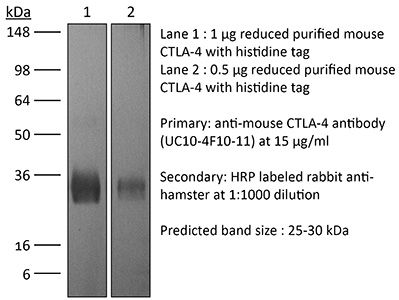
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CTLA-4 (CD152)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Armenian hamster IgG |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb polyclonal Armenian hamster IgG |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 6.5 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CTLA-4 IgG2a fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization Flow cytometry Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 6.5 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107598 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Triplett, T. A., et al (2018). "Reversal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated cancer immune suppression by systemic kynurenine depletion with a therapeutic enzyme" Nat Biotechnol 36(8): 758-764.
PubMed
Increased tryptophan (Trp) catabolism in the tumor microenvironment (TME) can mediate immune suppression by upregulation of interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) and/or ectopic expression of the predominantly liver-restricted enzyme tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). Whether these effects are due to Trp depletion in the TME or mediated by the accumulation of the IDO1 and/or TDO (hereafter referred to as IDO1/TDO) product kynurenine (Kyn) remains controversial. Here we show that administration of a pharmacologically optimized enzyme (PEGylated kynureninase; hereafter referred to as PEG-KYNase) that degrades Kyn into immunologically inert, nontoxic and readily cleared metabolites inhibits tumor growth. Enzyme treatment was associated with a marked increase in the tumor infiltration and proliferation of polyfunctional CD8(+) lymphocytes. We show that PEG-KYNase administration had substantial therapeutic effects when combined with approved checkpoint inhibitors or with a cancer vaccine for the treatment of large B16-F10 melanoma, 4T1 breast carcinoma or CT26 colon carcinoma tumors. PEG-KYNase mediated prolonged depletion of Kyn in the TME and reversed the modulatory effects of IDO1/TDO upregulation in the TME.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Makkouk, A., et al (2015). "Three steps to breaking immune tolerance to lymphoma: a microparticle approach" Cancer Immunol Res 3(4): 389-398.
PubMed
In situ immunization aims at generating antitumor immune responses through manipulating the tumor microenvironment. On the basis of recent advances in the understanding of antitumor immunity, we designed a three-step approach to in situ immunization to lymphoma: (i) inducing immunogenic tumor cell death with the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Doxorubicin enhances the expression of “eat-me” signals by dying tumor cells, facilitating their phagocytosis by dendritic cells (DC). Because of the vesicant activity of doxorubicin, microparticles made of biodegradable polymer poly(lactide-co-glycolide) or PLGA can safely deliver doxorubicin intratumorally and are effective vaccine adjuvants, (ii) enhancing T-cell activation using anti-OX40 and (iii) sustaining T-cell responses by checkpoint blockade using anti-CTLA-4. In vitro, doxorubicin microparticles were less cytotoxic to DCs than to B lymphoma cells, did not require internalization by tumor cells, and significantly enhanced phagocytosis of tumor cells by DCs as compared with soluble doxorubicin. In mice, this three-step therapy induced CD4- and CD8-dependent systemic immune responses that enhanced T-cell infiltration into distant tumors, leading to their eradication and significantly improving survival. Our findings demonstrate that systemic antitumor immune responses can be generated locally by three-step therapy and merit further investigation as an immunotherapy for patients with lymphoma.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Pletinckx, K., et al (2015). "Immature dendritic cells convert anergic nonregulatory T cells into Foxp3- IL-10+ regulatory T cells by engaging CD28 and CTLA-4" Eur J Immunol 45(2): 480-491.
PubMed
Anergic T cells can survive for long time periods passively in a hyporesponsive state without obvious active functions. Thus, the immunological reason for their maintenance is unclear. Here, we induced peptide-specific anergy in T cells from mice by coculturing these cells with immature murine dendritic cells (DCs). We found that these anergic, nonsuppressive IL-10(-) Foxp3(-) CTLA-4(+) CD25(low) Egr2(+) T cells could be converted into suppressive IL-10(+) Foxp3(-) CTLA-4(+) CD25(high) Egr2(+) cells resembling type-1 Treg cells (Tr1) when stimulated a second time by immature DCs in vitro. Addition of TGF-beta during anergy induction favored Foxp3(+) Treg-cell induction, while TGF-beta had little effect when added to the second stimulation. Expression of both CD28 and CTLA-4 molecules on anergic T cells was required to allow their conversion into Tr1-like cells. Suppressor activity was enabled via CD28-mediated CD25 upregulation, acting as an IL-2 sink, together with a CTLA-4-mediated inhibition of NFATc1/alpha activation to shut down IL-2-mediated proliferation. Together, these data provide evidence and mechanistical insights into how persistent anergic T cells may serve as a resting memory pool for Tr1-like cells.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Welten, S. P., et al (2015). "The viral context instructs the redundancy of costimulatory pathways in driving CD8(+) T cell expansion" Elife 4. doi : 10.7554/eLife.07486.
