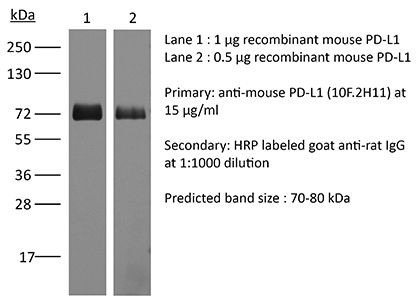
InVivoMAb anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Murine PD-L1 expressing CHO cells |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo blocking of PD-L1/CD80 (B7-1) interactions in vitro blocking of PD-L1/CD80 (B7-1) interactions ELISA Flow cytometry |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_2927503 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro blocking of PD-L1/CD80 (B7-1) interactions
Mott, K. R., et al (2014). "Inclusion of CD80 in HSV targets the recombinant virus to PD-L1 on DCs and allows productive infection and robust immune responses" PLoS One 9(1): e87617.
PubMed
CD80 plays a critical role in stimulation of T cells and subsequent control of infection. To investigate the effect of CD80 on HSV-1 infection, we constructed a recombinant HSV-1 virus that expresses two copies of the CD80 gene in place of the latency associated transcript (LAT). This mutant virus (HSV-CD80) expressed high levels of CD80 and had similar virus replication kinetics as control viruses in rabbit skin cells. In contrast to parental virus, this CD80 expressing recombinant virus replicated efficiently in immature dendritic cells (DCs). Additionally, the susceptibility of immature DCs to HSV-CD80 infection was mediated by CD80 binding to PD-L1 on DCs. This interaction also contributed to a significant increase in T cell activation. Taken together, these results suggest that inclusion of CD80 as a vaccine adjuvant may promote increased vaccine efficacy by enhancing the immune response directly and also indirectly by targeting to DC.
in vivo blocking of PD-L1/CD80 (B7-1) interactions
in vitro blocking of PD-L1/CD80 (B7-1) interactions
ELISA
Flow Cytometry
Paterson, A. M., et al (2011). "The programmed death-1 ligand 1:B7-1 pathway restrains diabetogenic effector T cells in vivo" J Immunol 187(3): 1097-1105.
PubMed
Programmed death-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a coinhibitory molecule that negatively regulates multiple tolerance checkpoints. In the NOD mouse model, PD-L1 regulates the development of diabetes. PD-L1 has two binding partners, programmed death-1 and B7-1, but the significance of the PD-L1:B7-1 interaction in regulating self-reactive T cell responses is not yet clear. To investigate this issue in NOD mice, we have compared the effects of two anti-PD-L1 Abs that have different blocking activities. Anti-PD-L1 mAb 10F.2H11 sterically and functionally blocks only PD-L1:B7-1 interactions, whereas anti-PD-L1 mAb 10F.9G2 blocks both PD-L1:B7-1 and PD-L1:programmed death-1 interactions. Both Abs had potent, yet distinct effects in accelerating diabetes in NOD mice: the single-blocker 10F.2H11 mAb was more effective at precipitating diabetes in older (13-wk-old) than in younger (6- to 7-wk-old) mice, whereas the dual-blocker 10F.9G2 mAb rapidly induced diabetes in NOD mice of both ages. Similarly, 10F.2H11 accelerated diabetes in recipients of T cells from diabetic, but not prediabetic mice, whereas 10F.9G2 was effective in both settings. Both anti-PD-L1 mAbs precipitated diabetes in adoptive transfer models of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell-driven diabetes. Taken together, these data demonstrate that the PD-L1:B7-1 pathway inhibits potentially pathogenic self-reactive effector CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell responses in vivo, and suggest that the immunoinhibitory functions of this pathway may be particularly important during the later phases of diabetogenesis.
in vivo blocking of PD-L1/CD80 (B7-1) interactions
Yang, J., et al (2011). "The novel costimulatory programmed death ligand 1/B7.1 pathway is functional in inhibiting alloimmune responses in vivo" J Immunol 187(3): 1113-1119.
