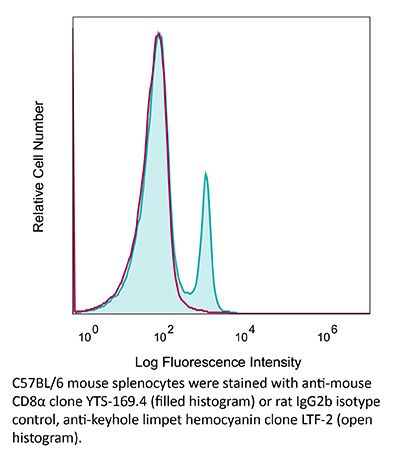
InVivoPlus anti-mouse CD8α
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | CBA mouse thymocytes |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin* |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Aggregation* |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10950145 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Vashist, N., et al (2018). "Influenza-Activated ILC1s Contribute to Antiviral Immunity Partially Influenced by Differential GITR Expression" Front Immunol 9: 505.
PubMed
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) represent diversified subsets of effector cells as well as immune regulators of mucosal immunity and are classified into group 1 ILCs, group 2 ILCs, and group 3 ILCs. Group 1 ILCs encompass natural killer (NK) cells and non-NK ILCs (ILC1s) and mediate their functionality via the rapid production of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. The current knowledge of ILC1s mainly associates them to inflammatory processes. Much less is known about their regulation during infection and their capacity to interact with cells of the adaptive immune system. The present study dissected the role of ILC1s during early influenza A virus infection, thereby revealing their impact on the antiviral response. Exploiting in vitro and in vivo H1N1 infection systems, a cross-talk of ILC1s with cells of the innate and the adaptive immunity was demonstrated, which contributes to anti-influenza immunity. A novel association of ILC1 functionality and the expression of the glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) was observed, which hints toward a so far undescribed role of GITR in regulating ILC1 responsiveness. Overexpression of GITR inhibits IFN-gamma production by ILC1s, whereas partial reduction of GITR expression can reverse this effect, thereby regulating ILC1 functionality. These new insights into ILC1 biology define potential intervention targets to modulate the functional properties of ILC1s, thus contributing toward the development of new immune interventions against influenza.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Triplett, T. A., et al (2018). "Reversal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated cancer immune suppression by systemic kynurenine depletion with a therapeutic enzyme" Nat Biotechnol 36(8): 758-764.
PubMed
Increased tryptophan (Trp) catabolism in the tumor microenvironment (TME) can mediate immune suppression by upregulation of interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) and/or ectopic expression of the predominantly liver-restricted enzyme tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). Whether these effects are due to Trp depletion in the TME or mediated by the accumulation of the IDO1 and/or TDO (hereafter referred to as IDO1/TDO) product kynurenine (Kyn) remains controversial. Here we show that administration of a pharmacologically optimized enzyme (PEGylated kynureninase; hereafter referred to as PEG-KYNase) that degrades Kyn into immunologically inert, nontoxic and readily cleared metabolites inhibits tumor growth. Enzyme treatment was associated with a marked increase in the tumor infiltration and proliferation of polyfunctional CD8(+) lymphocytes. We show that PEG-KYNase administration had substantial therapeutic effects when combined with approved checkpoint inhibitors or with a cancer vaccine for the treatment of large B16-F10 melanoma, 4T1 breast carcinoma or CT26 colon carcinoma tumors. PEG-KYNase mediated prolonged depletion of Kyn in the TME and reversed the modulatory effects of IDO1/TDO upregulation in the TME.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Li, Z., et al (2015). "Pre-treatment of allogeneic bone marrow recipients with the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 transiently enhances hematopoietic chimerism without promoting donor-specific skin allograft tolerance" Transpl Immunol 33(2): 125-129.
PubMed
Hematopoietic chimerism established by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is known to promote donor-specific organ allograft tolerance; however, clinical application is limited by the need for toxic host conditioning and “megadoses” of donor bone marrow cells. A potential solution to this problem has been suggested by the observation that recipient bone marrow mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 promotes chimerism in congenic bone marrow transplantation experiments in mice. Here we report that a single subcutaneous dose of 10mg/kg AMD3100 in recipient C57BL/6 mice was able to enhance hematopoietic chimerism when complete MHC-mismatched BALB/c donor bone marrow cells were transplanted 1h after drug dosing. However, levels of chimerism measured 30days post-transplantation were not sustained when mice were reexamined on day 90 post-transplantation. Moreover, transient chimerism induced by this protocol did not support robust donor-specific skin allograft tolerance. Using the same transient immunosuppression protocol, we confirmed that “megadoses” of donor bone marrow cells could induce durable chimerism associated with donor-specific skin allograft tolerance without AMD3100 pre-treatment. We conclude that in this protocol AMD3100 pretreatment may empty bone marrow niches that become reoccupied by allogeneic donor hematopoietic progenitor cells but not by true long-lived donor hematopoietic stem cells, resulting in short-lived chimerism and failure to support durable donor-specific allograft tolerance.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Burrack, K. S., et al (2015). "Myeloid Cell Arg1 Inhibits Control of Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection by Suppressing Antiviral T Cells" PLoS Pathog 11(10): e1005191.
