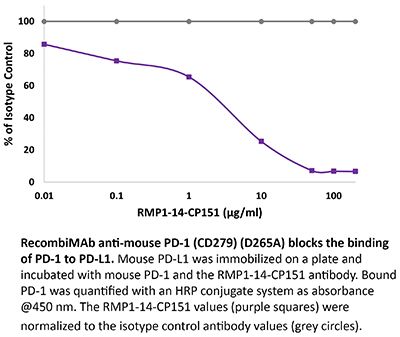
RecombiMAb anti-mouse PD-1 (CD279) (D265A)
(switched from rat IgG2a)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb mouse IgG2a (D265A) isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Mutations | D265A |
| Immunogen | Syrian Hamster BKH cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo blocking of PD-1/PD-L signaling* *Reported for the original rat IgG2a RMP1-14 antibody |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL gel clotting assay |
| Aggregation |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from CHO cell supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_2927525 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Combination of a therapeutic cancer vaccine targeting the endogenous retroviral envelope protein ERVMER34-1 with immune-oncology agents facilitates expansion of neoepitope-specific T cells and promotes tumor control.
In J Immunother Cancer on 13 May 2025 by Maldonado, M. D. M., Gracia-Hernandez, M., et al.
PubMed
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are remnants of retrovirus germline infections that occurred over the course of evolution and constitute between 5% and 8% of the human genome. While ERVs tend to be epigenetically silenced in normal adult human tissues, they are often overexpressed in carcinomas and may represent novel immunotherapeutic targets. This study characterizes the ERV envelope protein ERVMER34-1 as a target for a therapeutic cancer vaccine.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Peptide-Drug Conjugate for Therapeutic Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Breast Cancer.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 March 2025 by Lepland, A., Peranzoni, E., et al.
PubMed
In triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), pro-tumoral macrophages promote metastasis and suppress the immune response. To target these cells, a previously identified CD206 (mannose receptor)-binding peptide, mUNO was engineered to enhance its affinity and proteolytic stability. The new rationally designed peptide, MACTIDE, includes a trypsin inhibitor loop, from the Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor-I. Binding studies to recombinant CD206 revealed a 15-fold lower KD for MACTIDE compared to parental mUNO. Mass spectrometry further demonstrated a 5-fold increase in MACTIDE's half-life in tumor lysates compared to mUNO. Homing studies in TNBC-bearing mice shows that fluorescein (FAM)-MACTIDE precisely targeted CD206+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) upon intravenous, intraperitoneal, and even oral administration, with minimal liver accumulation. MACTIDE was conjugated to Verteporfin, an FDA-approved photosensitizer and YAP/TAZ pathway inhibitor to create the conjugate MACTIDE-V. In the orthotopic 4T1 TNBC mouse model, non-irradiated MACTIDE-V-treated mice exhibited anti-tumoral effects comparable to those treated with irradiated MACTIDE-V, with fewer signs of toxicity, prompting further investigation into the laser-independent activity of the conjugate. In vitro studies using bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages showed that MACTIDE-V excluded YAP from the nucleus, increased phagocytic activity, and upregulated several genes associated with cytotoxic anti-tumoral macrophages. In mouse models of TNBC, MACTIDE-V slowed primary tumor growth, suppressed lung metastases, and increased markers of phagocytosis and antigen presentation in TAM and monocytes, increasing the tumor infiltration of several lymphocyte subsets. MACTIDE-V is proposed as a promising peptide-drug conjugate for modulating macrophage function in breast cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CREB-binding protein/P300 bromodomain inhibition reduces neutrophil accumulation and activates antitumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer.
In JCI Insight on 17 September 2024 by Yuan, X., Hao, X., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) have been shown to promote immunosuppression and tumor progression, and a high TAN frequency predicts poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Dysregulation of CREB-binding protein (CBP)/P300 function has been observed with multiple cancer types. The bromodomain (BRD) of CBP/P300 has been shown to regulate its activity. In this study, we found that IACS-70654, a selective CBP/P300 BRD inhibitor, reduced TANs and inhibited the growth of neutrophil-enriched TNBC models. In the bone marrow, CBP/P300 BRD inhibition reduced the tumor-driven abnormal differentiation and proliferation of neutrophil progenitors. Inhibition of CBP/P300 BRD also stimulated the immune response by inducing an IFN response and MHCI expression in tumor cells and increasing tumor-infiltrated cytotoxic T cells. Moreover, IACS-70654 improved the response of a neutrophil-enriched TNBC model to docetaxel and immune checkpoint blockade. This provides a rationale for combining a CBP/P300 BRD inhibitor with standard-of-care therapies in future clinical trials for neutrophil-enriched TNBC.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Therapeutic Tumor Macrophage Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Through a Peptide-Drug Conjugate
In bioRxiv on 12 August 2024 by Lepland, A., Peranzoni, E., et al.
-