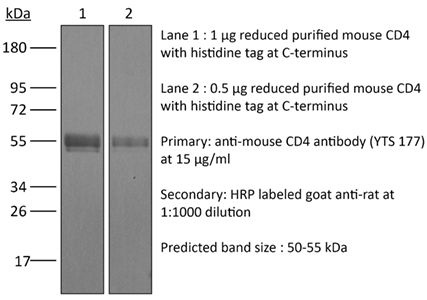
InVivoPlus anti-mouse CD4
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse Spleen Cells |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo blockade of CD4+ T-cell responses Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin* |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107642 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo blockade of CD4+ T-cell responses
Li, Z., et al (2015). "Pre-treatment of allogeneic bone marrow recipients with the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 transiently enhances hematopoietic chimerism without promoting donor-specific skin allograft tolerance" Transpl Immunol 33(2): 125-129.
PubMed
Hematopoietic chimerism established by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is known to promote donor-specific organ allograft tolerance; however, clinical application is limited by the need for toxic host conditioning and “megadoses” of donor bone marrow cells. A potential solution to this problem has been suggested by the observation that recipient bone marrow mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 promotes chimerism in congenic bone marrow transplantation experiments in mice. Here we report that a single subcutaneous dose of 10mg/kg AMD3100 in recipient C57BL/6 mice was able to enhance hematopoietic chimerism when complete MHC-mismatched BALB/c donor bone marrow cells were transplanted 1h after drug dosing. However, levels of chimerism measured 30days post-transplantation were not sustained when mice were reexamined on day 90 post-transplantation. Moreover, transient chimerism induced by this protocol did not support robust donor-specific skin allograft tolerance. Using the same transient immunosuppression protocol, we confirmed that “megadoses” of donor bone marrow cells could induce durable chimerism associated with donor-specific skin allograft tolerance without AMD3100 pre-treatment. We conclude that in this protocol AMD3100 pretreatment may empty bone marrow niches that become reoccupied by allogeneic donor hematopoietic progenitor cells but not by true long-lived donor hematopoietic stem cells, resulting in short-lived chimerism and failure to support durable donor-specific allograft tolerance.
in vivo blockade of CD4+ T-cell responses
Mayer, C. T., et al (2014). "Anti-CD4 treatment inhibits autoimmunity in scurfy mice through the attenuation of co-stimulatory signals" J Autoimmun 50: 23-32.
PubMed
A major concept in autoimmunity is that disruption of Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) predisposes to breach of tolerance. This is exemplified by the Foxp3-linked disorder termed IPEX (immunodysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked) which affects newborn children. There has been considerable clinical interest in the role of non-depleting anti-CD4 antibodies as a means of upregulating the function of Foxp3(+) Tregs in order to control detrimental inflammatory responses such as transplant rejection. However, according to the paradigm of a Treg-dependent mechanism of action, the effectiveness of anti-CD4 antibodies as a therapy for human autoimmune diseases is unclear considering that Treg function might be intrinsically impaired. Specifically, anti-CD4 therapy is expected to fail in patients suffering from the IPEX syndrome due to the lack of functional Foxp3(+) Tregs. Taking advantage of natural Foxp3 mutant scurfy (sf) mice closely resembling the IPEX syndrome, and genetically engineered mice depleted of Foxp3(+) Tregs, we report here that anti-CD4 treatment induces tolerance independent of Foxp3(+) Tregs. This so far undefined mechanism is dependent on the recessive non-infectious tolerization of autoreactive T cells. Treg-independent tolerance alone is powerful enough to suppress both the onset and severity of autoimmunity and reduces clinically relevant autoantibody levels and liver fibrosis. Mechanistically, tolerance induction requires the concomitant activation of autoreactive T cells and is associated with the down-regulation of the co-stimulatory TNF-receptor superfamily members OX40 and CD30 sustaining CD4(+) T cell survival. In the light of ongoing clinical trials, our results highlight an unexpected potency of anti-CD4 antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Particularly, CD4 blockade might represent a novel therapeutic option for the human IPEX syndrome.
in vivo blockade of CD4+ T-cell responses
Rocca, C. J., et al (2014). "rAAV9 combined with renal vein injection is optimal for kidney-targeted gene delivery: conclusion of a comparative study" Gene Ther 21(6): 618-628.
