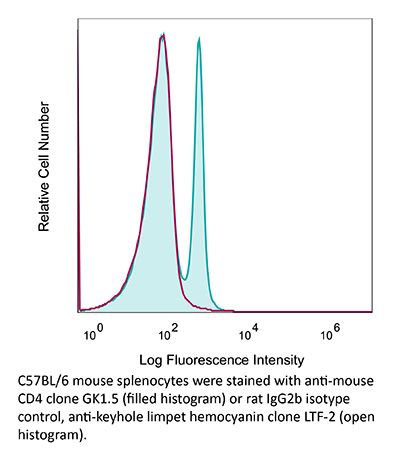
InVivoPlus anti-mouse CD4
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 6.5 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CTL clone V4 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion Flow cytometry Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 6.5 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin* |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* |
<5% Determined by DLS |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107636 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Budda, S. A. and L. A. Zenewicz (2018). "IL-22 deficiency increases CD4 T cell responses to mucosal immunization" Vaccine 36(25): 3694-3700.
PubMed
Mucosal vaccines are a promising platform for combatting infectious diseases for which we still lack effective preventative measures. Optimizing these vaccines to generate the best protective immune responses with the least complicated immunization regimen is imperative. Mucosal barriers are the first line of defense against many pathogens and, as such, we looked to their biology for strategies to improve vaccine delivery. Interleukin-22 (IL-22) is a key cytokine in both healthy and inflamed mucosal tissues. IL-22 promotes epithelial cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis, upregulates mucin and antimicrobial peptides, all of which promote mucosal barrier integrity. In this study, we find that IL-22 impairs the development of a T cell response during mucosal immunization. Compared to wild-type control mice, IL-22 deficient mice had increased antigen-specific CD4 T cell responses to intrarectal immunization using a protein and cholera toxin adjuvant vaccine. When immunized systemically with the same protein antigen adsorbed to alum, no differences in the CD4 T cell response between wild-type and IL-22 deficient mice were detected. This suggests that transiently inhibiting IL-22 during mucosal vaccination could enhance T cell responses. The broad-applicability of this proposed approach would allow for improvement of many existing mucosal vaccine regimens and have positive implications in the development of more efficacious mucosal vaccines.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Balogh, K. N., et al (2018). "Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor protects cancer cells from immunogenic cell death and impairs anti-tumor immune responses" PLoS One 13(6): e0197702.
PubMed
The Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) is an inflammatory cytokine that is overexpressed in a number of cancer types, with increased MIF expression often correlating with tumor aggressiveness and poor patient outcomes. In this study, we aimed to better understand the link between primary tumor expression of MIF and increased tumor growth. Using the MMTV-PyMT murine model of breast cancer, we observed that elevated MIF expression promoted tumor appearance and growth. Supporting this, we confirmed our previous observation that higher MIF expression supported tumor growth in the 4T1 murine model of breast cancer. We subsequently discovered that loss of MIF expression in 4T1 cells led to decreased cell numbers and increased apoptosis in vitro under reduced serum culture conditions. We hypothesized that this increase in cell death would promote detection by the host immune system in vivo, which could explain the observed impairment in tumor growth. Supporting this, we demonstrated that loss of MIF expression in the primary tumor led to an increased abundance of intra-tumoral IFNgamma-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and that depletion of T cells from mice bearing MIF-deficient tumors restored growth to the level of MIF-expressing tumors. Furthermore, we found that MIF depletion from the tumor cells resulted in greater numbers of activated intra-tumoral dendritic cells (DCs). Lastly, we demonstrated that loss of MIF expression led to a robust induction of a specialized form of cell death, immunogenic cell death (ICD), in vitro. Together, our data suggests a model in which MIF expression in the primary tumor dampens the anti-tumor immune response, promoting tumor growth.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Moynihan, K. D., et al (2016). "Eradication of large established tumors in mice by combination immunotherapy that engages innate and adaptive immune responses" Nat Med. doi : 10.1038/nm.4200.
PubMed
Checkpoint blockade with antibodies specific for cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein (CTLA)-4 or programmed cell death 1 (PDCD1; also known as PD-1) elicits durable tumor regression in metastatic cancer, but these dramatic responses are confined to a minority of patients. This suboptimal outcome is probably due in part to the complex network of immunosuppressive pathways present in advanced tumors, which are unlikely to be overcome by intervention at a single signaling checkpoint. Here we describe a combination immunotherapy that recruits a variety of innate and adaptive immune cells to eliminate large tumor burdens in syngeneic tumor models and a genetically engineered mouse model of melanoma; to our knowledge tumors of this size have not previously been curable by treatments relying on endogenous immunity. Maximal antitumor efficacy required four components: a tumor-antigen-targeting antibody, a recombinant interleukin-2 with an extended half-life, anti-PD-1 and a powerful T cell vaccine. Depletion experiments revealed that CD8+ T cells, cross-presenting dendritic cells and several other innate immune cell subsets were required for tumor regression. Effective treatment induced infiltration of immune cells and production of inflammatory cytokines in the tumor, enhanced antibody-mediated tumor antigen uptake and promoted antigen spreading. These results demonstrate the capacity of an elicited endogenous immune response to destroy large, established tumors and elucidate essential characteristics of combination immunotherapies that are capable of curing a majority of tumors in experimental settings typically viewed as intractable.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Zander, R. A., et al (2015). "PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity" Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641.
PubMed
The differentiation and protective capacity of Plasmodium-specific T cells are regulated by both positive and negative signals during malaria, but the molecular and cellular details remain poorly defined. Here we show that malaria patients and Plasmodium-infected rodents exhibit atypical expression of the co-stimulatory receptor OX40 on CD4 T cells and that therapeutic enhancement of OX40 signaling enhances helper CD4 T cell activity, humoral immunity, and parasite clearance in rodents. However, these beneficial effects of OX40 signaling are abrogated following coordinate blockade of PD-1 co-inhibitory pathways, which are also upregulated during malaria and associated with elevated parasitemia. Co-administration of biologics blocking PD-1 and promoting OX40 signaling induces excessive interferon-gamma that directly limits helper T cell-mediated support of humoral immunity and decreases parasite control. Our results show that targeting OX40 can enhance Plasmodium control and that crosstalk between co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory pathways in pathogen-specific CD4 T cells can impact pathogen clearance.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Liu, G., et al (2015). "IL-27 Signaling Is Crucial for Survival of Mice Infected with African Trypanosomes via Preventing Lethal Effects of CD4+ T Cells and IFN-gamma" PLoS Pathog 11(7): e1005065.