PubMed
Arthritogenic alphaviruses, including Ross River virus (RRV) and chikungunya virus (CHIKV), are responsible for explosive epidemics involving millions of cases. These mosquito-transmitted viruses cause inflammation and injury in skeletal muscle and joint tissues that results in debilitating pain. We previously showed that arginase 1 (Arg1) was highly expressed in myeloid cells in the infected and inflamed musculoskeletal tissues of RRV- and CHIKV-infected mice, and specific deletion of Arg1 from myeloid cells resulted in enhanced viral control. Here, we show that Arg1, along with other genes associated with suppressive myeloid cells, is induced in PBMCs isolated from CHIKV-infected patients during the acute phase as well as the chronic phase, and that high Arg1 expression levels were associated with high viral loads and disease severity. Depletion of both CD4 and CD8 T cells from RRV-infected Arg1-deficient mice restored viral loads to levels detected in T cell-depleted wild-type mice. Moreover, Arg1-expressing myeloid cells inhibited virus-specific T cells in the inflamed and infected musculoskeletal tissues, but not lymphoid tissues, following RRV infection in mice, including suppression of interferon-gamma and CD69 expression. Collectively, these data enhance our understanding of the immune response following arthritogenic alphavirus infection and suggest that immunosuppressive myeloid cells may contribute to the duration or severity of these debilitating infections.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Carmi, Y., et al (2015). "Allogeneic IgG combined with dendritic cell stimuli induce antitumour T-cell immunity" Nature 521(7550): 99-104.
PubMed
Whereas cancers grow within host tissues and evade host immunity through immune-editing and immunosuppression, tumours are rarely transmissible between individuals. Much like transplanted allogeneic organs, allogeneic tumours are reliably rejected by host T cells, even when the tumour and host share the same major histocompatibility complex alleles, the most potent determinants of transplant rejection. How such tumour-eradicating immunity is initiated remains unknown, although elucidating this process could provide the basis for inducing similar responses against naturally arising tumours. Here we find that allogeneic tumour rejection is initiated in mice by naturally occurring tumour-binding IgG antibodies, which enable dendritic cells (DCs) to internalize tumour antigens and subsequently activate tumour-reactive T cells. We exploited this mechanism to treat autologous and autochthonous tumours successfully. Either systemic administration of DCs loaded with allogeneic-IgG-coated tumour cells or intratumoral injection of allogeneic IgG in combination with DC stimuli induced potent T-cell-mediated antitumour immune responses, resulting in tumour eradication in mouse models of melanoma, pancreas, lung and breast cancer. Moreover, this strategy led to eradication of distant tumours and metastases, as well as the injected primary tumours. To assess the clinical relevance of these findings, we studied antibodies and cells from patients with lung cancer. T cells from these patients responded vigorously to autologous tumour antigens after culture with allogeneic-IgG-loaded DCs, recapitulating our findings in mice. These results reveal that tumour-binding allogeneic IgG can induce powerful antitumour immunity that can be exploited for cancer immunotherapy.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Wensveen, F. M., et al (2015). "NK cells link obesity-induced adipose stress to inflammation and insulin resistance" Nat Immunol 16(4): 376-385.
PubMed
An important cause of obesity-induced insulin resistance is chronic systemic inflammation originating in visceral adipose tissue (VAT). VAT inflammation is associated with the accumulation of proinflammatory macrophages in adipose tissue, but the immunological signals that trigger their accumulation remain unknown. We found that a phenotypically distinct population of tissue-resident natural killer (NK) cells represented a crucial link between obesity-induced adipose stress and VAT inflammation. Obesity drove the upregulation of ligands of the NK cell-activating receptor NCR1 on adipocytes; this stimulated NK cell proliferation and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production, which in turn triggered the differentiation of proinflammatory macrophages and promoted insulin resistance. Deficiency of NK cells, NCR1 or IFN-gamma prevented the accumulation of proinflammatory macrophages in VAT and greatly ameliorated insulin sensitivity. Thus NK cells are key regulators of macrophage polarization and insulin resistance in response to obesity-induced adipocyte stress.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Krupnick, A. S., et al (2014). "Central memory CD8+ T lymphocytes mediate lung allograft acceptance" J Clin Invest 124(3): 1130-1143.
PubMed
Memory T lymphocytes are commonly viewed as a major barrier for long-term survival of organ allografts and are thought to accelerate rejection responses due to their rapid infiltration into allografts, low threshold for activation, and ability to produce inflammatory mediators. Because memory T cells are usually associated with rejection, preclinical protocols have been developed to target this population in transplant recipients. Here, using a murine model, we found that costimulatory blockade-mediated lung allograft acceptance depended on the rapid infiltration of the graft by central memory CD8+ T cells (CD44(hi)CD62L(hi)CCR7+). Chemokine receptor signaling and alloantigen recognition were required for trafficking of these memory T cells to lung allografts. Intravital 2-photon imaging revealed that CCR7 expression on CD8+ T cells was critical for formation of stable synapses with antigen-presenting cells, resulting in IFN-gamma production, which induced NO and downregulated alloimmune responses. Thus, we describe a critical role for CD8+ central memory T cells in lung allograft acceptance and highlight the need for tailored approaches for tolerance induction in the lung.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Pastille, E., et al (2014). "Transient ablation of regulatory T cells improves antitumor immunity in colitis-associated colon cancer" Cancer Res 74(16): 4258-4269.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Treg) are supportive to cancer development in most tissues, but their role in colitis-associated colon cancer (CAC) remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) Treg in a mouse model of CAC and in patients with colon cancer. These Treg were increased strongly in number in a mouse model of CAC and in the peripheral blood of patients with colon cancer, exhibiting an activated phenotype as defined by elevated expression of GARP, CD103, CTLA-4, and IL10, along with an increased suppressive effect on the proliferation and Th1 cytokine expression of CD4(+)CD25(-) responder T cells ex vivo. Transient ablation of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) Treg during tumor development in the CAC model suppressed tumor outgrowth and distribution, accompanied by an increased number of CD8(+)IFNgamma/granzyme B-producing effector T cells. Conversely, inactivation of IL10 in Treg did not elevate the antitumor response but instead further boosted tumor development. Our results establish a tumor-promoting function for Treg during CAC formation, but they also suggest that a selective, transient ablation of Treg can evoke antitumor responses, with implications for immunotherapeutic interventions in patients with CAC.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Dai, M., et al (2013). "Long-lasting complete regression of established mouse tumors by counteracting Th2 inflammation" J Immunother 36(4): 248-257.