PubMed
Signals delivered by costimulatory molecules are implicated in driving T cell expansion. The requirements for these signals, however, vary from dispensable to essential in different infections. We examined the underlying mechanisms of this differential T cell costimulation dependence and found that the viral context determined the dependence on CD28/B7-mediated costimulation for expansion of naive and memory CD8(+) T cells, indicating that the requirement for costimulatory signals is not imprinted. Notably, related to the high-level costimulatory molecule expression induced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), CD28/B7-mediated costimulation was dispensable for accumulation of LCMV-specific CD8(+) T cells because of redundancy with the costimulatory pathways induced by TNF receptor family members (i.e., CD27, OX40, and 4-1BB). Type I IFN signaling in viral-specific CD8(+) T cells is slightly redundant with costimulatory signals. These results highlight that pathogen-specific conditions differentially and uniquely dictate the utilization of costimulatory pathways allowing shaping of effector and memory antigen-specific CD8(+) T cell responses.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Honda, T., et al (2014). "Tuning of antigen sensitivity by T cell receptor-dependent negative feedback controls T cell effector function in inflamed tissues" Immunity 40(2): 235-247.
PubMed
Activated T cells must mediate effector responses sufficiently to clear pathogens while avoiding excessive tissue damage. Here we have combined dynamic intravital microscopy with ex vivo assessments of T cell cytokine responses to generate a detailed spatiotemporal picture of CD4(+) T cell effector regulation in the skin. In response to antigen, effector T cells arrested transiently on antigen-presenting cells, briefly producing cytokine and then resuming migration. Antigen recognition led to upregulation of the programmed death-1 (PD-1) glycoprotein by T cells and blocking its canonical ligand, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), lengthened the duration of migration arrest and cytokine production, showing that PD-1 interaction with PD-L1 is a major negative feedback regulator of antigen responsiveness. We speculate that the immune system employs T cell recruitment, transient activation, and rapid desensitization to allow the T cell response to rapidly adjust to changes in antigen presentation and minimize collateral injury to the host.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Mittal, D., et al (2014). "Antimetastatic effects of blocking PD-1 and the adenosine A2A receptor" Cancer Res 74(14): 3652-3658.
PubMed
Adenosine targeting is an attractive new approach to cancer treatment, but no clinical study has yet examined adenosine inhibition in oncology despite the safe clinical profile of adenosine A2A receptor inhibitors (A2ARi) in Parkinson disease. Metastasis is the main cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and therefore we have studied experimental and spontaneous mouse models of melanoma and breast cancer metastasis to demonstrate the efficacy and mechanism of a combination of A2ARi in combination with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb). This combination significantly reduces metastatic burden and prolongs the life of mice compared with either monotherapy alone. Importantly, the combination was only effective when the tumor expressed high levels of CD73, suggesting a tumor biomarker that at a minimum could be used to stratify patients that might receive this combination. The mechanism of the combination therapy was critically dependent on NK cells and IFNgamma, and to a lesser extent, CD8(+) T cells and the effector molecule, perforin. Overall, these results provide a strong rationale to use A2ARi with anti-PD-1 mAb for the treatment of minimal residual and metastatic disease.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Rabenstein, H., et al (2014). "Differential kinetics of antigen dependency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells" J Immunol 192(8): 3507-3517.
PubMed
Ag recognition via the TCR is necessary for the expansion of specific T cells that then contribute to adaptive immunity as effector and memory cells. Because CD4+ and CD8+ T cells differ in terms of their priming APCs and MHC ligands we compared their requirements of Ag persistence during their expansion phase side by side. Proliferation and effector differentiation of TCR transgenic and polyclonal mouse T cells were thus analyzed after transient and continuous TCR signals. Following equally strong stimulation, CD4+ T cell proliferation depended on prolonged Ag presence, whereas CD8+ T cells were able to divide and differentiate into effector cells despite discontinued Ag presentation. CD4+ T cell proliferation was neither affected by Th lineage or memory differentiation nor blocked by coinhibitory signals or missing inflammatory stimuli. Continued CD8+ T cell proliferation was truly independent of self-peptide/MHC-derived signals. The subset divergence was also illustrated by surprisingly broad transcriptional differences supporting a stronger propensity of CD8+ T cells to programmed expansion. These T cell data indicate an intrinsic difference between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells regarding the processing of TCR signals for proliferation. We also found that the presentation of a MHC class II-restricted peptide is more efficiently prolonged by dendritic cell activation in vivo than a class I bound one. In summary, our data demonstrate that CD4+ T cells require continuous stimulation for clonal expansion, whereas CD8+ T cells can divide following a much shorter TCR signal.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Zhu, Y., et al (2014). "CSF1/CSF1R blockade reprograms tumor-infiltrating macrophages and improves response to T-cell checkpoint immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer models" Cancer Res 74(18): 5057-5069.
