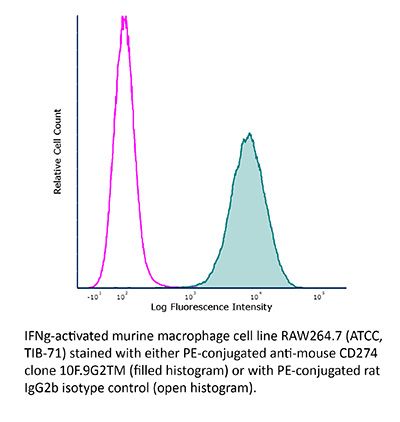
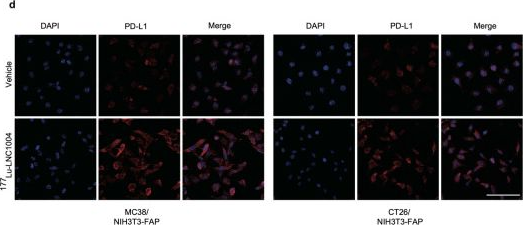
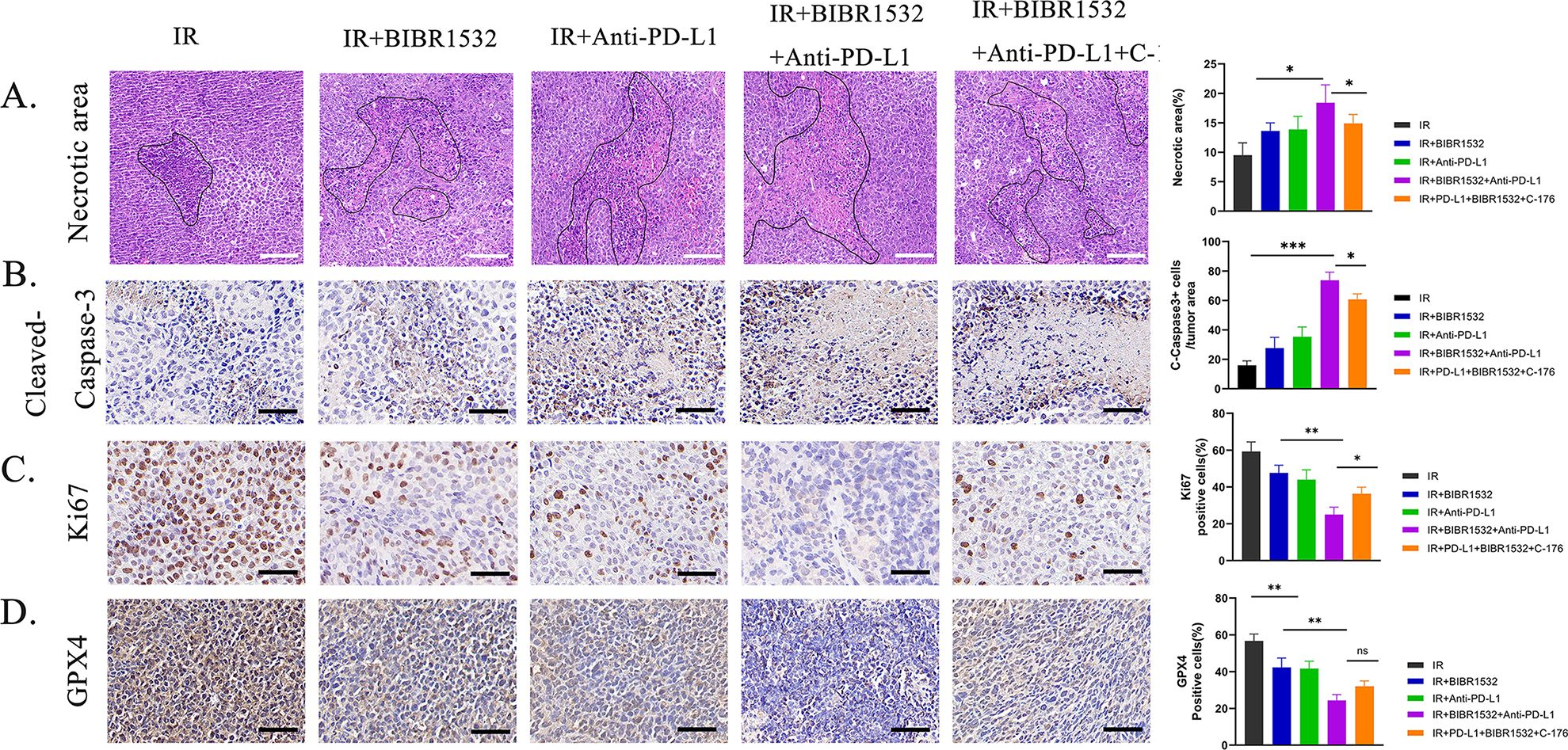
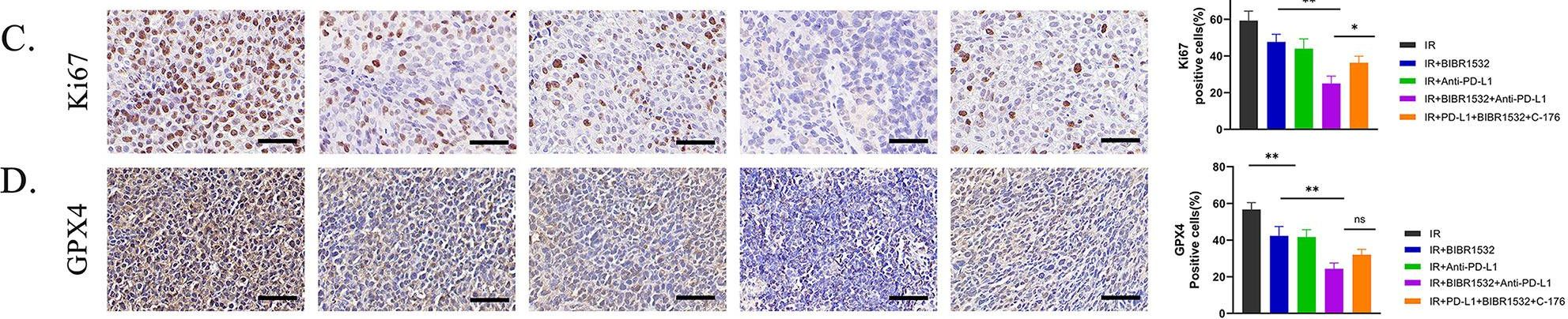
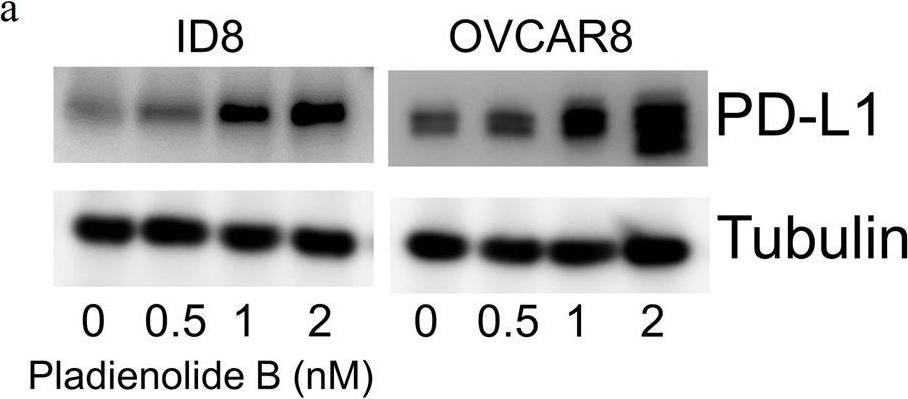
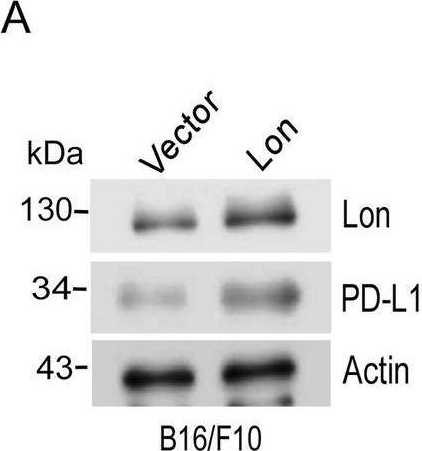
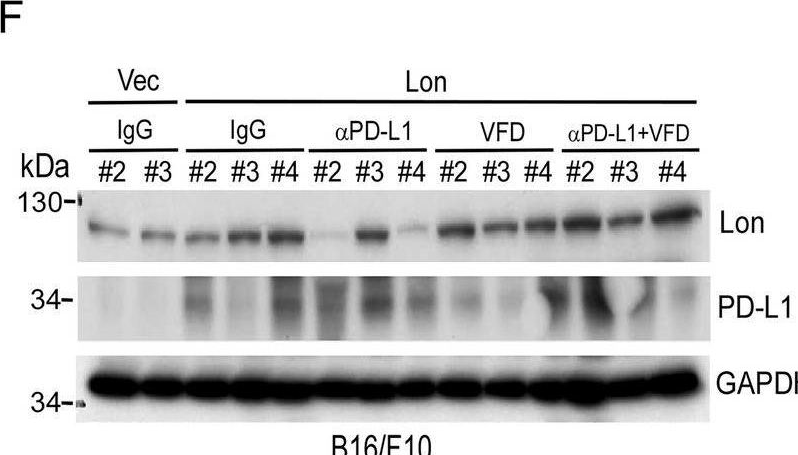
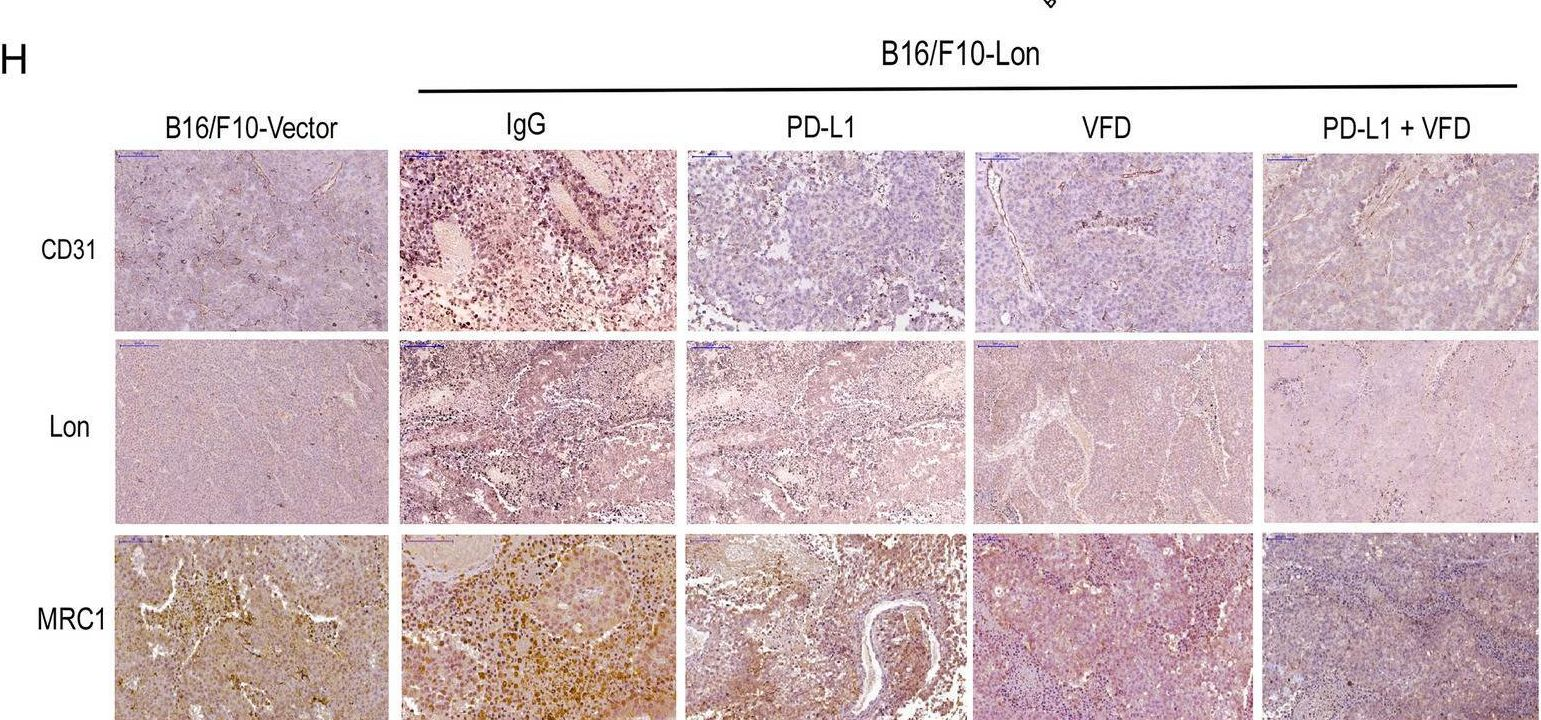
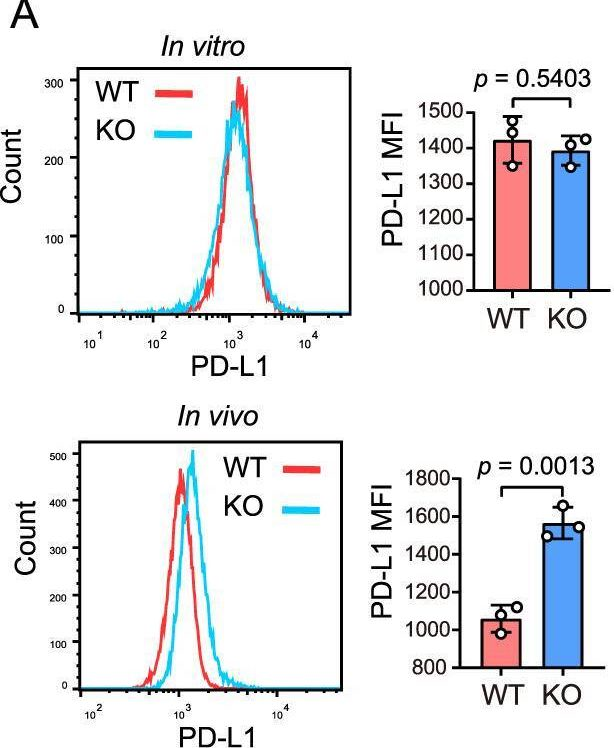
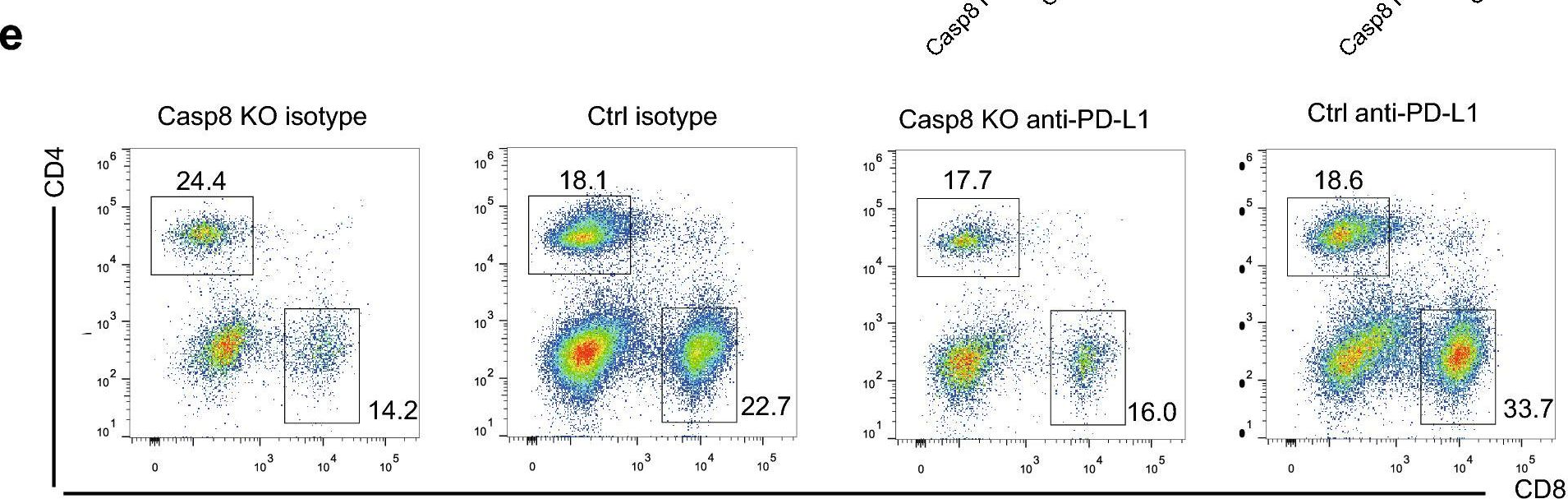
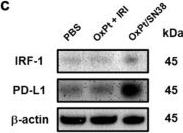
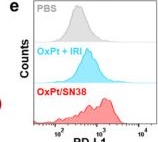
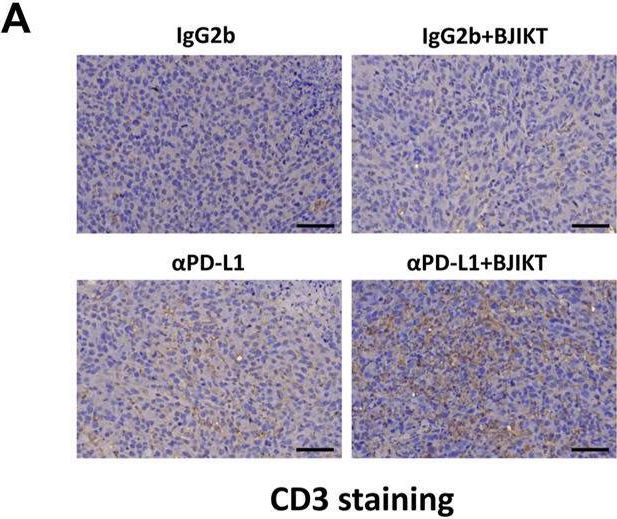
InVivoMAb anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 6.5 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CD274 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo PD-L1 blockade in vitro PD-L1 blockade Immunofluorescence Immunohistochemistry (frozen) Flow cytometry Western blot in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 6.5 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10949073 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip
Sivakumar R, Chan M, Shin JS, Nishida-Aoki N, Kenerson HL, Elemento O, Beltran H, Yeung R, Gujral TS (2019). "Organotypic tumor slice cultures provide a versatile platform for immuno-oncology and drug discovery" Oncoimmunology 8(12):e1670019.