PubMed
40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.”}” data-sheets-userformat=”{“2″:14851,”3”:{“1″:0},”4”:{“1″:2,”2″:16777215},”12″:0,”14”:{“1″:2,”2″:1521491},”15″:”Roboto, sans-serif”,”16″:12}”>Mice with intraperitoneal ID8 ovarian carcinoma or subcutaneous SW1 melanoma were injected with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to CD137PD-1CTLA4 7-15 days after tumor initiation. Survival of mice with ID8 tumors tripled and >40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Bivas-Benita, M., et al (2013). "Airway CD8(+) T cells induced by pulmonary DNA immunization mediate protective anti-viral immunity" Mucosal Immunol 6(1): 156-166.
PubMed
Vaccination strategies for protection against a number of respiratory pathogens must induce T-cell populations in both the pulmonary airways and peripheral lymphoid organs. In this study, we show that pulmonary immunization using plasmid DNA formulated with the polymer polyethyleneimine (PEI-DNA) induced antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells in the airways that persisted long after antigen local clearance. The persistence of the cells was not mediated by local lymphocyte proliferation or persistent antigen presentation within the lung or airways. These vaccine-induced CD8(+) T cells effectively mediated protective immunity against respiratory challenges with vaccinia virus and influenza virus. Moreover, this protection was not dependent upon the recruitment of T cells from peripheral sites. These findings demonstrate that pulmonary immunization with PEI-DNA is an efficient approach for inducing robust pulmonary CD8(+) T-cell populations that are effective at protecting against respiratory pathogens.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Sledzinska, A., et al (2013). "TGF-beta signalling is required for CD4(+) T cell homeostasis but dispensable for regulatory T cell function" PLoS Biol 11(10): e1001674.
PubMed
TGF-beta is widely held to be critical for the maintenance and function of regulatory T (T(reg)) cells and thus peripheral tolerance. This is highlighted by constitutive ablation of TGF-beta receptor (TR) during thymic development in mice, which leads to a lethal autoimmune syndrome. Here we describe that TGF-beta-driven peripheral tolerance is not regulated by TGF-beta signalling on mature CD4(+) T cells. Inducible TR2 ablation specifically on CD4(+) T cells did not result in a lethal autoinflammation. Transfer of these TR2-deficient CD4(+) T cells to lymphopenic recipients resulted in colitis, but not overt autoimmunity. In contrast, thymic ablation of TR2 in combination with lymphopenia led to lethal multi-organ inflammation. Interestingly, deletion of TR2 on mature CD4(+) T cells does not result in the collapse of the T(reg) cell population as observed in constitutive models. Instead, a pronounced enlargement of both regulatory and effector memory T cell pools was observed. This expansion is cell-intrinsic and seems to be caused by increased T cell receptor sensitivity independently of common gamma chain-dependent cytokine signals. The expression of Foxp3 and other regulatory T cells markers was not dependent on TGF-beta signalling and the TR2-deficient T(reg) cells retained their suppressive function both in vitro and in vivo. In summary, absence of TGF-beta signalling on mature CD4(+) T cells is not responsible for breakdown of peripheral tolerance, but rather controls homeostasis of mature T cells in adult mice.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Krieg, C., et al (2010). "Improved IL-2 immunotherapy by selective stimulation of IL-2 receptors on lymphocytes and endothelial cells" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(26): 11906-11911.
PubMed
IL-2 immunotherapy is an attractive treatment option for certain metastatic cancers. However, administration of IL-2 to patients can lead, by ill-defined mechanisms, to toxic adverse effects including severe pulmonary edema. Here, we show that IL-2-induced pulmonary edema is caused by direct interaction of IL-2 with functional IL-2 receptors (IL-2R) on lung endothelial cells in vivo. Treatment of mice with high-dose IL-2 led to efficient expansion of effector immune cells expressing high levels of IL-2Rbetagamma, including CD8(+) T cells and natural killer cells, which resulted in a considerable antitumor response against s.c. and pulmonary B16 melanoma nodules. However, high-dose IL-2 treatment also affected immune cell lineage marker-negative CD31(+) pulmonary endothelial cells via binding to functional alphabetagamma IL-2Rs, expressed at low to intermediate levels on these cells, thus causing pulmonary edema. Notably, IL-2-mediated pulmonary edema was abrogated by a blocking antibody to IL-2Ralpha (CD25), genetic disruption of CD25, or the use of IL-2Rbetagamma-directed IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes, thereby interfering with IL-2 binding to IL-2Ralphabetagamma(+) pulmonary endothelial cells. Moreover, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes led to vigorous activation of IL-2Rbetagamma(+) effector immune cells, which generated a dramatic antitumor response. Thus, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes might improve current strategies of IL-2-based tumor immunotherapy.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Shariff, H., et al (2010). "Intermittent antibody-based combination therapy removes alloantibodies and achieves indefinite heart transplant survival in presensitized recipients" Transplantation 90(3): 270-278.
