InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD8α
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 6.5 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse Spleen Cells or Thymocyte Membranes |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion Immunofluorescence Flow cytometry Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 6.5 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107671 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
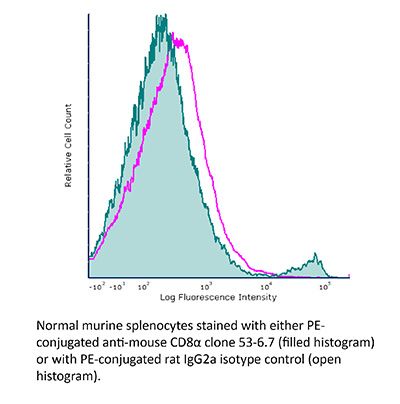
Flow Cytometry
Wang, W., et al (2018). "RIP1 Kinase Drives Macrophage-Mediated Adaptive Immune Tolerance in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancer Cell 34(5): 757-774 e757.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is characterized by immune tolerance and immunotherapeutic resistance. We discovered upregulation of receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1 (RIP1) in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in PDA. To study its role in oncogenic progression, we developed a selective small-molecule RIP1 inhibitor with high in vivo exposure. Targeting RIP1 reprogrammed TAMs toward an MHCII(hi)TNFalpha(+)IFNgamma(+) immunogenic phenotype in a STAT1-dependent manner. RIP1 inhibition in TAMs resulted in cytotoxic T cell activation and T helper cell differentiation toward a mixed Th1/Th17 phenotype, leading to tumor immunity in mice and in organotypic models of human PDA. Targeting RIP1 synergized with PD1-and inducible co-stimulator-based immunotherapies. Tumor-promoting effects of RIP1 were independent of its co-association with RIP3. Collectively, our work describes RIP1 as a checkpoint kinase governing tumor immunity.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Christensen, A. D., et al (2015). "Depletion of regulatory T cells in a hapten-induced inflammation model results in prolonged and increased inflammation driven by T cells" Clin Exp Immunol 179(3): 485-499.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Tregs ) are known to play an immunosuppressive role in the response of contact hypersensitivity (CHS), but neither the dynamics of Tregs during the CHS response nor the exaggerated inflammatory response after depletion of Tregs has been characterized in detail. In this study we show that the number of Tregs in the challenged tissue peak at the same time as the ear-swelling reaches its maximum on day 1 after challenge, whereas the number of Tregs in the draining lymph nodes peaks at day 2. As expected, depletion of Tregs by injection of a monoclonal antibody to CD25 prior to sensitization led to a prolonged and sustained inflammatory response which was dependent upon CD8 T cells, and co-stimulatory blockade with cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4-immunoglobulin (CTLA-4-Ig) suppressed the exaggerated inflammation. In contrast, blockade of the interleukin (IL)-10-receptor (IL-10R) did not further increase the exaggerated inflammatory response in the Treg -depleted mice. In the absence of Tregs , the response changed from a mainly acute reaction with heavy infiltration of neutrophils to a sustained response with more chronic characteristics (fewer neutrophils and dominated by macrophages). Furthermore, depletion of Tregs enhanced the release of cytokines and chemokines locally in the inflamed ear and augmented serum levels of the systemic inflammatory mediators serum amyloid (SAP) and haptoglobin early in the response.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Yamada, D. H., et al (2015). "Suppression of Fcgamma-receptor-mediated antibody effector function during persistent viral infection" Immunity 42(2): 379-390.
PubMed
Understanding how viruses subvert host immunity and persist is essential for developing strategies to eliminate infection. T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection is well described, but effects on antibody-mediated effector activity are unclear. Herein, we show that increased amounts of immune complexes generated in mice persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) suppressed multiple Fcgamma-receptor (FcgammaR) functions. The high amounts of immune complexes suppressed antibody-mediated cell depletion, therapeutic antibody-killing of LCMV infected cells and human CD20-expressing tumors, as well as reduced immune complex-mediated cross-presentation to T cells. Suppression of FcgammaR activity was not due to inhibitory FcgammaRs or high concentrations of free antibody, and proper FcgammaR functions were restored when persistently infected mice specifically lacked immune complexes. Thus, we identify a mechanism of immunosuppression during viral persistence with implications for understanding effective antibody activity aimed at pathogen control.
