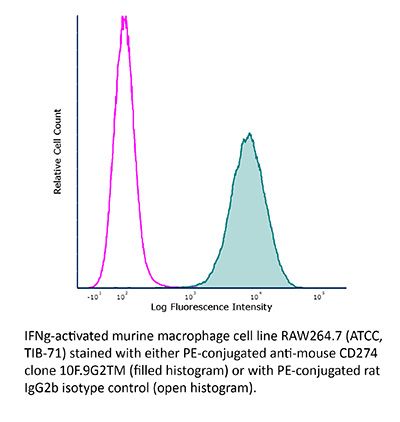
InVivoPlus anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 6.5 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CD274 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo PD-L1 blockade in vitro PD-L1 blockade Immunofluorescence Immunohistochemistry (frozen) Flow cytometry Western blot in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 6.5 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin* |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10949073 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip
Sivakumar R, Chan M, Shin JS, Nishida-Aoki N, Kenerson HL, Elemento O, Beltran H, Yeung R, Gujral TS (2019). "Organotypic tumor slice cultures provide a versatile platform for immuno-oncology and drug discovery" Oncoimmunology 8(12):e1670019.
PubMed
Organotypic tumor slices represent a physiologically-relevant culture system for studying the tumor microenvironment. Systematic characterization of the tumor slice culture system will enable its effective application for translational research. Here, using flow cytometry-based immunophenotyping, we performed a comprehensive characterization of the immune cell composition in organotypic tumor slices prepared from four syngeneic mouse tumor models and a human liver tumor. We found that the immune cell compositions of organotypic tumor slices prepared on the same day as the tumor cores were harvested are similar. Differences were primarily observed in the lymphocyte population of a clinical hepatocellular carcinoma case. Viable populations of immune cells persisted in the tumor slices for 7 days. Despite some changes in the immune cell populations, we showed the utility of mouse tumor slices for assessing responses to immune-modulatory agents. Further, we demonstrated the ability to use patient-derived xenograft tumor slices for assessing responses to targeted and cytotoxic drugs. Overall, tumor slices provide a broadly useful platform for studying the tumor microenvironment and evaluating the preclinical efficacy of cancer therapeutics.
in vitro PD-L1 blockade
Passariello M, D', Alise AM, Esposito A, Vetrei C, Froechlich G, Scarselli E, Nicosia A, De Lorenzo C (2019). "Novel Human Anti-PD-L1 mAbs Inhibit Immune-Independent Tumor Cell Growth and PD-L1 Associated Intracellular Signalling" Sci Rep 9(1):13
PubMed
The novel antibody-based immunotherapy in oncology exploits the activation of immune system mediated by immunomodulatory antibodies specific for immune checkpoints. Among them, the programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is of particular interest as it is expressed not only on T-cells, but also on other immune cells and on a large variety of cancer cells, such as breast cancer cells, considering its high expression in both ErbB2-positive and Triple Negative Breast Cancers. We demonstrate here that PD-L1_1, a novel anti-PD-L1 T -cell stimulating antibody, inhibits PD-L1-tumor cell growth also by affecting the intracellular MAPK pathway and by activating caspase 3. Similar in vitro results were obtained for the first time here also with the clinically validated anti-PD-L1 mAb Atezolizumab and in vivo with another validated anti-mouse anti-PD-L1 mAb. Moreover, we found that two high affinity variants of PD-L1_1 inhibited tumor cell viability more efficiently than the parental PD-L1_1 by affecting the same MAPK pathways with a more potent effect. Altogether, these results shed light on the role of PD-L1 in cancer cells and suggest that PD-L1_1 and its high affinity variants could become powerful antitumor weapons to be used alone or in combination with other drugs such as the anti-ErbB2 cAb already successfully tested in in vitro combinatorial treatments.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Stathopoulou, C., et al (2018). "PD-1 Inhibitory Receptor Downregulates Asparaginyl Endopeptidase and Maintains Foxp3 Transcription Factor Stability in Induced Regulatory T Cells" Immunity 49(2): 247-263 e247.
PubMed
CD4(+) T cell differentiation into multiple T helper (Th) cell lineages is critical for optimal adaptive immune responses. This report identifies an intrinsic mechanism by which programmed death-1 receptor (PD-1) signaling imparted regulatory phenotype to Foxp3(+) Th1 cells (denoted as Tbet(+)iTregPDL1 cells) and inducible regulatory T (iTreg) cells. Tbet(+)iTregPDL1 cells prevented inflammation in murine models of experimental colitis and experimental graft versus host disease (GvHD). Programmed death ligand-1 (PDL-1) binding to PD-1 imparted regulatory function to Tbet(+)iTregPDL1 cells and iTreg cells by specifically downregulating endo-lysosomal protease asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP). AEP regulated Foxp3 stability and blocking AEP imparted regulatory function in Tbet(+)iTreg cells. Also, Aep(-/-) iTreg cells significantly inhibited GvHD and maintained Foxp3 expression. PD-1-mediated Foxp3 maintenance in Tbet(+) Th1 cells occurred both in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and during chronic viral infection. Collectively, this report has identified an intrinsic function for PD-1 in maintaining Foxp3 through proteolytic pathway.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Grasselly, C., et al (2018). "The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent" Front Immunol 9: 2100.
PubMed
In spite of impressive response rates in multiple cancer types, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are active in only a minority of patients. Alternative strategies currently aim to combine immunotherapies with conventional agents such as cytotoxic chemotherapies. Here, we performed a study of PD-1 or PDL-1 blockade in combination with reference chemotherapies in four fully immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. We analyzed both the in vivo antitumor response, and the tumor immune infiltrate 4 days after the first treatment. in vivo tumor growth experiments revealed variable responsiveness to ICIs between models. We observed enhanced antitumor effects of the combination of immunotherapy with chemotherapy in the MC38 colon and MB49 bladder models, a lack of response in the 4T1 breast model, and an inhibition of ICIs activity in the MBT-2 bladder model. Flow cytometry analysis of tumor samples showed significant differences in all models between untreated and treated mice. At baseline, all the tumor models studied were predominantly infiltrated with cells harboring an immunosuppressive phenotype. Early alterations of the tumor immune infiltrate after treatment were found to be highly variable. We found that the balance between effector cells and immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment could be altered with some treatment combinations, but this effect was not always correlated with an impact on in vivo tumor growth. These results show that the combination of cytotoxic chemotherapy with ICIs may result in enhanced, similar or reduced antitumor activity, in a model- and regimen-dependent fashion. The present investigations should help to select appropriate combination regimens for ICIs.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Aloulou, M., et al (2016). "Follicular regulatory T cells can be specific for the immunizing antigen and derive from naive T cells" Nat Commun 7: 10579.