PubMed
BACKGROUND: It is well established that primed/memory T cells play a critical role in heart transplant rejection. This contributes to the challenges faced in the transplant clinic because current treatments that are efficient in controlling naive T cell alloresponses have limited efficacy on primed T cell responders. METHODS: Fully MHC-mismatched heart transplantation was performed from BALB/c to C57BL/6 mice presensitized with BALB/c splenocytes 14 days pretransplantation. A combination therapy comprising CD70-, CD154-, and CD8-specific antibodies (Abs) was administered at day 0 and 4 posttransplantation with rapamycin on days 0 to 4. RESULTS: The Ab combination therapy extended heart transplant survival in presensitized recipients from median survival time 8 days (MST) to MST 78 days. A decrease in the number of splenic interferon-gamma-secreting cells measured by ELISpot assay was seen in the treated group compared with the untreated controls. However, graft-infiltrating CD8+ and CD4+ T cells persisted despite treatment and the number of intragraft CD4+ T cells increased at day 30 posttransplantation. When an additional “rescue therapy” comprising the same Abs was readministered at days 30, 60, and 90 posttransplantation, T cell infiltration was reduced and indefinite graft survival was observed. Furthermore, rescue therapy resulted in gradual decrease in titer and, by day 90 posttransplantation, the complete loss of the preexisting, donor-specific Abs. CONCLUSION: We conclude that our Ab combination therapy extends allograft survival in presensitized recipients. When combined with intermittent Ab-mediated rescue therapy, this results in indefinite allograft survival and a loss of the preexisting, donor-specific Abs from the circulation.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Kish, D. D., et al (2009). "CD8 T cells producing IL-17 and IFN-gamma initiate the innate immune response required for responses to antigen skin challenge" J Immunol 182(10): 5949-5959.
PubMed
Effector CD8 T cell recruitment into the skin in response to Ag challenge requires prior CXCL1/KC-directed neutrophil infiltration. Mechanisms inducing CXCL1 production and the dynamics of neutrophil-CD8 T cell interactions during elicitation of Ag-specific responses in the skin were investigated. CXCL1 and CXCL2/MIP-2 were produced within 3-6 h of Ag challenge at 10-fold higher levels in skin challenge sites of Ag-sensitized vs nonsensitized mice. In the challenge sites of sensitized mice this production decreased at 6-9 h postchallenge to near the levels observed in skin challenge sites of nonsensitized mice but rose to a second peak 12 h after challenge. The elevated early neutrophil chemoattractant production at 3-6 h after skin challenge of sensitized animals required both IFN-gamma and IL-17, produced by distinct populations of Ag-primed CD8 T cells in response to Ag challenge. Although induced by the Ag-primed CD8 T cells, the early CXCL1 and CXCL2 production was accompanied by neutrophil but not CD8 T cell infiltration into the skin Ag challenge site. Infiltration of the CD8 T cells into the challenge site was not observed until 18-24 h after challenge. These results demonstrate an intricate series of early interactions between Ag-specific and innate immune components that regulate the sequential infiltration of neutrophils and then effector T cells into the skin to mediate an immune response.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Therapeutic inhibition of USP7 promotes antitumor immune responses.
In J Immunother Cancer on 25 September 2025 by Muchowicz, A., Głuchowska, K. M., et al.
PubMed
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 7 (USP7) is a deubiquitinating enzyme that removes ubiquitin from specific protein substrates to modify their degradation rates thereby regulating crucial cellular processes integral to cancer. Conspicuously, overexpression of USP7 is strongly associated with the progression and poor prognosis in various cancers. Therefore, the design of potent and selective USP7 inhibitors poses an attractive therapeutic approach. The mechanism of action of USP7 inhibitors in cancer cells relies on MDM2 depletion and the restoration of p53.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Lactylation-driven MVP upregulation boosts immunotherapy resistance by inhibiting PD-L1 degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In J Immunother Cancer on 21 September 2025 by Liu, S., Pan, Y., et al.
PubMed
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent malignancy and the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have emerged as first-line therapies for advanced HCC, substantially improving clinical outcomes. However, resistance to ICIs remains a major therapeutic challenge. Lactylation, a recently identified post-translational modification, has been implicated in tumor progression, although its role in ICIs resistance in HCC remains unclear.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Overcoming immunotherapy resistance in bladder cancer with a novel antibody-drug conjugate RC48.
In J Immunother Cancer on 11 August 2025 by Xiao, J., Liu, J., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown limited response rates in bladder cancer. RC48-antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) shows potential for combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors. This study aimed to elucidate RC48-ADC's mechanism in sensitizing tumors to immunotherapy and identify optimal combination strategies.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Oncogenic activation of SMYD3-SHCBP1 promotes breast cancer development and is coupled with resistance to immune therapy.
In Cell Death Dis on 29 March 2025 by Mo, L., Deng, M., et al.
PubMed
Breast cancer initiation and progression are driven by various oncogenic factors and their effects on the surrounding microenvironments. Through integrative analysis of ChIP-sequencing and RNA-sequencing with fast proliferating mammary epithelial cells from pregnant Brca1MKO and wild type (WT) mice, we found that elevated Smyd3-Shcbp1 signaling is featured with activation of the Ras-MAPK pathway and increased transcription activity in both premalignant mammary epithelium and tumor cells. Smyd3-Shcbp1 signaling shapes the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment (TIME) and is associated with immune therapy resistance to PD1 antibody treatment. Trametinib, a potent inhibitor of MEK/MAPK, could reverse the expression of Smyd3 and Shcbp1 in both Brca1 mutant and WT tumor bearing mice. We further demonstrated that the combinatory treatment of trametinib together with PD1 antibody enhances the function of effector T cells, sensitizing tumors with elevated Smyd3 and Shcbp1 signaling to αPD1 treatment. This study advances the understanding of breast tumor progression and provides a new selective strategy for breast cancer patients.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lipid nanoparticles deliver DNA-encoded biologics and induce potent protective immunity.
In Mol Cancer on 13 January 2025 by Chai, D., Wang, J., et al.