PubMed
Cancer immunotherapy generally offers limited clinical benefit without coordinated strategies to mitigate the immunosuppressive nature of the tumor microenvironment. Critical drivers of immune escape in the tumor microenvironment include tumor-associated macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, which not only mediate immune suppression, but also promote metastatic dissemination and impart resistance to cytotoxic therapies. Thus, strategies to ablate the effects of these myeloid cell populations may offer great therapeutic potential. In this report, we demonstrate in a mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) that inhibiting signaling by the myeloid growth factor receptor CSF1R can functionally reprogram macrophage responses that enhance antigen presentation and productive antitumor T-cell responses. Investigations of this response revealed that CSF1R blockade also upregulated T-cell checkpoint molecules, including PDL1 and CTLA4, thereby restraining beneficial therapeutic effects. We found that PD1 and CTLA4 antagonists showed limited efficacy as single agents to restrain PDAC growth, but that combining these agents with CSF1R blockade potently elicited tumor regressions, even in larger established tumors. Taken together, our findings provide a rationale to reprogram immunosuppressive myeloid cell populations in the tumor microenvironment under conditions that can significantly empower the therapeutic effects of checkpoint-based immunotherapeutics.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Allard, B., et al (2013). "Targeting CD73 enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs" Clin Cancer Res 19(20): 5626-5635.
PubMed
PURPOSE: Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) that block programmed death (PD)-1 or cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen (CTLA-4) receptors have been associated with durable clinical responses against a variety of cancer types and hold great potential as novel cancer therapeutics. Recent evidence suggest that targeted blockade of multiple immunosuppressive pathways can induce synergistic antitumor responses. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: In this study, we investigated whether targeted blockade of CD73, an ectonucleotidase that catabolizes the hydrolysis of extracellular adenosine monophosphate (AMP) to adenosine, can enhance the antitumor activity of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 mAbs against transplanted and chemically induced mouse tumors. RESULTS: Anti-CD73 mAb significantly enhanced the activity of both anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 mAbs against MC38-OVA (colon) and RM-1 (prostate) subcutaneous tumors, and established metastatic 4T1.2 breast cancer. Anti-CD73 mAb also significantly enhanced the activity of anti-PD-1 mAb against 3-methylcholanthrene (MCA)-induced fibrosarcomas. Gene-targeted mice revealed that single-agent therapies and combinatorial treatments were dependent on host IFN-gamma and CD8(+) T cells, but independent of perforin. Interestingly, anti-CD73 mAb preferentially synergized with anti-PD-1 mAb. We investigated the effect of extracellular adenosine on tumor-infiltrating T cells and showed that activation of A2A adenosine receptor enhances PD-1 expression, but not CTLA-4 expression, on tumor-specific CD8+ T cells and CD4+ Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, our study revealed that targeted blockade of CD73 can enhance the therapeutic activity of anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs and may thus potentiate therapeutic strategies targeting immune checkpoint inhibitors in general.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Hafalla, J. C., et al (2012). "The CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways independently regulate host resistance to Plasmodium-induced acute immune pathology" PLoS Pathog 8(2): e1002504.
PubMed
The balance between pro-inflammatory and regulatory immune responses in determining optimal T cell activation is vital for the successful resolution of microbial infections. This balance is maintained in part by the negative regulators of T cell activation, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L, which dampen effector responses during chronic infections. However, their role in acute infections, such as malaria, remains less clear. In this study, we determined the contribution of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L to the regulation of T cell responses during Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA)-induced experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) in susceptible (C57BL/6) and resistant (BALB/c) mice. We found that the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T cells correlates with the extent of pro-inflammatory responses induced during PbA infection, being higher in C57BL/6 than in BALB/c mice. Thus, ECM develops despite high levels of expression of these inhibitory receptors. However, antibody-mediated blockade of either the CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1, but not the PD-1/PD-L2, pathways during PbA-infection in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice resulted in higher levels of T cell activation, enhanced IFN-gamma production, increased intravascular arrest of both parasitised erythrocytes and CD8(+) T cells to the brain, and augmented incidence of ECM. Thus, in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 represent essential, independent and non-redundant pathways for maintaining T cell homeostasis during a virulent malaria infection. Moreover, neutralisation of IFN-gamma or depletion of CD8(+) T cells during PbA infection was shown to reverse the pathologic effects of regulatory pathway blockade, highlighting that the aetiology of ECM in the BALB/c mice is similar to that in C57BL/6 mice. In summary, our results underscore the differential and complex regulation that governs immune responses to malaria parasites.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Haque, A., et al (2010). "CD4+ natural regulatory T cells prevent experimental cerebral malaria via CTLA-4 when expanded in vivo" PLoS Pathog 6(12): e1001221.