PubMed
T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells are a subset of Foxp3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells that form in response to immunization or infection, which localize to the germinal centre where they control the magnitude of the response. Despite an increased interest in the role of Tfr cells in humoral immunity, many fundamental aspects of their biology remain unknown, including whether they recognize self- or foreign antigen. Here we show that Tfr cells can be specific for the immunizing antigen, irrespective of whether it is a self- or foreign antigen. We show that, in addition to developing from thymic derived Treg cells, Tfr cells can also arise from Foxp3(-) precursors in a PD-L1-dependent manner, if the adjuvant used is one that supports T-cell plasticity. These findings have important implications for Tfr cell biology and for improving vaccine efficacy by formulating vaccines that modify the Tfr:Tfh cell ratio.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Ngiow, S. F., et al (2015). "A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1" Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811.
PubMed
Despite successes, thus far, a significant proportion of the patients treated with anti-PD1 antibodies have failed to respond. We use mouse tumor models of anti-PD1 sensitivity and resistance and flow cytometry to assess tumor-infiltrating immune cells immediately after therapy. We demonstrate that the expression levels of T-cell PD1 (PD1(lo)), myeloid, and T-cell PDL1 (PDL1(hi)) in the tumor microenvironment inversely correlate and dictate the efficacy of anti-PD1 mAb and function of intratumor CD8(+) T cells. In sensitive tumors, we reveal a threshold for PD1 downregulation on tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T cells below which the release of adaptive immune resistance is achieved. In contrast, PD1(hi) T cells in resistant tumors fail to be rescued by anti-PD1 therapy and remain dysfunctional unless intratumor PDL1(lo) immune cells are targeted. Intratumor Tregs are partly responsible for the development of anti-PD1-resistant tumors and PD1(hi) CD8(+) T cells. Our analyses provide a framework to interrogate intratumor CD8(+) T-cell PD1 and immune PDL1 levels and response in human cancer. Cancer Res; 75(18); 3800-11. (c)2015 AACR.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al (2015). "Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer" Nature 520(7547): 373-377.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors result in impressive clinical responses, but optimal results will require combination with each other and other therapies. This raises fundamental questions about mechanisms of non-redundancy and resistance. Here we report major tumour regressions in a subset of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with an anti-CTLA4 antibody (anti-CTLA4) and radiation, and reproduced this effect in mouse models. Although combined treatment improved responses in irradiated and unirradiated tumours, resistance was common. Unbiased analyses of mice revealed that resistance was due to upregulation of PD-L1 on melanoma cells and associated with T-cell exhaustion. Accordingly, optimal response in melanoma and other cancer types requires radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1/PD-1. Anti-CTLA4 predominantly inhibits T-regulatory cells (Treg cells), thereby increasing the CD8 T-cell to Treg (CD8/Treg) ratio. Radiation enhances the diversity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire of intratumoral T cells. Together, anti-CTLA4 promotes expansion of T cells, while radiation shapes the TCR repertoire of the expanded peripheral clones. Addition of PD-L1 blockade reverses T-cell exhaustion to mitigate depression in the CD8/Treg ratio and further encourages oligoclonal T-cell expansion. Similarly to results from mice, patients on our clinical trial with melanoma showing high PD-L1 did not respond to radiation plus anti-CTLA4, demonstrated persistent T-cell exhaustion, and rapidly progressed. Thus, PD-L1 on melanoma cells allows tumours to escape anti-CTLA4-based therapy, and the combination of radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1 promotes response and immunity through distinct mechanisms.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Kim, J., et al (2015). "Memory programming in CD8(+) T-cell differentiation is intrinsic and is not determined by CD4 help" Nat Commun 6: 7994.
PubMed
CD8(+) T cells activated without CD4(+) T-cell help are impaired in memory expansion. To understand the underlying cellular mechanism, here we track the dynamics of helper-deficient CD8(+) T-cell response to a minor histocompatibility antigen by phenotypic and in vivo imaging analyses. Helper-deficient CD8(+) T cells show reduced burst expansion, rapid peripheral egress, delayed antigen clearance and continuous activation, and are eventually exhausted. Contrary to the general consensus that CD4 help encodes memory programmes in CD8(+) T cells and helper-deficient CD8(+) T cells are abortive, these cells can differentiate into effectors and memory precursors. Importantly, accelerating antigen clearance or simply increasing the burst effector size enables generation of memory cells by CD8(+) T cells, regardless of CD4 help. These results suggest that the memory programme is CD8(+) T-cell-intrinsic, and provide insight into the role of CD4 help in CD8(+) T-cell responses.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Jaworska, K., et al (2015). "Both PD-1 ligands protect the kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury" J Immunol 194(1): 325-333.
PubMed
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common problem in hospitalized patients that enhances morbidity and mortality and promotes the development of chronic and end-stage renal disease. Ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) is one of the major causes of AKI and is characterized by uncontrolled renal inflammation and tubular epithelial cell death. Our recent studies demonstrated that regulatory T cells (Tregs) protect the kidney from ischemia reperfusion-induced inflammation and injury. Blockade of programmed death-1 (PD-1) on the surface of Tregs, prior to adoptive transfer, negates their ability to protect against ischemic kidney injury. The present study was designed to investigate the role of the known PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, in kidney IRI. Administration of PD-L1 or PD-L2 blocking Abs prior to mild or moderate kidney IRI significantly exacerbated the loss of renal function, renal inflammation, and acute tubular necrosis compared with mice receiving isotype control Abs. Interestingly, blockade of both PD-1 ligands resulted in worse injury, dysfunction, and inflammation than did blocking either ligand alone. Genetic deficiency of either PD-1 ligand also exacerbated kidney dysfunction and acute tubular necrosis after subthreshold ischemia. Bone marrow chimeric studies revealed that PD-L1 expressed on non-bone marrow-derived cells is critical for this resistance to IRI. Finally, blockade of either PD-1 ligand negated the protective ability of adoptively transferred Tregs in IRI. These findings suggest that PD-L1 and PD-L2 are nonredundant aspects of the natural protective response to ischemic injury and may be novel therapeutic targets for AKI.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Tkachev, V., et al (2015). "Programmed death-1 controls T cell survival by regulating oxidative metabolism" J Immunol 194(12): 5789-5800.