PubMed
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for mRNA delivery have advanced significantly, but LNP-mediated DNA delivery still faces clinical challenges. This study compared various LNP formulations for delivering DNA-encoded biologics, assessing their expression efficacy and the protective immunity generated by LNP-encapsulated DNA in different models. The LNP formulation used in Moderna's Spikevax mRNA vaccine (LNP-M) demonstrated a stable nanoparticle structure, high expression efficiency, and low toxicity. Notably, a DNA vaccine encoding the spike protein, delivered via LNP-M, induced stronger antigen-specific antibody and T cell immune responses compared to electroporation. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis revealed that the LNP-M/pSpike vaccine enhanced CD80 activation signaling in CD8+ T cells, NK cells, macrophages, and DCs, while reducing the immunosuppressive signals. The enrichment of TCR and BCR by LNP-M/pSpike suggested an increase in immune response specificity and diversity. Additionally, LNP-M effectively delivered DNA-encoded antigens, such as mouse PD-L1 and p53R172H, or monoclonal antibodies targeting mouse PD1 and human p53R282W. This approach inhibited tumor growth or metastasis in several mouse models. The long-term anti-tumor effects of LNP-M-delivered anti-p53R282W antibody relied on memory CD8+ T cell responses and enhanced MHC-I signaling from APCs to CD8+ T cells. These results highlight LNP-M as a promising and effective platform for delivering DNA-based vaccines and cancer immunotherapies.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
FAP-targeted radioligand therapy with 68Ga/177Lu-DOTA-2P(FAPI)2 enhance immunogenicity and synergize with PD-L1 inhibitors for improved antitumor efficacy.
In J Immunother Cancer on 11 January 2025 by Chen, J., Zhou, Y., et al.
PubMed
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-targeted radioligand therapy, with immunomodulatory effects, has shown efficacy in both preclinical and clinical studies. We recently reported on a novel dimeric FAP-targeting radiopharmaceutical, 68Ga/177Lu-DOTA-2P(FAPI)2, which demonstrated increased tumor uptake and prolonged retention in various cancers. However, further exploration is required to understand the therapeutic efficacy and underlying mechanisms of combining 68Ga/177Lu-DOTA-2P(FAPI)2 radioligand therapy with PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
An Engineered Self-biomineralized Oncolytic Adenovirus Induces Effective Antitumor Immunity and Synergizes With Immune Checkpoint Blockade.
In Cancer Immunol Res on 4 November 2024 by Wang, S., Yang, X., et al.
PubMed
Oncolytic adenoviruses (oADV) are promising cancer treatment agents. However, in vivo hepatic sequestration and the host immunologic response against the agents limit the therapeutic potential of oADVs. In this study, we present a combined method with a rational design for improving oADV infection efficiency, immunogenicity, and treatment efficacy by self-biomineralization. We integrated the biomimetic nucleopeptide W6p into the capsid of oADV using reverse genetics, allowing calcium phosphate mineralization to be biologically induced on the surface of oADV under physiologic conditions, resulting in a mineral exterior. This self-biomineralized, modified oADV (oADV-W6-CaP) enhanced infection efficiency and therapeutic efficacy in coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR)-negative cancer cells wherein protecting them against neutralization by preexisting neutralizing antibodies. In subcutaneous mouse tumor models, systemic injection of oADV-W6-CaP demonstrated improved antitumor effectiveness, which was associated with increased T-cell infiltration and CD8+ T-cell activation. In addition, the anticancer immune response elicited by oADV-W6-CaP was dependent on CD8+ T cells, which mediated long-term immunologic memory and systemic antitumor immunity against the same tumor. Finally, the addition of PD1 or CD47 inhibition boosted the anticancer effects of oADV-W6-CaP and increased the rate of complete tumor clearance in tumor-bearing animals. The self-biomineralized oADV shifted the suppressive tumor microenvironment from a "cold" to "hot" state and synergized with immune checkpoint blockade to exert outstanding tumoricidal effects, demonstrating promising potential for cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The Oncolytic virus VT1092M and an Anti-PD-L1 antibody synergize to induce systemic antitumor immunity in a murine bilateral tumor model.
In Transl Oncol on 1 August 2024 by Zhu, W., Shao, M., et al.
PubMed
This study investigated the synergistic potential of an oncolytic herpes simplex virus armed with interleukin 12 (VT1092M) in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors for enhancing antitumor responses. The potential of this combination treatment to induce systemic antitumor immunity was assessed using bilateral subcutaneous tumor and tumor re-challenge mouse models. The antitumor efficacy of various OV and ICI treatment combinations and the underlying mechanisms were explored through diverse analytical techniques, including flow cytometry and RNA sequencing. Using VT1092M, either alone or in combination with an anti-PD-L1 antibody, significantly reduced the sizes of both the injected and untreated abscopal tumors in a bilateral tumor mouse model. The combination therapy demonstrated superior antitumor efficacy to the other treatment conditions tested, which was accompanied by an increase in T cell numbers and CD8+T cell activation. Results from the survival and tumor re-challenge experiments showed that the combination therapy elicited long-term, tumor-specific immune responses, which were associated with tumor clearance and prolonged survival. Immune cell depletion assays identified CD8+T cells as the crucial mediators of systemic antitumor immunity during combination therapy. In conclusion, the combination of VT1092M and PD-L1 blockade emerged as a potent inducer of antitumor immune responses, surpassing the efficacy of each monotherapy. This synergistic approach holds promise for achieving robust and sustained antitumor immunity, with potential implications for preventing tumor metastasis in patients with cancer.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Pharmacology
Radiofrequency radiation reshapes tumor immune microenvironment into antitumor phenotype in pulmonary metastatic melanoma by inducing active transformation of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T and NK cells.