PubMed
Organotypic tumor slices represent a physiologically-relevant culture system for studying the tumor microenvironment. Systematic characterization of the tumor slice culture system will enable its effective application for translational research. Here, using flow cytometry-based immunophenotyping, we performed a comprehensive characterization of the immune cell composition in organotypic tumor slices prepared from four syngeneic mouse tumor models and a human liver tumor. We found that the immune cell compositions of organotypic tumor slices prepared on the same day as the tumor cores were harvested are similar. Differences were primarily observed in the lymphocyte population of a clinical hepatocellular carcinoma case. Viable populations of immune cells persisted in the tumor slices for 7 days. Despite some changes in the immune cell populations, we showed the utility of mouse tumor slices for assessing responses to immune-modulatory agents. Further, we demonstrated the ability to use patient-derived xenograft tumor slices for assessing responses to targeted and cytotoxic drugs. Overall, tumor slices provide a broadly useful platform for studying the tumor microenvironment and evaluating the preclinical efficacy of cancer therapeutics.
in vitro PD-L1 blockade
Passariello M, D', Alise AM, Esposito A, Vetrei C, Froechlich G, Scarselli E, Nicosia A, De Lorenzo C (2019). "Novel Human Anti-PD-L1 mAbs Inhibit Immune-Independent Tumor Cell Growth and PD-L1 Associated Intracellular Signalling" Sci Rep 9(1):13
PubMed
The novel antibody-based immunotherapy in oncology exploits the activation of immune system mediated by immunomodulatory antibodies specific for immune checkpoints. Among them, the programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is of particular interest as it is expressed not only on T-cells, but also on other immune cells and on a large variety of cancer cells, such as breast cancer cells, considering its high expression in both ErbB2-positive and Triple Negative Breast Cancers. We demonstrate here that PD-L1_1, a novel anti-PD-L1 T -cell stimulating antibody, inhibits PD-L1-tumor cell growth also by affecting the intracellular MAPK pathway and by activating caspase 3. Similar in vitro results were obtained for the first time here also with the clinically validated anti-PD-L1 mAb Atezolizumab and in vivo with another validated anti-mouse anti-PD-L1 mAb. Moreover, we found that two high affinity variants of PD-L1_1 inhibited tumor cell viability more efficiently than the parental PD-L1_1 by affecting the same MAPK pathways with a more potent effect. Altogether, these results shed light on the role of PD-L1 in cancer cells and suggest that PD-L1_1 and its high affinity variants could become powerful antitumor weapons to be used alone or in combination with other drugs such as the anti-ErbB2 cAb already successfully tested in in vitro combinatorial treatments.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Stathopoulou, C., et al (2018). "PD-1 Inhibitory Receptor Downregulates Asparaginyl Endopeptidase and Maintains Foxp3 Transcription Factor Stability in Induced Regulatory T Cells" Immunity 49(2): 247-263 e247.
PubMed
CD4(+) T cell differentiation into multiple T helper (Th) cell lineages is critical for optimal adaptive immune responses. This report identifies an intrinsic mechanism by which programmed death-1 receptor (PD-1) signaling imparted regulatory phenotype to Foxp3(+) Th1 cells (denoted as Tbet(+)iTregPDL1 cells) and inducible regulatory T (iTreg) cells. Tbet(+)iTregPDL1 cells prevented inflammation in murine models of experimental colitis and experimental graft versus host disease (GvHD). Programmed death ligand-1 (PDL-1) binding to PD-1 imparted regulatory function to Tbet(+)iTregPDL1 cells and iTreg cells by specifically downregulating endo-lysosomal protease asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP). AEP regulated Foxp3 stability and blocking AEP imparted regulatory function in Tbet(+)iTreg cells. Also, Aep(-/-) iTreg cells significantly inhibited GvHD and maintained Foxp3 expression. PD-1-mediated Foxp3 maintenance in Tbet(+) Th1 cells occurred both in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and during chronic viral infection. Collectively, this report has identified an intrinsic function for PD-1 in maintaining Foxp3 through proteolytic pathway.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Grasselly, C., et al (2018). "The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent" Front Immunol 9: 2100.
PubMed
In spite of impressive response rates in multiple cancer types, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are active in only a minority of patients. Alternative strategies currently aim to combine immunotherapies with conventional agents such as cytotoxic chemotherapies. Here, we performed a study of PD-1 or PDL-1 blockade in combination with reference chemotherapies in four fully immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. We analyzed both the in vivo antitumor response, and the tumor immune infiltrate 4 days after the first treatment. in vivo tumor growth experiments revealed variable responsiveness to ICIs between models. We observed enhanced antitumor effects of the combination of immunotherapy with chemotherapy in the MC38 colon and MB49 bladder models, a lack of response in the 4T1 breast model, and an inhibition of ICIs activity in the MBT-2 bladder model. Flow cytometry analysis of tumor samples showed significant differences in all models between untreated and treated mice. At baseline, all the tumor models studied were predominantly infiltrated with cells harboring an immunosuppressive phenotype. Early alterations of the tumor immune infiltrate after treatment were found to be highly variable. We found that the balance between effector cells and immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment could be altered with some treatment combinations, but this effect was not always correlated with an impact on in vivo tumor growth. These results show that the combination of cytotoxic chemotherapy with ICIs may result in enhanced, similar or reduced antitumor activity, in a model- and regimen-dependent fashion. The present investigations should help to select appropriate combination regimens for ICIs.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Aloulou, M., et al (2016). "Follicular regulatory T cells can be specific for the immunizing antigen and derive from naive T cells" Nat Commun 7: 10579.
PubMed
T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells are a subset of Foxp3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells that form in response to immunization or infection, which localize to the germinal centre where they control the magnitude of the response. Despite an increased interest in the role of Tfr cells in humoral immunity, many fundamental aspects of their biology remain unknown, including whether they recognize self- or foreign antigen. Here we show that Tfr cells can be specific for the immunizing antigen, irrespective of whether it is a self- or foreign antigen. We show that, in addition to developing from thymic derived Treg cells, Tfr cells can also arise from Foxp3(-) precursors in a PD-L1-dependent manner, if the adjuvant used is one that supports T-cell plasticity. These findings have important implications for Tfr cell biology and for improving vaccine efficacy by formulating vaccines that modify the Tfr:Tfh cell ratio.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Ngiow, S. F., et al (2015). "A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1" Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811.