PubMed
African trypanosomes are extracellular protozoan parasites causing a chronic debilitating disease associated with a persistent inflammatory response. Maintaining the balance of the inflammatory response via downregulation of activation of M1-type myeloid cells was previously shown to be crucial to allow prolonged survival. Here we demonstrate that infection with African trypanosomes of IL-27 receptor-deficient (IL-27R-/-) mice results in severe liver immunopathology and dramatically reduced survival as compared to wild-type mice. This coincides with the development of an exacerbated Th1-mediated immune response with overactivation of CD4+ T cells and strongly enhanced production of inflammatory cytokines including IFN-gamma. What is important is that IL-10 production was not impaired in infected IL-27R-/- mice. Depletion of CD4+ T cells in infected IL-27R-/- mice resulted in a dramatically reduced production of IFN-gamma, preventing the early mortality of infected IL-27R-/- mice. This was accompanied by a significantly reduced inflammatory response and a major amelioration of liver pathology. These results could be mimicked by treating IL-27R-/- mice with a neutralizing anti-IFN-gamma antibody. Thus, our data identify IL-27 signaling as a novel pathway to prevent early mortality via inhibiting hyperactivation of CD4+ Th1 cells and their excessive secretion of IFN-gamma during infection with African trypanosomes. These data are the first to demonstrate the essential role of IL-27 signaling in regulating immune responses to extracellular protozoan infections.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Kim, J., et al (2015). "Memory programming in CD8(+) T-cell differentiation is intrinsic and is not determined by CD4 help" Nat Commun 6: 7994.
PubMed
CD8(+) T cells activated without CD4(+) T-cell help are impaired in memory expansion. To understand the underlying cellular mechanism, here we track the dynamics of helper-deficient CD8(+) T-cell response to a minor histocompatibility antigen by phenotypic and in vivo imaging analyses. Helper-deficient CD8(+) T cells show reduced burst expansion, rapid peripheral egress, delayed antigen clearance and continuous activation, and are eventually exhausted. Contrary to the general consensus that CD4 help encodes memory programmes in CD8(+) T cells and helper-deficient CD8(+) T cells are abortive, these cells can differentiate into effectors and memory precursors. Importantly, accelerating antigen clearance or simply increasing the burst effector size enables generation of memory cells by CD8(+) T cells, regardless of CD4 help. These results suggest that the memory programme is CD8(+) T-cell-intrinsic, and provide insight into the role of CD4 help in CD8(+) T-cell responses.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Guo, L., et al (2015). "Innate immunological function of TH2 cells in vivo" Nat Immunol 16(10): 1051-1059.
PubMed
Type 2 helper T cells (TH2 cells) produce interleukin 13 (IL-13) when stimulated by papain or house dust mite extract (HDM) and induce eosinophilic inflammation. This innate response is dependent on IL-33 but not T cell antigen receptors (TCRs). While type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2 cells) are the dominant innate producers of IL-13 in naive mice, we found here that helminth-infected mice had more TH2 cells compared to uninfected mice, and thes e cells became major mediators of innate type 2 responses. TH2 cells made important contributions to HDM-induced antigen-nonspecific eosinophilic inflammation and protected mice recovering from infection with Ascaris suum against subsequent infection with the phylogenetically distant nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Our findings reveal a previously unappreciated role for effector TH2 cells during TCR-independent innate-like immune responses.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Christensen, A. D., et al (2015). "Depletion of regulatory T cells in a hapten-induced inflammation model results in prolonged and increased inflammation driven by T cells" Clin Exp Immunol 179(3): 485-499.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Tregs ) are known to play an immunosuppressive role in the response of contact hypersensitivity (CHS), but neither the dynamics of Tregs during the CHS response nor the exaggerated inflammatory response after depletion of Tregs has been characterized in detail. In this study we show that the number of Tregs in the challenged tissue peak at the same time as the ear-swelling reaches its maximum on day 1 after challenge, whereas the number of Tregs in the draining lymph nodes peaks at day 2. As expected, depletion of Tregs by injection of a monoclonal antibody to CD25 prior to sensitization led to a prolonged and sustained inflammatory response which was dependent upon CD8 T cells, and co-stimulatory blockade with cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4-immunoglobulin (CTLA-4-Ig) suppressed the exaggerated inflammation. In contrast, blockade of the interleukin (IL)-10-receptor (IL-10R) did not further increase the exaggerated inflammatory response in the Treg -depleted mice. In the absence of Tregs , the response changed from a mainly acute reaction with heavy infiltration of neutrophils to a sustained response with more chronic characteristics (fewer neutrophils and dominated by macrophages). Furthermore, depletion of Tregs enhanced the release of cytokines and chemokines locally in the inflamed ear and augmented serum levels of the systemic inflammatory mediators serum amyloid (SAP) and haptoglobin early in the response.
Evans, E. E., et al (2015). "Antibody Blockade of Semaphorin 4D Promotes Immune Infiltration into Tumor and Enhances Response to Other Immunomodulatory Therapies" Cancer Immunol Res 3(6): 689-701.
PubMed
Semaphorin 4D (SEMA4D, CD100) and its receptor plexin-B1 (PLXNB1) are broadly expressed in murine and human tumors, and their expression has been shown to correlate with invasive disease in several human tumors. SEMA4D normally functions to regulate the motility and differentiation of multiple cell types, including those of the immune, vascular, and nervous systems. In the setting of cancer, SEMA4D-PLXNB1 interactions have been reported to affect vascular stabilization and transactivation of ERBB2, but effects on immune-cell trafficking in the tumor microenvironment (TME) have not been investigated. We describe a novel immunomodulatory function of SEMA4D, whereby strong expression of SEMA4D at the invasive margins of actively growing tumors influences the infiltration and distribution of leukocytes in the TME. Antibody neutralization of SEMA4D disrupts this gradient of expression, enhances recruitment of activated monocytes and lymphocytes into the tumor, and shifts the balance of cells and cytokines toward a proinflammatory and antitumor milieu within the TME. This orchestrated change in the tumor architecture was associated with durable tumor rejection in murine Colon26 and ERBB2(+) mammary carcinoma models. The immunomodulatory activity of anti-SEMA4D antibody can be enhanced by combination with other immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibition and chemotherapy. Strikingly, the combination of anti-SEMA4D antibody with antibody to CTLA-4 acts synergistically to promote complete tumor rejection and survival. Inhibition of SEMA4D represents a novel mechanism and therapeutic strategy to promote functional immune infiltration into the TME and inhibit tumor progression.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Vanpouille-Box, C., et al (2015). "TGFbeta Is a Master Regulator of Radiation Therapy-Induced Antitumor Immunity" Cancer Res 75(11): 2232-2242.
