or BEVirs, a novel tumour-targeted vaccinia virus platform for intra-tumour delivery of these immunomodulatory molecules. We characterized virus-mediated TCE-secretion, TCE specificity and functionality from infected colorectal cancer cells and patient tumour samples, as well as TCE cytotoxicity in spheroid models, in the presence and absence of T cells. Importantly, we show regression of colorectal tumours in both syngeneic and xenograft mouse models. Our data suggest that a different profile of cytokines may contribute to the pro-inflammatory and immune effects driven by T cells in the tumour microenvironment to provide long-lasting immunity and abscopal effects. We establish combination regimens with immune checkpoint inhibitors for aggressive colorectal peritoneal metastases. We also observe a significant reduction in lung metastases of colorectal tumours through intravenous delivery of our oncolytic virus driven T-cell based combination immunotherapy to target colorectal tumours and FAP-positive stromal cells or CTLA4-positive Treg cells in the tumour microenvironment. In summary, we devised a novel combination strategy for the treatment of colorectal cancers using oncolytic vaccinia virus to enhance immune-payload delivery and boost T cell responses within tumours.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Qiu H, Zmina PM, Huang AY, Askew D, Bedogni B (2018). "Inhibiting Notch1 enhances immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma by preventing Notch1 dependent immune suppressive properties" Cancer Lett .
PubMed
We have previously shown that Notch1 plays a critical role in modulating melanoma tumor cell growth and survival. Here we show that Notch1 also contributes to an immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). Notch1 inhibition reduces immune suppressive cells (i.e. MDSCs and Tregs) while allowing the recruitment of functional CD8(+) T cells, leading to a decrease in the Tregs/CD8(+) ratio, a key parameter in assessing positive responses to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Inhibition of Notch1 improves the antitumor activity of nivolumab and ipilimumab, particularly when given in combination. Mechanistically, tumor-associated Notch1 regulates the expression of several chemokines involved in MDSCs and Tregs recruitment. Among them, CCL5, IL6 and IL8, or MIP2 in mouse, were consistently reduced by Notch1 depletion in several human and mouse melanoma cell lines. Notch1 controls the transcription of IL8 and IL6; and the secretion of CCL5 likely by inhibiting the expression of SNAP23, a member of the SNAREs family of proteins involved in cell exocytosis. Inhibition of SNAP23 decreases CCL5 secretion similarly to Notch1 inhibition. Hence, targeting Notch1 would affect both melanoma intrinsic growth/survival properties, and provide an immune-responsive TME, thus improving immune therapy efficacy.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Assessing Human Treg Suppression at Single-Cell Resolution Using Mass Cytometry.
In Bio Protoc on 20 August 2025 by Søndergaard, J. N., Tulyeu, J., et al.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are essential for maintaining immune balance by controlling the activation and expansion of other immune cells. Conventional suppression assays often rely on co-culturing purified cell populations, which limits multiplexed phenotyping and physiological relevance. This protocol describes a high-dimensional, single-cell assay for profiling Treg-mediated suppression within a peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) system. Tregs are first isolated by cell sorting and then reintroduced into autologous PBMCs at defined ratios. A 52-marker mass cytometry (CyTOF) panel is used to quantify cell division and phenotypic responses across multiple immune subsets. This approach allows for integrated analysis of Treg function with broad compatibility for patient profiling and drug evaluation. Key features • Quantifies Treg-mediated suppression in autologous PBMCs at single-cell resolution. • Enables high-dimensional phenotyping and proliferation tracking across multiple immune subsets using a 52-marker CyTOF panel. • Maintains physiological relevance by assessing suppression in a complex PBMC environment. • Compatible with patient-derived samples and drug perturbation experiments for translational immunology applications.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Reactivation of CTLA4-expressing T cells accelerates resolution of lung fibrosis in a humanized mouse model.
In J Clin Invest on 15 May 2025 by Yadav, S., Anbalagan, M., et al.
