RecombiMAb anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1) (D265A)
(switched from rat IgG2b)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb mouse IgG1 (D265A) isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Mutations | D265A |
| Immunogen | Mouse CD274 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo PD-L1 blockade* Immunofluorescence* Immunohistochemistry (frozen)* Flow cytometry* Western blot* *Reported for the original rat IgG2b 10F.9G2 antibody |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
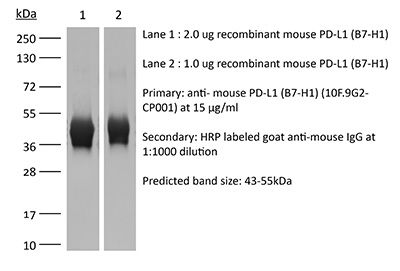
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from HEK293 cell supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
IL33-induced lipid droplet formation in mature low-density neutrophils drives colorectal cancer liver metastasis.
In Cell Mol Immunol on 1 December 2025 by Zhang, Y., Yu, S., et al.
PubMed
The microenvironment of distant organs affects the colonization and growth of disseminated tumor cells. It remains unclear how tumor-associated neutrophils are influenced by the microenvironment of distant organs. Here, we demonstrate that mature low-density neutrophils in colorectal cancer patients abnormally accumulate neutral lipids and induce the reactivation of dormant tumor cells, a process regulated by hepatic stellate cells. Mechanistically, activated hepatic stellate cells increased DGAT1/2-dependent lipid droplet synthesis in low-density neutrophils through the secretion of IL33, thereby maintaining the survival and immunosuppressive function of these neutrophils. The uptake of lipids from lipid-laden low-density neutrophils drives dormant tumor cell reactivation through the potentiation of β-oxidation and the stimulation of protumorigenic eicosanoid synthesis. In mouse models, targeting IL33 blocked neutrophil lipid synthesis, decreased the colonization of colorectal cancer cells in the liver, and enhanced the efficacy of immunotherapy. Overall, our study revealed that lipid accumulation in mature low-density neutrophils regulates the growth of dormant tumor cells and antitumor immunity to facilitate colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Targeting IL33 could be a promising therapeutic approach for colorectal cancer liver metastases.
-