PubMed
The coinhibitory receptor programmed death-1 (PD-1) maintains immune homeostasis by negatively regulating T cell function and survival. Blockade of PD-1 increases the severity of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), but the interplay between PD-1 inhibition and T cell metabolism is not well studied. We found that both murine and human alloreactive T cells concomitantly upregulated PD-1 expression and increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. This PD-1(Hi)ROS(Hi) phenotype was specific to alloreactive T cells and was not observed in syngeneic T cells during homeostatic proliferation. Blockade of PD-1 signaling decreased both mitochondrial H2O2 and total cellular ROS levels, and PD-1-driven increases in ROS were dependent upon the oxidation of fatty acids, because treatment with etomoxir nullified changes in ROS levels following PD-1 blockade. Downstream of PD-1, elevated ROS levels impaired T cell survival in a process reversed by antioxidants. Furthermore, PD-1-driven changes in ROS were fundamental to establishing a cell’s susceptibility to subsequent metabolic inhibition, because blockade of PD-1 decreased the efficacy of later F1F0-ATP synthase modulation. These data indicate that PD-1 facilitates apoptosis in alloreactive T cells by increasing ROS in a process dependent upon the oxidation of fat. In addition, blockade of PD-1 undermines the potential for subsequent metabolic inhibition, an important consideration given the increasing use of anti-PD-1 therapies in the clinic.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Zander, R. A., et al (2015). "PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity" Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641.
PubMed
The differentiation and protective capacity of Plasmodium-specific T cells are regulated by both positive and negative signals during malaria, but the molecular and cellular details remain poorly defined. Here we show that malaria patients and Plasmodium-infected rodents exhibit atypical expression of the co-stimulatory receptor OX40 on CD4 T cells and that therapeutic enhancement of OX40 signaling enhances helper CD4 T cell activity, humoral immunity, and parasite clearance in rodents. However, these beneficial effects of OX40 signaling are abrogated following coordinate blockade of PD-1 co-inhibitory pathways, which are also upregulated during malaria and associated with elevated parasitemia. Co-administration of biologics blocking PD-1 and promoting OX40 signaling induces excessive interferon-gamma that directly limits helper T cell-mediated support of humoral immunity and decreases parasite control. Our results show that targeting OX40 can enhance Plasmodium control and that crosstalk between co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory pathways in pathogen-specific CD4 T cells can impact pathogen clearance.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Dolina, J. S., et al (2014). "Liver-primed CD8+ T cells suppress antiviral adaptive immunity through galectin-9-independent T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin 3 engagement of high-mobility group box 1 in mice" Hepatology 59(4): 1351-1365.
PubMed
The liver is a tolerogenic environment exploited by persistent infections, such as hepatitis B (HBV) and C (HCV) viruses. In a murine model of intravenous hepatotropic adenovirus infection, liver-primed antiviral CD8(+) T cells fail to produce proinflammatory cytokines and do not display cytolytic activity characteristic of effector CD8(+) T cells generated by infection at an extrahepatic, that is, subcutaneous, site. Importantly, liver-generated CD8(+) T cells also appear to have a T-regulatory (Treg) cell function exemplified by their ability to limit proliferation of antigen-specific T-effector (Teff ) cells in vitro and in vivo via T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin 3 (Tim-3) expressed by the CD8(+) Treg cells. Regulatory activity did not require recognition of the canonical Tim-3 ligand, galectin-9, but was dependent on CD8(+) Treg cell-surface Tim-3 binding to the alarmin, high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB-1). CONCLUSION: Virus-specific Tim-3(+) CD8(+) T cells operating through HMGB-1 recognition in the setting of acute and chronic viral infections of the liver may act to dampen hepatic T-cell responses in the liver microenvironment and, as a consequence, limit immune-mediated tissue injury or promote the establishment of persistent infections.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Deng, L., et al (2014). "Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice" J Clin Invest 124(2): 687-695.
PubMed
High-dose ionizing irradiation (IR) results in direct tumor cell death and augments tumor-specific immunity, which enhances tumor control both locally and distantly. Unfortunately, local relapses often occur following IR treatment, indicating that IR-induced responses are inadequate to maintain antitumor immunity. Therapeutic blockade of the T cell negative regulator programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1, also called B7-H1) can enhance T cell effector function when PD-L1 is expressed in chronically inflamed tissues and tumors. Here, we demonstrate that PD-L1 was upregulated in the tumor microenvironment after IR. Administration of anti-PD-L1 enhanced the efficacy of IR through a cytotoxic T cell-dependent mechanism. Concomitant with IR-mediated tumor regression, we observed that IR and anti-PD-L1 synergistically reduced the local accumulation of tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which suppress T cells and alter the tumor immune microenvironment. Furthermore, activation of cytotoxic T cells with combination therapy mediated the reduction of MDSCs in tumors through the cytotoxic actions of TNF. Our data provide evidence for a close interaction between IR, T cells, and the PD-L1/PD-1 axis and establish a basis for the rational design of combination therapy with immune modulators and radiotherapy.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Rutigliano, J. A., et al (2014). "Highly pathological influenza A virus infection is associated with augmented expression of PD-1 by functionally compromised virus-specific CD8+ T cells" J Virol 88(3): 1636-1651.