Immunofluorescence
Finisguerra, V., et al (2015). "MET is required for the recruitment of anti-tumoural neutrophils" Nature 522(7556): 349-353.
PubMed
Mutations or amplification of the MET proto-oncogene are involved in the pathogenesis of several tumours, which rely on the constitutive engagement of this pathway for their growth and survival. However, MET is expressed not only by cancer cells but also by tumour-associated stromal cells, although its precise role in this compartment is not well characterized. Here we show that MET is required for neutrophil chemoattraction and cytotoxicity in response to its ligand hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Met deletion in mouse neutrophils enhances tumour growth and metastasis. This phenotype correlates with reduced neutrophil infiltration to both the primary tumour and metastatic sites. Similarly, Met is necessary for neutrophil transudation during colitis, skin rash or peritonitis. Mechanistically, Met is induced by tumour-derived tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha or other inflammatory stimuli in both mouse and human neutrophils. This induction is instrumental for neutrophil transmigration across an activated endothelium and for inducible nitric oxide synthase production upon HGF stimulation. Consequently, HGF/MET-dependent nitric oxide release by neutrophils promotes cancer cell killing, which abates tumour growth and metastasis. After systemic administration of a MET kinase inhibitor, we prove that the therapeutic benefit of MET targeting in cancer cells is partly countered by the pro-tumoural effect arising from MET blockade in neutrophils. Our work identifies an unprecedented role of MET in neutrophils, suggests a potential ‘Achilles’ heel’ of MET-targeted therapies in cancer, and supports the rationale for evaluating anti-MET drugs in certain inflammatory diseases.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Uddin, M. N., et al (2014). "TNF-alpha-dependent hematopoiesis following Bcl11b deletion in T cells restricts metastatic melanoma" J Immunol 192(4): 1946-1953.
PubMed
Using several tumor models, we demonstrate that mice deficient in Bcl11b in T cells, although having reduced numbers of T cells in the peripheral lymphoid organs, developed significantly less tumors compared with wild-type mice. Bcl11b(-/-) CD4(+) T cells, with elevated TNF-alpha levels, but not the Bcl11b(-/-) CD8(+) T cells, were required for the reduced tumor burden, as were NK1.1(+) cells, found in increased numbers in Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice. Among NK1.1(+) cells, the NK cell population was predominant in number and was the only population displaying elevated granzyme B levels and increased degranulation, although not increased proliferation. Although the number of myeloid-derived suppressor cells was increased in the lungs with metastatic tumors of Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice, their arginase-1 levels were severely reduced. The increase in NK cell and myeloid-derived suppressor cell numbers was associated with increased bone marrow and splenic hematopoiesis. Finally, the reduced tumor burden, increased numbers of NK cells in the lung, and increased hematopoiesis in Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice were all dependent on TNF-alpha. Moreover, TNF-alpha treatment of wild-type mice also reduced the tumor burden and increased hematopoiesis and the numbers and activity of NK cells in the lung. In vitro treatment with TNF-alpha of lineage-negative hematopoietic progenitors increased NK and myeloid differentiation, further supporting a role of TNF-alpha in promoting hematopoiesis. These studies reveal a novel role for TNF-alpha in the antitumor immune response, specifically in stimulating hematopoiesis and increasing the numbers and activity of NK cells.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Walsh, K. B., et al (2014). "Animal model of respiratory syncytial virus: CD8+ T cells cause a cytokine storm that is chemically tractable by sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor agonist therapy" J Virol 88(11): 6281-6293.