PubMed
Studies in malaria patients indicate that higher frequencies of peripheral blood CD4(+) Foxp3(+) CD25(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells correlate with increased blood parasitemia. This observation implies that Treg cells impair pathogen clearance and thus may be detrimental to the host during infection. In C57BL/6 mice infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA, depletion of Foxp3(+) cells did not improve parasite control or disease outcome. In contrast, elevating frequencies of natural Treg cells in vivo using IL-2/anti-IL-2 complexes resulted in complete protection against severe disease. This protection was entirely dependent upon Foxp3(+) cells and resulted in lower parasite biomass, impaired antigen-specific CD4(+) T and CD8(+) T cell responses that would normally promote parasite tissue sequestration in this model, and reduced recruitment of conventional T cells to the brain. Furthermore, Foxp3(+) cell-mediated protection was dependent upon CTLA-4 but not IL-10. These data show that T cell-mediated parasite tissue sequestration can be reduced by regulatory T cells in a mouse model of malaria, thereby limiting malaria-induced immune pathology.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization
Noval Rivas, M., et al (2009). "Reviving function in CD4+ T cells adapted to persistent systemic antigen" J Immunol 183(7): 4284-4291.
PubMed
In bone marrow-transplanted patients, chronic graft-versus-host disease is a complication that results from the persistent stimulation of recipient minor histocompatibility Ag (mHA)-specific T cells contained within the graft. In this study, we developed a mouse model where persistent stimulation of donor T cells by recipient’s mHA led to multiorgan T cell infiltration. Exposure to systemic mHA, however, deeply modified T cell function and chronically stimulated T cells developed a long-lasting state of unresponsiveness, or immune adaptation, characterized by their inability to mediate organ immune damages in vivo. However, analysis of the gene expression profile of adapted CD4+ T cells revealed the specific coexpression of genes known to promote differentiation and function of Th1 effector cells as well as genes coding for proteins that control T cell activity, such as cell surface-negative costimulatory molecules and regulatory cytokines. Strikingly, blockade of negative costimulation abolished T cell adaptation and stimulated strong IFN-gamma production and severe multiorgan wasting disease. Negative costimulation was also shown to control lethal LPS-induced toxic shock in mice with adapted T cells, as well as the capacity of adapted T cells to reject skin graft. Our results demonstrate that negative costimulation is the molecular mechanism used by CD4+ T cells to adapt their activity in response to persistent antigenic stimulation. The effector function of CD4+ T cells that have adapted to chronic Ag presentation can be activated by stimuli strong enough to overcome regulatory signals delivered to the T cells by negative costimulation.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Rowe, J. H., et al (2009). "Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 blockade augments the T-cell response primed by attenuated Listeria monocytogenes resulting in more rapid clearance of virulent bacterial challenge" Immunology 128(1 Suppl): e471-478.
PubMed
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) uniformly suppresses antigen-specific T cells during chronic infection with bacterial, parasitic or viral pathogens. However, the importance of CTLA-4 in controlling the T-cell response during acute infection or after priming with live attenuated vaccine vectors has not been well characterized. Since strategies aimed at blocking CTLA-4 are being actively developed to therapeutically augment T-cell-mediated immunity, the effects of CTLA-4 blockade on T-cell activation during these conditions need to be more clearly defined. We have examined the role of CTLA-4 in a prime-challenge model of acute bacterial infection using both attenuated and virulent strains of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Although Foxp3(+) CD4(+) T cells are the predominant CTLA-4-expressing cell type in naive mice, antigen-specific Foxp3(-) CD4(+) cells upregulate CTLA-4 expression after primary L. monocytogenes infection. Blockade of CTLA-4 results in increased numbers of L. monocytogenes-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells after primary infection with attenuated L. monocytogenes, and confers more rapid bacterial clearance after secondary challenge with virulent L. monocytogenes. Accordingly, CTLA-4 plays an important suppressive role in T-cell priming and protective immunity in a prime-challenge model of acute bacterial infection.
Product Citations
-
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
The transcription factor ZEB2 mediates the antitumor efficacy of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer.
In Cell Death Dis on 7 November 2025 by Wang, J., Liu, F., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) offers an in vivo approach to activate CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (CD8+TILs) in cases of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). A large fraction of NSCLC patients is unresponsive to ICBs and relapse due to the development of dysfunctional CD8+TILs with impaired cytotoxicity. Therefore, an improved understanding of regulator(s) that favor the development of cytotoxic Teff cells over dysfunctional CD8+TILs is required for the success of ICB therapy in NSCLC patients. Here, our metaVIPER-based scRNA-seq analysis of deep CD8+ cell scRNA-seq data from 14 treatment-naïve NSCLC patients revealed that the master regulon ZEB2 may drive CD8+ differentiation along the cytotoxic effector trajectory in NSCLC tumors. In vitro, ZEB2 acts downstream of T-bet to stimulate lung tumor-reactive Teff cell differentiation. This T-bet/ZEB2 axis displays immunotherapeutic effects on KP.SIY lung tumors independent of ICB therapy and mediates the therapeutic effects of murine serum albumin-fused IL-2 + IL-12 combination immunotherapy (IL2-MSA + IL12-MSA) in mice. IL2-MSA + IL12-MSA operates through a parallel STAT4/FOXO1-mediated mechanism that promotes CD8+TIL T-bet/ZEB2 expression and lung tumor-reactive Teff cell differentiation. In conclusion, immunotherapeutic regimens that support ZEB2 activity in CD8+ cells may show promise in NSCLC patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CRISPR screens in the context of immune selection identifyCHD1andMAP3K7as mediators of cancer immunotherapy resistance
In bioRxiv on 18 April 2025 by Watterson, A., Picco, G., et al.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Lung Cancer-Intrinsic SOX2 Expression Mediates Resistance to Checkpoint Blockade Therapy by Inducing Treg-Dependent CD8+ T-cell Exclusion.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 2 April 2025 by Torres-Mejia, E., Weng, S., et al.