PubMed
One question that continues to challenge influenza A research is why some strains of virus are so devastating compared to their more mild counterparts. We approached this question from an immunological perspective, investigating the CD8(+) T cell response in a mouse model system comparing high- and low-pathological influenza virus infections. Our findings reveal that the early (day 0 to 5) viral titer was not the determining factor in the outcome of disease. Instead, increased numbers of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells and elevated effector function on a per-cell basis were found in the low-pathological infection and correlated with reduced illness and later-time-point (day 6 to 10) viral titer. High-pathological infection was associated with increased PD-1 expression on influenza virus-specific CD8(+) T cells, and blockade of PD-L1 in vivo led to reduced virus titers and increased CD8(+) T cell numbers in high- but not low-pathological infection, though T cell functionality was not restored. These data show that high-pathological acute influenza virus infection is associated with a dysregulated CD8(+) T cell response, which is likely caused by the more highly inflamed airway microenvironment during the early days of infection. Therapeutic approaches specifically aimed at modulating innate airway inflammation may therefore promote efficient CD8(+) T cell activity. We show that during a severe influenza virus infection, one type of immune cell, the CD8 T cell, is less abundant and less functional than in a more mild infection. This dysregulated T cell phenotype correlates with a lower rate of virus clearance in the severe infection and is partially regulated by the expression of a suppressive coreceptor called PD-1. Treatment with an antibody that blocks PD-1 improves T cell functionality and increases virus clearance.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Yang, X., et al (2014). "Targeting the tumor microenvironment with interferon-beta bridges innate and adaptive immune responses" Cancer Cell 25(1): 37-48.
PubMed
Antibodies (Abs) that preferentially target oncogenic receptors have been increasingly used for cancer therapy, but tumors often acquire intrinsic Ab resistance after prolonged and costly treatment. Herein we armed the Ab with IFNbeta and observed that it is more potent than the first generation of Ab for controlling Ab-resistant tumors. This strategy controls Ab resistance by rebridging suppressed innate and adaptive immunity in the tumor microenvironment. Mechanistically, Ab-IFNbeta therapy primarily and directly targets intratumoral dendritic cells, which reactivate CTL by increasing antigen cross-presentation within the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, blocking PD-L1, which is induced by Ab-IFNbeta treatment, overcomes treatment-acquired resistance and completely eradicates established tumors. This study establishes a next-generation Ab-based immunotherapy that targets and eradicates established Ab-resistant tumors.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Dietze, K. K., et al (2013). "Combining regulatory T cell depletion and inhibitory receptor blockade improves reactivation of exhausted virus-specific CD8+ T cells and efficiently reduces chronic retroviral loads" PLoS Pathog 9(12): e1003798.
PubMed
Chronic infections with human viruses, such as HIV and HCV, or mouse viruses, such as LCMV or Friend Virus (FV), result in functional exhaustion of CD8(+) T cells. Two main mechanisms have been described that mediate this exhaustion: expression of inhibitory receptors on CD8(+) T cells and expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) that suppress CD8(+) T cell activity. Several studies show that blockage of one of these pathways results in reactivation of CD8(+) T cells and partial reduction in chronic viral loads. Using blocking antibodies against PD-1 ligand and Tim-3 and transgenic mice in which Tregs can be selectively ablated, we compared these two treatment strategies and combined them for the first time in a model of chronic retrovirus infection. Blocking inhibitory receptors was more efficient than transient depletion of Tregs in reactivating exhausted CD8(+) T cells and reducing viral set points. However, a combination therapy was superior to any single treatment and further augmented CD8(+) T cell responses and resulted in a sustained reduction in chronic viral loads. These results demonstrate that Tregs and inhibitory receptors are non-overlapping factors in the maintenance of chronic viral infections and that immunotherapies targeting both pathways may be a promising strategy to treat chronic infectious diseases.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Immunofluorescence
Willimsky, G., et al (2013). "Virus-induced hepatocellular carcinomas cause antigen-specific local tolerance" J Clin Invest 123(3): 1032-1043.
PubMed
T cell surveillance is often effective against virus-associated tumors because of their high immunogenicity. It is not clear why surveillance occasionally fails, particularly against hepatitis B virus- or hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We established a transgenic murine model of virus-induced HCC by hepatocyte-specific adenovirus-induced activation of the oncogenic SV40 large T antigen (TAg). Adenovirus infection induced cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) targeted against the virus and TAg, leading to clearance of the infected cells. Despite the presence of functional, antigen-specific T cells, a few virus-infected cells escaped immune clearance and progressed to HCC. These cells expressed TAg at levels similar to HCC isolated from neonatal TAg-tolerant mice, suggesting that CTL clearance does not select for cells with low immunogenicity. Virus-infected mice revealed significantly greater T cell infiltration in early-stage HCC compared with that in late-stage HCC, demonstrating progressive local immune suppression through inefficient T cell infiltration. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 were expressed in all TAg-specific CD8+ T cells and HCC, respectively, which contributed to local tumor-antigen-specific tolerance. Thus, we have developed a model of virus-induced HCC that may allow for a better understanding of human HCC.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Hafalla, J. C., et al (2012). "The CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways independently regulate host resistance to Plasmodium-induced acute immune pathology" PLoS Pathog 8(2): e1002504.
PubMed
The balance between pro-inflammatory and regulatory immune responses in determining optimal T cell activation is vital for the successful resolution of microbial infections. This balance is maintained in part by the negative regulators of T cell activation, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L, which dampen effector responses during chronic infections. However, their role in acute infections, such as malaria, remains less clear. In this study, we determined the contribution of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L to the regulation of T cell responses during Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA)-induced experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) in susceptible (C57BL/6) and resistant (BALB/c) mice. We found that the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T cells correlates with the extent of pro-inflammatory responses induced during PbA infection, being higher in C57BL/6 than in BALB/c mice. Thus, ECM develops despite high levels of expression of these inhibitory receptors. However, antibody-mediated blockade of either the CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1, but not the PD-1/PD-L2, pathways during PbA-infection in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice resulted in higher levels of T cell activation, enhanced IFN-gamma production, increased intravascular arrest of both parasitised erythrocytes and CD8(+) T cells to the brain, and augmented incidence of ECM. Thus, in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 represent essential, independent and non-redundant pathways for maintaining T cell homeostasis during a virulent malaria infection. Moreover, neutralisation of IFN-gamma or depletion of CD8(+) T cells during PbA infection was shown to reverse the pathologic effects of regulatory pathway blockade, highlighting that the aetiology of ECM in the BALB/c mice is similar to that in C57BL/6 mice. In summary, our results underscore the differential and complex regulation that governs immune responses to malaria parasites.
