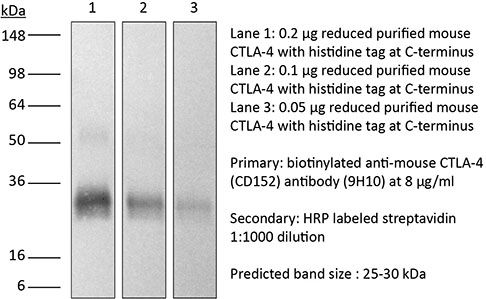
InVivoPlus anti-mouse CTLA-4 (CD152)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Syrian hamster IgG |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus polyclonal Syrian hamster IgG |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CTLA-4-human IgG1 fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin* |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10950184 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Ariyan, C. E., et al (2018). "Robust Antitumor Responses Result from Local Chemotherapy and CTLA-4 Blockade" Cancer Immunol Res 6(2): 189-200.
PubMed
Clinical responses to immunotherapy have been associated with augmentation of preexisting immune responses, manifested by heightened inflammation in the tumor microenvironment. However, many tumors have a noninflamed microenvironment, and response rates to immunotherapy in melanoma have been <50%. We approached this problem by utilizing immunotherapy (CTLA-4 blockade) combined with chemotherapy to induce local inflammation. In murine models of melanoma and prostate cancer, the combination of chemotherapy and CTLA-4 blockade induced a shift in the cellular composition of the tumor microenvironment, with infiltrating CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cells increasing the CD8/Foxp3 T-cell ratio. These changes were associated with improved survival of the mice. To translate these findings into a clinical setting, 26 patients with advanced melanoma were treated locally by isolated limb infusion with the nitrogen mustard alkylating agent melphalan followed by systemic administration of CTLA-4 blocking antibody (ipilimumab) in a phase II trial. This combination of local chemotherapy with systemic checkpoint blockade inhibitor resulted in a response rate of 85% at 3 months (62% complete and 23% partial response rate) and a 58% progression-free survival at 1 year. The clinical response was associated with increased T-cell infiltration, similar to that seen in the murine models. Together, our findings suggest that local chemotherapy combined with checkpoint blockade-based immunotherapy results in a durable response to cancer therapy.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Gao, J., et al (2016). "Loss of IFN-gamma Pathway Genes in Tumor Cells as a Mechanism of Resistance to Anti-CTLA-4 Therapy" Cell 167(2): 397-404 e399.
PubMed
Antibody blockade of the inhibitory CTLA-4 pathway has led to clinical benefit in a subset of patients with metastatic melanoma. Anti-CTLA-4 enhances T cell responses, including production of IFN-gamma, which is a critical cytokine for host immune responses. However, the role of IFN-gamma signaling in tumor cells in the setting of anti-CTLA-4 therapy remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that patients identified as non-responders to anti-CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) have tumors with genomic defects in IFN-gamma pathway genes. Furthermore, mice bearing melanoma tumors with knockdown of IFN-gamma receptor 1 (IFNGR1) have impaired tumor rejection upon anti-CTLA-4 therapy. These data highlight that loss of the IFN-gamma signaling pathway is associated with primary resistance to anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Our findings demonstrate the importance of tumor genomic data, especially IFN-gamma related genes, as prognostic information for patients selected to receive treatment with immune checkpoint therapy.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Bartkowiak, T., et al (2015). "Unique potential of 4-1BB agonist antibody to promote durable regression of HPV+ tumors when combined with an E6/E7 peptide vaccine" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(38): E5290-5299.
PubMed
Antibody modulation of T-cell coinhibitory (e.g., CTLA-4) or costimulatory (e.g., 4-1BB) receptors promotes clinical responses to a variety of cancers. Therapeutic cancer vaccination, in contrast, has produced limited clinical benefit and no curative therapies. The E6 and E7 oncoproteins of human papilloma virus (HPV) drive the majority of genital cancers, and many oropharyngeal tumors. We discovered 15-19 amino acid peptides from HPV-16 E6/E7 for which induction of T-cell immunity correlates with disease-free survival in patients treated for high-grade cervical neoplasia. We report here that intranasal vaccination with these peptides and the adjuvant alpha-galactosylceramide elicits systemic and mucosal T-cell responses leading to reduced HPV(+) TC-1 tumor growth and prolonged survival in mice. We hypothesized that the inability of these T cells to fully reject established tumors resulted from suppression in the tumor microenvironment which could be ameliorated through checkpoint modulation. Combining this E6/E7 peptide vaccine with checkpoint blockade produced only modest benefit; however, coadministration with a 4-1BB agonist antibody promoted durable regression of established genital TC-1 tumors. Relative to other therapies tested, this combination of vaccine and alpha4-1BB promoted the highest CD8(+) versus regulatory FoxP3(+) T-cell ratios, elicited 2- to 5-fold higher infiltration by E7-specific CTL, and evoked higher densities of highly cytotoxic TcEO (T cytotoxic Eomesodermin) CD8 (>70-fold) and ThEO (T helper Eomesodermin) CD4 (>17-fold) T cells. These findings have immediate clinical relevance both in terms of the direct clinical utility of the vaccine studied and in illustrating the potential of 4-1BB antibody to convert therapeutic E6/E7 vaccines already in clinical trials into curative therapies.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al (2015). "Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer" Nature 520(7547): 373-377.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors result in impressive clinical responses, but optimal results will require combination with each other and other therapies. This raises fundamental questions about mechanisms of non-redundancy and resistance. Here we report major tumour regressions in a subset of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with an anti-CTLA4 antibody (anti-CTLA4) and radiation, and reproduced this effect in mouse models. Although combined treatment improved responses in irradiated and unirradiated tumours, resistance was common. Unbiased analyses of mice revealed that resistance was due to upregulation of PD-L1 on melanoma cells and associated with T-cell exhaustion. Accordingly, optimal response in melanoma and other cancer types requires radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1/PD-1. Anti-CTLA4 predominantly inhibits T-regulatory cells (Treg cells), thereby increasing the CD8 T-cell to Treg (CD8/Treg) ratio. Radiation enhances the diversity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire of intratumoral T cells. Together, anti-CTLA4 promotes expansion of T cells, while radiation shapes the TCR repertoire of the expanded peripheral clones. Addition of PD-L1 blockade reverses T-cell exhaustion to mitigate depression in the CD8/Treg ratio and further encourages oligoclonal T-cell expansion. Similarly to results from mice, patients on our clinical trial with melanoma showing high PD-L1 did not respond to radiation plus anti-CTLA4, demonstrated persistent T-cell exhaustion, and rapidly progressed. Thus, PD-L1 on melanoma cells allows tumours to escape anti-CTLA4-based therapy, and the combination of radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1 promotes response and immunity through distinct mechanisms.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Spranger, S., et al (2015). "Melanoma-intrinsic beta-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity" Nature 523(7559): 231-235.
