Catalog #CP146
RecombiMAb anti-mouse CTLA-4 (CD152)
Clone
9H10-CP146
Reactivities
Mouse
Product Citations
1
Isotype
Mouse IgG1
(switched from Syrian hamster IgG)
(switched from Syrian hamster IgG)
You may also be interested in:
Product Description
The 9H10-CP146 monoclonal antibody is a chimeric version of the original 9H10 antibody. The variable domain sequences are identical to the original 9H10 but the constant region sequences have been switched from Syrian hamster IgG to mouse IgG1. 9H10-CP146 reacts with mouse CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4) also known as CD152. CTLA-4 is a 33 kDa cell surface receptor encoded by the Ctla4 gene that belongs to the CD28 family of the Ig superfamily. CTLA-4 is expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes. CTLA-4 is structurally similar to the T-cell co-stimulatory protein, CD28, and both molecules bind to the B7 family members B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86). Upon ligand binding, CTLA-4 negatively regulates cell-mediated immune responses. CTLA-4 plays roles in induction and/or maintenance of immunological tolerance, thymocyte development, and regulation of protective immunity. The critical role of CTLA-4 in immune down-regulation has been demonstrated in CTLA-4 deficient mice, which succumb at 3-5 weeks of age due to the development of a lymphoproliferative disease. CTLA-4 is among a group of inhibitory receptors being explored as cancer treatment targets through immune checkpoint blockade. The 9H10 antibody has been shown to promote T cell co-stimulation by blocking CTLA-4 binding to the B7 co-receptors, allowing for CD28 binding.
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus mouse IgG1 isotype control, unknown specificity |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
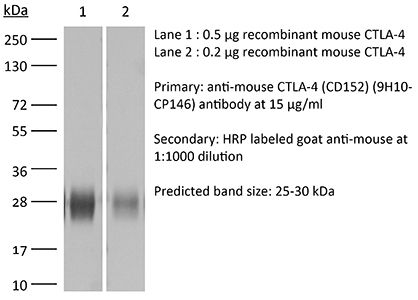
| Immunogen | Mouse CTLA-4-human IgG1 fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CTLA-4 neutralization* in vitro CTLA-4 neutralization* Western blot *Reported for the original Syrian hamster IgG 9H10 antibody |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL gel clotting assay |
| Aggregation |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from CHO cell supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2927521 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
High PD-1 and CTLA-4 expression correlates with host immune suppression in patients and a mouse model infected with Echinococcus multilocularis.
In Parasit Vectors on 25 October 2024 by Sun, T., Yang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE), a fatal disease caused by Echinococcus multilocularis, often affects the liver, with tumor-like growth. However, the mechanism by which E. multilocularis evades host immune surveillance remains unclear.
-
View More