In Acta Pharmacol Sin on 1 July 2024 by Jiao, J. Z., Zhang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Immunosuppression by the tumor microenvironment is a pivotal factor contributing to tumor progression and immunotherapy resistance. Priming the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) has emerged as a promising strategy for improving the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. In this study we investigated the effects of noninvasive radiofrequency radiation (RFR) exposure on tumor progression and TIME phenotype, as well as the antitumor potential of PD-1 blockage in a model of pulmonary metastatic melanoma (PMM). Mouse model of PMM was established by tail vein injection of B16F10 cells. From day 3 after injection, the mice were exposed to RFR at an average specific absorption rate of 9.7 W/kg for 1 h per day for 14 days. After RFR exposure, lung tissues were harvested and RNAs were extracted for transcriptome sequencing; PMM-infiltrating immune cells were isolated for single-cell RNA-seq analysis. We showed that RFR exposure significantly impeded PMM progression accompanied by remodeled TIME of PMM via altering the proportion and transcription profile of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. RFR exposure increased the activation and cytotoxicity signatures of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells, particularly in the early activation subset with upregulated genes associated with T cell cytotoxicity. The PD-1 checkpoint pathway was upregulated by RFR exposure in CD8+ T cells. RFR exposure also augmented NK cell subsets with increased cytotoxic characteristics in PMM. RFR exposure enhanced the effector function of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and NK cells, evidenced by increased expression of cytotoxic molecules. RFR-induced inhibition of PMM growth was mediated by RFR-activated CD8+ T cells and NK cells. We conclude that noninvasive RFR exposure induces antitumor remodeling of the TIME, leading to inhibition of tumor progression, which provides a promising novel strategy for TIME priming and potential combination with cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Fasting-Mimicking Diet Inhibits Autophagy and Synergizes with Chemotherapy to Promote T-Cell-Dependent Leukemia-Free Survival.
In Cancers (Basel) on 16 December 2023 by Buono, R., Tucci, J., et al.
PubMed
Fasting mimicking diets (FMDs) are effective in the treatment of many solid tumors in mouse models, but their effect on hematologic malignancies is poorly understood, particularly in combination with standard therapies. Here we show that cycles of a 3-day FMD given to high-fat-diet-fed mice once a week increased the efficacy of vincristine to improve survival from BCR-ABL B acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). In mice fed a standard diet, FMD cycles in combination with vincristine promoted cancer-free survival. RNA seq and protein assays revealed a vincristine-dependent decrease in the expression of multiple autophagy markers, which was exacerbated by the fasting/FMD conditions. The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine could substitute for fasting/FMD to promote cancer-free survival in combination with vincristine. In vitro, targeted inhibition of autophagy genes ULK1 and ATG9a strongly potentiated vincristine's toxicity. Moreover, anti-CD8 antibodies reversed the effects of vincristine plus fasting/FMD in promoting leukemia-free survival in mice, indicating a central role of the immune system in this response. Thus, the inhibition of autophagy and enhancement of immune responses appear to be mediators of the fasting/FMD-dependent cancer-free survival in ALL mice.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
HRS mediates tumor immune evasion by regulating proteostasis-associated interferon pathway activation.
In Cell Rep on 28 November 2023 by Zhang, W., Yang, J., et al.
PubMed
By sorting receptor tyrosine kinases into endolysosomes, the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) are thought to attenuate oncogenic signaling in tumor cells. Paradoxically, ESCRT members are upregulated in tumors. Here, we show that disruption of hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS), a pivotal ESCRT component, inhibited tumor growth by promoting CD8+ T cell infiltration in melanoma and colon cancer mouse models. HRS ablation led to misfolded protein accumulation and triggered endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, resulting in the activation of the type I interferon pathway in an inositol-requiring enzyme-1α (IRE1α)/X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1)-dependent manner. HRS was upregulated in tumor cells with high tumor mutational burden (TMB). HRS expression associates with the response to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade therapy in melanoma patients with high TMB tumors. HRS ablation sensitized anti-PD-1 treatment in mouse melanoma models. Our study shows a mechanism by which tumor cells with high TMB evade immune surveillance and suggests HRS as a promising target to improve immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
Ablation of ERO1A induces lethal endoplasmic reticulum stress responses and immunogenic cell death to activate anti-tumor immunity.
In Cell Rep Med on 17 October 2023 by Liu, L., Li, S., et al.
PubMed
Immunophenotyping of the tumor microenvironment (TME) is essential for enhancing immunotherapy efficacy. However, strategies for characterizing the TME exhibit significant heterogeneity. Here, we show that endoplasmic reticular oxidoreductase-1α (ERO1A) mediates an immune-suppressive TME and attenuates the response to PD-1 blockade. Ablation of ERO1A in tumor cells substantially incites anti-tumor T cell immunity and promotes the efficacy of aPD-1 in therapeutic models. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analyses confirm that ERO1A correlates with immunosuppression and dysfunction of CD8+ T cells along anti-PD-1 treatment. In human lung cancer, high ERO1A expression is associated with a higher risk of recurrence following neoadjuvant immunotherapy. Mechanistically, ERO1A ablation impairs the balance between IRE1α and PERK signaling activities and induces lethal unfolded protein responses in tumor cells undergoing endoplasmic reticulum stress, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity via immunogenic cell death. These findings reveal how tumor ERO1A induces immunosuppression, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Taxanes trigger cancer cell killing in vivo by inducing non-canonical T cell cytotoxicity.
In Cancer Cell on 12 June 2023 by Vennin, C., Cattaneo, C. M., et al.
PubMed
Although treatment with taxanes does not always lead to clinical benefit, all patients are at risk of their detrimental side effects such as peripheral neuropathy. Understanding the in vivo mode of action of taxanes can help design improved treatment regimens. Here, we demonstrate that in vivo, taxanes directly trigger T cells to selectively kill cancer cells in a non-canonical, T cell receptor-independent manner. Mechanistically, taxanes induce T cells to release cytotoxic extracellular vesicles, which lead to apoptosis specifically in tumor cells while leaving healthy epithelial cells intact. We exploit these findings to develop an effective therapeutic approach, based on transfer of T cells pre-treated with taxanes ex vivo, thereby avoiding toxicity of systemic treatment. Our study reveals a different in vivo mode of action of one of the most commonly used chemotherapies, and opens avenues to harness T cell-dependent anti-tumor effects of taxanes while avoiding systemic toxicity.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
Aurora A kinase inhibition compromises its antitumor efficacy by elevating PD-L1 expression.