PubMed
Melanoma treatment is being revolutionized by the development of effective immunotherapeutic approaches. These strategies include blockade of immune-inhibitory receptors on activated T cells; for example, using monoclonal antibodies against CTLA-4, PD-1, and PD-L1 (refs 3-5). However, only a subset of patients responds to these treatments, and data suggest that therapeutic benefit is preferentially achieved in patients with a pre-existing T-cell response against their tumour, as evidenced by a baseline CD8(+) T-cell infiltration within the tumour microenvironment. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie the presence or absence of a spontaneous anti-tumour T-cell response in subsets of cases, therefore, should enable the development of therapeutic solutions for patients lacking a T-cell infiltrate. Here we identify a melanoma-cell-intrinsic oncogenic pathway that contributes to a lack of T-cell infiltration in melanoma. Molecular analysis of human metastatic melanoma samples revealed a correlation between activation of the WNT/beta-catenin signalling pathway and absence of a T-cell gene expression signature. Using autochthonous mouse melanoma models we identified the mechanism by which tumour-intrinsic active beta-catenin signalling results in T-cell exclusion and resistance to anti-PD-L1/anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody therapy. Specific oncogenic signals, therefore, can mediate cancer immune evasion and resistance to immunotherapies, pointing to new candidate targets for immune potentiation.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Stephan, S. B., et al (2015). "Biopolymer implants enhance the efficacy of adoptive T-cell therapy" Nat Biotechnol 33(1): 97-101.
PubMed
Although adoptive T-cell therapy holds promise for the treatment of many cancers, its clinical utility has been limited by problems in delivering targeted lymphocytes to tumor sites, and the cells’ inefficient expansion in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Here we describe a bioactive polymer implant capable of delivering, expanding and dispersing tumor-reactive T cells. The approach can be used to treat inoperable or incompletely removed tumors by situating implants near them or at resection sites. Using a mouse breast cancer resection model, we show that the implants effectively support tumor-targeting T cells throughout resection beds and associated lymph nodes, and reduce tumor relapse compared to conventional delivery modalities. In a multifocal ovarian cancer model, we demonstrate that polymer-delivered T cells trigger regression, whereas injected tumor-reactive lymphocytes have little curative effect. Scaffold-based T-cell delivery may provide a viable treatment option for inoperable tumors and reduce the rate of metastatic relapse after surgery.
in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization
Krummey, S. M., et al (2014). "Candida-elicited murine Th17 cells express high Ctla-4 compared with Th1 cells and are resistant to costimulation blockade" J Immunol 192(5): 2495-2504.