PubMed
Tissue regenerative responses involve complex interactions between resident structural and immune cells. Recent reports indicate that accumulation of senescent cells during injury repair contributes to pathological tissue fibrosis. Using tissue-based spatial transcriptomics and proteomics, we identified upregulation of the immune checkpoint protein, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA4), on CD8+ T cells adjacent to regions of active fibrogenesis in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in a repetitive bleomycin lung injury murine model of persistent fibrosis. In humanized CTLA4-knockin mice, treatment with ipilimumab, an FDA-approved drug that targets CTLA4, resulted in accelerated lung epithelial regeneration and diminished fibrosis from repetitive bleomycin injury. Ipilimumab treatment resulted in the expansion of Cd3e+ T cells, diminished accumulation of senescent cells, and robust expansion of type 2 alveolar epithelial cells, facultative progenitor cells of the alveolar epithelium. Ex vivo activation of isolated CTLA4-expressing CD8+ cells from mice with established fibrosis resulted in enhanced cytolysis of senescent cells, suggesting that impaired immune-mediated clearance of these cells contributes to persistence of lung fibrosis in this murine model. Our studies support the concept that endogenous immune surveillance of senescent cells may be essential in promoting tissue regenerative responses that facilitate the resolution of fibrosis.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Single cell suppression profiling of human regulatory T cells.
In Nat Commun on 3 February 2025 by Søndergaard, J. N., Tulyeu, J., et al.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Treg) play an important role in regulating immune homeostasis in health and disease. Traditionally their suppressive function has been assayed by mixing purified cell populations, which does not provide an accurate picture of a physiologically relevant response. To overcome this limitation, we here develop 'single cell suppression profiling of human Tregs' (scSPOT). scSPOT uses a 52-marker CyTOF panel, a cell division detection algorithm, and a whole PBMC system to assess the effect of Tregs on all other cell types simultaneously. In this head-to-head comparison, we find Tregs having the clearest suppressive effects on effector memory CD8 T cells through partial division arrest, cell cycle inhibition, and effector molecule downregulation. Additionally, scSPOT identifies a Treg phenotypic split previously observed in viral infection and propose modes of action by the FDA-approved drugs Ipilimumab and Tazemetostat. scSPOT is thus scalable, robust, widely applicable, and may be used to better understand Treg immunobiology and screen for therapeutic compounds.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Immune checkpoint landscape of human atherosclerosis and influence of cardiometabolic factors.
In Nat Cardiovasc Res on 1 December 2024 by Barcia Durán, J. G., Das, D., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapies can increase the risk of cardiovascular events in survivors of cancer by worsening atherosclerosis. Here we map the expression of immune checkpoints (ICs) within human carotid and coronary atherosclerotic plaques, revealing a network of immune cell interactions that ICI treatments can unintentionally target in arteries. We identify a population of mature, regulatory CCR7+FSCN1+ dendritic cells, similar to those described in tumors, as a hub of IC-mediated signaling within plaques. Additionally, we show that type 2 diabetes and lipid-lowering therapies alter immune cell interactions through PD-1, CTLA4, LAG3 and other IC targets in clinical development, impacting plaque inflammation. This comprehensive map of the IC interactome in healthy and cardiometabolic disease states provides a framework for understanding the potential adverse and beneficial impacts of approved and investigational ICIs on atherosclerosis, setting the stage for designing ICI strategies that minimize cardiovascular disease risk in cancer survivors.
-
-
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Modeling immune checkpoint inhibitor associated myocarditis in vitro and its therapeutic implications.
In J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus on 1 December 2024 by Jensen, G., Wang, X., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis is the most lethal side effect of immune checkpoint blockade. Myocarditis leads to persistently increased mortality and lacks effective treatments. The development of patient-relevant disease models may enable disease prediction, increased understanding of disease pathophysiology, and the development of effective treatment strategies. Here, we report a new method to model immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis in vitro via a co-culture of activated primary human immune cells, human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, and FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors to recapitulate myocarditis in vitro. Significant cardiomyocyte necrosis, arrhythmia development, and sarcomere destruction occur, replicating clinical findings from myocarditis. This tissue culture myocarditis phenotype may rely on an induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte antigen-specific CD8+ T cell response. The administration of dexamethasone rescued cardiomyocyte viability, morphology, and electrophysiology and suppressed inflammatory cytokine production. In conclusion, we detail how this platform can effectively model and provide critical information about the morphological and electrophysiological changes induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis. We have also validated the ability of this platform to screen potential medications to treat immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis. This work establishes a robust, scalable model for identifying new therapies and risk factors, which is valuable in delineating the nature of interactions between the immune system and the heart during myocarditis.