PubMed
Despite successes, thus far, a significant proportion of the patients treated with anti-PD1 antibodies have failed to respond. We use mouse tumor models of anti-PD1 sensitivity and resistance and flow cytometry to assess tumor-infiltrating immune cells immediately after therapy. We demonstrate that the expression levels of T-cell PD1 (PD1(lo)), myeloid, and T-cell PDL1 (PDL1(hi)) in the tumor microenvironment inversely correlate and dictate the efficacy of anti-PD1 mAb and function of intratumor CD8(+) T cells. In sensitive tumors, we reveal a threshold for PD1 downregulation on tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T cells below which the release of adaptive immune resistance is achieved. In contrast, PD1(hi) T cells in resistant tumors fail to be rescued by anti-PD1 therapy and remain dysfunctional unless intratumor PDL1(lo) immune cells are targeted. Intratumor Tregs are partly responsible for the development of anti-PD1-resistant tumors and PD1(hi) CD8(+) T cells. Our analyses provide a framework to interrogate intratumor CD8(+) T-cell PD1 and immune PDL1 levels and response in human cancer. Cancer Res; 75(18); 3800-11. (c)2015 AACR.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al (2015). "Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer" Nature 520(7547): 373-377.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors result in impressive clinical responses, but optimal results will require combination with each other and other therapies. This raises fundamental questions about mechanisms of non-redundancy and resistance. Here we report major tumour regressions in a subset of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with an anti-CTLA4 antibody (anti-CTLA4) and radiation, and reproduced this effect in mouse models. Although combined treatment improved responses in irradiated and unirradiated tumours, resistance was common. Unbiased analyses of mice revealed that resistance was due to upregulation of PD-L1 on melanoma cells and associated with T-cell exhaustion. Accordingly, optimal response in melanoma and other cancer types requires radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1/PD-1. Anti-CTLA4 predominantly inhibits T-regulatory cells (Treg cells), thereby increasing the CD8 T-cell to Treg (CD8/Treg) ratio. Radiation enhances the diversity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire of intratumoral T cells. Together, anti-CTLA4 promotes expansion of T cells, while radiation shapes the TCR repertoire of the expanded peripheral clones. Addition of PD-L1 blockade reverses T-cell exhaustion to mitigate depression in the CD8/Treg ratio and further encourages oligoclonal T-cell expansion. Similarly to results from mice, patients on our clinical trial with melanoma showing high PD-L1 did not respond to radiation plus anti-CTLA4, demonstrated persistent T-cell exhaustion, and rapidly progressed. Thus, PD-L1 on melanoma cells allows tumours to escape anti-CTLA4-based therapy, and the combination of radiation, anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-L1 promotes response and immunity through distinct mechanisms.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Kim, J., et al (2015). "Memory programming in CD8(+) T-cell differentiation is intrinsic and is not determined by CD4 help" Nat Commun 6: 7994.
PubMed
CD8(+) T cells activated without CD4(+) T-cell help are impaired in memory expansion. To understand the underlying cellular mechanism, here we track the dynamics of helper-deficient CD8(+) T-cell response to a minor histocompatibility antigen by phenotypic and in vivo imaging analyses. Helper-deficient CD8(+) T cells show reduced burst expansion, rapid peripheral egress, delayed antigen clearance and continuous activation, and are eventually exhausted. Contrary to the general consensus that CD4 help encodes memory programmes in CD8(+) T cells and helper-deficient CD8(+) T cells are abortive, these cells can differentiate into effectors and memory precursors. Importantly, accelerating antigen clearance or simply increasing the burst effector size enables generation of memory cells by CD8(+) T cells, regardless of CD4 help. These results suggest that the memory programme is CD8(+) T-cell-intrinsic, and provide insight into the role of CD4 help in CD8(+) T-cell responses.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Jaworska, K., et al (2015). "Both PD-1 ligands protect the kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury" J Immunol 194(1): 325-333.
PubMed
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common problem in hospitalized patients that enhances morbidity and mortality and promotes the development of chronic and end-stage renal disease. Ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) is one of the major causes of AKI and is characterized by uncontrolled renal inflammation and tubular epithelial cell death. Our recent studies demonstrated that regulatory T cells (Tregs) protect the kidney from ischemia reperfusion-induced inflammation and injury. Blockade of programmed death-1 (PD-1) on the surface of Tregs, prior to adoptive transfer, negates their ability to protect against ischemic kidney injury. The present study was designed to investigate the role of the known PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, in kidney IRI. Administration of PD-L1 or PD-L2 blocking Abs prior to mild or moderate kidney IRI significantly exacerbated the loss of renal function, renal inflammation, and acute tubular necrosis compared with mice receiving isotype control Abs. Interestingly, blockade of both PD-1 ligands resulted in worse injury, dysfunction, and inflammation than did blocking either ligand alone. Genetic deficiency of either PD-1 ligand also exacerbated kidney dysfunction and acute tubular necrosis after subthreshold ischemia. Bone marrow chimeric studies revealed that PD-L1 expressed on non-bone marrow-derived cells is critical for this resistance to IRI. Finally, blockade of either PD-1 ligand negated the protective ability of adoptively transferred Tregs in IRI. These findings suggest that PD-L1 and PD-L2 are nonredundant aspects of the natural protective response to ischemic injury and may be novel therapeutic targets for AKI.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Tkachev, V., et al (2015). "Programmed death-1 controls T cell survival by regulating oxidative metabolism" J Immunol 194(12): 5789-5800.
PubMed
The coinhibitory receptor programmed death-1 (PD-1) maintains immune homeostasis by negatively regulating T cell function and survival. Blockade of PD-1 increases the severity of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), but the interplay between PD-1 inhibition and T cell metabolism is not well studied. We found that both murine and human alloreactive T cells concomitantly upregulated PD-1 expression and increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. This PD-1(Hi)ROS(Hi) phenotype was specific to alloreactive T cells and was not observed in syngeneic T cells during homeostatic proliferation. Blockade of PD-1 signaling decreased both mitochondrial H2O2 and total cellular ROS levels, and PD-1-driven increases in ROS were dependent upon the oxidation of fatty acids, because treatment with etomoxir nullified changes in ROS levels following PD-1 blockade. Downstream of PD-1, elevated ROS levels impaired T cell survival in a process reversed by antioxidants. Furthermore, PD-1-driven changes in ROS were fundamental to establishing a cell’s susceptibility to subsequent metabolic inhibition, because blockade of PD-1 decreased the efficacy of later F1F0-ATP synthase modulation. These data indicate that PD-1 facilitates apoptosis in alloreactive T cells by increasing ROS in a process dependent upon the oxidation of fat. In addition, blockade of PD-1 undermines the potential for subsequent metabolic inhibition, an important consideration given the increasing use of anti-PD-1 therapies in the clinic.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Zander, R. A., et al (2015). "PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity" Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641.
PubMed
The differentiation and protective capacity of Plasmodium-specific T cells are regulated by both positive and negative signals during malaria, but the molecular and cellular details remain poorly defined. Here we show that malaria patients and Plasmodium-infected rodents exhibit atypical expression of the co-stimulatory receptor OX40 on CD4 T cells and that therapeutic enhancement of OX40 signaling enhances helper CD4 T cell activity, humoral immunity, and parasite clearance in rodents. However, these beneficial effects of OX40 signaling are abrogated following coordinate blockade of PD-1 co-inhibitory pathways, which are also upregulated during malaria and associated with elevated parasitemia. Co-administration of biologics blocking PD-1 and promoting OX40 signaling induces excessive interferon-gamma that directly limits helper T cell-mediated support of humoral immunity and decreases parasite control. Our results show that targeting OX40 can enhance Plasmodium control and that crosstalk between co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory pathways in pathogen-specific CD4 T cells can impact pathogen clearance.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Dolina, J. S., et al (2014). "Liver-primed CD8+ T cells suppress antiviral adaptive immunity through galectin-9-independent T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin 3 engagement of high-mobility group box 1 in mice" Hepatology 59(4): 1351-1365.