PubMed
The programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1)/programmed death 1 (PD1) costimulatory pathway plays an important role in the inhibition of alloimmune responses as well as in the induction and maintenance of peripheral tolerance. It has been demonstrated recently that PDL1 also can bind B7.1 to inhibit T cell responses in vitro. Using the bm12 into B6 heart transplant model, we investigated the functional significance of this interaction in alloimmune responses in vivo. PD1 blockade unlike PDL1 blockade failed to accelerate bm12 allograft rejection, suggesting a role for an additional binding partner for PDL1 other than PD1 in transplant rejection. PDL1 blockade was able to accelerate allograft rejection in B7.2-deficient recipients but not B7.1-deficient recipients, indicating that PDL1 interaction with B7.1 was important in inhibiting rejection. Administration of the novel 2H11 anti-PDL1 mAb, which only blocks the PDL1-B7.1 interaction, aggravated chronic injury of bm12 allografts in B6 recipients. Aggravated chronic injury was associated with an increased frequency of alloreactive IFN-gamma-, IL-4-, and IL-6-producing splenocytes and a decreased percentage of regulatory T cells in the recipients. Using an in vitro cell culture assay, blockade of the interaction of PDL1 on dendritic cells with B7.1 on T cells increased IFN-gamma production from alloreactive CD4(+) T cells, whereas blockade of dendritic cell B7.1 interaction with T cell PDL1 did not. These data indicate that PDL1 interaction with B7.1 plays an important role in the inhibition of alloimmune responses in vivo and suggests a dominant direction for PDL1 and B7.1 interaction.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Quantifying treatment response to a macrophage-targeted therapy in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors after exposure to conventional chemotherapy.
In Front Immunol on 13 May 2025 by Bess, S. N., Smart, G. K., et al.
PubMed
Conventional chemotherapeutic agents, such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), can exert anti-tumor effects through immunogenic cell death (ICD) induction. Researchers have found hallmarks that quantify ICD (such as the translocation of HMGB1 and calreticulin). Although chemotherapeutic agents can induce ICD, they increase the expression of immune checkpoints, limiting their effectiveness. Studies have emphasized the importance of investigating the heterogeneous responses of cells co-localized in a solid tumor (macrophages, tumor cells, etc.) to ICD induction. However, these studies were performed in vivo, which limits the collection of information on cell-cell interactions due to model complexity.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Extracellular vesicle-packaged lncRNA from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes immune evasion by downregulating HLA-A in pancreatic cancer.
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 July 2024 by Yao, H., Huang, C., et al.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is characterised by immune evasion that contribute to poor prognosis. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play a pivotal role in orchestrating the PDAC tumour microenvironment. We investigated the role of CAF-derived extracellular vesicle (EV)-packaged long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in immune evasion and explored gene therapy using engineered EVs loading small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) as a potential therapeutic strategy. Our findings highlight the significance of EV-packaged lncRNA RP11-161H23.5 from CAF in promoting PDAC immune evasion by downregulating HLA-A expression, a key component of antigen presentation. Mechanistically, RP11-161H23.5 forms a complex with CNOT4, a subunit of the mRNA deadenylase CCR4-NOT complex, enhancing the degradation of HLA-A mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail. This immune evasion mechanism compromises the anti-tumour immune response. To combat this, we propose an innovative approach utilising engineered EVs as natural and biocompatible nanocarriers for siRNA-based gene therapy and this strategy holds promise for enhancing the effectiveness of immunotherapy in PDAC. Overall, our study sheds light on the critical role of CAF-derived EV-packaged lncRNA RP11-161H23.5/CNOT4/HLA-A axis in PDAC immune evasion and presents a novel avenue for therapeutic intervention.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Integrin αvβ6 mediates the immune escape through regulation of PD-L1 and serves as a novel marker for immunotherapy of colon carcinoma.
In Am J Cancer Res on 11 June 2024 by Yu, J., E, T., et al.
PubMed
The immune escape of colon cancer and its role in the response to immunotherapies such as PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors have long been of great interest. The positive outcomes of immunotherapy are limited by the immunosuppressive nature of the tumor microenvironment. Integrin αvβ6, which can regulate the progression of colon cancer, was recently reported to be involved in the immune suppression of colon cancer. In the present study, we explored the correlation between αvβ6 and PD-L1 expression by immunohistochemistry of colon cancer tissues. Then, the regulation of PD-L1 signaling by αvβ6 in colon cancer cells was demonstrated. We constructed an in vivo model and performed immunophenotyping experiments to analyze further the regulation of the immune response by αvβ6. The role of αvβ6 in the response to anti-PD-1 therapy in colon cancer was also verified. αvβ6-positive tissues exhibited increased PD-L1 expression. Inhibition of αvβ6 not only downregulated constitutive PD-L1 expression but also decreased IFN-γ-induced PD-L1 expression. In addition, αvβ6-induced PD-L1 expression was suppressed by the ERK inhibitor PD98059, and knockdown of the β6-ERK2 binding site had the equivalent effect. αvβ6 decreased CD8+ T cell infiltration and granzyme B expression in CD8+ T cells in colon cancer patients. Furthermore, mice engrafted with αvβ6-expressing colon cancer cells exhibited an unsatisfactory response to anti-PD-1 therapy, and anti-PD-1-induced increases in CD4+ and CD8+ T cell infiltration could be inhibited by αvβ6. These results indicate that αvβ6 mediates immune escape in colon cancer by upregulating PD-L1 through the ERK/MAPK pathway. Moreover, αvβ6 could serve as a marker for the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in colon cancer.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
Targeting the HSP47-collagen axis inhibits brain metastasis by reversing M2 microglial polarization and restoring anti-tumor immunity.