In J Clin Invest on 1 May 2023 by Wang, X., Huang, J., et al.
PubMed
Aurora A plays a critical role in G2/M transition and mitosis, making it an attractive target for cancer treatment. Aurora A inhibitors showed remarkable antitumor effects in preclinical studies, but unsatisfactory outcomes in clinical trials have greatly limited their development. In this study, the Aurora A inhibitor alisertib upregulated programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in a panel of tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. Upregulation of the checkpoint protein PD-L1 reduced antitumor immunity in immune-competent mice, paradoxically inhibiting the antitumor effects of alisertib. Mechanistically, Aurora A directly bound to and phosphorylated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), suppressing PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. Aurora A inhibition by alisertib activated the cGAS/stimulator of IFN genes (STING)/NF-κB pathway and promoted PD-L1 expression. Combining alisertib with anti-PD-L1 antibody improved antitumor immunity and enhanced the antitumor effects of alisertib in immune-competent mice. Our results, which reveal the immunomodulatory functions of Aurora A inhibitors and provide a plausible explanation for the poor clinical outcomes with their use, offer a potential approach to improve the antitumor efficacy of these inhibitors.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus molossinus (Japanese wild mouse)
EHBP1L1 Drives Immune Evasion in Renal Cell Carcinoma through Binding and Stabilizing JAK1.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 April 2023 by Pan, Y., Shu, G., et al.
PubMed
High lymphocyte infiltration and immunosuppression characterize the tumor microenvironment (TME) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). There is an urgent need to elucidate how tumor cells escape the immune attack and to develop novel therapeutic targets to enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) in RCC. Overactivated IFN-γ-induced JAK/STAT signaling involves in such TME, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, EH domain-binding protein 1-like protein 1 (EHBP1L1) is identified as a crucial mediator of IFN-γ/JAK1/STAT1/PD-L1 signaling in RCC. EHBP1L1 is highly expressed in RCC, and high EHBP1L1 expression levels are correlated with poor prognosis and resistance to ICB. EHBP1L1 depletion significantly inhibits tumor growth, which is attributed to enhanced CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Mechanistically, EHBP1L1 interacts with and stabilizes JAK1. By competing with SOCS1, EHBP1L1 protects JAK1 from proteasomal degradation, which leads to elevated JAK1 protein levels and JAK1/STAT1/PD-L1 signaling activity, thereby forming an immunosuppressive TME. Furthermore, the combination of EHBP1L1 inhibition and ICB reprograms the immunosuppressive TME and prevents tumor immune evasion, thus significantly reinforcing the therapeutic efficacy of ICB in RCC patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models. These findings reveal the vital role of EHBP1L1 in immune evasion in RCC, which may be a potential complement for ICB therapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
BCAT2 Shapes a Noninflamed Tumor Microenvironment and Induces Resistance to Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immunotherapy by Negatively Regulating Proinflammatory Chemokines and Anticancer Immunity.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 March 2023 by Cai, Z., Chen, J., et al.
PubMed
To improve response rate of monotherapy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), it is necessary to find an emerging target in combination therapy. Through analyzing tumor microenvironment (TME)-related indicators, it is validated that BCAT2 shapes a noninflamed TME in bladder cancer. The outcomes of multiomics indicate that BCAT2 has an inhibitory effect on cytotoxic lymphocyte recruitment by restraining activities of proinflammatory cytokine/chemokine-related pathways and T-cell-chemotaxis pathway. Immunoassays reveal that secretion of CD8+ T-cell-related chemokines keeps a robust negative correlation with BCAT2, generating a decreasing tendency of CD8+ T cells around BCAT2+ tumor cells from far to near. Cotreatment of BCAT2 deficiency and anti-PD-1 antibody has a synergistic effect in vivo, implying the potential of BCAT2 in combination therapy. Moreover, the value of BCAT2 in predicting efficacy of immunotherapy is validated in multiple immunotherapy cohorts. Together, as a key molecule in TME, BCAT2 is an emerging target in combination with ICB and a biomarker of guiding precision therapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
Tumor necroptosis-mediated shedding of cell surface proteins promotes metastasis of breast cancer by suppressing anti-tumor immunity.
In Breast Cancer Res on 26 January 2023 by Liu, Z., Choksi, S., et al.