PubMed
Effector and memory T cells may cross-react with allogeneic Ags to mediate graft rejection. Whereas the costimulation properties of Th1 cells are well studied, relatively little is known about the costimulation requirements of microbe-elicited Th17 cells. The costimulation blocker CTLA-4 Ig has been ineffective in the treatment of several Th17-driven autoimmune diseases and is associated with severe acute rejection following renal transplantation, leading us to investigate whether Th17 cells play a role in CD28/CTLA-4 blockade-resistant alloreactivity. We established an Ag-specific model in which Th1 and Th17 cells were elicited via Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Candida albicans immunization, respectively. C. albicans immunization elicited a higher frequency of Th17 cells and conferred resistance to costimulation blockade following transplantation. Compared with the M. tuberculosis group, C. albicans-elicited Th17 cells contained a higher frequency of IL-17(+)IFN-gamma(+) producers and a lower frequency of IL-10(+) and IL-10(+)IL-17(+) cells. Importantly, Th17 cells differentially regulated the CD28/CTLA-4 pathway, expressing similarly high CD28 but significantly greater amounts of CTLA-4 compared with Th1 cells. Ex vivo blockade experiments demonstrated that Th17 cells are more sensitive to CTLA-4 coinhibition and therefore less susceptible to CTLA-4 Ig. These novel insights into the differential regulation of CTLA-4 coinhibition on CD4(+) T cells have implications for the immunomodulation of pathologic T cell responses during transplantation and autoimmunity.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Ozdemir, B. C., et al (2014). "Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival" Cancer Cell 25(6): 719-734.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is associated with marked fibrosis and stromal myofibroblasts, but their functional contribution remains unknown. Transgenic mice with the ability to delete alphaSMA(+) myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer were generated. Depletion starting at either noninvasive precursor (pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia) or the PDAC stage led to invasive, undifferentiated tumors with enhanced hypoxia, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and cancer stem cells, with diminished animal survival. In PDAC patients, fewer myofibroblasts in their tumors also correlated with reduced survival. Suppressed immune surveillance with increased CD4(+)Foxp3(+) Tregs was observed in myofibroblast-depleted mouse tumors. Although myofibroblast-depleted tumors did not respond to gemcitabine, anti-CTLA4 immunotherapy reversed disease acceleration and prolonged animal survival. This study underscores the need for caution in targeting carcinoma-associated fibroblasts in PDAC.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Hervieu, A., et al (2013). "Dacarbazine-mediated upregulation of NKG2D ligands on tumor cells activates NK and CD8 T cells and restrains melanoma growth" J Invest Dermatol 133(2): 499-508.
PubMed
Dacarbazine (DTIC) is a cytotoxic drug widely used for melanoma treatment. However, the putative contribution of anticancer immune responses in the efficacy of DTIC has not been evaluated. By testing how DTIC affects host immune responses to cancer in a mouse model of melanoma, we unexpectedly found that both natural killer (NK) and CD8(+) T cells were indispensable for DTIC therapeutic effect. Although DTIC did not directly affect immune cells, it triggered the upregulation of NKG2D ligands on tumor cells, leading to NK cell activation and IFNgamma secretion in mice and humans. NK cell-derived IFNgamma subsequently favored upregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on tumor cells, rendering them sensitive to cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells. Accordingly, DTIC markedly enhanced cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 inhibition efficacy in vivo in an NK-dependent manner. These results underscore the immunogenic properties of DTIC and provide a rationale to combine DTIC with immunotherapeutic agents that relieve immunosuppression in vivo.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Goding, S. R., et al (2013). "Restoring immune function of tumor-specific CD4+ T cells during recurrence of melanoma" J Immunol 190(9): 4899-4909.
PubMed
Recurrent solid malignancies are often refractory to standard therapies. Although adoptive T cell transfer may benefit select individuals, the majority of patients succumb to their disease. To address this important clinical dilemma, we developed a mouse melanoma model in which initial regression of advanced disease was followed by tumor recurrence. During recurrence, Foxp3(+) tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells became PD-1(+) and represented >60% of the tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells in the host. Concomitantly, tumor-specific CD4(+) T effector cells showed traits of chronic exhaustion, as evidenced by their high expression of the PD-1, TIM-3, 2B4, TIGIT, and LAG-3 inhibitory molecules. Although blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway with anti-PD-L1 Abs or depletion of tumor-specific regulatory T cells (Tregs) alone failed to reverse tumor recurrence, the combination of PD-L1 blockade with tumor-specific Treg depletion effectively mediated disease regression. Furthermore, blockade with a combination of anti-PD-L1 and anti-LAG-3 Abs overcame the requirement to deplete tumor-specific Tregs. In contrast, successful treatment of primary melanoma with adoptive cell therapy required only Treg depletion or Ab therapy, underscoring the differences in the characteristics of treatment between primary and relapsing cancer. These data highlight the need for preclinical development of combined immunotherapy approaches specifically targeting recurrent disease.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Waitz, R., et al (2012). "Potent induction of tumor immunity by combining tumor cryoablation with anti-CTLA-4 therapy" Cancer Res 72(2): 430-439.
PubMed
Thermal ablation to destroy tumor tissue may help activate tumor-specific T cells by elevating the presentation of tumor antigens to the immune system. However, the antitumor activity of these T cells may be restrained by their expression of the inhibitory T-cell coreceptor CTLA-4, the target of the recently U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved antibody drug ipilumimab. By relieving this restraint, CTLA-4-blocking antibodies such as ipilumimab can promote tumor rejection, but the full scope of their most suitable applications has yet to be fully determined. In this study, we offer a preclinical proof-of-concept in the TRAMP C2 mouse model of prostate cancer that CTLA-4 blockade cooperates with cryoablation of a primary tumor to prevent the outgrowth of secondary tumors seeded by challenge at a distant site. Although growth of secondary tumors was unaffected by cryoablation alone, the combination treatment was sufficient to slow growth or trigger rejection. In addition, secondary tumors were highly infiltrated by CD4(+) T cells and CD8(+) T cells, and there was a significant increase in the ratio of intratumoral T effector cells to CD4(+)FoxP3(+) T regulatory cells, compared with monotherapy. These findings documented for the first time an effect of this immunotherapeutic intervention on the intratumoral accumulation and systemic expansion of CD8(+) T cells specific for the TRAMP C2-specific antigen SPAS-1. Although cryoablation is currently used to treat a targeted tumor nodule, our results suggest that combination therapy with CTLA-4 blockade will augment antitumor immunity and rejection of tumor metastases in this setting.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Balachandran, V. P., et al (2011). "Imatinib potentiates antitumor T cell responses in gastrointestinal stromal tumor through the inhibition of Ido" Nat Med 17(9): 1094-1100.