PubMed
Effective gene therapy strategies for the treatment of kidney disorders remain elusive. We report an optimized kidney-targeted gene delivery strategy using recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) administered via retrograde renal vein injection in mice. Renal vein injection of rAAV consistently resulted in superior kidney transduction compared with tail vein injection using as little as half the tail vein dose. We compared rAAV5, 6, 8 and 9, containing either green fluorescent protein (GFP) or luciferase reporter genes driven by the Cytomegalovirus promoter. We demonstrated that although rAAV6 and 8 injected via renal vein transduced the kidney, transgene expression was mainly restricted to the medulla. Transgene expression was systematically low after rAAV5 injection, attributed to T-cell immune response, which could be overcome by transient immunosuppression. However, rAAV9 was the only serotype that permitted high-transduction efficiency of both the cortex and medulla. Moreover, both the glomeruli and tubules were targeted, with a higher efficiency within the glomeruli. To improve the specificity of kidney-targeted gene delivery with rAAV9, we used the parathyroid hormone receptor ‘kidney-specific’ promoter. We obtained a more efficient transgene expression within the kidney, and a significant reduction in other tissues. Our work represents the first comprehensive and clinically relevant study for kidney gene delivery.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer.
In Nat Commun on 1 April 2024 by Cheng, M., Chen, S., et al.
PubMed
Interplay between innate and adaptive immune cells is important for the antitumor immune response. However, the tumor microenvironment may turn immune suppressive, and tumor associated macrophages are playing a role in this transition. Here, we show that CD276, expressed on tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), play a role in diminishing the immune response against tumors. Using a model of tumors induced by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitrosamine in BLCA male mice we show that genetic ablation of CD276 in TAMs blocks efferocytosis and enhances the expression of the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) of TAMs. This in turn increases CD4 + and cytotoxic CD8 + T cell infiltration of the tumor. Combined single cell RNA sequencing and functional experiments reveal that CD276 activates the lysosomal signaling pathway and the transcription factor JUN to regulate the expression of AXL and MerTK, resulting in enhanced efferocytosis in TAMs. Proving the principle, we show that simultaneous blockade of CD276 and PD-1 restrain tumor growth better than any of the components as a single intervention. Taken together, our study supports a role for CD276 in efferocytosis by TAMs, which is potentially targetable for combination immune therapy.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
Carfilzomib modulates tumor microenvironment to potentiate immune checkpoint therapy for cancer.
In EMBO Mol Med on 11 January 2022 by Zhou, Q., Liang, J., et al.
PubMed
Impressive clinical benefit is seen in clinic with PD-1 inhibitors on portion of cancer patients. Yet, there remains an urgent need to develop effective synergizers to expand their clinical application. Tumor-associated macrophage (TAM), a type of M2-polarized macrophage, eliminates or suppresses T-cell-mediated anti-tumor responses. Transforming TAMs into M1 macrophages is an attractive strategy of anti-tumor therapy. Here, we conducted a high-throughput screening and found that Carfilzomib potently drove M2 macrophages to express M1 cytokines, phagocytose tumor cells, and present antigens to T cells. Mechanistically, Carfilzomib elicited unfolded protein response (UPR), activated IRE1α to recruit TRAF2, and activated NF-κB to transcribe genes encoding M1 markers in M2 macrophages. In vivo, Carfilzomib effectively rewired tumor microenvironment through reprogramming TAMs into M1-like macrophages and shrank autochthonous lung cancers in transgenic mouse model. More importantly, Carfilzomib synergized with PD-1 antibody to almost completely regress autochthonous lung cancers. Given the safety profiles of Carfilzomib in clinic, our work suggested a potentially immediate application of combinational treatment with Carfilzomib and PD-1 inhibitors for patients with solid tumors.
-