Immunohistochemistry (frozen)
Immunofluorescence
Riella, L. V., et al (2011). "Essential role of PDL1 expression on nonhematopoietic donor cells in acquired tolerance to vascularized cardiac allografts" Am J Transplant 11(4): 832-840.
PubMed
The PD1:PDL1 pathway is an essential negative costimulatory pathway that plays a key role in regulating the alloimune response. PDL1 is expressed not only on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) but also cardiac endothelium. In this study, we investigated the importance of PDL1 expression on donor cardiac allograft in acquired transplantation tolerance in a fully MHC-mismatched model. We generated PDL1 chimeric mice on B6 background that expressed PDL1 on either hematopoietic cells or nonhematopoietic cells of the heart. Sham animals were used as controls. These hearts were then transplanted into BALB/c recipients and treated with CTLA4-Ig to induce tolerance. Cardiac endothelium showed significant expression of PDL1, which was upregulated upon transplantation. While the absence of PDL1 on hematopoietic cells of the heart resulted in delayed rejection and prevented long-term tolerance in most but not all recipients, we observed an accelerated and early graft rejection of all donor allografts that lacked PDL1 on the endothelium. Moreover, PDL1-deficient endothelium hearts had significant higher frequency of IFN-gamma-producing alloreactive cells as well as higher frequency of CD8(+) effector T cells. These findings demonstrate that PDL1 expression mainly on donor endothelium is functionally important in a fully allogeneic mismatched model for the induction of cardiac allograft tolerance
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Zhang, L., et al (2009). "PD-1/PD-L1 interactions inhibit antitumor immune responses in a murine acute myeloid leukemia model" Blood 114(8): 1545-1552.
PubMed
Negative regulatory mechanisms within the solid tumor microenvironment inhibit antitumor T-cell function, leading to evasion from immune attack. One inhibitory mechanism is up-regulation of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expressed on tumor or stromal cells which binds to programmed death-1 (PD-1) on activated T cells. PD-1/PD-L1 engagement results in diminished antitumor T-cell responses and correlates with poor outcome in murine and human solid cancers. In contrast to available data in solid tumors, little is known regarding involvement of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in immune escape by hematopoietic cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML). To investigate this hypothesis, we used the murine leukemia, C1498. When transferred intravenously, C1498 cells grew progressively and apparently evaded immune destruction. Low levels of PD-L1 expression were found on C1498 cells grown in vitro. However, PD-L1 expression was up-regulated on C1498 cells when grown in vivo. PD-1(-/-) mice challenged with C1498 cells generated augmented antitumor T-cell responses, showed decreased AML burden in the blood and other organs, and survived significantly longer than did wild-type mice. Similar results were obtained with a PD-L1 blocking antibody. These data suggest the importance of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in immune evasion by a hematologic malignancy, providing a rationale for clinical trials targeting this pathway in leukemia patients.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
Chromatin looping-based CRISPR screen identifies TLK2 as chromatin loop formation regulator in cancer stemness plasticity.
In Nat Commun on 21 October 2025 by Wang, Z., Liu, F., et al.
PubMed
Targeting cancer cell plasticity through chromatin organization is an emerging research area, yet the molecular mechanisms that govern chromatin loop formation remain unclear. Here, we develop a CRISPR screen based on our engineered live-cell CTCF-cohesin contact reporters to identify regulators of chromatin loops. Our findings reveal that tousled-like kinase 2 (TLK2) functions as a key regulator of chromatin loop formation during the cancer stemness transition. Mechanistically, TLK2 phosphorylates DYNLL1, enhancing its interaction with CTCF to promote CTCF-cohesin hub formation at the KLF4 locus. Suppressing TLK2 impairs cancer stemness plasticity, sensitizes cancer cells to cytotoxic stress in vitro, and reduces lung metastases and enhances immunotherapy response in breast cancer mouse models. Clinically, elevated TLK2 expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Collectively, these findings identify TLK2 as a potential therapeutic target for mitigating cancer stemness plasticity, highlighting chromatin loop-targeting therapy as a promising strategy to eradicate cancer stem cells.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Tumor neoantigens as key drivers of significant anti - tumor immunity in triple - negative breast cancer mouse models.
In Neoplasia on 1 September 2025 by Her, Y., Kim, J. Y., et al.
PubMed
Recent studies have highlighted the therapeutic potential of targeting tumor neoantigens in solid tumors; however, its efficacy in breast cancer remains unclear. Here, we evaluate the impact of tumor neoantigen-targeted strategies in a syngeneic mouse mammary carcinoma model. Mice previously exposed to 4T1 tumor cells (PETCs) or treated with tumor cell-derived lysates (TdLs) exhibited robust antitumor immunity, leading to reduced tumor growth and metastasis through tumor immune microenvironment remodeling. TdL administration in mice harboring orthotopic tumors significantly enhanced the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade, suggesting its potential as an immunotherapeutic adjuvant. To further optimize neoantigen-based approaches, we developed a lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-based delivery system for neoantigen peptides, which effectively suppressed tumor progression and metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, this strategy promoted antigen-specific T cell activation and reshaped the tumor immune landscape, enhancing immune-mediated tumor rejection. These findings underscore the therapeutic promise of personalized tumor neoantigen-targeted immunotherapy in breast cancer and support its further evaluation in clinical settings.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages and blocking PD-L1 via engineered outer membrane vesicles to enhance T cell infiltration and cytotoxic functions.
In J Nanobiotechnology on 15 July 2025 by Chen, Z., Wang, B., et al.