PubMed
Imatinib mesylate targets mutated KIT oncoproteins in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) and produces a clinical response in 80% of patients. The mechanism is believed to depend predominantly on the inhibition of KIT-driven signals for tumor-cell survival and proliferation. Using a mouse model of spontaneous GIST, we found that the immune system contributes substantially to the antitumor effects of imatinib. Imatinib therapy activated CD8(+) T cells and induced regulatory T cell (T(reg) cell) apoptosis within the tumor by reducing tumor-cell expression of the immunosuppressive enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (Ido). Concurrent immunotherapy augmented the efficacy of imatinib in mouse GIST. In freshly obtained human GIST specimens, the T cell profile correlated with imatinib sensitivity and IDO expression. Thus, T cells are crucial to the antitumor effects of imatinib in GIST, and concomitant immunotherapy may further improve outcomes in human cancers treated with targeted agents.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Pedicord, V. A., et al (2011). "Single dose of anti-CTLA-4 enhances CD8+ T-cell memory formation, function, and maintenance" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(1): 266-271.
PubMed
CTLA-4, an Ig superfamily molecule with homology to CD28, is one of the most potent negative regulators of T-cell responses. In vivo blockade of CTLA-4 exacerbates autoimmunity, enhances tumor-specific T-cell responses, and may inhibit the induction of T-cell anergy. Clinical trials of CTLA-4-blocking antibodies to augment T-cell responses to malignant melanoma are at an advanced stage; however, little is known about the effects of CTLA-4 blockade on memory CD8(+) T-cell responses and the formation and maintenance of long-term CD8(+) T-cell memory. In our studies, we show that during in vivo memory CD8(+) T-cell responses to Listeria monocytogenes infection, CTLA-4 blockade enhances bacterial clearance and increases memory CD8(+) T-cell expansion. This is followed by an accumulation of memory cells that are capable of producing the effector cytokines IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. We also demonstrate that in a vaccination setting, blocking CTLA-4 during CD8(+) T-cell priming leads to increased expansion and maintenance of antigen-specific memory CD8(+) T cells without adversely affecting the overall T-cell repertoire. This leads to an increase in memory cell effector function and improved protective immunity against further bacterial challenges. These results indicate that transient blockade of CTLA-4 enhances memory CD8(+) T-cell responses and support the possible use of CTLA-4-blocking antibodies during vaccination to augment memory formation and maintenance.
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization
Quezada, S. A., et al (2010). "Tumor-reactive CD4(+) T cells develop cytotoxic activity and eradicate large established melanoma after transfer into lymphopenic hosts" J Exp Med 207(3): 637-650.
PubMed
Adoptive transfer of large numbers of tumor-reactive CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) expanded and differentiated in vitro has shown promising clinical activity against cancer. However, such protocols are complicated by extensive ex vivo manipulations of tumor-reactive cells and have largely focused on CD8(+) CTLs, with much less emphasis on the role and contribution of CD4(+) T cells. Using a mouse model of advanced melanoma, we found that transfer of small numbers of naive tumor-reactive CD4(+) T cells into lymphopenic recipients induces substantial T cell expansion, differentiation, and regression of large established tumors without the need for in vitro manipulation. Surprisingly, CD4(+) T cells developed cytotoxic activity, and tumor rejection was dependent on class II-restricted recognition of tumors by tumor-reactive CD4(+) T cells. Furthermore, blockade of the coinhibitory receptor CTL-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) on the transferred CD4(+) T cells resulted in greater expansion of effector T cells, diminished accumulation of tumor-reactive regulatory T cells, and superior antitumor activity capable of inducing regression of spontaneous mouse melanoma. These findings suggest a novel potential therapeutic role for cytotoxic CD4(+) T cells and CTLA-4 blockade in cancer immunotherapy, and demonstrate the potential advantages of differentiating tumor-reactive CD4(+) cells in vivo over current protocols favoring in vitro expansion and differentiation.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Developing a therapeutic elastase that stimulates anti-tumor immunity by selectively killing cancer cells.
In Cell Rep Med on 18 November 2025 by Gujar, R., Cui, C., et al.
PubMed
Recent clinical studies highlight the effectiveness of combining cytotoxic agents with immunotherapies, emphasizing the need for next-generation treatments that integrate both therapeutic approaches. Here, we use 30 cancer cell lines, 15 tumor models, and 45 patient samples to develop N17350, a therapeutic elastase that targets the "neutrophil elastase pathway" to induce tumor regression and stimulate anti-tumor immunity. N17350 leverages linker histone H1.0 and H1.2, proteins elevated in many cancers, to trigger immunogenic cancer cell death while preserving immune cells. Intra-tumoral N17350 administration induces rapid, genotype-independent tumor regression, triggering CD8+ T cell activation to promote durable responses and enable checkpoint inhibitor efficacy in refractory models. N17350 maintains potency with repeated dosing and across diverse treatment histories, including resistance to chemotherapies and checkpoint inhibitors. These findings support the advancement of N17350 to first-in-human clinical trials as a cytotoxic agent designed to stimulate anti-tumor immunity by selectively killing cancer cells.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
LncRNA-CTD suppresses metastasis and immune evasion by modulating snail1 and MHC-I expression in colorectal cancer.