In Cell Rep Med on 21 May 2024 by Wang, L., Li, C., et al.
PubMed
Brain metastases (BrMs) are the leading cause of death in patients with solid cancers. BrMs exhibit a highly immunosuppressive milieu and poor response to immunotherapies; however, the underlying mechanism remains largely unclear. Here, we show that upregulation of HSP47 in tumor cells drives metastatic colonization and outgrowth in the brain by creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment. HSP47-mediated collagen deposition in the metastatic niche promotes microglial polarization to the M2 phenotype via the α2β1 integrin/nuclear factor κB pathway, which upregulates the anti-inflammatory cytokines and represses CD8+ T cell anti-tumor responses. Depletion of microglia reverses HSP47-induced inactivation of CD8+ T cells and abolishes BrM. Col003, an inhibitor disrupting HSP47-collagen association restores an anti-tumor immunity and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in BrM-bearing mice. Our study supports that HSP47 is a critical determinant of M2 microglial polarization and immunosuppression and that blocking the HSP47-collagen axis represents a promising therapeutic strategy against brain metastatic tumors.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Cancer cell genetics shaping of the tumor microenvironment reveals myeloid cell-centric exploitable vulnerabilities in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Nat Commun on 22 March 2024 by Ramirez, C. F. A., Taranto, D., et al.
PubMed
Myeloid cells are abundant and plastic immune cell subsets in the liver, to which pro-tumorigenic, inflammatory and immunosuppressive roles have been assigned in the course of tumorigenesis. Yet several aspects underlying their dynamic alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression remain elusive, including the impact of distinct genetic mutations in shaping a cancer-permissive tumor microenvironment (TME). Here, in newly generated, clinically-relevant somatic female HCC mouse models, we identify cancer genetics' specific and stage-dependent alterations of the liver TME associated with distinct histopathological and malignant HCC features. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-activated, NrasG12D-driven tumors exhibit a mixed phenotype of prominent inflammation and immunosuppression in a T cell-excluded TME. Mechanistically, we report a NrasG12D cancer cell-driven, MEK-ERK1/2-SP1-dependent GM-CSF secretion enabling the accumulation of immunosuppressive and proinflammatory monocyte-derived Ly6Clow cells. GM-CSF blockade curbs the accumulation of these cells, reduces inflammation, induces cancer cell death and prolongs animal survival. Furthermore, GM-CSF neutralization synergizes with a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor to restrain HCC outgrowth. These findings underscore the profound alterations of the myeloid TME consequential to MAPK pathway activation intensity and the potential of GM-CSF inhibition as a myeloid-centric therapy tailored to subsets of HCC patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Disruption of MerTK increases the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitor by enhancing ferroptosis and immune response in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Rep Med on 20 February 2024 by Wang, S., Zhu, L., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, particularly PD-1/PD-L1 blockades, have been approved for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, high resistance rates still limit their efficacy, highlighting the urgent need to understand the underlying mechanisms and develop strategies for overcoming the resistance. In this study, we demonstrate that HCC with high MER proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase (MerTK) expression exhibits anti-PD-1/PD-L1 resistance in two syngeneic mouse models and in patients who received anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Mechanistically, MerTK renders HCC resistant to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 by limiting ferroptosis with the upregulation of SLC7A11 via the ERK/SP1 pathway and facilitating the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) with the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Sitravatinib, an inhibitor of MerTK, sensitizes resistant HCC to anti-PD-L1 therapy by promoting tumor ferroptosis and decreasing MDSC infiltration into the TME. In conclusion, we find that MerTK could serve as a predictive biomarker for patient stratification and as a promising target to overcome anti-PD-1/PD-L1 resistance in HCC.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lymph node and tumor-associated PD-L1+ macrophages antagonize dendritic cell vaccines by suppressing CD8+ T cells.