PubMed
The liver is a tolerogenic environment exploited by persistent infections, such as hepatitis B (HBV) and C (HCV) viruses. In a murine model of intravenous hepatotropic adenovirus infection, liver-primed antiviral CD8(+) T cells fail to produce proinflammatory cytokines and do not display cytolytic activity characteristic of effector CD8(+) T cells generated by infection at an extrahepatic, that is, subcutaneous, site. Importantly, liver-generated CD8(+) T cells also appear to have a T-regulatory (Treg) cell function exemplified by their ability to limit proliferation of antigen-specific T-effector (Teff ) cells in vitro and in vivo via T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin 3 (Tim-3) expressed by the CD8(+) Treg cells. Regulatory activity did not require recognition of the canonical Tim-3 ligand, galectin-9, but was dependent on CD8(+) Treg cell-surface Tim-3 binding to the alarmin, high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB-1). CONCLUSION: Virus-specific Tim-3(+) CD8(+) T cells operating through HMGB-1 recognition in the setting of acute and chronic viral infections of the liver may act to dampen hepatic T-cell responses in the liver microenvironment and, as a consequence, limit immune-mediated tissue injury or promote the establishment of persistent infections.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Deng, L., et al (2014). "Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice" J Clin Invest 124(2): 687-695.
PubMed
High-dose ionizing irradiation (IR) results in direct tumor cell death and augments tumor-specific immunity, which enhances tumor control both locally and distantly. Unfortunately, local relapses often occur following IR treatment, indicating that IR-induced responses are inadequate to maintain antitumor immunity. Therapeutic blockade of the T cell negative regulator programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1, also called B7-H1) can enhance T cell effector function when PD-L1 is expressed in chronically inflamed tissues and tumors. Here, we demonstrate that PD-L1 was upregulated in the tumor microenvironment after IR. Administration of anti-PD-L1 enhanced the efficacy of IR through a cytotoxic T cell-dependent mechanism. Concomitant with IR-mediated tumor regression, we observed that IR and anti-PD-L1 synergistically reduced the local accumulation of tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which suppress T cells and alter the tumor immune microenvironment. Furthermore, activation of cytotoxic T cells with combination therapy mediated the reduction of MDSCs in tumors through the cytotoxic actions of TNF. Our data provide evidence for a close interaction between IR, T cells, and the PD-L1/PD-1 axis and establish a basis for the rational design of combination therapy with immune modulators and radiotherapy.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Flow Cytometry
Rutigliano, J. A., et al (2014). "Highly pathological influenza A virus infection is associated with augmented expression of PD-1 by functionally compromised virus-specific CD8+ T cells" J Virol 88(3): 1636-1651.
PubMed
One question that continues to challenge influenza A research is why some strains of virus are so devastating compared to their more mild counterparts. We approached this question from an immunological perspective, investigating the CD8(+) T cell response in a mouse model system comparing high- and low-pathological influenza virus infections. Our findings reveal that the early (day 0 to 5) viral titer was not the determining factor in the outcome of disease. Instead, increased numbers of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells and elevated effector function on a per-cell basis were found in the low-pathological infection and correlated with reduced illness and later-time-point (day 6 to 10) viral titer. High-pathological infection was associated with increased PD-1 expression on influenza virus-specific CD8(+) T cells, and blockade of PD-L1 in vivo led to reduced virus titers and increased CD8(+) T cell numbers in high- but not low-pathological infection, though T cell functionality was not restored. These data show that high-pathological acute influenza virus infection is associated with a dysregulated CD8(+) T cell response, which is likely caused by the more highly inflamed airway microenvironment during the early days of infection. Therapeutic approaches specifically aimed at modulating innate airway inflammation may therefore promote efficient CD8(+) T cell activity. We show that during a severe influenza virus infection, one type of immune cell, the CD8 T cell, is less abundant and less functional than in a more mild infection. This dysregulated T cell phenotype correlates with a lower rate of virus clearance in the severe infection and is partially regulated by the expression of a suppressive coreceptor called PD-1. Treatment with an antibody that blocks PD-1 improves T cell functionality and increases virus clearance.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Yang, X., et al (2014). "Targeting the tumor microenvironment with interferon-beta bridges innate and adaptive immune responses" Cancer Cell 25(1): 37-48.
PubMed
Antibodies (Abs) that preferentially target oncogenic receptors have been increasingly used for cancer therapy, but tumors often acquire intrinsic Ab resistance after prolonged and costly treatment. Herein we armed the Ab with IFNbeta and observed that it is more potent than the first generation of Ab for controlling Ab-resistant tumors. This strategy controls Ab resistance by rebridging suppressed innate and adaptive immunity in the tumor microenvironment. Mechanistically, Ab-IFNbeta therapy primarily and directly targets intratumoral dendritic cells, which reactivate CTL by increasing antigen cross-presentation within the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, blocking PD-L1, which is induced by Ab-IFNbeta treatment, overcomes treatment-acquired resistance and completely eradicates established tumors. This study establishes a next-generation Ab-based immunotherapy that targets and eradicates established Ab-resistant tumors.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Dietze, K. K., et al (2013). "Combining regulatory T cell depletion and inhibitory receptor blockade improves reactivation of exhausted virus-specific CD8+ T cells and efficiently reduces chronic retroviral loads" PLoS Pathog 9(12): e1003798.
PubMed
Chronic infections with human viruses, such as HIV and HCV, or mouse viruses, such as LCMV or Friend Virus (FV), result in functional exhaustion of CD8(+) T cells. Two main mechanisms have been described that mediate this exhaustion: expression of inhibitory receptors on CD8(+) T cells and expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) that suppress CD8(+) T cell activity. Several studies show that blockage of one of these pathways results in reactivation of CD8(+) T cells and partial reduction in chronic viral loads. Using blocking antibodies against PD-1 ligand and Tim-3 and transgenic mice in which Tregs can be selectively ablated, we compared these two treatment strategies and combined them for the first time in a model of chronic retrovirus infection. Blocking inhibitory receptors was more efficient than transient depletion of Tregs in reactivating exhausted CD8(+) T cells and reducing viral set points. However, a combination therapy was superior to any single treatment and further augmented CD8(+) T cell responses and resulted in a sustained reduction in chronic viral loads. These results demonstrate that Tregs and inhibitory receptors are non-overlapping factors in the maintenance of chronic viral infections and that immunotherapies targeting both pathways may be a promising strategy to treat chronic infectious diseases.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Immunofluorescence
Willimsky, G., et al (2013). "Virus-induced hepatocellular carcinomas cause antigen-specific local tolerance" J Clin Invest 123(3): 1032-1043.
PubMed
T cell surveillance is often effective against virus-associated tumors because of their high immunogenicity. It is not clear why surveillance occasionally fails, particularly against hepatitis B virus- or hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We established a transgenic murine model of virus-induced HCC by hepatocyte-specific adenovirus-induced activation of the oncogenic SV40 large T antigen (TAg). Adenovirus infection induced cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) targeted against the virus and TAg, leading to clearance of the infected cells. Despite the presence of functional, antigen-specific T cells, a few virus-infected cells escaped immune clearance and progressed to HCC. These cells expressed TAg at levels similar to HCC isolated from neonatal TAg-tolerant mice, suggesting that CTL clearance does not select for cells with low immunogenicity. Virus-infected mice revealed significantly greater T cell infiltration in early-stage HCC compared with that in late-stage HCC, demonstrating progressive local immune suppression through inefficient T cell infiltration. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 were expressed in all TAg-specific CD8+ T cells and HCC, respectively, which contributed to local tumor-antigen-specific tolerance. Thus, we have developed a model of virus-induced HCC that may allow for a better understanding of human HCC.
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Hafalla, J. C., et al (2012). "The CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways independently regulate host resistance to Plasmodium-induced acute immune pathology" PLoS Pathog 8(2): e1002504.