In J Immunother Cancer on 15 September 2025 by Xu, N., Qiu, H., et al.
PubMed
Distant metastasis and immune evasion are the major obstacles for successful colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment. The link between metastasis and immune evasion, as well as their therapeutic significance, remains unclear.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Tumor-associated MerTK promotes a pro-inflammatory microenvironment and enhances immune checkpoint inhibitor response in triple-negative breast cancer.
In Front Oncol on 20 May 2025 by Crossman, B. E., Harmon, R. L., et al.
PubMed
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype of breast cancer with no targeted treatment modalities. Currently, combination chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy are options for many TNBC patients; however, their efficacy is limited. Understanding what makes TNBCs responsive to immune therapy is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Anti-CTLA4 treatment reduces lymphedema risk potentially through a systemic expansion of the FOXP3+ Treg population.
In Nat Commun on 30 December 2024 by Wolf, S., Madanchi, M., et al.
PubMed
Secondary lymphedema is a common sequel of oncologic surgery and presents a global health burden still lacking pharmacological treatment. The infiltration of the lymphedematous extremities with CD4+T cells influences lymphedema onset and emerges as a promising therapy target. Here, we show that the modulation of CD4+FOXP3+CD25+regulatory T (Treg) cells upon anti-CTLA4 treatment protects against lymphedema development in patients with melanoma and in a mouse lymphedema model. A retrospective evaluation of a melanoma patient registry reveals that anti-CTLA4 reduces lymphedema risk; in parallel, anti-CTLA4 reduces edema and improves lymphatic function in a mouse-tail lymphedema model. This protective effect of anti-CTLA4 correlates with a systemic expansion of Tregs, both in the animal model and in patients with melanoma. Our data thus show that anti-CTLA4 with its lymphedema-protective and anti-tumor properties is a promising candidate for more diverse application in the clinics.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
-
Pathology
T cell-mediated microglial activation triggers myelin pathology in a mouse model of amyloidosis.
In Nat Neurosci on 1 August 2024 by Kedia, S., Ji, H., et al.
PubMed
Age-related myelin damage induces inflammatory responses, yet its involvement in Alzheimer's disease remains uncertain, despite age being a major risk factor. Using a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, we found that amyloidosis itself triggers age-related oligodendrocyte and myelin damage. Mechanistically, CD8+ T cells promote the progressive accumulation of abnormally interferon-activated microglia that display myelin-damaging activity. Thus, our data suggest that immune responses against myelinating oligodendrocytes may contribute to neurodegenerative diseases with amyloidosis.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Noncovalently particle-anchored cytokines with prolonged tumor retention safely elicit potent antitumor immunity.
In Sci Adv on 19 April 2024 by Niu, L., Jang, E., et al.
PubMed
Preclinical studies have shown that immunostimulatory cytokines elicit antitumor immune responses but their clinical use is limited by severe immune-related adverse events upon systemic administration. Here, we report a facile and versatile strategy for noncovalently anchoring potent Fc-fused cytokine molecules to the surface of size-discrete particles decorated with Fc-binding peptide for local administration. Following intratumoral injection, particle-anchored Fc cytokines exhibit size-dependent intratumoral retention. The 1-micrometer particle prolongs intratumoral retention of Fc cytokine for over a week and has minimal systemic exposure, thereby eliciting antitumor immunity while eliminating systemic toxicity caused by circulating cytokines. In addition, the combination of these particle-anchored cytokines with immune checkpoint blockade antibodies safely promotes tumor regression in various syngeneic tumor models and genetically engineered murine tumor models and elicits systemic antitumor immunity against tumor rechallenge. Our formulation strategy renders a safe and tumor-agnostic approach that uncouples cytokines' immunostimulatory properties from their systemic toxicities for potential clinical application.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
SMARCAL1 is a dual regulator of innate immune signaling and PD-L1 expression that promotes tumor immune evasion.
In Cell on 15 February 2024 by Leuzzi, G., Vasciaveo, A., et al.
PubMed
Genomic instability can trigger cancer-intrinsic innate immune responses that promote tumor rejection. However, cancer cells often evade these responses by overexpressing immune checkpoint regulators, such as PD-L1. Here, we identify the SNF2-family DNA translocase SMARCAL1 as a factor that favors tumor immune evasion by a dual mechanism involving both the suppression of innate immune signaling and the induction of PD-L1-mediated immune checkpoint responses. Mechanistically, SMARCAL1 limits endogenous DNA damage, thereby suppressing cGAS-STING-dependent signaling during cancer cell growth. Simultaneously, it cooperates with the AP-1 family member JUN to maintain chromatin accessibility at a PD-L1 transcriptional regulatory element, thereby promoting PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. SMARCAL1 loss hinders the ability of tumor cells to induce PD-L1 in response to genomic instability, enhances anti-tumor immune responses and sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint blockade in a mouse melanoma model. Collectively, these studies uncover SMARCAL1 as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Electrostatic-driven Interactions Enhance Intratumoral Retention and Antitumor Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Antibodies
In bioRxiv on 23 December 2023 by Mohanty, R. P., Pan, Y., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Cancer immunotherapy responses persist after lymph node resection
In bioRxiv on 22 September 2023 by Zhou, H., Baish, J. W., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The GPCR-Gαs-PKA signaling axis promotes T cell dysfunction and cancer immunotherapy failure.