PubMed
Tumor cell-intrinsic signaling pathways can drastically affect the tumor immune microenvironment, promoting tumor progression and resistance to immunotherapy by excluding immune cell populations from the tumor. Several tumor cell-intrinsic pathways have been reported to modulate myeloid-cell and T-cell infiltration, creating "cold" tumors. However, clinical evidence suggests that excluding cytotoxic T cells from the tumor core also mediates immune evasion. In this study, we find that tumor cell-intrinsic SOX2 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer induces the exclusion of cytotoxic T cells from the tumor core and promotes resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy. Mechanistically, tumor cell-intrinsic SOX2 expression upregulates CCL2 in tumor cells, resulting in increased recruitment of regulatory T cells (Treg). CD8+ T-cell exclusion depended on Treg-mediated suppression of tumor vasculature. Depleting tumor-infiltrating Tregs via glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor-related protein restored CD8+ T-cell infiltration and, when combined with checkpoint blockade therapy, reduced tumor growth. These results show that tumor cell-intrinsic SOX2 expression in lung cancer serves as a mechanism of immunotherapy resistance and provide evidence to support future studies investigating whether patients with non-small cell lung cancer with SOX2-dependent CD8+ T-cell exclusion would benefit from the depletion of glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein-positive Tregs.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
TIMP1 Mediates Astrocyte-Dependent Local Immunosuppression in Brain Metastasis Acting on Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells.
In Cancer Discov on 13 January 2025 by Priego, N., de Pablos-Aragoneses, A., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapies against brain metastases have shown clinical benefits when applied to asymptomatic patients, but they are largely ineffective in symptomatic cases for unknown reasons. Here, we dissect the heterogeneity in metastasis-associated astrocytes using single-cell RNA sequencing and report a population that blocks the antitumoral activity of infiltrating T cells. This protumoral activity is mediated by the secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP1) from a cluster of pSTAT3+ astrocytes that acts on CD63+ CD8+ T cells to modulate their function. Using genetic and pharmacologic approaches in mouse and human brain metastasis models, we demonstrate that combining immune checkpoint blockade antibodies with the inhibition of astrocyte-mediated local immunosuppression may benefit patients with symptomatic brain metastases. We further reveal that the presence of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in liquid biopsies provides a biomarker to select patients for this combined immunotherapy. Overall, our findings demonstrate an unexpected immunomodulatory role for astrocytes in brain metastases with clinical implications. Significance: This study presents a significant advancement in understanding immune modulation in brain tumors and offers new insights into the potential therapeutic interventions for brain metastases. See related commentary by Lorger and James, p. 11.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Enhancing Tumor Immunity with IL-12 and PD-1 Blockade: A Strategy for Inducing Robust Central Memory T Cell Responses in Resistant Cancer Model.
In Antibodies (Basel) on 20 November 2024 by Chen, F., Wu, K., et al.
PubMed
Background: Although immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have demonstrated efficacy in treating advanced cancers, their therapeutic success remains limited for many patients, with initial responders often experiencing resistance and relapse. Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a powerful cytokine for antitumor immunotherapy, enhancing both lymphocyte recruitment into tumors and immune cell activation. Methods: In this study, we successfully produced mouse interleukin-12 (mIL12) through eukaryotic recombinant expression. In vivo, mIL12 exhibited significant control of tumor immunity in ICI-resistant and aggressive tumor models. Further mechanistic analysis indicated that treatment with mIL12 led to a substantial increase in tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T, CD8+ T, cDC1, and CD103+ cDC1 cells. Results: Our data underscore the potential of a combined therapeutic strategy involving IL-12 with PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade to elicit a potent antitumor immune response. Notably, the co-administration of mIL12 and PD-1 blockade significantly enhanced the presence of central memory T cells (TCM) within tumors. Conclusions: This study is the first to provide evidence that the combination of mIL12 and PD-1 blockers promotes the generation of TCM, potentially contributing to a robust and durable antitumor effect.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Inhibition of CTLA-4 accelerates atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic mice by modulating the Th1/Th2 balance via the NF-κB signaling pathway.
In Heliyon on 15 September 2024 by Zhao, M. L., Liang, C., et al.