PubMed
T cells directed to endogenous tumor antigens are powerful mediators of tumor regression. Recent immunotherapy advances have identified effective interventions to unleash tumor-specific T-cell activity in patients who naturally develop them. Eliciting T-cell responses to a patient’s individual tumor remains a major challenge. Radiation therapy can induce immune responses to model antigens expressed by tumors, but it remains unclear whether it can effectively prime T cells specific for endogenous antigens expressed by poorly immunogenic tumors. We hypothesized that TGFbeta activity is a major obstacle hindering the ability of radiation to generate an in situ tumor vaccine. Here, we show that antibody-mediated TGFbeta neutralization during radiation therapy effectively generates CD8(+) T-cell responses to multiple endogenous tumor antigens in poorly immunogenic mouse carcinomas. Generated T cells were effective at causing regression of irradiated tumors and nonirradiated lung metastases or synchronous tumors (abscopal effect). Gene signatures associated with IFNgamma and immune-mediated rejection were detected in tumors treated with radiation therapy and TGFbeta blockade in combination but not as single agents. Upregulation of programmed death (PD) ligand-1 and -2 in neoplastic and myeloid cells and PD-1 on intratumoral T cells limited tumor rejection, resulting in rapid recurrence. Addition of anti-PD-1 antibodies extended survival achieved with radiation and TGFbeta blockade. Thus, TGFbeta is a fundamental regulator of radiation therapy’s ability to generate an in situ tumor vaccine. The combination of local radiation therapy with TGFbeta neutralization offers a novel individualized strategy for vaccinating patients against their tumors.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Uddin, M. N., et al (2014). "TNF-alpha-dependent hematopoiesis following Bcl11b deletion in T cells restricts metastatic melanoma" J Immunol 192(4): 1946-1953.
PubMed
Using several tumor models, we demonstrate that mice deficient in Bcl11b in T cells, although having reduced numbers of T cells in the peripheral lymphoid organs, developed significantly less tumors compared with wild-type mice. Bcl11b(-/-) CD4(+) T cells, with elevated TNF-alpha levels, but not the Bcl11b(-/-) CD8(+) T cells, were required for the reduced tumor burden, as were NK1.1(+) cells, found in increased numbers in Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice. Among NK1.1(+) cells, the NK cell population was predominant in number and was the only population displaying elevated granzyme B levels and increased degranulation, although not increased proliferation. Although the number of myeloid-derived suppressor cells was increased in the lungs with metastatic tumors of Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice, their arginase-1 levels were severely reduced. The increase in NK cell and myeloid-derived suppressor cell numbers was associated with increased bone marrow and splenic hematopoiesis. Finally, the reduced tumor burden, increased numbers of NK cells in the lung, and increased hematopoiesis in Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice were all dependent on TNF-alpha. Moreover, TNF-alpha treatment of wild-type mice also reduced the tumor burden and increased hematopoiesis and the numbers and activity of NK cells in the lung. In vitro treatment with TNF-alpha of lineage-negative hematopoietic progenitors increased NK and myeloid differentiation, further supporting a role of TNF-alpha in promoting hematopoiesis. These studies reveal a novel role for TNF-alpha in the antitumor immune response, specifically in stimulating hematopoiesis and increasing the numbers and activity of NK cells.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Church, S. E., et al (2014). "Tumor-specific CD4+ T cells maintain effector and memory tumor-specific CD8+ T cells" Eur J Immunol 44(1): 69-79.
PubMed
Immunotherapies that augment antitumor T cells have had recent success for treating patients with cancer. Here we examined whether tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells enhance CD8(+) T-cell adoptive immunotherapy in a lymphopenic environment. Our model employed physiological doses of tyrosinase-related protein 1-specific CD4(+) transgenic T cells-CD4(+) T cells and pmel-CD8(+) T cells that when transferred individually were subtherapeutic; however, when transferred together provided significant (p
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Krupnick, A. S., et al (2014). "Central memory CD8+ T lymphocytes mediate lung allograft acceptance" J Clin Invest 124(3): 1130-1143.
PubMed
Memory T lymphocytes are commonly viewed as a major barrier for long-term survival of organ allografts and are thought to accelerate rejection responses due to their rapid infiltration into allografts, low threshold for activation, and ability to produce inflammatory mediators. Because memory T cells are usually associated with rejection, preclinical protocols have been developed to target this population in transplant recipients. Here, using a murine model, we found that costimulatory blockade-mediated lung allograft acceptance depended on the rapid infiltration of the graft by central memory CD8+ T cells (CD44(hi)CD62L(hi)CCR7+). Chemokine receptor signaling and alloantigen recognition were required for trafficking of these memory T cells to lung allografts. Intravital 2-photon imaging revealed that CCR7 expression on CD8+ T cells was critical for formation of stable synapses with antigen-presenting cells, resulting in IFN-gamma production, which induced NO and downregulated alloimmune responses. Thus, we describe a critical role for CD8+ central memory T cells in lung allograft acceptance and highlight the need for tailored approaches for tolerance induction in the lung.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Xin, L., et al (2014). "Commensal microbes drive intestinal inflammation by IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells through ICOSL and OX40L costimulation in the absence of B7-1 and B7-2" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(29): 10672-10677.