In Cell Rep Med on 16 January 2024 by Sprooten, J., Vanmeerbeek, I., et al.
PubMed
Current immunotherapies provide limited benefits against T cell-depleted tumors, calling for therapeutic innovation. Using multi-omics integration of cancer patient data, we predict a type I interferon (IFN) responseHIGH state of dendritic cell (DC) vaccines, with efficacious clinical impact. However, preclinical DC vaccines recapitulating this state by combining immunogenic cancer cell death with induction of type I IFN responses fail to regress mouse tumors lacking T cell infiltrates. Here, in lymph nodes (LNs), instead of activating CD4+/CD8+ T cells, DCs stimulate immunosuppressive programmed death-ligand 1-positive (PD-L1+) LN-associated macrophages (LAMs). Moreover, DC vaccines also stimulate PD-L1+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). This creates two anatomically distinct niches of PD-L1+ macrophages that suppress CD8+ T cells. Accordingly, a combination of PD-L1 blockade with DC vaccines achieves significant tumor regression by depleting PD-L1+ macrophages, suppressing myeloid inflammation, and de-inhibiting effector/stem-like memory T cells. Importantly, clinical DC vaccines also potentiate T cell-suppressive PD-L1+ TAMs in glioblastoma patients. We propose that a multimodal immunotherapy and vaccination regimen is mandatory to overcome T cell-depleted tumors.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Converting bacteria into autologous tumor vaccine via surface biomineralization of calcium carbonate for enhanced immunotherapy.
In Acta Pharm Sin B on 1 December 2023 by Guo, L., Ding, J., et al.
PubMed
Autologous cancer vaccine that stimulates tumor-specific immune responses for personalized immunotherapy holds great potential for tumor therapy. However, its efficacy is still suboptimal due to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (ITM). Here, we report a new type of bacteria-based autologous cancer vaccine by employing calcium carbonate (CaCO3) biomineralized Salmonella (Sal) as an in-situ cancer vaccine producer and systematical ITM regulator. CaCO3 can be facilely coated on the Sal surface with calcium ionophore A23187 co-loading, and such biomineralization did not affect the bioactivities of the bacteria. Upon intratumoral accumulation, the CaCO3 shell was decomposed at an acidic microenvironment to attenuate tumor acidity, accompanied by the release of Sal and Ca2+/A23187. Specifically, Sal served as a cancer vaccine producer by inducing cancer cells' immunogenic cell death (ICD) and promoting the gap junction formation between tumor cells and dendritic cells (DCs) to promote antigen presentation. Ca2+, on the other hand, was internalized into various types of immune cells with the aid of A23187 and synergized with Sal to systematically regulate the immune system, including DCs maturation, macrophages polarization, and T cells activation. As a result, such bio-vaccine achieved remarkable efficacy against both primary and metastatic tumors by eliciting potent anti-tumor immunity with full biocompatibility. This work demonstrated the potential of bioengineered bacteria as bio-active vaccines for enhanced tumor immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Cancer cell genetics shaping of the tumor microenvironment reveals myeloid cell-centric exploitable vulnerabilities in hepatocellular carcinoma
In bioRxiv on 1 November 2023 by Ramirez, C. F., Taranto, D., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
YTHDF2 inhibition potentiates radiotherapy antitumor efficacy.
In Cancer Cell on 10 July 2023 by Wang, L., Dou, X., et al.
PubMed
RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is implicated in cancer progression. However, the impact of m6A on the antitumor effects of radiotherapy and the related mechanisms are unknown. Here we show that ionizing radiation (IR) induces immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) expansion and YTHDF2 expression in both murine models and humans. Following IR, loss of Ythdf2 in myeloid cells augments antitumor immunity and overcomes tumor radioresistance by altering MDSC differentiation and inhibiting MDSC infiltration and suppressive function. The remodeling of the landscape of MDSC populations by local IR is reversed by Ythdf2 deficiency. IR-induced YTHDF2 expression relies on NF-κB signaling; YTHDF2 in turn leads to NF-κB activation by directly binding and degrading transcripts encoding negative regulators of NF-κB signaling, resulting in an IR-YTHDF2-NF-κB circuit. Pharmacological inhibition of YTHDF2 overcomes MDSC-induced immunosuppression and improves combined IR and/or anti-PD-L1 treatment. Thus, YTHDF2 is a promising target to improve radiotherapy (RT) and RT/immunotherapy combinations.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
IL-2 is inactivated by the acidic pH environment of tumors enabling engineering of a pH-selective mutein.