PubMed
The balance between pro-inflammatory and regulatory immune responses in determining optimal T cell activation is vital for the successful resolution of microbial infections. This balance is maintained in part by the negative regulators of T cell activation, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L, which dampen effector responses during chronic infections. However, their role in acute infections, such as malaria, remains less clear. In this study, we determined the contribution of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L to the regulation of T cell responses during Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA)-induced experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) in susceptible (C57BL/6) and resistant (BALB/c) mice. We found that the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T cells correlates with the extent of pro-inflammatory responses induced during PbA infection, being higher in C57BL/6 than in BALB/c mice. Thus, ECM develops despite high levels of expression of these inhibitory receptors. However, antibody-mediated blockade of either the CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1, but not the PD-1/PD-L2, pathways during PbA-infection in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice resulted in higher levels of T cell activation, enhanced IFN-gamma production, increased intravascular arrest of both parasitised erythrocytes and CD8(+) T cells to the brain, and augmented incidence of ECM. Thus, in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 represent essential, independent and non-redundant pathways for maintaining T cell homeostasis during a virulent malaria infection. Moreover, neutralisation of IFN-gamma or depletion of CD8(+) T cells during PbA infection was shown to reverse the pathologic effects of regulatory pathway blockade, highlighting that the aetiology of ECM in the BALB/c mice is similar to that in C57BL/6 mice. In summary, our results underscore the differential and complex regulation that governs immune responses to malaria parasites.
Immunohistochemistry (frozen)
Immunofluorescence
Riella, L. V., et al (2011). "Essential role of PDL1 expression on nonhematopoietic donor cells in acquired tolerance to vascularized cardiac allografts" Am J Transplant 11(4): 832-840.
PubMed
The PD1:PDL1 pathway is an essential negative costimulatory pathway that plays a key role in regulating the alloimune response. PDL1 is expressed not only on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) but also cardiac endothelium. In this study, we investigated the importance of PDL1 expression on donor cardiac allograft in acquired transplantation tolerance in a fully MHC-mismatched model. We generated PDL1 chimeric mice on B6 background that expressed PDL1 on either hematopoietic cells or nonhematopoietic cells of the heart. Sham animals were used as controls. These hearts were then transplanted into BALB/c recipients and treated with CTLA4-Ig to induce tolerance. Cardiac endothelium showed significant expression of PDL1, which was upregulated upon transplantation. While the absence of PDL1 on hematopoietic cells of the heart resulted in delayed rejection and prevented long-term tolerance in most but not all recipients, we observed an accelerated and early graft rejection of all donor allografts that lacked PDL1 on the endothelium. Moreover, PDL1-deficient endothelium hearts had significant higher frequency of IFN-gamma-producing alloreactive cells as well as higher frequency of CD8(+) effector T cells. These findings demonstrate that PDL1 expression mainly on donor endothelium is functionally important in a fully allogeneic mismatched model for the induction of cardiac allograft tolerance
in vivo PD-L1 blockade
Zhang, L., et al (2009). "PD-1/PD-L1 interactions inhibit antitumor immune responses in a murine acute myeloid leukemia model" Blood 114(8): 1545-1552.
PubMed
Negative regulatory mechanisms within the solid tumor microenvironment inhibit antitumor T-cell function, leading to evasion from immune attack. One inhibitory mechanism is up-regulation of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expressed on tumor or stromal cells which binds to programmed death-1 (PD-1) on activated T cells. PD-1/PD-L1 engagement results in diminished antitumor T-cell responses and correlates with poor outcome in murine and human solid cancers. In contrast to available data in solid tumors, little is known regarding involvement of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in immune escape by hematopoietic cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML). To investigate this hypothesis, we used the murine leukemia, C1498. When transferred intravenously, C1498 cells grew progressively and apparently evaded immune destruction. Low levels of PD-L1 expression were found on C1498 cells grown in vitro. However, PD-L1 expression was up-regulated on C1498 cells when grown in vivo. PD-1(-/-) mice challenged with C1498 cells generated augmented antitumor T-cell responses, showed decreased AML burden in the blood and other organs, and survived significantly longer than did wild-type mice. Similar results were obtained with a PD-L1 blocking antibody. These data suggest the importance of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in immune evasion by a hematologic malignancy, providing a rationale for clinical trials targeting this pathway in leukemia patients.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Probiotic-inspired hybrid nanovesicles for enhancing immune checkpoint therapy efficiency via tumor immune microenvironment modulation.
In Bioact Mater on 1 February 2026 by Wang, F., Fan, J., et al.
PubMed
Immunologically "cold" tumors, characterized by low immune cells infiltration, represent a significant obstacle to the success of immune checkpoint therapy. Intestinal microbiome therapy has emerged as a potential strategy to overcome this challenge by reprogramming the immune microenvironment. However, its clinical application is constrained by unresolved safety concerns. To address these challenges, we fused Escherichia coli-secreted outer membrane vesicle (OMV) with the macrophage membrane vector (RV) to construct hybrid nanovesicle (ROMV) and encapsulated the bacterial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), forming ROMV/TMAO. ROMV/TMAO mimicked the beneficial functions of intestinal probiotics by leveraging the immunomodulatory properties of OMV and TMAO, combined with the tumor-homing capabilities of RV. In human lung cancer organoids and multiple tumor models, selective tumor targeting and accumulation of ROMV/TMAO facilitated M1 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages and enhanced CD8+ T lymphocyte infiltration, ultimately inhibiting tumor growth. When combined with ROMV/TMAO, the immune checkpoint inhibitor α-PD-L1 exhibited superior antitumor efficacy than monotherapy. This study introduces a probiotic-inspired nanotherapeutic strategy for augmenting immune checkpoint therapy outcomes while addressing microbiome therapy safety challenges.
-
-
-
Cardiovascular biology
PD-L1+ neutrophils trigger pulmonary endothelial pyroptosis via an oxidative phosphorylation-dependent mechanism in sepsis.
In Respir Res on 24 November 2025 by Ma, C., Wang, L., et al.
PubMed
Sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by microvascular dysfunction, uncontrolled inflammation, and pulmonary edema, leading to high morbidity and mortality. Despite their clinical importance, targeted therapies are lacking. Neutrophils play a critical role in sepsis-induced lung injury, but the specific contributions of PD-L1+ neutrophils remain poorly understood. The aim of this study was to elucidate the role of PD-L1+ neutrophils in endothelial injury and the underlying mechanisms during sepsis.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
TREM2 facilitates gastric cancer progression and immune evasion via inhibiting TRIM21-mediated STAT1 degradation in tumor-associated macrophages.
In Cell Death Dis on 18 November 2025 by Zhang, Z., Yu, K., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play a crucial role in fostering an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, promoting cancer progression, contributing to immune evasion and resistance to immunotherapy. However, the mechanisms by which TAMs exert these effects in gastric cancer (GC) remain unclear. Human TAMs were isolated from GC patients through magnetic sorting for RNA sequencing. THP-1 cell line and mice bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) induced TAMs were applied for functional assays. Two in-house tumor microarrays were utilized for validation: the Zhongshan Cohort, comprising 135 patients, and the Zhongshan Flow Cytometry (ZSFC) Cohort, which included 60 patients. In this study, we identified a significant accumulation of TREM2+ TAMs in GC tissues, correlating with poor prognosis. Functional assays revealed that targeting TREM2+ TAMs suppressed GC progression both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, TREM2 stabilized signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) by preventing its ubiquitination mediated by Tripartite Motif Containing 21 (TRIM21), while simultaneously promoting STAT1 phosphorylation via spleen-associated tyrosine kinase (SYK), leading to upregulation of CCL8 and PD-L1, fostering an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, depletion of TREM2+ TAMs significantly enhanced the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in GC allograft models. Collectively, our findings establish TREM2+ TAMs as key drivers of GC progression and immune evasion. Targeting TREM2+ TAMs represents a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome resistance to anti-PD-L1 therapy and reshape the tumor immune microenvironment.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Targeting tumor-intrinsic BCL9 reverses immunotherapy resistance by eliciting macrophage-mediated phagocytosis and antigen presentation.
In Nat Commun on 17 November 2025 by Wu, S. Y., Zhu, Y. Y., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) benefit some cancer patients but de novo resistance remains poorly understood. Analyzing transcriptional data from two clinical trial cohorts, GO30140 and IMbrave150, we find B cell lymphoma 9 (BCL9), a Wnt/β-catenin co-factor, associated with resistance. We develop a BCL9-targeting peptide, hsBCL9Z96, which suppresses tumor growth in combination with anti-PD-L1 ab in preclinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) mouse models. Multi-omics analyses implicate targeting BCL9 inhibits BMP4 secretion and downregulates CD24 on tumor cells, reprogramming macrophages toward a tumor-suppressive phenotype and promoting macrophage phagocytosis. This in turn rejuvenates T cell immunity via enhanced macrophage-mediated antigen presentation. Our data extend our understanding of how tumor-derived Wnt/β-catenin signaling impedes the innate and adaptive immune responses in the tumor microenvironment and provide preliminary evidence that targeting BCL9 is a promising preclinical strategy to mitigate ICI resistance in HCC.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Targeting asparagine potentiates anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in gastric cancer by enhancing CD8+ T cell anti-tumor response.