PubMed
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) critically undermines the efficacy of T cell-based tumor immunotherapy by impeding CD8+ T cell infiltration and cytotoxic function, primarily through tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and immune checkpoint molecules such as programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1). Here, we present a multifunctional nanoplatform, IN@OMV-PDL1nb, designed to simultaneously inhibit TAM-derived immunosuppressive metabolite itaconic acid (ITA) by targeting immune-responsive gene 1 (IRG1) and block PD-L1 within the TME. Engineered outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) serve as precision delivery vehicles for the IRG1 inhibitor IRG1-IN-1 (IN) and as carriers for PD-L1 nanobody release, activated by matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2). IN@OMV-PDL1nb effectively inhibits IRG1 expression in TAMs, thus reducing the accumulation of ITA, restoring chemokines (CXCL9 and CXCL10) secretion, and enhancing CD8+ T cells infiltration within tumors. The released PD-L1 nanobody protects CD8+ T cells, preserving their tumoricidal activity. In murine tumor models, IN@OMV-PDL1nb significantly inhibited tumor growth, increased survival, and enhanced antigen presentation and T cell recruitment. Additionally, IN@OMV-PDL1nb induced robust adaptive immunity, facilitating antigen-specific immune memory that prevented tumor recurrence and metastasis. This dual-targeting approach offers a promising strategy to overcome TME-driven immunosuppression in tumor immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cardiovascular biology
Targeting PD-L1 for Ischemic Stroke Recovery: Age-Dependent Modulation of Immune and BBB Pathways.
In CNS Neurosci Ther on 1 July 2025 by Hang, H., Xu, C., et al.
PubMed
Aging has a profound impact on the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke and the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. This study aims to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) monoclonal antibody (mAb) in modulating immune responses and neurovascular repair following ischemic stroke, with a focus on age-dependent differences.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Targeted activation of junctional adhesion molecule-like protein+ CD8+ T cells enhances immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Chin J Cancer Res on 30 April 2025 by Chen, H., Xiao, Z., et al.
PubMed
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) play a crucial role in the therapeutic approach to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent research has indicated that junctional adhesion molecule-like protein (JAML) enhances the antitumor activity of CD8+ T cells. Our study investigates the role of JAML+ CD8+ T cells in HCC.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
TET2 promotes tumor antigen presentation and T cell IFN-γ, which is enhanced by vitamin C.
In JCI Insight on 22 November 2024 by Cheng, M., Chu, A. K. Y., et al.
PubMed
Immune evasion by tumors is promoted by low T cell infiltration, ineffective T cell activity directed against the tumor, and reduced tumor antigen presentation. The TET2 DNA dioxygenase gene is frequently mutated in hematopoietic malignancies and loss of TET enzymatic activity is found in a variety of solid tumors. We showed previously that vitamin C (VC), a cofactor of TET2, enhances tumor-associated T cell recruitment and checkpoint inhibitor therapy responses in a TET2-dependent manner. Using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis performed on B16-OVA melanoma tumors, we have shown here that an additional function for TET2 in tumors is to promote expression of certain antigen presentation machinery genes, which is potently enhanced by VC. Consistently, VC promoted antigen presentation in cell-based and tumor assays in a TET2-dependent manner. Quantifying intercellular signaling from the scRNA-seq dataset showed that T cell-derived IFN-γ-induced signaling within the tumor and tumor microenvironment requires tumor-associated TET2 expression, which is enhanced by VC treatment. Analysis of patient tumor samples indicated that TET activity directly correlates with antigen presentation gene expression and with patient outcomes. Our results demonstrate the importance of tumor-associated TET2 activity as a critical mediator of tumor immunity, which is augmented by high-dose VC therapy.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Cancer Research
-
In vivo experiments
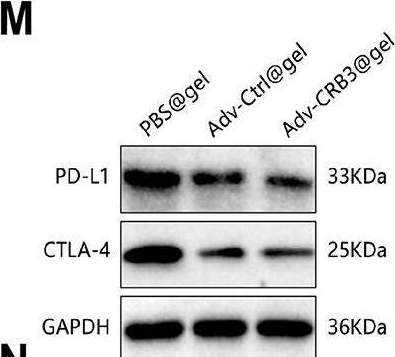
Novel combination therapy using recombinant oncolytic adenovirus silk hydrogel and PD-L1 inhibitor for bladder cancer treatment.
In J Nanobiotechnology on 18 October 2024 by Zhang, W., Zhang, J., et al.
PubMed
Recombinant oncolytic adenovirus offers a novel and promising cancer treatment approach, but its standalone efficacy remains limited. This study investigates a combination treatment strategy by co-administering recombinant oncolytic Adv-loaded silk hydrogel with a PD-L1 inhibitor for patients with bladder cancer to enhance treatment outcomes. Bladder cancer tissues from mice were collected and subjected to single-cell sequencing, identifying CRB3 as a key gene in malignant cells. Differential expression and functional enrichment analyses were performed, validating CRB3's inhibitory role through in vitro experiments showing suppression of bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Recombinant oncolytic adenoviruses encoding CRB3 and GM-CSF were constructed and encapsulated in silk hydrogel to enhance drug loading and release efficiency. In vivo experiments demonstrated that the nano-composite hydrogel significantly inhibited tumor growth and increased immune infiltration in tumor tissues. Co-administration of adenovirus silk hydrogel (Adv-CRB3@gel) with a PD-L1 inhibitor significantly enhanced T-cell infiltration and tumor killing. The combination of recombinant oncolytic Adv-loaded nano-composite hydrogel encoding CRB3 and GM-CSF with a PD-L1 inhibitor improves bladder cancer treatment outcomes by effectively recruiting T cells, providing a novel therapeutic strategy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis reveals the distinct features of colorectal cancer with or without Fusobacterium nucleatum infection in PD-L1 blockade therapy.
In Heliyon on 30 September 2024 by Ding, T., Chen, Q., et al.
PubMed
MSS/pMMR patients are unresponsive to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in colorectal cancer (CRC), but the mechanisms are unclear. A better understanding of immunotherapy resistance in CRC may lead to more precise treatment and expand the benefit of immunotherapy to patients. In this study, we constructed mouse model of subcutaneous CRC tumor received anti-PD-L1 treatment with or without fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum) infection. Then we used single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to explore the comprehensive landscape of the tumor microenvironment (TME). Our data delineated the composition, subclonal diversity and putative function of distinct cells, tracked the developmental trajectory of tumor cells and highlighted cell-cell interactions. We found different compositions and functions of both tumor cells and immune cells. Single anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treated tumor exhibited two specific clusters which might be resistant to PD-L1 blockade. The accumulation of immune cells, including T cell, NK cell and pro-inflammatory macrophage subset in tumors infected with F. nucleatum may be one of the reasons for the increased sensitivity to PD-L1 blockade. Thus, targeting F. nucleatum to change the composition of tumor cell subclusters and enliven the immune response might help to overcome immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) resistance.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Rationally designed catalytic nanoplatform for enhanced chemoimmunotherapy via deploying endogenous plus exogenous copper and remodeling tumor microenvironment.