PubMed
Though an increased risk of atherosclerosis is associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibody therapy, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer cell plasticity defines response to immunotherapy in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
In Nat Commun on 24 June 2024 by Lorenzo-Sanz, L., Lopez-Cerda, M., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) approaches have changed the therapeutic landscape for many tumor types. However, half of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) patients remain unresponsive or develop resistance. Here, we show that, during cSCC progression in male mice, cancer cells acquire epithelial/mesenchymal plasticity and change their immune checkpoint (IC) ligand profile according to their features, dictating the IC pathways involved in immune evasion. Epithelial cancer cells, through the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, and mesenchymal cancer cells, through the CTLA-4/CD80 and TIGIT/CD155 pathways, differentially block antitumor immune responses and determine the response to ICB therapies. Accordingly, the anti-PD-L1/TIGIT combination is the most effective strategy for blocking the growth of cSCCs that contain both epithelial and mesenchymal cancer cells. The expression of E-cadherin/Vimentin/CD80/CD155 proteins in cSCC, HNSCC and melanoma patient samples predicts response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Collectively, our findings indicate that the selection of ICB therapies should take into account the epithelial/mesenchymal features of cancer cells.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Clinical drug screening reveals clofazimine potentiates the efficacy while reducing the toxicity of anti-PD-1 and CTLA-4 immunotherapy.
In Cancer Cell on 13 May 2024 by Xue, G., Li, X., et al.
PubMed
Emerging as the most potent and durable combinational immunotherapy, dual anti-PD-1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy notoriously increases grade 3-5 immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in patients. Accordingly, attempts to improve the antitumor potency of anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 ICB by including additional therapeutics have been largely discouraged due to concerns of further increasing fatal toxicity. Here, we screened ∼3,000 Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs and identified clofazimine as a potential third agent to optimize anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 ICB. Remarkably, clofazimine outperforms ICB dose reduction or steroid treatment in reversing lethality of irAEs, but unlike the detrimental effect of steroids on antitumor efficacy, clofazimine potentiates curative responses in anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 ICB. Mechanistically, clofazimine promotes E2F1 activation in CD8+ T cells to overcome resistance and counteracts pathogenic Th17 cells to abolish irAEs. Collectively, clofazimine potentiates the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 ICB, curbs intractable irAEs, and may fill a desperate clinical need to improve patient survival.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Blocking the CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways during pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis improves immunity, reduces disease severity, and increases the survival of infected mice.
In Front Immunol on 19 March 2024 by Preite, N. W., Borges, B. M., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint pathways, i.e., coinhibitory pathways expressed as feedback following immune activation, are crucial for controlling an excessive immune response. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) are the central classical checkpoint inhibitory (CPI) molecules used for the control of neoplasms and some infectious diseases, including some fungal infections. As the immunosuppression of severe paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM), a chronic granulomatous fungal disease, was shown to be associated with the expression of coinhibitory molecules, we hypothesized that the inhibition of CTLA-4 and PD-1 could have a beneficial effect on pulmonary PCM. To this end, C57BL/6 mice were infected with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeasts and treated with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) α-CTLA-4, α-PD-1, control IgG, or PBS. We verified that blockade of CTLA-4 and PD-1 reduced the fungal load in the lungs and fungal dissemination to the liver and spleen and decreased the size of pulmonary lesions, resulting in increased survival of mice. Compared with PBS-treated infected mice, significantly increased levels of many pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines were observed in the lungs of α-CTLA-4-treated mice, but a drastic reduction in the liver was observed following PD-1 blockade. In the lungs of α-CPI and IgG-treated mice, there were no changes in the frequency of inflammatory leukocytes, but a significant reduction in the total number of these cells was observed. Compared with PBS-treated controls, α-CPI- and IgG-treated mice exhibited reduced pulmonary infiltration of several myeloid cell subpopulations and decreased expression of costimulatory molecules. In addition, a decreased number of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells but sustained numbers of Th1, Th2, and Th17 T cells were detected. An expressive reduction in several Treg subpopulations and their maturation and suppressive molecules, in addition to reduced numbers of Treg, TCD4+, and TCD8+ cells expressing costimulatory and coinhibitory molecules of immunity, were also detected. The novel cellular and humoral profiles established in the lungs of α-CTLA-4 and α-PD-1-treated mice but not in control IgG-treated mice were more efficient at controlling fungal growth and dissemination without causing increased tissue pathology due to excessive inflammation. This is the first study demonstrating the efficacy of CPI blockade in the treatment of pulmonary PCM, and further studies combining the use of immunotherapy with antifungal drugs are encouraged.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Directly Modulate T Cell Gene Expression and Signaling and Promote Development of Effector-Exhausted T Cells in Murine Tumors.
In J Immunol on 15 February 2024 by Ibrahim, M. L., Zheng, H., et al.