In Nat Immunol on 1 August 2023 by Wu, V. H., Yung, B. S., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) targeting PD-1 and CTLA-4 has revolutionized cancer treatment. However, many cancers do not respond to ICB, prompting the search for additional strategies to achieve durable responses. G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the most intensively studied drug targets but are underexplored in immuno-oncology. Here, we cross-integrated large singe-cell RNA-sequencing datasets from CD8+ T cells covering 19 distinct cancer types and identified an enrichment of Gαs-coupled GPCRs on exhausted CD8+ T cells. These include EP2, EP4, A2AR, β1AR and β2AR, all of which promote T cell dysfunction. We also developed transgenic mice expressing a chemogenetic CD8-restricted Gαs-DREADD to activate CD8-restricted Gαs signaling and show that a Gαs-PKA signaling axis promotes CD8+ T cell dysfunction and immunotherapy failure. These data indicate that Gαs-GPCRs are druggable immune checkpoints that might be targeted to enhance the response to ICB immunotherapies.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Defining the spatial distribution of extracellular adenosine revealed a myeloid-dependent immunosuppressive microenvironment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
In J Immunother Cancer on 1 August 2023 by Graziano, V., Dannhorn, A., et al.
PubMed
The prognosis for patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains extremely poor. It has been suggested that the adenosine pathway contributes to the ability of PDAC to evade the immune system and hence, its resistance to immuno-oncology therapies (IOT), by generating extracellular adenosine (eAdo).
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Priming a vascular-selective cytokine response permits CD8+ T-cell entry into tumors.
In Nat Commun on 14 April 2023 by Kim, D. J., Anandh, S., et al.
PubMed
Targeting DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) has immunomodulatory and anti-neoplastic activity, especially when paired with cancer immunotherapies. Here we explore the immunoregulatory functions of DNMT1 in the tumor vasculature of female mice. Dnmt1 deletion in endothelial cells (ECs) impairs tumor growth while priming expression of cytokine-driven cell adhesion molecules and chemokines important for CD8+ T-cell trafficking across the vasculature; consequently, the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) is enhanced. We find that the proangiogenic factor FGF2 promotes ERK-mediated DNMT1 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation to repress transcription of the chemokines Cxcl9/Cxcl10 in ECs. Targeting Dnmt1 in ECs reduces proliferation but augments Th1 chemokine production and extravasation of CD8+ T-cells, suggesting DNMT1 programs immunologically anergic tumor vasculature. Our study is in good accord with preclinical observations that pharmacologically disrupting DNMT1 enhances the activity of ICB but suggests an epigenetic pathway presumed to be targeted in cancer cells is also operative in the tumor vasculature.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Breast cancer cells survive chemotherapy by activating targetable immune-modulatory programs characterized by PD-L1 or CD80.
In Nat Cancer on 1 December 2022 by Shahbandi, A., Chiu, F. Y., et al.
PubMed
Breast cancer cells must avoid intrinsic and extrinsic cell death to relapse following chemotherapy. Entering senescence enables survival from mitotic catastrophe, apoptosis and nutrient deprivation, but mechanisms of immune evasion are poorly understood. Here we show that breast tumors surviving chemotherapy activate complex programs of immune modulation. Characterization of residual disease revealed distinct tumor cell populations. The first population was characterized by interferon response genes, typified by Cd274, whose expression required chemotherapy to enhance chromatin accessibility, enabling recruitment of IRF1 transcription factor. A second population was characterized by p53 signaling, typified by CD80 expression. Treating mammary tumors with chemotherapy followed by targeting the PD-L1 and/or CD80 axes resulted in marked accumulation of T cells and improved response; however, even combination strategies failed to fully eradicate tumors in the majority of cases. Our findings reveal the challenge of eliminating residual disease populated by senescent cells expressing redundant immune inhibitory pathways and highlight the need for rational immune targeting strategies.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
CD8+ T cells induce interferon-responsive oligodendrocytes and microglia in white matter aging.
In Nat Neurosci on 1 November 2022 by Kaya, T., Mattugini, N., et al.