-
-
Immunopotentiating effects of herb-partitioned moxibustion on the spleens of cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed rats.
In Chin Med on 18 February 2024 by Xiong, L., Tian, Y., et al.
PubMed
To investigate the effec of the herb-partitioned moxibustion on T-lymphocyte activity in immunosuppressed rats through differential modulation of the immune checkpoint molecules CD28 and CTLA-4.
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Oncolytic virus driven T-cell-based combination immunotherapy platform for colorectal cancer.
In Front Immunol on 22 November 2022 by Crupi, M. J. F., Taha, Z., et al.
PubMed
Colorectal cancer is the third most diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, highlighting an urgent need for new therapeutic options and combination strategies for patients. The orchestration of potent T cell responses against human cancers is necessary for effective antitumour immunity. However, regression of a limited number of cancers has been induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors, T cell engagers (TCEs) and/or oncolytic viruses. Although one TCE has been FDA-approved for the treatment of hematological malignancies, many challenges exist for the treatment of solid cancers. Here, we show that TCEs targeting CEACAM5 and CD3 stimulate robust activation of CD4 and CD8-positive T cells in in vitro co-culture models with colorectal cancer cells, but in vivo efficacy is hindered by a lack of TCE retention in the tumour microenvironment and short TCE half-life, as demonstrated by HiBiT bioluminescent TCE-tagging technology. To overcome these limitations, we engineered Bispecific Engager Viruses, or BEVirs, a novel tumour-targeted vaccinia virus platform for intra-tumour delivery of these immunomodulatory molecules. We characterized virus-mediated TCE-secretion, TCE specificity and functionality from infected colorectal cancer cells and patient tumour samples, as well as TCE cytotoxicity in spheroid models, in the presence and absence of T cells. Importantly, we show regression of colorectal tumours in both syngeneic and xenograft mouse models. Our data suggest that a different profile of cytokines may contribute to the pro-inflammatory and immune effects driven by T cells in the tumour microenvironment to provide long-lasting immunity and abscopal effects. We establish combination regimens with immune checkpoint inhibitors for aggressive colorectal peritoneal metastases. We also observe a significant reduction in lung metastases of colorectal tumours through intravenous delivery of our oncolytic virus driven T-cell based combination immunotherapy to target colorectal tumours and FAP-positive stromal cells or CTLA4-positive Treg cells in the tumour microenvironment. In summary, we devised a novel combination strategy for the treatment of colorectal cancers using oncolytic vaccinia virus to enhance immune-payload delivery and boost T cell responses within tumours.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inhibiting Notch1 enhances immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma by preventing Notch1 dependent immune suppressive properties.
In Cancer Lett on 10 October 2018 by Qiu, H., Zmina, P. M., et al.
PubMed
We have previously shown that Notch1 plays a critical role in modulating melanoma tumor cell growth and survival. Here we show that Notch1 also contributes to an immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). Notch1 inhibition reduces immune suppressive cells (i.e. MDSCs and Tregs) while allowing the recruitment of functional CD8(+) T cells, leading to a decrease in the Tregs/CD8(+) ratio, a key parameter in assessing positive responses to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Inhibition of Notch1 improves the antitumor activity of nivolumab and ipilimumab, particularly when given in combination. Mechanistically, tumor-associated Notch1 regulates the expression of several chemokines involved in MDSCs and Tregs recruitment. Among them, CCL5, IL6 and IL8, or MIP2 in mouse, were consistently reduced by Notch1 depletion in several human and mouse melanoma cell lines. Notch1 controls the transcription of IL8 and IL6; and the secretion of CCL5 likely by inhibiting the expression of SNAP23, a member of the SNAREs family of proteins involved in cell exocytosis. Inhibition of SNAP23 decreases CCL5 secretion similarly to Notch1 inhibition. Hence, targeting Notch1 would affect both melanoma intrinsic growth/survival properties, and provide an immune-responsive TME, thus improving immune therapy efficacy.
-