In Front Immunol on 13 November 2025 by Ge, M., Wang, L., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapy efficacy in gastric cancer (GC) is often constrained by the tumor microenvironment (TME), which is profoundly influenced by aberrant metabolism. Asparagine, an amino acid critical for neoplastic proliferation, also modulates CD8+ T cell metabolic programming. We investigated the impact of targeting asparagine on the GC immune microenvironment and its potential to synergize with anti-PD-L1 therapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Injectable Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Polypeptide Hydrogels as Drug Depots for Antitumor Chemo-Immunotherapy.
In Pharmaceutics on 11 November 2025 by Liang, S., Wang, T., et al.
PubMed
Background: The potential of injectable hydrogels as drug depots lies in their ability to achieve local and sustained co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and immunostimulants for combined tumor therapy. Method: In this study, we devised a localized chemo-immunotherapeutic strategy by co-loading the chemotherapeutic drug, oxaliplatin (OXA), and the immune-checkpoint blockade (ICB) antibody, anti-programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (anti-PD-L1), into a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-responsive injectable poly(L-glutamic acid) hydrogel (MMP-gel). Results: The in situ gelation of hydrogels enables local retention of OXA and model antibody IgG, as well as MMP-triggered sustained release. Meanwhile, the OXA-loaded MMP-gel caused the immunogenic cell death (ICD) of tumor cells. When administered intratumorally in mice carrying B16F10 melanoma, the MMP-gel co-loaded with OXA and anti-PD-L1 (OXA&anti-PD-L1@MMP-gel) demonstrated superior tumor suppression efficacy and prolonged the survival time of the animals with low systemic toxicity. Meanwhile, the OXA&anti-PD-L1@MMP-gel induced an increase in CD8+ T cells and M1 macrophages within tumors, and a decrease in Treg cells and M2 macrophages, demonstrating that the drug-loaded system enhanced the antitumor immune response. Moreover, the OXA&anti-PD-L1@MMP-gel effectively inhibited the growth of distal tumors in a bilateral-tumor experiment. Conclusions: Consequently, the responsive hydrogel-based chemo-immunotherapy holds potential in tumor treatment.
-
-
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
The transcription factor ZEB2 mediates the antitumor efficacy of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer.
In Cell Death Dis on 7 November 2025 by Wang, J., Liu, F., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) offers an in vivo approach to activate CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (CD8+TILs) in cases of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). A large fraction of NSCLC patients is unresponsive to ICBs and relapse due to the development of dysfunctional CD8+TILs with impaired cytotoxicity. Therefore, an improved understanding of regulator(s) that favor the development of cytotoxic Teff cells over dysfunctional CD8+TILs is required for the success of ICB therapy in NSCLC patients. Here, our metaVIPER-based scRNA-seq analysis of deep CD8+ cell scRNA-seq data from 14 treatment-naïve NSCLC patients revealed that the master regulon ZEB2 may drive CD8+ differentiation along the cytotoxic effector trajectory in NSCLC tumors. In vitro, ZEB2 acts downstream of T-bet to stimulate lung tumor-reactive Teff cell differentiation. This T-bet/ZEB2 axis displays immunotherapeutic effects on KP.SIY lung tumors independent of ICB therapy and mediates the therapeutic effects of murine serum albumin-fused IL-2 + IL-12 combination immunotherapy (IL2-MSA + IL12-MSA) in mice. IL2-MSA + IL12-MSA operates through a parallel STAT4/FOXO1-mediated mechanism that promotes CD8+TIL T-bet/ZEB2 expression and lung tumor-reactive Teff cell differentiation. In conclusion, immunotherapeutic regimens that support ZEB2 activity in CD8+ cells may show promise in NSCLC patients.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
-
Cancer Research
Brain tumors induce widespread disruption of calvarial bone and alteration of skull marrow immune landscape.
In Nat Neurosci on 1 November 2025 by Dubey, A., Yamashita, E., et al.
PubMed
The skull marrow niche has recently been identified as a reservoir that supplies the brain with monocytes and neutrophils in the context of disease and injury, but its role in brain cancers remains unknown. Here we show that glioblastoma, the most malignant type of brain tumor, induces calvarial bone abnormalities in murine models and patients with glioblastoma, altering osteoclast activities and increasing the number of skull channels in mice. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed glioblastoma-mediated alterations in the immune landscape of skull marrow and femoral bone marrow, including expansion of neutrophils and deterioration of various B cell subsets. In vivo inhibition of bone resorption reduced bone abnormalities, but promoted tumor progression in mesenchymal subtype tumors. This also abolished the survival benefit of the checkpoint inhibitor anti-PD-L1, by reducing activated T cell and increasing inflammatory neutrophil numbers. Together, these data provide insight into how brain tumors affect skull bone and the immune environment.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
COVID-19
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines sensitize tumours to immune checkpoint blockade.
In Nature on 1 November 2025 by Grippin, A., Marconi, C., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) extend survival in many patients with cancer but are ineffective in patients without pre-existing immunity1-9. Although personalized mRNA cancer vaccines sensitize tumours to ICIs by directing immune attacks against preselected antigens, personalized vaccines are limited by complex and time-intensive manufacturing processes10-14. Here we show that mRNA vaccines targeting SARS-CoV-2 also sensitize tumours to ICIs. In preclinical models, SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines led to a substantial increase in type I interferon, enabling innate immune cells to prime CD8+ T cells that target tumour-associated antigens. Concomitant ICI treatment is required for maximal efficacy in immunologically cold tumours, which respond by increasing PD-L1 expression. Similar correlates of vaccination response are found in humans, including increases in type I interferon, myeloid-lymphoid activation in healthy volunteers and PD-L1 expression on tumours. Moreover, receipt of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines within 100 days of initiating ICI is associated with significantly improved median and three-year overall survival in multiple large retrospective cohorts. This benefit is similar among patients with immunologically cold tumours. Together, these results demonstrate that clinically available mRNA vaccines targeting non-tumour-related antigens are potent immune modulators capable of sensitizing tumours to ICIs.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Ultrasound-Stimulated Microbubble Cavitation Combined With Anti-PD-L1 Blockade Inhibits the Progression of MC38 Tumors and Alters the Composition of Gut Microbiota in Mice.
In Int J Microbiol on 27 October 2025 by Li, H., Yang, G., et al.
PubMed
PD-L1 inhibitor immunotherapies have achieved significant advances in cancer treatment, yet only a subset of patients benefits, with response rates varying widely. Previous studies demonstrated that ultrasonic-stimulated microbubble cavitation (USMC) enhances the antitumor effects of PD-L1 inhibitors, suppressing tumor progression and prolonging survival in murine models. Given the gut microbiome's critical role in antitumor immunity and treatment efficacy, the interplay between USMC, immunotherapy, and gut microbiota remains poorly understood. To investigate this relationship, we conducted 16S rDNA sequencing to analyze the gut microbiota in mice across four treatment groups: control (ck), USMC group (um), PD-L1 inhibitor (pdl1), and USMC+PD-L1 inhibitor (um-pdl1). Our results revealed significant variations in gut microbial composition and abundance among the groups. Notably, we identified a correlation between commensal microbiota profiles and therapeutic responses. Mice treated with pdl1 alone or in combination with um exhibited marked reductions in tumor volume and weight, along with prolonged survival and concurrent shifts in gut microbiota. Multimatrix correlation analysis further identified four bacterial genera (Akkermansia, Bacteroides, Escherichia-Shigella, and Enterococcus) positively associated with treatment efficacy in the pdl1 and um-pdl1 groups. In summary, our findings preliminarily reveal substantial alterations in gut microbiota following tumor development, with the um-pdl1 regimen exerting a pronounced influence on microbial composition.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
αTIGIT-IL2 achieves tumor regression by promoting tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cell fragility in mouse models.
In Nat Commun on 17 October 2025 by Wang, T., Xu, Y., et al.