In J Nanobiotechnology on 9 September 2024 by Sun, D., Yu, L., et al.
PubMed
Chemodynamic therapy represents a novel tumor therapeutic modality via triggering catalytic reactions in tumors to yield highly toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS). Nevertheless, low efficiency catalytic ability, potential systemic toxicity and inefficient tumor targeting, have hindered the efficacy of chemodynamic therapy. Herein, a rationally designed catalytic nanoplatform, composed of folate acid conjugated liposomes loaded with copper peroxide (CP) and chloroquine (CQ; a clinical drug) (denoted as CC@LPF), could power maximal tumor cytotoxicity, mechanistically via maneuvering endogenous and exogenous copper for a highly efficient catalytic reaction. Despite a massive autophagosome accumulation elicited by CP-powered autophagic initiation and CQ-induced autolysosomal blockage, the robust ROS, but not aberrant autophagy, underlies the synergistic tumor inhibition. Otherwise, this combined mode also elicits an early onset, above all, long-term high-level existence of immunogenic cell death markers, associated with ROS and aberrant autophagy -triggered endoplasmic reticulum stress. Besides, CC@LPF, with tumor targeting capability and selective tumor cytotoxicity, could elicit intratumor dendritic cells (mainly attributed to CQ) and tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells, upon combining with PD-L1 therapeutic antibody, further induce significant anti-tumor effect. Collectively, the rationally designed nanoplatform, CC@LPF, could enhance tumor chemoimmunotherapy via deploying endogenous plus exogenous copper and remodeling tumor microenvironment.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Miniaturized Fab' imaging probe derived from a clinical antibody: Characterization and imaging in CRISPRi-attenuated mammary tumor models.
In iScience on 16 August 2024 by Gupta, S., Pal, R., et al.
PubMed
Clinical imaging-assisted oncosurgical navigation requires cancer-specific miniaturized optical imaging probes. We report a near-infrared (NIR) Fab'-based epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-specific probe carrying 3 NIR fluorophores (Fab'-800CW), which retained high-affinity binding to EGFR ectodomain (equilibrium KDE = 1 nM). Fab'-800CW showed a robust 4-times gain of fluorescence intensity (FI) and a 20% lifetime (FLT) increase under the conditions mimicking intracellular degradation. The probe was tested by using triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines obtained by applying CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) effect of EGFR-targeting sgRNA and dCas9-KRAB chimera coexpression in MDA-MB-231 cells (WT cells). FI imaging in cell culture proved a 50% EGFR expression attenuation by CRISPRi. FI imaging in animals harboring attenuated or WT TNBC tumors with ex vivo corroboration identified differences between WT and CRISPRi tumors FI at 30 min post injection. Our results suggest the feasibility of EGFR expression imaging using a Fab'-based probe relevant for imaging-guided cancer surgery.
-
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Cancer Research
Conditionally replicative adenovirus as a therapy for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.
In Mol Ther Oncol on 20 June 2024 by Nikrad, J. A., Galvin, R. T., et al.
PubMed
Oncolytic adenoviruses (Ads) stand out as a promising strategy for the targeted infection and lysis of tumor cells, with well-established clinical utility across various malignancies. This study delves into the therapeutic potential of oncolytic Ads in the context of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs). Specifically, we evaluate conditionally replicative adenoviruses (CRAds) driven by the cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) promoter, as selective agents against MPNSTs, demonstrating their preferential targeting of MPNST cells compared with non-malignant Schwann cell control. COX2-driven CRAds, particularly those with modified fiber-knobs exhibit superior binding affinity toward MPNST cells and demonstrate efficient and preferential replication and lysis of MPNST cells, with minimal impact on non-malignant control cells. In vivo experiments involving intratumoral CRAd injections in immunocompromised mice with human MPNST xenografts significantly extend survival and reduce tumor growth rate compared with controls. Moreover, in immunocompetent mouse models with MPNST-like allografts, CRAd injections induce a robust infiltration of CD8+ T cells into the tumor microenvironment (TME), indicating the potential to promote a pro-inflammatory response. These findings underscore oncolytic Ads as promising, selective, and minimally toxic agents for MPNST therapy, warranting further exploration.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A CD36-dependent non-canonical lipid metabolism program promotes immune escape and resistance to hypomethylating agent therapy in AML.
In Cell Rep Med on 18 June 2024 by Guo, H. Z., Feng, R. X., et al.
PubMed
Environmental lipids are essential for fueling tumor energetics, but whether these exogenous lipids transported into cancer cells facilitate immune escape remains unclear. Here, we find that CD36, a transporter for exogenous lipids, promotes acute myeloid leukemia (AML) immune evasion. We show that, separately from its established role in lipid oxidation, CD36 on AML cells senses oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) to prime the TLR4-LYN-MYD88-nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, and exogenous palmitate transfer via CD36 further potentiates this innate immune pathway by supporting ZDHHC6-mediated MYD88 palmitoylation. Subsequently, NF-κB drives the expression of immunosuppressive genes that inhibit anti-tumor T cell responses. Notably, high-fat-diet or hypomethylating agent decitabine treatment boosts the immunosuppressive potential of AML cells by hijacking CD36-dependent innate immune signaling, leading to a dampened therapeutic effect. This work is of translational interest because lipid restriction by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved lipid-lowering statin drugs improves the efficacy of decitabine therapy by weakening leukemic CD36-mediated immunosuppression.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Secreted antigen A peptidoglycan hydrolase is essential for Enterococcus faecium cell separation and priming of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
In Elife on 10 June 2024 by Klupt, S., Fam, K. T., et al.