PubMed
The costimulatory B7-1 (CD80)/B7-2 (CD86) molecules, along with T-cell receptor stimulation, together facilitate T-cell activation. This explains why in vivo B7 costimulation neutralization efficiently silences a variety of human autoimmune disorders. Paradoxically, however, B7 blockade also potently moderates accumulation of immune-suppressive regulatory T cells (Tregs) essential for protection against multiorgan systemic autoimmunity. Here we show that B7 deprivation in mice overrides the necessity for Tregs in averting systemic autoimmunity and inflammation in extraintestinal tissues, whereas peripherally induced Tregs retained in the absence of B7 selectively mitigate intestinal inflammation caused by Th17 effector CD4(+) T cells. The need for additional immune suppression in the intestine reflects commensal microbe-driven T-cell activation through the accessory costimulation molecules ICOSL and OX40L. Eradication of commensal enteric bacteria mitigates intestinal inflammation and IL-17 production triggered by Treg depletion in B7-deficient mice, whereas re-establishing intestinal colonization with Candida albicans primes expansion of Th17 cells with commensal specificity. Thus, neutralizing B7 costimulation uncovers an essential role for Tregs in selectively averting intestinal inflammation by Th17 CD4(+) T cells with commensal microbe specificity.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Hervieu, A., et al (2013). "Dacarbazine-mediated upregulation of NKG2D ligands on tumor cells activates NK and CD8 T cells and restrains melanoma growth" J Invest Dermatol 133(2): 499-508.
PubMed
Dacarbazine (DTIC) is a cytotoxic drug widely used for melanoma treatment. However, the putative contribution of anticancer immune responses in the efficacy of DTIC has not been evaluated. By testing how DTIC affects host immune responses to cancer in a mouse model of melanoma, we unexpectedly found that both natural killer (NK) and CD8(+) T cells were indispensable for DTIC therapeutic effect. Although DTIC did not directly affect immune cells, it triggered the upregulation of NKG2D ligands on tumor cells, leading to NK cell activation and IFNgamma secretion in mice and humans. NK cell-derived IFNgamma subsequently favored upregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on tumor cells, rendering them sensitive to cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells. Accordingly, DTIC markedly enhanced cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 inhibition efficacy in vivo in an NK-dependent manner. These results underscore the immunogenic properties of DTIC and provide a rationale to combine DTIC with immunotherapeutic agents that relieve immunosuppression in vivo.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Dai, M., et al (2013). "Long-lasting complete regression of established mouse tumors by counteracting Th2 inflammation" J Immunother 36(4): 248-257.
PubMed
40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.”}” data-sheets-userformat=”{“2″:14851,”3”:{“1″:0},”4”:{“1″:2,”2″:16777215},”12″:0,”14”:{“1″:2,”2″:1521491},”15″:”Roboto, sans-serif”,”16″:12}”>Mice with intraperitoneal ID8 ovarian carcinoma or subcutaneous SW1 melanoma were injected with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to CD137PD-1CTLA4 7-15 days after tumor initiation. Survival of mice with ID8 tumors tripled and >40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Butler, N. S., et al (2012). "Therapeutic blockade of PD-L1 and LAG-3 rapidly clears established blood-stage Plasmodium infection" Nat Immunol 13(2): 188-195.
PubMed
Infection of erythrocytes with Plasmodium species induces clinical malaria. Parasite-specific CD4(+) T cells correlate with lower parasite burdens and severity of human malaria and are needed to control blood-stage infection in mice. However, the characteristics of CD4(+) T cells that determine protection or parasite persistence remain unknown. Here we show that infection of humans with Plasmodium falciparum resulted in higher expression of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 associated with T cell dysfunction. In vivo blockade of the PD-1 ligand PD-L1 and the inhibitory receptor LAG-3 restored CD4(+) T cell function, amplified the number of follicular helper T cells and germinal-center B cells and plasmablasts, enhanced protective antibodies and rapidly cleared blood-stage malaria in mice. Thus, chronic malaria drives specific T cell dysfunction, and proper function can be restored by inhibitory therapies to enhance parasite control.
in vivo CD4+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Krieg, C., et al (2010). "Improved IL-2 immunotherapy by selective stimulation of IL-2 receptors on lymphocytes and endothelial cells" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(26): 11906-11911.
PubMed
IL-2 immunotherapy is an attractive treatment option for certain metastatic cancers. However, administration of IL-2 to patients can lead, by ill-defined mechanisms, to toxic adverse effects including severe pulmonary edema. Here, we show that IL-2-induced pulmonary edema is caused by direct interaction of IL-2 with functional IL-2 receptors (IL-2R) on lung endothelial cells in vivo. Treatment of mice with high-dose IL-2 led to efficient expansion of effector immune cells expressing high levels of IL-2Rbetagamma, including CD8(+) T cells and natural killer cells, which resulted in a considerable antitumor response against s.c. and pulmonary B16 melanoma nodules. However, high-dose IL-2 treatment also affected immune cell lineage marker-negative CD31(+) pulmonary endothelial cells via binding to functional alphabetagamma IL-2Rs, expressed at low to intermediate levels on these cells, thus causing pulmonary edema. Notably, IL-2-mediated pulmonary edema was abrogated by a blocking antibody to IL-2Ralpha (CD25), genetic disruption of CD25, or the use of IL-2Rbetagamma-directed IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes, thereby interfering with IL-2 binding to IL-2Ralphabetagamma(+) pulmonary endothelial cells. Moreover, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes led to vigorous activation of IL-2Rbetagamma(+) effector immune cells, which generated a dramatic antitumor response. Thus, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes might improve current strategies of IL-2-based tumor immunotherapy.
Product Citations
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Neuroscience
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Gut microbiota and brain-resident CD4+ T cells shape behavioral outcomes in autism spectrum disorder.
In Nat Commun on 11 July 2025 by Park, J. C., Sim, M. A., et al.
PubMed
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by alterations in social, repetitive, and anxiety-like behaviors. While emerging evidence suggest a gut-brain etiology in ASD, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. To dissect this axis, we developed a germ-free BTBR mouse model for ASD. The absence of gut microbiota in male mice ameliorates ASD-associated behaviors and reduces populations of inflammatory brain-resident T cells. Additionally, CD4+ T cell depletion mitigates neuroinflammation and ASD behaviors, suggesting a gut-immune-brain axis. We identify several microbial and metabolic regulators of ASD, particularly those relevant to the glutamate/GABA ratio and 3-hydroxyglutaric acid. Using an in silico metabolite prediction model, we propose Limosilactobacillus reuteri IMB015 (IMB015) to be a probiotic candidate. Administration of IMB015 reduces the glutamate/GABA ratio and neuroinflammation, resulting in improved behaviors. Here we report a gut-immune-brain axis in which the gut microbiota and its metabolites can modulate brain-resident immune cells and ASD-associated behaviors.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Diverse cell types establish a pathogenic immune environment in peripheral neuropathy.