PubMed
Administration of IL-2 may promote the suppressive function and proliferation of Treg cells that cause immune tolerance in patients with cancer, which causes low-dose IL-2 to fail in achieving an optimal anti-tumor effect. Here, we designed an immunocytokine by fusing IL-2 and an anti-TIGIT monoclonal antibody, named αTIGIT-IL2, that targets Treg cells and promotes their fragility in the tumor milieu. These fragile-like Treg cells show impaired suppressive function and high IFN-γ production, triggering an immune-reactive tumor microenvironment. Such inflammation leads to the recruitment and functional reprogramming of intratumoral neutrophils, improving cross-talk between neutrophils and CD8+ T cells and enhancing the antitumor ability of CD8+ T cells. Combination therapy with αTIGIT-IL2 and PD-1 blocker could eliminate triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) tumors resistant to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. These findings provide the basis for developing a new generation of immunocytokines that target Treg cells and promote their fragility in the tumor milieu, resulting in robust antitumor immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Macrophage repolarization by immune checkpoint blockade drives T cell engagement in the tumor microenvironment.
In iScience on 17 October 2025 by Kwok, T., Silva-Junior, I. A., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapy combinations can improve patient outcomes, yet the interactions within the tumor microenvironment (TME) that drive therapeutic synergy are poorly understood. Tumor establishment drives monocyte recruitment and differentiation into tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), which have essential roles in coordinating immune responses and are thus attractive targets for therapeutic modulation. In a murine model of combination anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (anti-PD-L1) checkpoint blockade, tumor control was associated with increased infiltration of CD8+ T cells and M1-like repolarization of TAMs. Live-cell imaging of the tumor microenvironment revealed close contacts between tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and TAMs, in which the extent of the contact interfaces increased with combination immunotherapy. Treatment with anti-PD-L1 was able to increase macrophage expression of pro-inflammatory factors and phagocytic activity, suggesting a role for TAMs in reactivating CD8+ T cells in the TME. However, co-treatment with anti-PD-1 was ultimately necessary for tumor control, indicating the need for combination targeting of the TME.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Munc13-4 mediates tumor immune evasion by regulating the sorting and secretion of PD-L1 via exosomes.
In Nat Commun on 13 October 2025 by Liu, C., Liu, D., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-derived exosomes carry programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which binds programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) on T cells, suppressing immune responses locally and systemically. However, the mechanisms governing exosomal PD-L1 sorting and secretion remain elusive. Here, we identify Munc13-4 as a crucial regulator of this process. Deletion of Munc13-4 in breast tumors enhances T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity, suppresses tumor growth, and improves the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Mechanistically, Munc13-4 collaborates with hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS), Rab27, and SNAREs to facilitate PD-L1 sorting and secretion via exosomes. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis of the Munc13-4-Rab27a complex provide structural insights into exosome secretion. Importantly, PD-L1 sorting relies on a ternary complex composed of Munc13-4, PD-L1 and HRS, which is regulated by interferon gamma (IFNγ) signaling. A designed peptide that disrupts Munc13-4-PD-L1 interaction impedes PD-L1 sorting, enhances antitumor immunity, and suppresses tumor growth, highlighting the therapeutic potential of targeting this pathway.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
β-glucan combined with PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade suppresses pancreatic tumor growth after ablation therapy.
In Clinics (Sao Paulo) on 12 October 2025 by Wu, S., Sun, X., et al.
PubMed
To explore whether β-glucan combined with anti-PD-L1 reverses the immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment (TME) in residual pancreatic cancer after Microwave Ablation (MWA).
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Ligand-receptor interactions induce and mediate regulatory functions of BATF3+ B cells.
In Sci Adv on 10 October 2025 by Yan, H., Wang, R., et al.
PubMed
B cells express many protein ligands, yet their regulatory functions are incompletely understood. We profiled ligand expression across murine B sublineage cells, including those activated by defined receptor signals, and assessed their regulatory capacities and specificities through in silico analysis of ligand-receptor interactions. Consequently, we identified a B cell subset that expressed cytokine interleukin-27 (IL-27) and chemokine CXCL10. Through the IL-27-IL-27 receptor interaction, these IL-27/CXCL10-producing B cells targeted CD40-activated B cells in vitro and, upon induction by immunization and viral infection, optimized antibody responses and antiviral immunity in vivo. Also present in breast cancer tumors and retained there through CXCL10-CXCR3 interaction-mediated self-targeting, these cells promoted B cell PD-L1 expression and immune evasion. Mechanistically, Il27 and Cxcl10 transcription was induced by synergizing Toll-like receptor (TLR) and CD40 signals and driven by coinduced transcription factor BATF3, which directly targeted these genes. By applying a discovery framework focusing on regulatory cells, our findings expand the recognized scope of B cell regulatory functions.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
VISTA expressed on tumor cells is regulated by m6A and influences immune microenvironment through STAT3/CCL22 in NSCLC.
In J Transl Med on 2 October 2025 by Xu, H., Shen, K., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapy is playing an increasingly vital role in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), yet the challenge of immune evasion remains prevalent. Therefore, investigating the regulatory mechanisms of the tumor immune microenvironment could yield significant benefits.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Potentiating cancer immunotherapies with modular albumin-hitchhiking nanobody-STING agonist conjugates.
In Nat Biomed Eng on 1 October 2025 by Kimmel, B. R., Arora, K., et al.
PubMed
The enhancement of antitumour immunity via agonists of the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway is limited by pharmacological barriers. Here we show that the covalent conjugation of a STING agonist to anti-albumin nanobodies via site-selective bioconjugation chemistries prolongs the circulation of the agonist in the blood and increases its accumulation in tumour tissue, stimulating innate immune programmes that increased the infiltration of activated natural killer cells and T cells, which potently inhibited the growth of mouse tumours. The technology is modular, as demonstrated by the recombinant integration of a second nanobody domain targeting programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which further increased the accumulation of the agonist in tumours while blocking immunosuppressive PD-1/PD-L1 interactions. The bivalent nanobody-STING agonist conjugate stimulated robust antigen-specific T-cell responses and long-lasting immunological memory and conferred enhanced therapeutic efficacy. It was also effective as a neoadjuvant treatment to adoptive T-cell therapy. As a modular approach, hitchhiking STING agonists on serum albumin may serve as a broadly applicable strategy for augmenting the potency of systemically administered cancer immunotherapies.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
FK228 reshapes tumor microenvironment to enhance anti-PD-L1 efficacy.
In Oncogene on 1 October 2025 by Gong, L., Tian, L., et al.
PubMed
The lack of a favorable tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) results in limited response rates to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) across human solid tumors, necessitating the development of novel combination strategies. In this study, we repurposed FK228, an US FDA-approved histone deacetylase inhibitor that is used clinically in non-solid tumor treatment, as a novel ICB sensitizer in solid tumors and revealed the diverse regulatory functions of FK228 in the TIME. FK228 serves as a novel necroptosis inducer in cancer cells by triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress. This in turn enhances the immunogenicity of cancer cells and increases the infiltration of tumor-killing immunocytes, including CD8+ T and natural killer cells, particularly activating tumor-infiltrated CD8+ T cells. Meanwhile, FK228 treatment shifts macrophages toward the pro-inflammatory phenotype. Moreover, the combined use of FK228 and a PD-L1 inhibitor significantly delay tumor growth and extend the survival of tumor bearing mice. Overall, our findings reveal new possibilities for the clinical application of FK228 in solid tumors and underscore the critical role of histone deacetylases in maintaining the immune-unfavorable TIME.
-
-
Distinct TIME Modulation by Anti-PD-1/PD-L1, VEGF, and CTLA-4 Blockade Provides a Rationale for Triplet Therapy in HCC.
In Clin Mol Hepatol on 25 September 2025 by Iwamoto, H., Koga, H., et al.
PubMed
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Novel oncolytic adenovirus-based PEPvIII vaccine displays a super antitumor effect in glioma models.
In J Immunother Cancer on 25 September 2025 by Chen, Y., Ren, L., et al.
PubMed
Currently, an epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII)-specific peptide (PEPvIII) vaccine has not achieved satisfactory outcomes in several clinical trials for glioblastoma. This is probably due to the poor immunogenicity of the PEPvIII peptide vaccine and the harshly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Hence, identifying strategies to enhance tumor-specific T cell immune responses and reverse immune suppression is crucial for achieving the maximum beneficial therapeutic effect.
-