PubMed
The cytokine storm is an intensified, dysregulated, tissue-injurious inflammatory response driven by cytokine and immune cell components. The cytokine storm during influenza virus infection, whereby the amplified innate immune response is primarily responsible for pulmonary damage, has been well characterized. Now we describe a novel event where virus-specific T cells induce a cytokine storm. The paramyxovirus pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) is a model of human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV). Unexpectedly, when C57BL/6 mice were infected with PVM, the innate inflammatory response was undetectable until day 5 postinfection, at which time CD8(+) T cells infiltrated into the lung, initiating a cytokine storm by their production of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Administration of an immunomodulatory sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 (S1P1R) agonist significantly inhibited PVM-elicited cytokine storm by blunting the PVM-specific CD8(+) T cell response, resulting in diminished pulmonary disease and enhanced survival. IMPORTANCE: A dysregulated overly exuberant immune response, termed a “cytokine storm,” accompanies virus-induced acute respiratory diseases (VARV), is primarily responsible for the accompanying high morbidity and mortality, and can be controlled therapeutically in influenza virus infection of mice and ferrets by administration of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor (S1P1R) agonists. Here, two novel findings are recorded. First, in contrast to influenza infection, where the cytokine storm is initiated early by the innate immune system, for pneumonia virus of mice (PVM), a model of RSV, the cytokine storm is initiated late in infection by the adaptive immune response: specifically, by virus-specific CD8 T cells via their release of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. Blockading these cytokines with neutralizing antibodies blunts the cytokine storm and protects the host. Second, PVM infection is controlled by administration of an S1P1R agonist.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Hervieu, A., et al (2013). "Dacarbazine-mediated upregulation of NKG2D ligands on tumor cells activates NK and CD8 T cells and restrains melanoma growth" J Invest Dermatol 133(2): 499-508.
PubMed
Dacarbazine (DTIC) is a cytotoxic drug widely used for melanoma treatment. However, the putative contribution of anticancer immune responses in the efficacy of DTIC has not been evaluated. By testing how DTIC affects host immune responses to cancer in a mouse model of melanoma, we unexpectedly found that both natural killer (NK) and CD8(+) T cells were indispensable for DTIC therapeutic effect. Although DTIC did not directly affect immune cells, it triggered the upregulation of NKG2D ligands on tumor cells, leading to NK cell activation and IFNgamma secretion in mice and humans. NK cell-derived IFNgamma subsequently favored upregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on tumor cells, rendering them sensitive to cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells. Accordingly, DTIC markedly enhanced cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 inhibition efficacy in vivo in an NK-dependent manner. These results underscore the immunogenic properties of DTIC and provide a rationale to combine DTIC with immunotherapeutic agents that relieve immunosuppression in vivo.
Immunofluorescence
Schwager, K., et al (2013). "The immunocytokine L19-IL2 eradicates cancer when used in combination with CTLA-4 blockade or with L19-TNF" J Invest Dermatol 133(3): 751-758.
PubMed
Systemic high-dose IL2 promotes long-term survival in a subset of metastatic melanoma patients, but this treatment is accompanied by severe toxicities. The immunocytokine L19-IL2, in which IL2 is fused to the human L19 antibody capable of selective accumulation on tumor neovasculature, has recently shown encouraging clinical activity in patients with metastatic melanoma. In this study, we have investigated the therapeutic performance of L19-IL2, administered systemically in combination with a murine anti-CTLA-4 antibody or with a second clinical-stage immunocytokine (L19-TNF) in two syngeneic immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. We observed complete tumor eradications when L19-IL2 was used in combination with CTLA-4 blockade. Interestingly, mice cured from F9 tumors developed new lesions when rechallenged with tumor cells after therapy, whereas mice cured from CT26 tumors were resistant to tumor rechallenge. Similarly, L19-IL2 induced complete remissions when administered in a single intratumoral injection in combination with L19-TNF, whereas the two components did not lead to cures when administered as single agents. These findings provide a rationale for combination trials in melanoma, as the individual therapeutic agents have been extensively studied in clinical trials, and the antigen recognized by the L19 antibody has an identical sequence in mouse and man.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Cyktor, J. C., et al (2013). "Clonal expansions of CD8+ T cells with IL-10 secreting capacity occur during chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection" PLoS One 8(3): e58612.