PubMed
A hallmark of nervous system aging is a decline of white matter volume and function, but the underlying mechanisms leading to white matter pathology are unknown. In the present study, we found age-related alterations of oligodendrocyte cell state with a reduction in total oligodendrocyte density in aging murine white matter. Using single-cell RNA-sequencing, we identified interferon (IFN)-responsive oligodendrocytes, which localize in proximity to CD8+ T cells in aging white matter. Absence of functional lymphocytes decreased the number of IFN-responsive oligodendrocytes and rescued oligodendrocyte loss, whereas T-cell checkpoint inhibition worsened the aging response. In addition, we identified a subpopulation of lymphocyte-dependent, IFN-responsive microglia in the vicinity of the CD8+ T cells in aging white matter. In summary, we provide evidence that CD8+ T-cell-induced, IFN-responsive oligodendrocytes and microglia are important modifiers of white matter aging.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
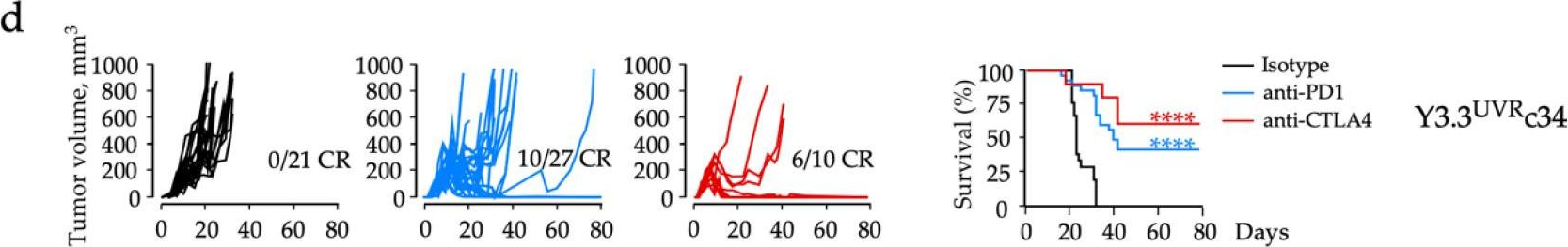
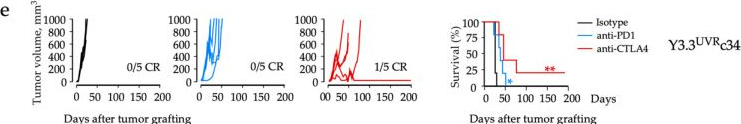
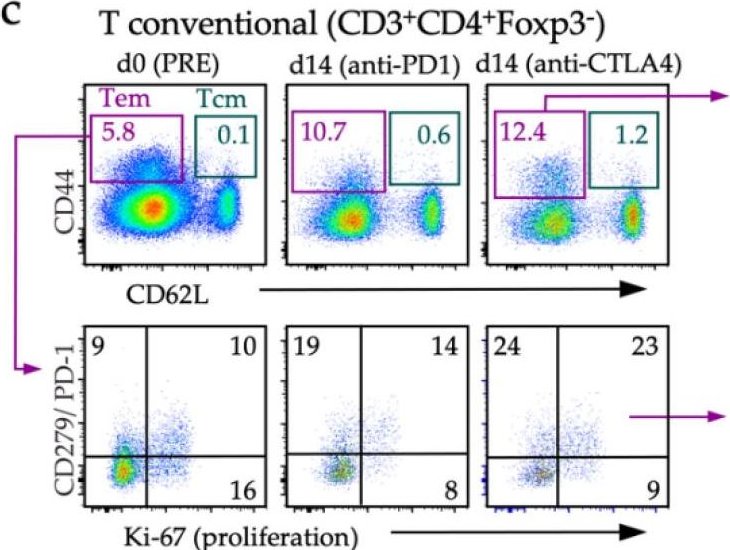
Durable Responses to Anti-PD1 and Anti-CTLA4 in a Preclinical Model of Melanoma Displaying Key Immunotherapy Response Biomarkers.
In Cancers (Basel) on 3 October 2022 by Shklovskaya, E., Pedersen, B., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapy has transformed the management of patients with advanced melanoma, with five-year overall survival rates reaching 52% for combination immunotherapies blocking the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA4) and programmed cell death-1 (PD1) immune axes. Yet, our understanding of local and systemic determinants of immunotherapy response and resistance is restrained by the paucity of preclinical models, particularly those for anti-PD1 monotherapy. We have therefore generated a novel murine model of melanoma by integrating key immunotherapy response biomarkers into the model development workflow. The resulting YUMM3.3UVRc34 (BrafV600E; Cdkn2a-/-) model demonstrated high mutation burden and response to interferon (IFN)γ, including induced expression of antigen-presenting molecule MHC-I and the principal PD1 ligand PD-L1, consistent with phenotypes of human melanoma biopsies from patients subsequently responding to anti-PD1 monotherapy. Syngeneic immunosufficient mice bearing YUMM3.3UVRc34 tumors demonstrated durable responses to anti-PD1, anti-CTLA4, or combined treatment. Immunotherapy responses were associated with early on-treatment changes in the tumor microenvironment and circulating T-cell subsets, and systemic immunological memory underlying protection from tumor recurrence. Local and systemic immunological landscapes associated with immunotherapy response in the YUMM3.3UVRc34 melanoma model recapitulate immunotherapy responses observed in melanoma patients and identify discrete immunological mechanisms underlying the durability of responses to anti-PD1 and anti-CTLA4 treatments.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The Wnt Pathway Inhibitor RXC004 Blocks Tumor Growth and Reverses Immune Evasion in Wnt Ligand-dependent Cancer Models.
In Cancer Res Commun on 1 September 2022 by Phillips, C., Bhamra, I., et al.