In J Neuroinflammation on 23 May 2025 by Choi, J., Strickland, A., et al.
PubMed
Neuroinflammation plays a complex and context-dependent role in many neurodegenerative diseases. We identified a key pathogenic function of macrophages in a mouse model of a rare human congenital neuropathy in which SARM1, the central executioner of axon degeneration, is activated by hypomorphic mutations in the axon survival factor NMNAT2. Macrophage depletion blocked and reversed neuropathic phenotypes in this sarmopathy model, revealing SARM1-dependent neuroimmune mechanisms as key drivers of disease pathogenesis. In this study, we investigated the impact of chronic subacute SARM1 activation on the peripheral nerve milieu using single cell/nucleus RNA-sequencing (sc/snRNA-seq). Our analyses reveal an expansion of immune cells (macrophages and T lymphocytes) and repair Schwann cells, as well as significant transcriptional alterations to a wide range of nerve-resident cell types. Notably, endoneurial fibroblasts show increased expression of chemokines (Ccl9, Cxcl5) and complement components (C3, C4b, C6) in response to chronic SARM1 activation, indicating enhanced immune cell recruitment and immune response regulation by non-immune nerve-resident cells. Analysis of CD45+ immune cells in sciatic nerves revealed an expansion of an Il1b+ macrophage subpopulation with increased expression of markers associated with phagocytosis and T cell activation/proliferation. We also found a significant increase in T cells in sarmopathic nerves. Remarkably, T cell depletion rescued motor phenotypes in the sarmopathy model. These findings delineate the significant changes chronic SARM1 activation induces in peripheral nerves and highlights the potential of immunomodulatory therapies for SARM1-dependent peripheral neurodegenerative disease.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Antitumor CD4+ T Helper 1 Cells Target and Control the Outgrowth of Disseminated Cancer Cells.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 2 May 2025 by Ganesan, R., Lee, M. C., et al.
PubMed
Detection of disseminated cancer cells (DCC) in the bone marrow (BM) of patients with breast cancer is a critical predictor of late recurrence and distant metastasis. Conventional therapies often fail to completely eradicate DCCs in patients. In this study, we demonstrate that intratumoral priming of antitumor CD4+ T helper 1 (Th1) cells was able to eliminate the DCC burden in distant organs and prevent overt metastasis, independent of CD8+ T cells. Intratumoral priming of tumor antigen-specific CD4+ Th1 cells enhanced their migration to the BM and distant metastatic site to selectively target DCC burden. The majority of these intratumorally activated CD4+ T cells were CD4+PD1- T cells, supporting their nonexhaustion stage. Phenotypic characterization revealed enhanced infiltration of memory CD4+ T cells and effector CD4+ T cells in the primary tumor, tumor-draining lymph node, and DCC-driven metastasis site. A robust migration of CD4+CCR7+CXCR3+ Th1 cells and CD4+CCR7-CXCR3+ Th1 cells into distant organs further revealed their potential role in eradicating DCC-driven metastasis. The intratumoral priming of antitumor CD4+ Th1 cells failed to eradicate DCC-driven metastasis in CD4- or IFN-γ knockout mice. Moreover, antitumor CD4+ Th1 cells, by increasing IFN-γ production, inhibited various molecular aspects and increased classical and nonclassical MHC molecule expression in DCCs. This reduced stemness and self-renewal while increasing immune recognition in DCCs of patients with breast cancer. These results unveil an immune basis for antitumor CD4+ Th1 cells that modulate DCC tumorigenesis to prevent recurrence and metastasis in patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
T Cells Instruct Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Resistance in Tumors Responsive to IL1 and TNFα Inflammation.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 3 February 2025 by Cho, N. W., Guldberg, S. M., et al.
PubMed
Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) is common, even in tumors with T-cell infiltration. We thus investigated consequences of ICI-induced T-cell infiltration in the microenvironment of resistant tumors. T cells and neutrophil numbers increased in ICI-resistant tumors following treatment, in contrast to ICI-responsive tumors. Resistant tumors were distinguished by high expression of IL1 receptor 1, enabling a synergistic response to IL1 and TNFα to induce G-CSF, CXCL1, and CXCL2 via NF-κB signaling, supporting immunosuppressive neutrophil accumulation in tumor. Perturbation of this inflammatory resistance circuit sensitized tumors to ICIs. Paradoxically, T cells drove this resistance circuit via TNFα both in vitro and in vivo. Evidence of this inflammatory resistance circuit and its impact also translated to human cancers. These data support a mechanism of ICI resistance, wherein treatment-induced T-cell activity can drive resistance in tumors responsive to IL1 and TNFα, with important therapeutic implications.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Donor MHC-specific thymus vaccination allows for immunocompatible allotransplantation.
In Cell Res on 1 February 2025 by Liu, Y., Feng, H., et al.
PubMed
Organ transplantation is the last-resort option to treat organ failure. However, less than 10% of patients benefit from this only option due to lack of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-matched donor organs and 25%-80% of donated organs could not find MHC-matched recipients. T cell allorecognition is the principal mechanism for allogeneic graft rejection. We herein present a "donor MHC-specific thymus vaccination" (DMTV) strategy to induce T cell tolerance to both autologous and allogeneic donor MHC. Allogeneic MHC molecules were expressed in the recipient thymus through adeno-associated virus-mediated delivery, which led to stable expression of allogeneic MHC together with the autologous MHC in the engineered thymus. During local T cell education, those T cells recognizing either autologous MHC or allogeneic MHC were equally depleted. We constructed C57BL/6-MHC and BALB/c-MHC dual immunocompatible mice via thymus vaccination of C57BL/6-MHC into the BALB/c thymus and observed long-term graft tolerance after transplantation of C57BL/6 skin and C57BL/6 mouse embryonic stem cells into the vaccinated BALB/c mice. We also validated our DMTV strategy in a bone marrow, liver, thymus (BLT)-humanized mouse model for immunocompatible allotransplantation of human embryonic stem cells. Our study suggests that the DMTV strategy is a potent avenue to introduce a donor compatible immune system in recipients, which overcomes the clinical dilemma of the extreme shortage of MHC-matched donor organs for treating patients with end-stage organ failure.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Cancer Research
Caerin 1.1/1.9-mediated antitumor immunity depends on IFNAR-Stat1 signalling of tumour infiltrating macrophage by autocrine IFNα and is enhanced by CD47 blockade.