PubMed
The exact role of CD8(+) T cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection has been heavily debated, yet it is generally accepted that CD8(+) T cells contribute to protection against Mtb. In this study, however, we show that the Mtb-susceptible CBA/J mouse strain accumulates large numbers of CD8(+) T cells in the lung as infection progresses, and that these cells display a dysfunctional and immunosuppressive phenotype (PD-1(+), Tim-3(+), CD122(+)). CD8(+) T cell expansions from the lungs of Mtb-infected CBA/J mice were also capable of secreting the immunosuppressive cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), although in vivo CD8(+) T cell depletion did not significantly alter Mtb burden. Further analysis revealed that pulmonary CD8(+) T cells from Mtb-infected CBA/J mice were clonally expanded, preferentially expressing T cell receptor (TcR) Vbeta chain 8 (8.2, 8.3) or Vbeta 14. Although Vbeta8(+) CD8(+) T cells were responsible for the majority of IL-10 production, in vivo depletion of Vbeta8(+) did not significantly change the outcome of Mtb infection, which we hypothesize was a consequence of their dual IL-10/IFN-gamma secreting profiles. Our data demonstrate that IL-10-secreting CD8(+) T cells can arise during chronic Mtb infection, although the significance of this T cell population in tuberculosis pathogenesis remains unclear.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Hafalla, J. C., et al (2012). "The CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways independently regulate host resistance to Plasmodium-induced acute immune pathology" PLoS Pathog 8(2): e1002504.
PubMed
The balance between pro-inflammatory and regulatory immune responses in determining optimal T cell activation is vital for the successful resolution of microbial infections. This balance is maintained in part by the negative regulators of T cell activation, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L, which dampen effector responses during chronic infections. However, their role in acute infections, such as malaria, remains less clear. In this study, we determined the contribution of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L to the regulation of T cell responses during Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA)-induced experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) in susceptible (C57BL/6) and resistant (BALB/c) mice. We found that the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T cells correlates with the extent of pro-inflammatory responses induced during PbA infection, being higher in C57BL/6 than in BALB/c mice. Thus, ECM develops despite high levels of expression of these inhibitory receptors. However, antibody-mediated blockade of either the CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1, but not the PD-1/PD-L2, pathways during PbA-infection in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice resulted in higher levels of T cell activation, enhanced IFN-gamma production, increased intravascular arrest of both parasitised erythrocytes and CD8(+) T cells to the brain, and augmented incidence of ECM. Thus, in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 represent essential, independent and non-redundant pathways for maintaining T cell homeostasis during a virulent malaria infection. Moreover, neutralisation of IFN-gamma or depletion of CD8(+) T cells during PbA infection was shown to reverse the pathologic effects of regulatory pathway blockade, highlighting that the aetiology of ECM in the BALB/c mice is similar to that in C57BL/6 mice. In summary, our results underscore the differential and complex regulation that governs immune responses to malaria parasites.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Chyou, S., et al (2011). "Coordinated regulation of lymph node vascular-stromal growth first by CD11c+ cells and then by T and B cells" J Immunol 187(11): 5558-5567.
PubMed
Lymph node blood vessels play important roles in the support and trafficking of immune cells. The blood vasculature is a component of the vascular-stromal compartment that also includes the lymphatic vasculature and fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs). During immune responses as lymph nodes swell, the blood vasculature undergoes a rapid proliferative growth that is initially dependent on CD11c(+) cells and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) but is independent of lymphocytes. The lymphatic vasculature grows with similar kinetics and VEGF dependence, suggesting coregulation of blood and lymphatic vascular growth, but lymphatic growth has been shown to be B cell dependent. In this article, we show that blood vascular, lymphatic, and FRC growth are coordinately regulated and identify two distinct phases of vascular-stromal growth–an initiation phase, characterized by upregulated vascular-stromal proliferation, and a subsequent expansion phase. The initiation phase is CD11c(+) cell dependent and T/B cell independent, whereas the expansion phase is dependent on B and T cells together. Using CCR7(-/-) mice and selective depletion of migratory skin dendritic cells, we show that endogenous skin-derived dendritic cells are not important during the initiation phase and uncover a modest regulatory role for CCR7. Finally, we show that FRC VEGF expression is upregulated during initiation and that dendritic cells can stimulate increased fibroblastic VEGF, suggesting the scenario that lymph node-resident CD11c(+) cells orchestrate the initiation of blood and lymphatic vascular growth in part by stimulating FRCs to upregulate VEGF. These results illustrate how the lymph node microenvironment is shaped by the cells it supports.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Kumar, D., et al (2011). "Intranasal administration of an inactivated Yersinia pestis vaccine with interleukin-12 generates protective immunity against pneumonic plague" Clin Vaccine Immunol 18(11): 1925-1935.