PubMed
Wnt signaling is implicated in the etiology of gastrointestinal tract cancers. Targeting Wnt signaling is challenging due to on-target toxicity concerns and lack of druggable pathway components. We describe the discovery and characterization of RXC004, a potent and selective inhibitor of the membrane-bound o-acyl transferase Porcupine, essential for Wnt ligand secretion. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion and safety pharmacology studies were conducted with RXC004 in vitro, and pharmacokinetic exposure assessed in vivo. RXC004 effects on proliferation and tumor metabolism were explored in genetically defined colorectal and pancreatic cancer models in vitro and in vivo. RXC004 effects on immune evasion were assessed in B16F10 immune "cold" and CT26 immune "hot" murine syngeneic models, and in human cell cocultures. RXC004 showed a promising pharmacokinetic profile, inhibited Wnt ligand palmitoylation, secretion, and pathway activation, and demonstrated potent antiproliferative effects in Wnt ligand-dependent (RNF43-mutant or RSPO3-fusion) colorectal and pancreatic cell lines. Reduced tumor growth and increased cancer cell differentiation were observed in SNU-1411 (RSPO3-fusion), AsPC1 and HPAF-II (both RNF43-mutant) xenograft models, with a therapeutic window versus Wnt homeostatic functions. Additional effects of RXC004 on tumor cell metabolism were confirmed in vitro and in vivo by glucose uptake and 18fluorodeoxyglucose-PET, respectively. RXC004 stimulated host tumor immunity; reducing resident myeloid-derived suppressor cells within B16F10 tumors and synergizing with anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) to increase CD8+/regulatory T cell ratios within CT26 tumors. Moreover, RXC004 reversed the immunosuppressive effects of HPAF-II cells cocultured with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, confirming the multiple anticancer mechanisms of this compound, which has progressed into phase II clinical trials.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Immune checkpoint blockade enhances chemophototherapy in a syngeneic pancreatic tumor model.
In APL Bioeng on 1 September 2022 by Ghosh, S., He, X., et al.
PubMed
Pancreatic cancer (PaCa) suffers from poor treatment options for locally advanced cases. Chemophototherapy (CPT) is an emerging anti-tumor modality, and porphyrin-phospholipid liposomes have been shown to be versatile drug carriers for CPT in preclinical rodent models. Here we show that in the syngeneic subcutaneous KPC PaCa tumor model, exhausted CD8+ T cells are localized in the tumor, and that CPT is enhanced in combination with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). Addition of ICB using anti-programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) antibodies resulted in ablation of medium-sized, established KPC tumors (∼200 mm3) without recurrence for over 100 days. Mice rejected subsequent tumor re-challenge. Flow cytometry and tumor slice analysis following injection of a fluorescently labeled anti-PD-1 antibody showed that CPT improved antibody delivery to the tumor microenvironment. Treatment of large established tumors (∼400 mm3) using with CPT and ICB induced appreciable tumor regression and delay in regrowth. Taken together, these data demonstrate the utility of combining CPT with immunotherapies.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lymphatic-preserving treatment sequencing with immune checkpoint inhibition unleashes cDC1-dependent antitumor immunity in HNSCC.
In Nat Commun on 25 July 2022 by Saddawi-Konefka, R., O'Farrell, A., et al.
PubMed
Despite the promise of immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI), therapeutic responses remain limited. This raises the possibility that standard of care treatments delivered in concert may compromise the tumor response. To address this, we employ tobacco-signature head and neck squamous cell carcinoma murine models in which we map tumor-draining lymphatics and develop models for regional lymphablation with surgery or radiation. We find that lymphablation eliminates the tumor ICI response, worsening overall survival and repolarizing the tumor- and peripheral-immune compartments. Mechanistically, within tumor-draining lymphatics, we observe an upregulation of conventional type I dendritic cells and type I interferon signaling and show that both are necessary for the ICI response and lost with lymphablation. Ultimately, we provide a mechanistic understanding of how standard oncologic therapies targeting regional lymphatics impact the tumor response to immune-oncology therapy in order to define rational, lymphatic-preserving treatment sequences that mobilize systemic antitumor immunity, achieve optimal tumor responses, control regional metastatic disease, and confer durable antitumor immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Bacterial Cellulose as Drug Delivery System for Optimizing Release of Immune Checkpoint Blocking Antibodies.
In Pharmaceutics on 25 June 2022 by Chung, C. K., Beekmann, U., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blocking therapy is a promising cancer treatment modality, though it has limitations such as systemic toxicity, which can often be traced to uncontrolled antibody spread. Controlling antibody release with delivery systems is, therefore, an attractive approach to reduce systemic antibody spread and potentially mitigate the side effects of checkpoint immunotherapy. Here, bacterial cellulose (BC) was produced and investigated as a delivery system for optimizing checkpoint-blocking antibody delivery. BC was produced in 24-well plates, and afterward, the edges were removed to obtain square-shaped BC samples with a surface of ~49 mm2. This customization was necessary to allow smooth in vivo implantation. Scanning electron microscopy revealed the dense cellulose network within BC. Human IgG antibody was included as the model antibody for loading and release studies. IgG antibody solution was injected into the center of BC samples. In vitro, all IgG was released within 24 to 48 h. Cell culture experiments demonstrated that BC neither exerted cytotoxic effects nor induced dendritic cell activation. Antibody binding assays demonstrated that BC does not hamper antibody function. Finally, antibody-loaded BC was implanted in mice, and serum measurements revealed that BC significantly reduced IgG and anti-CTLA-4 spread in mice. BC implantation did not induce side effects in mice. Altogether, BC is a promising and safe delivery system for optimizing the delivery and release of checkpoint-blocking antibodies.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Defining the spatial distribution of extracellular adenosine revealed a myeloid-dependent immunosuppressive microenvironment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
In bioRxiv on 25 May 2022 by Graziano, V., Dannhorn, A., et al.
-