In Sci Rep on 30 January 2025 by Li, J., Luo, Y., et al.
PubMed
Previously, we demonstrated that natural host-defence peptide caerin 1.1/caerin 1.9 (F1/F3) increases the efficacy of anti-PD-1 and therapeutic vaccine, in a HPV16 + TC-1 tumour model, but the anti-tumor mechanism of F1/F3 is still unclear. In this study, we explored the impact of F1/F3 on the tumor microenvironment in a transplanted B16 melanoma model, and further investigated the mechanism of action of F1/F3 using monoclonal antibodies to deplete relevant cells, gene knockout mice and flow cytometry. We show that F1/F3 is able to inhibit the growth of melanoma B16 tumour cells both in vitro and in vivo. Depletion of macrophages, blockade of IFNα receptor, and Stat1 inhibition each abolishes F1/F3-mediated antitumor responses. Subsequent analysis reveals that F1/F3 increases the tumour infiltration of inflammatory macrophages, upregulates the level of IFNα receptor, and promotes the secretion of IFNα by macrophages. Interestingly, F1/F3 upregulates CD47 level on tumour cells; and blocking CD47 increases F1/F3-mediated antitumor responses. Furthermore, F1/F3 intratumor injection, CD47 blockade, and therapeutic vaccination significantly increases the survival time of B16 tumour-bearing mice. These results indicate that F1/F3 may be effective to improve the efficacy of ICB and therapeutic vaccine-based immunotherapy for human epithelial cancers and warrants consideration for clinical trials.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Maternal asthma imprints fetal lung ILC2s via glucocorticoid signaling leading to worsened allergic airway inflammation in murine adult offspring.
In Nat Commun on 13 January 2025 by Takao, T., Matsui, A., et al.
PubMed
The root of asthma can be linked to early life, with prenatal environments influencing risk. We investigate the effects of maternal asthma on the offspring's lungs during fetal and adult life. Adult offspring of asthmatic mothers show an increase in lung group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) number and function with allergen-induced lung inflammation. Offspring of asthmatic mothers show phenotypic alteration of their lung ILC2s during fetal life, with increased expression of genes related to activation and glucocorticoid signaling. Furthermore, these offspring carry overlapping chromatin-accessible altered regions, including glucocorticoid receptor-binding regions in their lung ILC2s both at the fetal stage and adulthood, suggesting persistent prenatal epigenetic changes. Moreover, maternal exposure to glucocorticoids has similar effects on fetal lung ILC2s and contributes to allergen-induced lung inflammation during adulthood. Thus, asthma during pregnancy may have long-term effects on lung ILC2s in the offspring from the embryonic period, contributing to an increased risk of developing asthma.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Invention and characterization of a systemically administered, attenuated and killed bacteria-based multiple immune receptor agonist for anti-tumor immunotherapy.
In Front Immunol on 28 November 2024 by
PubMed
Activation of immune receptors, such as Toll-like (TLR), NOD-like (NLR) and Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) is critical for efficient innate and adaptive immunity. Gram-negative bacteria (G-NB) contain multiple TLR, NOD and STING agonists. Potential utility of G-NB for cancer immunotherapy is supported by observations of tumor regression in the setting of infection and Coley's Toxins. Coley reported that intravenous (i.v.) administration was likely most effective but produced uncontrollable toxicity. The discovery of TLRs and their agonists, particularly the potent TLR4 agonist lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-endotoxin, comprising ~75% of the outer membrane of G-NB, suggests that LPS may be both a critical active ingredient and responsible for dose-limiting i.v. toxicity of G-NB. This communication reports the production of killed, stabilized, intact bacteria products from non-pathogenic G-NB with ~96% reduction of LPS-endotoxin activity. One resulting product candidate, Decoy10, was resistant to standard methods of cell disruption and contained TLR2,4,8,9, NOD2 and STING agonist activity. Decoy10 also exhibited reduced i.v. toxicity in mice and rabbits, and a largely uncompromised ability to induce cytokine and chemokine secretion by human immune cells in vitro, all relative to unprocessed, parental bacterial cells. Decoy10 and a closely related product, Decoy20, produced single agent anti-tumor activity or combination-mediated durable regression of established subcutaneous, metastatic or orthotopic colorectal, hepatocellular (HCC), pancreatic, and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) tumors in mice, with induction of both innate and adaptive immunological memory (syngeneic and human tumor xenograft models). Decoy bacteria combination-mediated regressions were observed with a low-dose, oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), anti-PD-1 checkpoint therapy, low-dose cyclophosphamide (LDC), and/or a targeted antibody (rituximab). Efficient tumor eradication was associated with plasma expression of 15-23 cytokines and chemokines, broad induction of cytokine, chemokine, innate and adaptive immune pathway genes in tumors, cold to hot tumor inflammation signature transition, and required NK, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, collectively demonstrating a role for both innate and adaptive immune activation in the anti-tumor immune response.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Novel Arf1 Inhibitors Drive Cancer Stem Cell Aging and Potentiate Anti-Tumor Immunity.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 October 2024 by Wang, Y., Li, Q., et al.
PubMed
The small G protein Arf1 has been identified as playing a selective role in supporting cancer stem cells (CSCs), making it an attractive target for cancer therapy. However, the current Arf1 inhibitors have limited translational potential due to their high toxicity and low specificity. In this study, two new potent small-molecule inhibitors of Arf1, identified as DU101 and DU102, for cancer therapy are introduced. Preclinical tumor models demonstrate that these inhibitors triggered a cascade of aging in CSCs and enhance anti-tumor immunity in mouse cancer and PDX models. Through single-cell sequencing, the remodeling of the tumor immune microenvironment induced by these new Arf1 inhibitors is analyzed and an increase in tumor-associated CD8+ CD4+ double-positive T (DPT) cells is identified. These DPT cells exhibit superior features of active CD8 single-positive T cells and a higher percentage of TCF1+PD-1+, characteristic of stem-like T cells. The frequency of tumor-infiltrating stem-like DPT cells correlates with better disease-free survival (DFS) in cancer patients, indicating that these inhibitors may offer a novel cancer immunotherapy strategy by converting the cold tumor immune microenvironment into a hot one, thus expanding the potential for immunotherapy in cancer patients.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Metabolic Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Using Glutamine Antagonist JHU083 Drives Tumor Immunity in Myeloid-Rich Prostate and Bladder Cancers.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 2 July 2024 by Praharaj, M., Shen, F., et al.