PubMed
Inhalation of Yersinia pestis causes pneumonic plague, which rapidly progresses to death. A previously licensed killed whole-cell vaccine is presently unavailable due to its reactogenicity and inconclusive evidence of efficacy. The present study now shows that vaccination intranasally (i.n.) with inactivated Y. pestis CO92 (iYp) adjuvanted with interleukin-12 (IL-12) followed by an i.n. challenge with a lethal dose of Y. pestis CO92 prevented bacterial colonization and protected 100% of mice from pneumonic plague. Survival of the vaccinated mice correlated with levels of systemic and lung antibodies, reduced pulmonary pathology and proinflammatory cytokines, and the presence of lung lymphoid cell aggregates. Protection against pneumonic plague was partially dependent upon Fc receptors and could be transferred to naive mice with immune mouse serum. On the other hand, protection was not dependent upon complement, and following vaccination, depletion of CD4 and/or CD8 T cells before challenge did not affect survival. In summary, the results demonstrate the safety, immunogenicity, and protective efficacy of i.n. administered iYp plus IL-12 in a mouse model of pneumonic plague.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Simma, O., et al (2009). "Identification of an indispensable role for tyrosine kinase 2 in CTL-mediated tumor surveillance" Cancer Res 69(1): 203-211.
PubMed
We showed previously that Tyk2(-/-) natural killer cells lack the ability to lyse leukemic cells. As a consequence, the animals are leukemia prone. Here, we show that the impaired tumor surveillance extends to T cells. Challenging Tyk2(-/-) mice with EL4 thymoma significantly decreased disease latency. The crucial role of Tyk2 for CTL function was further characterized using the ovalbumin-expressing EG7 cells. Tyk2(-/-) OT-1 mice developed EG7-induced tumors significantly faster compared with wild-type (wt) controls. In vivo assays confirmed the defect in CD8(+) cytotoxicity on Tyk2 deficiency and clearly linked it to type I IFN signaling. An impaired CTL activity was only observed in IFNAR1(-/-) animals but not on IFNgamma or IL12p35 deficiency. Accordingly, EG7-induced tumors grew faster in IFNAR1(-/-) and Tyk2(-/-) but not in IFNgamma(-/-) or IL12p35(-/-) mice. Adoptive transfer experiments defined a key role of Tyk2 in CTL-mediated tumor surveillance. In contrast to wt OT-1 cells, Tyk2(-/-) OT-1 T cells were incapable of controlling EG7-induced tumor growth.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Genetics
-
Cancer Research
Epigenetic suppression of Nrf2-Slc40a1 axis induces ferroptosis and enhances immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer.
In J Immunother Cancer on 23 October 2025 by Zhang, Y., Yu, R., et al.
PubMed
Despite progress in immunotherapy for several solid tumors, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains largely unresponsive, primarily due to its profoundly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) characterized by limited CD8+ T cell infiltration. Novel strategies are needed to overcome this immune resistance and enhance the efficacy of checkpoint blockade.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
EP300 compromises antitumor immunity by increasing SOCS1 expression.
In J Immunother Cancer on 15 October 2025 by Zeng, Y., Zhou, Y., et al.
PubMed
Beyond supporting cancer cell proliferation, tumor growth relies on the ability of cancer cells to evade immune surveillance. Identifying novel molecules that promote tumor immune escape may help develop more effective immunotherapeutic strategies. The histone acetyltransferase E1A-binding protein p300 (EP300) is a key epigenetic regulator that modulates gene transcription through chromatin remodeling and acetylation of histones and transcription factors. However, its role in regulating immune evasion remains incompletely understood. This study investigates the impact of EP300 on tumor immune escape and suggests its potential as an immunotherapeutic target.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inhibiting KRAS with CD47 and immune checkpoint overcomes intrinsic resistance to combined KRAS and immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
In Cell Rep Med on 16 September 2025 by Hirade, K., Tanaka, N., et al.
PubMed
Although Kirsten rat sarcoma virus (KRAS) G12C inhibitors alter the treatment strategy for patients with KRAS G12C-mutant lung cancer, their efficacy remains insufficient to eliminate tumors. Here, we identify that inhibition of mutant KRAS promotes escape from macrophage phagocytosis by upregulating the expression of cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) and CD24. These proteins are induced by the binding of FOXA1 to the super-enhancer of CD47 and grainyhead-like transcription factor 2 (GRHL2) to the promoter of CD24, respectively. Whereas the addition of an anti-CD47 antibody restores macrophage phagocytosis, phagocytic macrophages induce programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, resulting in the suppression of CD8 T cell activation. Combination of a KRAS inhibitor with anti-CD47 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies achieves long-term survival in an orthotopic murine model recalcitrant to KRAS inhibition with immune checkpoint therapy. These results suggest that targeting KRAS with an anti-CD47 antibody and immune checkpoint blockade is a promising strategy, especially in immune-cold lung tumors.