PubMed
Enterococcus faecium is a microbiota species in humans that can modulate host immunity (Griffin and Hang, 2022), but has also acquired antibiotic resistance and is a major cause of hospital-associated infections (Van Tyne and Gilmore, 2014). Notably, diverse strains of E. faecium produce SagA, a highly conserved peptidoglycan hydrolase that is sufficient to promote intestinal immunity (Rangan et al., 2016; Pedicord et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2019) and immune checkpoint inhibitor antitumor activity (Griffin et al., 2021). However, the functions of SagA in E. faecium were unknown. Here, we report that deletion of sagA impaired E. faecium growth and resulted in bulged and clustered enterococci due to defective peptidoglycan cleavage and cell separation. Moreover, ΔsagA showed increased antibiotic sensitivity, yielded lower levels of active muropeptides, displayed reduced activation of the peptidoglycan pattern-recognition receptor NOD2, and failed to promote cancer immunotherapy. Importantly, the plasmid-based expression of SagA, but not its catalytically inactive mutant, restored ΔsagA growth, production of active muropeptides, and NOD2 activation. SagA is, therefore, essential for E. faecium growth, stress resistance, and activation of host immunity.
-
-
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Benzosceptrin C induces lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 and promotes antitumor immunity by targeting DHHC3.
In Cell Rep Med on 20 February 2024 by Wang, Q., Wang, J., et al.
PubMed
Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)/programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) blockade has become a mainstay of cancer immunotherapy. Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis with small molecules is an attractive approach to enhance antitumor immunity. Here, we identified a natural marine product, benzosceptrin C (BC), that enhances the cytotoxicity of T cells to cancer cells by reducing the abundance of PD-L1. Furthermore, BC exerts its antitumor effect in mice bearing MC38 tumors by activating tumor-infiltrating T cell immunity. Mechanistic studies suggest that BC can prevent palmitoylation of PD-L1 by inhibiting DHHC3 enzymatic activity. Subsequently, PD-L1 is transferred from the membrane to the cytoplasm and cannot return to the membrane via recycling endosomes, triggering lysosome-mediated degradation of PD-L1. Moreover, the combination of BC and anti-CTLA4 effectively enhances antitumor T cell immunity. Our findings reveal a previously unrecognized antitumor mechanism of BC and represent an alternative immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapeutic strategy to enhance the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
SMARCAL1 is a dual regulator of innate immune signaling and PD-L1 expression that promotes tumor immune evasion.
In Cell on 15 February 2024 by Leuzzi, G., Vasciaveo, A., et al.
PubMed
Genomic instability can trigger cancer-intrinsic innate immune responses that promote tumor rejection. However, cancer cells often evade these responses by overexpressing immune checkpoint regulators, such as PD-L1. Here, we identify the SNF2-family DNA translocase SMARCAL1 as a factor that favors tumor immune evasion by a dual mechanism involving both the suppression of innate immune signaling and the induction of PD-L1-mediated immune checkpoint responses. Mechanistically, SMARCAL1 limits endogenous DNA damage, thereby suppressing cGAS-STING-dependent signaling during cancer cell growth. Simultaneously, it cooperates with the AP-1 family member JUN to maintain chromatin accessibility at a PD-L1 transcriptional regulatory element, thereby promoting PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. SMARCAL1 loss hinders the ability of tumor cells to induce PD-L1 in response to genomic instability, enhances anti-tumor immune responses and sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint blockade in a mouse melanoma model. Collectively, these studies uncover SMARCAL1 as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Downregulation of N4-acetylcytidine modification in myeloid cells attenuates immunotherapy and exacerbates hepatocellular carcinoma progression.
In Br J Cancer on 1 February 2024 by Xu, N., Zhuo, J., et al.
PubMed
N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) is a conserved and abundant mRNA modification that controls protein expression by affecting translation efficiency and mRNA stability. Whether the ac4C modification of mRNA regulates hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development or affects the immunotherapy of HCC is unknown.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Anti-PD-L1 therapy altered inflammation but not survival in a lethal murine hepatitis virus-1 pneumonia model.
In Front Immunol on 23 January 2024 by Curran, C. S., Cui, X., et al.
PubMed
Because prior immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy in cancer patients presenting with COVID-19 may affect outcomes, we investigated the beta-coronavirus, murine hepatitis virus (MHV)-1, in a lethal pneumonia model in the absence (Study 1) or presence of prior programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) antibody (PD-L1mAb) treatment (Study 2).
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunohistochemistry
Targeting integrin α5 in fibroblasts potentiates colorectal cancer response to PD-L1 blockade by affecting extracellular-matrix deposition.
In J Immunother Cancer on 1 December 2023 by Lu, L., Gao, Y., et al.
PubMed
One reason patients with cancer cannot benefit from immunotherapy is the lack of immune cell infiltration in tumor tissues. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are emerging as central players in immune regulation that shapes tumor microenvironment (TME). Earlier we reported that integrin α5 was enriched in CAFs in colorectal cancer (CRC), however, its role in TME and cancer immunotherapy remains unclear. Here, we aimed to investigate the role for integrin α5 in fibroblasts in modulating antitumor immunity and therapeutic efficacy combined with checkpoint blockade in CRC.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
Aurora A kinase inhibition induces accumulation of SCLC tumor cells in mitosis with restored interferon signaling to increase response to PD-L1.
In Cell Rep Med on 21 November 2023 by Li, Y., Mahadevan, N. R., et al.
PubMed
Despite small cell lung cancers (SCLCs) having a high mutational burden, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) immunotherapy only modestly increases survival. A subset of SCLCs that lose their ASCL1 neuroendocrine phenotype and restore innate immune signaling (termed the "inflammatory" subtype) have durable responses to PD-L1. Some SCLCs are highly sensitive to Aurora kinase inhibitors, but early-phase trials show short-lived responses, suggesting effective therapeutic combinations are needed to increase their durability. Using immunocompetent SCLC genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) and syngeneic xenografts, we show durable efficacy with the combination of a highly specific Aurora A kinase inhibitor (LSN3321213) and PD-L1. LSN3321213 causes accumulation of tumor cells in mitosis with lower ASCL1 expression and higher expression of interferon target genes and antigen-presentation genes mimicking the inflammatory subtype in a cell-cycle-dependent manner. These data demonstrate that inflammatory gene expression is restored in mitosis in SCLC, which can be exploited by Aurora A kinase inhibition.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Secreted antigen A peptidoglycan hydrolase is essential forEnterococcus faeciumcell separation and priming of immune checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy
In bioRxiv on 19 November 2023 by Klupt, S., Fam, K. T., et al.
-