PubMed
Glutamine metabolism in tumor microenvironments critically regulates antitumor immunity. Using the glutamine-antagonist prodrug JHU083, we report potent tumor growth inhibition in urologic tumors by JHU083-reprogrammed tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and tumor-infiltrating monocytes. We show JHU083-mediated glutamine antagonism in tumor microenvironments induced by TNF, proinflammatory, and mTORC1 signaling in intratumoral TAM clusters. JHU083-reprogrammed TAMs also exhibited increased tumor cell phagocytosis and diminished proangiogenic capacities. In vivo inhibition of TAM glutamine consumption resulted in increased glycolysis, a broken tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and purine metabolism disruption. Although the antitumor effect of glutamine antagonism on tumor-infiltrating T cells was moderate, JHU083 promoted a stem cell-like phenotype in CD8+ T cells and decreased the abundance of regulatory T cells. Finally, JHU083 caused a global shutdown in glutamine-utilizing metabolic pathways in tumor cells, leading to reduced HIF-1α, c-MYC phosphorylation, and induction of tumor cell apoptosis, all key antitumor features. Altogether, our findings demonstrate that targeting glutamine with JHU083 led to suppressed tumor growth as well as reprogramming of immunosuppressive TAMs within prostate and bladder tumors that promoted antitumor immune responses. JHU083 can offer an effective therapeutic benefit for tumor types that are enriched in immunosuppressive TAMs.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A CD36-dependent non-canonical lipid metabolism program promotes immune escape and resistance to hypomethylating agent therapy in AML.
In Cell Rep Med on 18 June 2024 by Guo, H. Z., Feng, R. X., et al.
PubMed
Environmental lipids are essential for fueling tumor energetics, but whether these exogenous lipids transported into cancer cells facilitate immune escape remains unclear. Here, we find that CD36, a transporter for exogenous lipids, promotes acute myeloid leukemia (AML) immune evasion. We show that, separately from its established role in lipid oxidation, CD36 on AML cells senses oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) to prime the TLR4-LYN-MYD88-nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway, and exogenous palmitate transfer via CD36 further potentiates this innate immune pathway by supporting ZDHHC6-mediated MYD88 palmitoylation. Subsequently, NF-κB drives the expression of immunosuppressive genes that inhibit anti-tumor T cell responses. Notably, high-fat-diet or hypomethylating agent decitabine treatment boosts the immunosuppressive potential of AML cells by hijacking CD36-dependent innate immune signaling, leading to a dampened therapeutic effect. This work is of translational interest because lipid restriction by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved lipid-lowering statin drugs improves the efficacy of decitabine therapy by weakening leukemic CD36-mediated immunosuppression.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Immunogenicity and efficacy of CNA25 as a potential whole-cell vaccine against systemic candidiasis.
In EMBO Mol Med on 1 June 2024 by Sahu, S. R., Dutta, A., et al.
PubMed
Disseminated fungal infections account for ~1.5 million deaths per year worldwide, and mortality may increase further due to a rise in the number of immunocompromised individuals and drug-resistance fungal species. Since an approved antifungal vaccine is yet to be available, this study explored the immunogenicity and vaccine efficacy of a DNA polymerase mutant strain of Candida albicans. CNA25 is a pol32ΔΔ strain that exhibits growth defects and does not cause systemic candidiasis in mice. Immunized mice with live CNA25 were fully protected against C. albicans and C. parapsilosis but partially against C. tropicalis and C. glabrata infections. CNA25 induced steady expression of TLR2 and Dectin-1 receptors leading to a faster recognition and clearance by the immune system associated with the activation of protective immune responses mostly mediated by neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells, B cells, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Molecular blockade of Dectin-1, IL-17, IFNγ, and TNFα abolished resistance to reinfection. Altogether, this study suggested that CNA25 collectively activates innate, adaptive, and trained immunity to be a promising live whole-cell vaccine against systemic candidiasis.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Immunogenicity and efficacy of CNA25 as a potential whole-cell vaccine against systemic candidiasis.
In EMBO Molecular Medice on 1 June 2024 by Sahu, S. R., Dutta, A., et al.
Disseminated fungal infections account for ~1.5 million deaths per year worldwide, and mortality may increase further due to a rise in the number of immunocompromised individuals and drug-resistance fungal species. Since an approved antifungal vaccine is yet to be available, this study explored the immunogenicity and vaccine efficacy of a DNA polymerase mutant strain of Candida albicans. CNA25 is a pol32ΔΔ strain that exhibits growth defects and does not cause systemic candidiasis in mice. Immunized mice with live CNA25 were fully protected against C. albicans and C. parapsilosis but partially against C. tropicalis and C. glabrata infections. CNA25 induced steady expression of TLR2 and Dectin-1 receptors leading to a faster recognition and clearance by the immune system associated with the activation of protective immune responses mostly mediated by neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells, B cells, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Molecular blockade of Dectin-1, IL-17, IFNγ, and TNFα abolished resistance to reinfection. Altogether, this study suggested that CNA25 collectively activates innate, adaptive, and trained immunity to be a promising live whole-cell vaccine against systemic candidiasis. © 2024. The Author(s).
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
PGE2 limits effector expansion of tumour-infiltrating stem-like CD8+ T cells.
In Nature on 1 May 2024 by Lacher, S. B., Dörr, J., et al.