PubMed
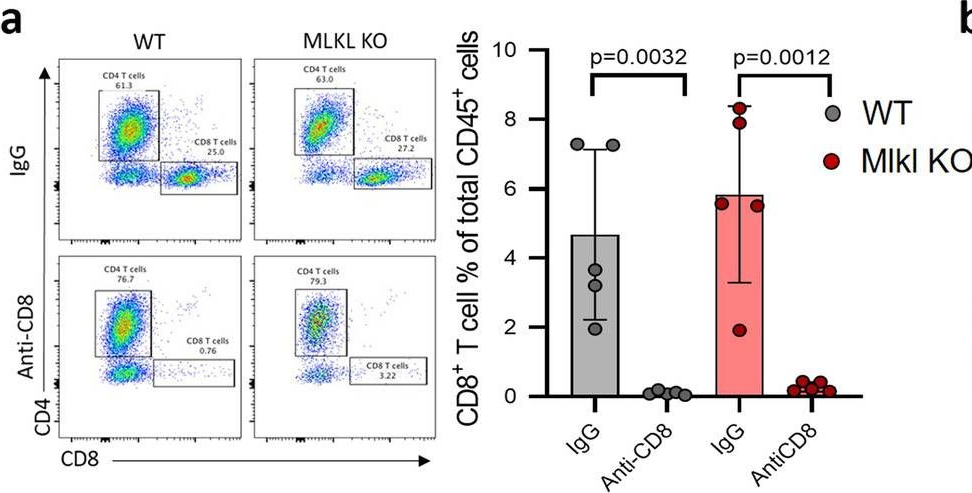
Necroptosis is a form of regulated necrosis and is executed by MLKL when MLKL is engaged in triggering the rupture of cell plasma membrane. MLKL activation also leads to the protease, ADAMs-mediated ectodomain shedding of cell surface proteins of necroptotic cells. Tumor necroptosis often happens in advanced solid tumors, and blocking necroptosis by MLKL deletion in breast cancer dramatically reduces tumor metastasis. It has been suggested that tumor necroptosis affects tumor progression through modulating the tumor microenvironment. However, the exact mechanism by which tumor necroptosis promotes tumor metastasis remains elusive. Here, we report that the ectodomain shedding of cell surface proteins of necroptotic cells is critical for the promoting effect of tumor necroptosis in tumor metastasis through inhibiting the anti-tumor activity of T cells. We found that blocking tumor necroptosis by MLKL deletion led to the dramatic reduction of tumor metastasis and significantly elevated anti-tumor activity of tumor-infiltrating and peripheral blood T cells. Importantly, the increased anti-tumor activity of T cells is a key cause for the reduced metastasis as the depletion of CD8+ T cells completely restored the level of metastasis in the Mlkl KO mice. Interestingly, the levels of some soluble cell surface proteins including sE-cadherin that are known to promote metastasis are also dramatically reduced in MLKL null tumors/mice. Administration of ADAMs pan inhibitor reduces the levels of soluble cell surface proteins in WT tumors/mice and leads to the dramatic decrease in metastasis. Finally, we showed the sE-cadherin/KLRG1 inhibitory receptor is the major pathway for necroptosis-mediated suppression of the anti-tumor activity of T cells and the promotion of metastasis. Hence, our study reveals a novel mechanism of tumor necroptosis-mediated promotion of metastasis and suggests that tumor necroptosis and necroptosis-activated ADAMs are potential targets for controlling metastasis.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Three-dimensional Imaging Reveals Immune-driven Tumor-associated High Endothelial Venules as a Key Correlate of Tumor Rejection Following Depletion of Regulatory T Cells.
In Cancer Res Commun on 15 December 2022 by Milutinovic, S., Abe, J., et al.
PubMed
High endothelial venules (HEV) are specialized post capillary venules that recruit naïve T cells and B cells into secondary lymphoid organs (SLO) such as lymph nodes (LN). Expansion of HEV networks in SLOs occurs following immune activation to support development of an effective immune response. In this study, we used a carcinogen-induced model of fibrosarcoma to examine HEV remodeling after depletion of regulatory T cells (Treg). We used light sheet fluorescence microscopy imaging to visualize entire HEV networks, subsequently applying computational tools to enable topological mapping and extraction of numerical descriptors of the networks. While these analyses revealed profound cancer- and immune-driven alterations to HEV networks within LNs, these changes did not identify successful responses to treatment. The presence of HEV networks within tumors did however clearly distinguish responders from nonresponders. Finally, we show that a successful treatment response is dependent on coupling tumor-associated HEV (TA-HEV) development to T-cell activation implying that T-cell activation acts as the trigger for development of TA-HEVs which subsequently serve to amplify the immune response by facilitating extravasation of T cells into the tumor mass.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
PRDM1/BLIMP1 induces cancer immune evasion by modulating the USP22-SPI1-PD-L1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
In Nat Commun on 12 December 2022 by Li, Q., Zhang, L., et al.
PubMed
Programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blockade have achieved some efficacy but only in a fraction of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) binds to its receptor PD1 on T cells to dampen antigen-tumor immune responses. However, the mechanisms underlying PD-L1 regulation are not fully elucidated. Herein, we identify that tumoral Prdm1 overexpression inhibits cell growth in immune-deficient mouse models. Further, tumoral Prdm1 overexpression upregulates PD-L1 levels, dampening anti-tumor immunity in vivo, and neutralizes the anti-tumor efficacy of Prdm1 overexpression in immune-competent mouse models. Mechanistically, PRDM1 enhances USP22 transcription, thus reducing SPI1 protein degradation through deubiquitination, which enhances PD-L1 transcription. Functionally, PD-1 mAb treatment reinforces the efficacy of Prdm1-overexpressing HCC immune-competent mouse models. Collectively, we demonstrate that the PRDM1-USP22-SPI1 axis regulates PD-L1 levels, resulting in infiltrated CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Furthermore, PRDM1 overexpression combined with PD-(L)1 mAb treatment provides a therapeutic strategy for HCC treatment.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Re-purposing the pro-senescence properties of doxorubicin to introduce immunotherapy in breast cancer brain metastasis.
In Cell Rep Med on 15 November 2022 by Uceda-Castro, R., Margarido, A. S., et al.
PubMed
An increasing number of breast cancer patients develop brain metastases (BM). Standard-of-care treatments are largely inefficient, and breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) patients are considered untreatable. Immunotherapies are not successfully employed in BCBM, in part because breast cancer is a "cold" tumor and also because the brain tissue has a unique immune landscape. Here, we generate and characterize immunocompetent models of BCBM derived from PyMT and Neu mammary tumors to test how harnessing the pro-senescence properties of doxorubicin can be used to prime the specific immune BCBM microenvironment. We reveal that BCBM senescent cells, induced by doxorubicin, trigger the recruitment of PD1-expressing T cells to the brain. Importantly, we demonstrate that induction of senescence with doxorubicin improves the efficacy of immunotherapy with anti-PD1 in BCBM in a CD8 T cell-dependent manner, thereby providing an optimized strategy to introduce immune-based treatments in this lethal disease. In addition, our BCBM models can be used for pre-clinical testing of other therapeutic strategies in the future.
-