In Sci Immunol on 9 December 2022 by Gaggero, S., Martinez-Fabregas, J., et al.
PubMed
Cytokines interact with their receptors in the extracellular space to control immune responses. How the physicochemical properties of the extracellular space influence cytokine signaling is incompletely elucidated. Here, we show that the activity of interleukin-2 (IL-2), a cytokine critical to T cell immunity, is profoundly affected by pH, limiting IL-2 signaling within the acidic environment of tumors. Generation of lactic acid by tumors limits STAT5 activation, effector differentiation, and antitumor immunity by CD8+ T cells and renders high-dose IL-2 therapy poorly effective. Directed evolution enabled selection of a pH-selective IL-2 mutein (Switch-2). Switch-2 binds the IL-2 receptor subunit IL-2Rα with higher affinity, triggers STAT5 activation, and drives CD8+ T cell effector function more potently at acidic pH than at neutral pH. Consequently, high-dose Switch-2 therapy induces potent immune activation and tumor rejection with reduced on-target toxicity in normal tissues. Last, we show that sensitivity to pH is a generalizable property of a diverse range of cytokines with broad relevance to immunity and immunotherapy in healthy and diseased tissues.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
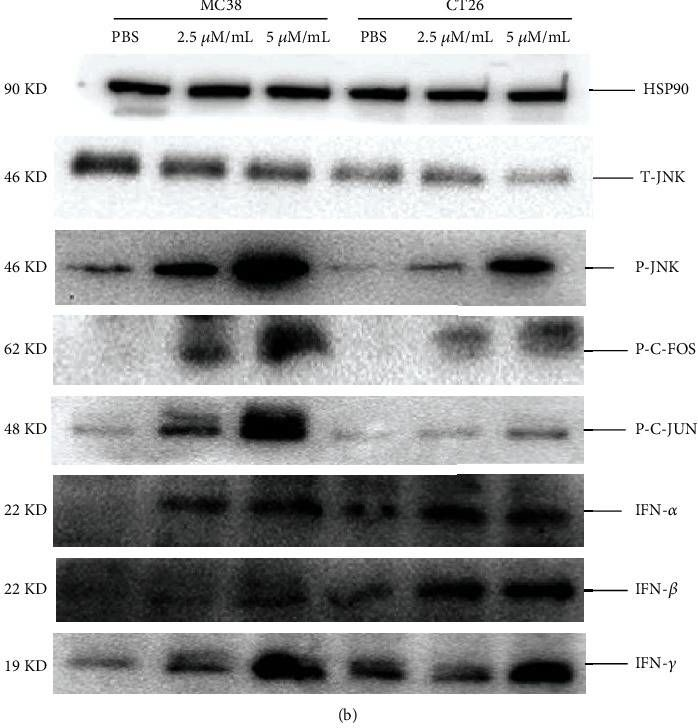
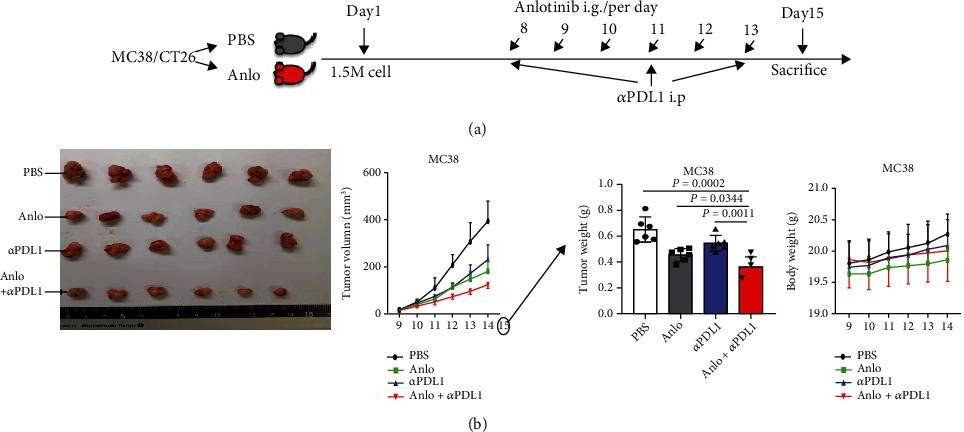
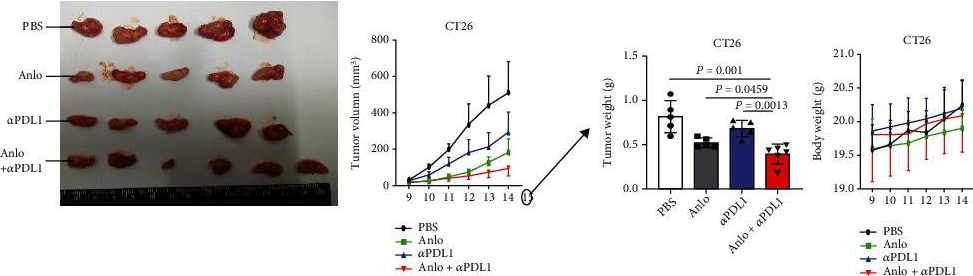
Anlotinib Benefits the αPDL1 Immunotherapy by Activating ROS/JNK/AP-1 Pathway to Upregulate PDL1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer.