PubMed
Cancer-specific TCF1+ stem-like CD8+ T cells can drive protective anticancer immunity through expansion and effector cell differentiation1-4; however, this response is dysfunctional in tumours. Current cancer immunotherapies2,5-9 can promote anticancer responses through TCF1+ stem-like CD8+ T cells in some but not all patients. This variation points towards currently ill-defined mechanisms that limit TCF1+CD8+ T cell-mediated anticancer immunity. Here we demonstrate that tumour-derived prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) restricts the proliferative expansion and effector differentiation of TCF1+CD8+ T cells within tumours, which promotes cancer immune escape. PGE2 does not affect the priming of TCF1+CD8+ T cells in draining lymph nodes. PGE2 acts through EP2 and EP4 (EP2/EP4) receptor signalling in CD8+ T cells to limit the intratumoural generation of early and late effector T cell populations that originate from TCF1+ tumour-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes (TILs). Ablation of EP2/EP4 signalling in cancer-specific CD8+ T cells rescues their expansion and effector differentiation within tumours and leads to tumour elimination in multiple mouse cancer models. Mechanistically, suppression of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) signalling pathway underlies the PGE2-mediated inhibition of TCF1+ TIL responses. Altogether, we uncover a key mechanism that restricts the IL-2 responsiveness of TCF1+ TILs and prevents anticancer T cell responses that originate from these cells. This study identifies the PGE2-EP2/EP4 axis as a molecular target to restore IL-2 responsiveness in anticancer TILs to achieve cancer immune control.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells attenuate the antitumor efficacy of radiopharmaceutical therapy using 90Y-NM600 in combination with androgen deprivation therapy in murine prostate tumors.
In J Immunother Cancer on 24 April 2024 by Muralidhar, A., Hernandez, R., et al.
PubMed
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is pivotal in treating recurrent prostate cancer and is often combined with external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) for localized disease. However, for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, EBRT is typically only used in the palliative setting, because of the inability to radiate all sites of disease. Systemic radiation treatments that preferentially irradiate cancer cells, known as radiopharmaceutical therapy or targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT), have demonstrable benefits for treating metastatic prostate cancer. Here, we explored the use of a novel TRT, 90Y-NM600, specifically in combination with ADT, in murine prostate tumor models.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer.
In Nat Commun on 1 April 2024 by Cheng, M., Chen, S., et al.
PubMed
Interplay between innate and adaptive immune cells is important for the antitumor immune response. However, the tumor microenvironment may turn immune suppressive, and tumor associated macrophages are playing a role in this transition. Here, we show that CD276, expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), play a role in diminishing the immune response against tumors. Using a model of tumors induced by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitrosamine in BLCA male mice we show that genetic ablation of CD276 in TAMs blocks efferocytosis and enhances the expression of the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) of TAMs. This in turn increases CD4 + and cytotoxic CD8 + T cell infiltration of the tumor. Combined single cell RNA sequencing and functional experiments reveal that CD276 activates the lysosomal signaling pathway and the transcription factor JUN to regulate the expression of AXL and MerTK, resulting in enhanced efferocytosis in TAMs. Proving the principle, we show that simultaneous blockade of CD276 and PD-1 restrain tumor growth better than any of the components as a single intervention. Taken together, our study supports a role for CD276 in efferocytosis by TAMs, which is potentially targetable for combination immune therapy.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Donor MHC-specific Thymus Vaccination for Immunocompatible Allotransplantation
In Research Square on 13 March 2024 by Liu, Y., Feng, H., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
COVID-19
A T cell-based SARS-CoV-2 spike protein vaccine provides protection without antibodies.
In JCI Insight on 8 March 2024 by Shi, J., Zheng, J., et al.
PubMed
SARS-CoV-2 spike-based vaccines are used to control the COVID-19 pandemic. However, emerging variants have become resistant to antibody neutralization and further mutations may lead to full resistance. We tested whether T cells alone could provide protection without antibodies. We designed a T cell-based vaccine in which SARS-CoV-2 spike sequences were rearranged and attached to ubiquitin. Immunization of mice with the vaccine induced no specific antibodies, but strong specific T cell responses. We challenged mice with SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain or an Omicron variant after the immunization and monitored survival or viral titers in the lungs. The mice were significantly protected against death and weight loss caused by the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain, and the viral titers in the lungs of mice challenged with the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain or the Omicron variant were significantly reduced. Importantly, depletion of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells led to significant loss of the protection. Our analyses of spike protein sequences of the variants indicated that fewer than one-third presented by dominant HLA alleles were mutated and that most of the mutated epitopes were in the subunit 1 region. As the subunit 2 region is conservative, the vaccines targeting spike protein are expected to protect against future variants due to the T cell responses.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
The efficacy of chemotherapy is limited by intratumoral senescent cells expressing PD-L2.
In Nat Cancer on 1 March 2024 by Chaib, S., Lopez-Dominguez, J. A., et al.
PubMed
Chemotherapy often generates intratumoral senescent cancer cells that strongly modify the tumor microenvironment, favoring immunosuppression and tumor growth. We discovered, through an unbiased proteomics screen, that the immune checkpoint inhibitor programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PD-L2) is highly upregulated upon induction of senescence in different types of cancer cells. PD-L2 is not required for cells to undergo senescence, but it is critical for senescent cells to evade the immune system and persist intratumorally. Indeed, after chemotherapy, PD-L2-deficient senescent cancer cells are rapidly eliminated and tumors do not produce the senescence-associated chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2. Accordingly, PD-L2-deficient pancreatic tumors fail to recruit myeloid-derived suppressor cells and undergo regression driven by CD8 T cells after chemotherapy. Finally, antibody-mediated blockade of PD-L2 strongly synergizes with chemotherapy causing remission of mammary tumors in mice. The combination of chemotherapy with anti-PD-L2 provides a therapeutic strategy that exploits vulnerabilities arising from therapy-induced senescence.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cancer Research
Somatic mouse models of gastric cancer reveal genotype-specific features of metastatic disease.
In Nat Cancer on 1 February 2024 by Leibold, J., Tsanov, K. M., et al.
PubMed
Metastatic gastric carcinoma is a highly lethal cancer that responds poorly to conventional and molecularly targeted therapies. Despite its clinical relevance, the mechanisms underlying the behavior and therapeutic response of this disease are poorly understood owing, in part, to a paucity of tractable models. Here we developed methods to somatically introduce different oncogenic lesions directly into the murine gastric epithelium. Genotypic configurations observed in patients produced metastatic gastric cancers that recapitulated the histological, molecular and clinical features of all nonviral molecular subtypes of the human disease. Applying this platform to both wild-type and immunodeficient mice revealed previously unappreciated links between the genotype, organotropism and immune surveillance of metastatic cells, which produced distinct patterns of metastasis that were mirrored in patients. Our results establish a highly portable platform for generating autochthonous cancer models with flexible genotypes and host backgrounds, which can unravel mechanisms of gastric tumorigenesis or test new therapeutic concepts.
-