PubMed
Epigenetic regulation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of cancer, including the regulation of antitumor immunity. The reversible nature of epigenetic modifications offers potential therapeutic avenues for cancer treatment. In particular, histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors (HDACis) have been shown to promote antitumor T cell immunity by regulating myeloid cell types, enhancing tumor Ag presentation, and increasing expression of chemokines. HDACis are currently being evaluated to determine whether they can increase the response rate of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients. Although the potential direct effect of HDACis on T cells likely impacts antitumor immunity, little is known about how HDAC inhibition alters the transcriptomic profile of T cells. In this article, we show that two clinical-stage HDACis profoundly impact gene expression and signaling networks in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. Specifically, HDACis promoted T cell effector function by enhancing expression of TNF-α and IFN-γ and increasing CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. Consistently, in a murine tumor model, HDACis led to enrichment of CD8+ T cell subsets with high expression of effector molecules (Prf1, Ifng, Gzmk, and Grmb) but also molecules associated with T cell exhaustion (Tox, Pdcd1, Lag3, and Havcr2). HDACis further generated a tumor microenvironment dominated by myeloid cells with immune suppressive signatures. These results indicate that HDACis directly and favorably augment T cell effector function but also increase their exhaustion signal in the tumor microenvironment, which may add a layer of complexity for achieving clinical benefit in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
INHBA/Activin A promotes tumor growth and induces resistance to anti-PD-L1 therapy by suppressing IFN-γ signaling
In bioRxiv on 8 December 2023 by Li, F., Gu, L., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Kruppel-like factor 2+ CD4 T cells avert microbiota-induced intestinal inflammation.
In Cell Rep on 28 November 2023 by Shao, T. Y., Jiang, T. T., et al.
PubMed
Intestinal colonization by antigenically foreign microbes necessitates expanded peripheral immune tolerance. Here we show commensal microbiota prime expansion of CD4 T cells unified by the Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) transcriptional regulator and an essential role for KLF2+ CD4 cells in averting microbiota-driven intestinal inflammation. CD4 cells with commensal specificity in secondary lymphoid organs and intestinal tissues are enriched for KLF2 expression, and distinct from FOXP3+ regulatory T cells or other differentiation lineages. Mice with conditional KLF2 deficiency in T cells develop spontaneous rectal prolapse and intestinal inflammation, phenotypes overturned by eliminating microbiota or reconstituting with donor KLF2+ cells. Activated KLF2+ cells selectively produce IL-10, and eliminating IL-10 overrides their suppressive function in vitro and protection against intestinal inflammation in vivo. Together with reduced KLF2+ CD4 cell accumulation in Crohn's disease, a necessity for the KLF2+ subpopulation of T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells in sustaining commensal tolerance is demonstrated.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Rigosertib promotes anti-tumor immunity via autophagic degradation of PD-L1 in colorectal cancer cells.
In Cancer Lett on 28 November 2023 by Zhou, X., Fu, D., et al.
PubMed
Rigosertib (RGS) is a benzyl styryl sulfone which exhibits impressive cytotoxicity in cancer cells. However, its modulating effect on tumor immune microenvironment remains elusive. In our experiments, compared with immunodeficient mouse model, increased tumor growth arrest and robust anti-tumor immunity were observed in RGS-treated colorectal cancer (CRC) isograft tumors in immunocompetent mice. Intriguingly, RGS markedly down-regulated programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in both vivo and in vitro. Meanwhile, RGS increased autophagic vacuole number in CRC cells as seen by transmission electron microscopy and immunofluorescence. Moreover, increased LC3-II level and tandem-mRFP- GFP- LC3 labeled vacuole accumulation demonstrated RGS-induced autophagic flux. Mechanistically, it is the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase-UNC-51-like kinase 1 (AMPK-ULK1) axis, rather than the canonical mTOR signaling pathway, that plays a pivotal role in RGS-induced autophagy. AMPK-ULK1 dependent autophagy inhibition, by either short interfering RNA or chemical inhibitors, blocked RGS-induced PD-L1 degradation. Finally, RGS exhibited synergistic anti-tumor activity with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 monoclonal antibody in the CRC isograft model. Furthermore, apart from the immunomodulatory effect, we also confirmed the direct cytotoxicity of RGS in inducing mitochondria-related apoptosis. Altogether, considering its PD-L1 inhibitory and cytotoxic effects, RGS could be a promising drug for CRC therapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Interactions of Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing LAMP3+ dendritic cells with CD4+ regulatory T cells and CD8+ exhausted T cells: synergistically remodeling of the immunosuppressive microenvironment in cervical cancer and therapeutic implication
In Cancer Commun (Lond) on 1 November 2023 by Qu, X., Wang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Cervical cancer (CC) is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide. Although immunotherapy has been applied in clinical practice, its therapeutic efficacy remains far from satisfactory, necessitating further investigation of the mechanism of CC immune remodeling and exploration of novel treatment targets. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism of CC immune remodeling and explore potential therapeutic targets.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Enzyme-mediated depletion of methylthioadenosine restores T cell function in MTAP-deficient tumors and reverses immunotherapy resistance.
In Cancer Cell on 9 October 2023 by Gjuka, D., Adib, E., et al.