In Oxid Med Cell Longev on 15 October 2022 by Luo, B., Zhang, S., et al.
PubMed
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the prevalent malignant tumors. This study is aimed at evaluating the mechanism of anlotinib (anlo) on tumor microenvironment (TME) in CRC, and its effects in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) therapy. Firstly, MC38 and CT26 cells were both exposed to different gradient concentrations of anlo for 72 h, to investigate the cell viability and synergetic therapy efficacy with ICIs by CCK8. The results showed that anlo could obviously inhibit cell growth and showed no synergistic efficacy therapy in combination with αPDL1 in vitro. Then, we found the upregulation of programmed cell death ligand 1(PDL1) expression both in vitro and in vivo after anlo treatment. In vivo, anlo could enhance the percentage of natural killer (NK) cells and M1 macrophage cells and decrease the percentage of M2 macrophage cells in TME. Moreover, we explored the mechanism and we proved that anlo could activate reactive oxygen species (ROS)/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/activator protein-1 (AP-1) signaling pathway to increase the expression levels of PDL1, IFN-α/β/γ, and CXCL2 in two cell lines in vitro. We also proved that anlo had synergistic effects with ICIs in vivo. Finally, it could also increase the mRNA and protein PDL1 expression levels in human cell lines, which was consistent with mouse CRC cell lines. However, there are still a few limitations. On one hand, the ROS/JNK/AP-1 pathway needs to be proved whether it can be activated in human cell lines. On the other hand, the mechanism behind ROS promoting phosphorylation of JNK needs to be explored.
-
-
-
In vitro experiments
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Reprogramming alveolar macrophage responses to TGF-β reveals CCR2+ monocyte activity that promotes bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome.
In J Clin Invest on 3 October 2022 by Liu, Z., Liao, F., et al.
PubMed
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is a major impediment to lung transplant survival and is generally resistant to medical therapy. Extracorporeal photophoresis (ECP) is an immunomodulatory therapy that shows promise in stabilizing BOS patients, but its mechanisms of action are unclear. In a mouse lung transplant model, we show that ECP blunts alloimmune responses and inhibits BOS through lowering airway TGF-β bioavailability without altering its expression. Surprisingly, ECP-treated leukocytes were primarily engulfed by alveolar macrophages (AMs), which were reprogrammed to become less responsive to TGF-β and reduce TGF-β bioavailability through secretion of the TGF-β antagonist decorin. In untreated recipients, high airway TGF-β activity stimulated AMs to express CCL2, leading to CCR2+ monocyte-driven BOS development. Moreover, we found TGF-β receptor 2-dependent differentiation of CCR2+ monocytes was required for the generation of monocyte-derived AMs, which in turn promoted BOS by expanding tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells that inflicted airway injury through Blimp-1-mediated granzyme B expression. Thus, through studying the effects of ECP, we have identified an AM functional plasticity that controls a TGF-β-dependent network that couples CCR2+ monocyte recruitment and differentiation to alloimmunity and BOS.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Reprogramming Alveolar Macrophage Responses to TGF-β Reveals CCR2+ Monocyte Activity that Promotes Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome
In bioRxiv on 28 January 2022 by Liu, Z., Liao, F., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The Interplay Between Regular T Cells and Immunotherapy in Cervical Cancer
In Research Square on 30 December 2020 by Xu, F., Zhang, F., et al.
-