-
-
Mouse Models and Experimental Protocols to Study Alloantibody-Mediated Transplant Rejection.
In Curr Protoc on 1 September 2025 by Zimmerer, J. M., Aldhahi, H., et al.
PubMed
Transplantation is the definitive treatment for patients with end-stage organ failure. Following allogeneic transplant, the recipient's immune system recognizes transplanted cells or organs as foreign. The immune system recognizes and targets the foreign tissue for damage through cell-mediated rejection (CMR) and/or antibody-mediated rejection (AMR). Immunosuppressive agents are utilized to protect the transplant from rejection and extend transplant function and survival. Despite advances in immunosuppressive agents, AMR remains a critical barrier to the success of transplantation. AMR occurs when B cells produce alloantibodies that bind the allograft causing antibody-dependent, complement-mediated or immune cell-mediated cytotoxic damage. Continued research on AMR is required to develop novel and effective therapeutic strategies. Murine AMR models have been utilized to investigate mechanisms mediating the production of posttransplant alloantibodies and the pathology of damage to the transplanted allograft. These models facilitating the investigation of cellular and molecular mechanisms of alloantibody production and allograft damage are critical to the development of novel therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat AMR. This article describes the methodologies used to study AMR in animal transplant models. These include protocols to detect and measure alloantibodies, allograft survival, AMR pathology, and effector immune cell responses following transplantation. © 2025 The Author(s). Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Alloserum transfer into immune-incompetent recipient mice to determine transplant organ susceptibility to AMR Basic Protocol 2: Allogeneic transplantation into immune-deficient mice to study critical cellular and molecular pathways impacting AMR Support Protocol 1: Quantification of posttransplant alloantibody titer Support Protocol 2: Monitoring of transplant allograft survival Support Protocol 3: Assessment of immunopathology and severity of AMR Basic Protocol 3: Analysis of posttransplant immunologic responses.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Coupling IL-2 with IL-10 to mitigate toxicity and enhance antitumor immunity.
In Cell Rep Med on 19 August 2025 by Ahn, J. J., Dudics, S., et al.
PubMed
Wild-type interleukin (IL)-2 induces anti-tumor immunity and toxicity, predominated by vascular leak syndrome (VLS) leading to edema, hypotension, organ toxicity, and regulatory T cell (Treg) expansion. Efforts to uncouple IL-2 toxicity from its potency have failed in the clinic. We hypothesize that IL-2 toxicity is driven by cytokine release syndrome (CRS) followed by VLS and that coupling IL-2 with IL-10 will ameliorate toxicity. Our data, generated using human primary cells, mouse models, and non-human primates, suggest that coupling of these cytokines prevents toxicity while retaining cytotoxic T cell activation and limiting Treg expansion. In syngeneic murine tumor models, DK210 epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), an IL-2/IL-10 fusion molecule targeted to EGFR via an anti-EGFR single-chain variable fragment (scFV), potently activates T cells and natural killer (NK) cells and elicits interferon (IFN)γ-dependent anti-tumor function without peripheral inflammatory toxicity or Treg accumulation. Therefore, combining IL-2 with IL-10 uncouples toxicity from immune activation, leading to a balanced and pleiotropic anti-tumor immune response.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Genetics
-
Cancer Research
Genetic and pharmacological targeting of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor action blocks tumor progression in mouse models of breast cancer.
In J Immunol on 1 August 2025 by Heard, M. A., Qian, J., et al.