PubMed
Chromosomal region 9p21 containing tumor suppressors CDKN2A/B and methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) is one of the most frequent genetic deletions in cancer. 9p21 loss is correlated with reduced tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. Previously thought to be caused by CDKN2A/B loss, we now show that it is loss of MTAP that leads to poor outcomes on ICI therapy and reduced TIL density. MTAP loss causes accumulation of methylthioadenosine (MTA) both intracellularly and extracellularly and profoundly impairs T cell function via the inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) and by adenosine receptor agonism. Administration of MTA-depleting enzymes reverses this immunosuppressive effect, increasing TILs and drastically impairing tumor growth and importantly, synergizes well with ICI therapy. As several studies have shown ICI resistance in 9p21/MTAP null/low patients, we propose that MTA degrading therapeutics may have substantial therapeutic benefit in these patients by enhancing ICI effectiveness.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Molecular, metabolic and functional CD4 T cell paralysis impedes tumor control
In bioRxiv on 17 April 2023 by Guo, M., Abd-Rabbo, D., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Combination IFNβ and Membrane-Stable CD40L Maximize Tumor Dendritic Cell Activation and Lymph Node Trafficking to Elicit Systemic T-cell Immunity.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 3 April 2023 by Zheng, H., Yu, X., et al.
PubMed
Oncolytic virus therapies induce the direct killing of tumor cells and activation of conventional dendritic cells (cDC); however, cDC activation has not been optimized with current therapies. We evaluated the adenoviral delivery of engineered membrane-stable CD40L (MEM40) and IFNβ to locally activate cDCs in mouse tumor models. Combined tumor MEM40 and IFNβ expression induced the highest cDC activation coupled with increased lymph node migration, increased systemic antitumor CD8+ T-cell responses, and regression of established tumors in a cDC1-dependent manner. MEM40 + IFNβ combined with checkpoint inhibitors led to effective control of distant tumors and lung metastases. An oncolytic adenovirus (MEM-288) expressing MEM40 + IFNβ in phase I clinical testing induced cancer cell loss concomitant with enhanced T-cell infiltration and increased systemic presence of tumor T-cell clonotypes in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. This approach to simultaneously target two major DC-activating pathways has the potential to significantly affect the solid tumor immunotherapy landscape.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Phosphoinositide acyl chain saturation drives CD8+ effector T cell signaling and function.
In Nat Immunol on 1 March 2023 by Edwards-Hicks, J., Apostolova, P., et al.
PubMed
How lipidome changes support CD8+ effector T (Teff) cell differentiation is not well understood. Here we show that, although naive T cells are rich in polyunsaturated phosphoinositides (PIPn with 3-4 double bonds), Teff cells have unique PIPn marked by saturated fatty acyl chains (0-2 double bonds). PIPn are precursors for second messengers. Polyunsaturated phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) exclusively supported signaling immediately upon T cell antigen receptor activation. In late Teff cells, activity of phospholipase C-γ1, the enzyme that cleaves PIP2 into downstream mediators, waned, and saturated PIPn became essential for sustained signaling. Saturated PIP was more rapidly converted to PIP2 with subsequent recruitment of phospholipase C-γ1, and loss of saturated PIPn impaired Teff cell fitness and function, even in cells with abundant polyunsaturated PIPn. Glucose was the substrate for de novo PIPn synthesis, and was rapidly utilized for saturated PIP2 generation. Thus, separate PIPn pools with distinct acyl chain compositions and metabolic dependencies drive important signaling events to initiate and then sustain effector function during CD8+ T cell differentiation.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Rigosertib promotes anti-tumor immunity via autophagic degradation of PD-L1 in colorectal cancer cells
In bioRxiv on 8 February 2023 by Zhou, X., Fu, D., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Suppression of Tumor or Host Intrinsic CMTM6 Drives Antitumor Cytotoxicity in a PD-L1-Independent Manner.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 3 February 2023 by Long, Y., Chen, R., et al.
PubMed
CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing protein 6 (CMTM6) is known to be a regulator of membranal programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) stability and a factor associated with malignancy progression, but the effects and mechanisms of CMTM6 on tumor growth, as well as its potential as a target for therapy, are still largely unknown. Here, we show that CMTM6 expression increased with tumor progression in both patients and mice. Ablation of CMTM6 significantly reduced human and murine tumor growth in a manner dependent on T-cell immunity. Tumor CMTM6 suppression broke resistance to immune-checkpoint inhibitors and remodeled the tumor immune microenvironment, as specific antitumor cytotoxicity was enhanced and contributed primarily to tumor inhibition. Without the PD-1/PD-L1 axis, CMTM6 suppression still significantly dampened tumor growth dependent on cytotoxic cells. Furthermore, we identified that CMTM6 was widely expressed on immune cells. T-cell CMTM6 levels increased with sustained immune activation and intratumoral immune exhaustion and affected T cell-intrinsic PD-L1 levels. Host CMTM6 knockout significantly restrained tumor growth in a manner dependent on CD8+ T cells and not entirely dependent on PD-L1. Thus, we developed and evaluated the antitumor efficacy of CMTM6-targeting adeno-associated virus (AAV), which effectively mobilized antitumor immunity and could be combined with various antitumor drugs. Our findings reveal that both tumor and host CMTM6 are involved in antitumor immunity with or without the PD-1/PD-L1 axis and that gene therapy targeting CMTM6 is a promising strategy for cancer immunotherapy.
-