PubMed
Effective small molecule therapies are a major unmet need in triple-negative breast cancer. Therefore, we examined the mechanism of action of a novel cancer therapeutic target in preclinical mouse models focusing on the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (CHRNA7). E0771 breast tumor cells were implanted into CHRNA7KO mice to determine the role of CHRNA7, which is expressed in tumor-associated myeloid immune cells. We observed that tumor-bearing CHRNA7KO mice had decreased survival and increased tumor burden linked to a CHRNA7-mediated reduction in immune cell activation. Based on the tumor permissive phenotype of CHRNA7KO mice, we tested the effect of a small molecule agonist of CHRNA7, AR-R17779, in several mouse models of breast cancer. For example, in both the E0771 tumor model and PyMT tumor models, treatment with AR-R17779 increased survival. In the 4T1 breast tumor model, treatment with AR-R17779 also increased survival, with a well-defined reduction in primary tumor burden and lung metastases. The antitumorigenic effects of AR-R17779 were linked to an adaptive immune response based on in vivo studies showing a survival benefit when AR-R17779 was administered as a combination therapy with anti-PD-L1, demonstrating that the effects of AR-R17779 were dependent on CD8 T cells, and in vitro studies showing AR-R17779 treatment of dendritic cells increased T cell activation. Together these findings supported the importance of CHRNA7 as a novel therapeutic target expressed on dendritic cells based on its role in potentiating the adaptive immune response in mouse models of breast cancer.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Orchestrating intratumoral DC-T cell immunity for enhanced tumor control via radiotherapy-activated TLR7/8 prodrugs in mice.
In Nat Commun on 1 July 2025 by Yin, X., Ding, Z., et al.
PubMed
Optimizing intratumoral dendritic cell (DC)-T cell responses is pivotal for effective cancer immunotherapy. However, the mechanistic governing these dynamics within the tumor microenvironment (TME) remains unclear, and strategies to improve their therapeutic potential are underexplored. Here, we show that precise radiotherapy activates the pro-TLR7/8 agonist imidazoquinoline (IMDQ) locally in preclinical tumor models, stimulating DCs to elicit T cell immunity without the need for further recruitment or causing systemic toxicity. Mechanistically, this synergistic approach triggers type I interferon via STING and MyD88 signaling pathways, strengthening local immune responses. Importantly, we reveal that fractionated, low-dose radiotherapy can effectively optimize local DC-T cell dynamics to control the irradiated tumor, while also promoting abscopal effect. Thus, our findings underscore the critical role of harnessing intratumoral DCs to reinvigorate pre-existing T cell immunity and provide mechanistic insights into improving both local and distal tumor control, opening new avenues for advancing cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
BRAF/MEK inhibition induces cell state transitions boosting immune checkpoint sensitivity in BRAFV600E-mutant glioma.
In Cell Rep Med on 17 June 2025 by Xing, Y. L., Panovska, D., et al.
PubMed
Resistance to v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF) plus mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibition (BRAFi+MEKi) in BRAFV600E-mutant gliomas drives rebound, progression, and high mortality, yet it remains poorly understood. This study addresses the urgent need to develop treatments for BRAFi+MEKi-resistant glioma using preclinical mouse models and patient-derived materials. BRAFi+MEKi reveals glioma plasticity by heightening cell state transitions along glial differentiation trajectories, giving rise to astrocyte- and immunomodulatory oligodendrocyte (OL)-like states. PD-L1 upregulation in OL-like cells links cell state transitions to immune evasion, possibly orchestrated by Galectin-3. BRAFi+MEKi induces interferon response signatures, tumor infiltration, and suppression of T cells. Combining BRAFi+MEKi with immune checkpoint inhibition enhances survival in a T cell-dependent manner, reinvigorates T cells, and outperforms individual or sequential therapies in mice. Elevated PD-L1 expression in BRAF-mutant versus BRAF-wild-type glioblastoma supports the rationale for PD-1 inhibition in patients. These findings underscore the potential of targeting glioma plasticity and highlight combination strategies to overcome therapy resistance in BRAFV600E-mutant high-grade glioma.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and PD-1 pathway dual blockade promotes antitumor immune responses by reversing CD8+ T-cell exhaustion in non-small cell lung cancer.
In Front Immunol on 4 June 2025 by Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapies targeting the programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)/programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) have shown great promise for a subset of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, safe and robust combination therapies are still needed to bring the benefit to broader patient populations.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inhibition of tumor-intrinsic NAT10 enhances antitumor immunity by triggering type I interferon response via MYC/CDK2/DNMT1 pathway.
In Nat Commun on 3 June 2025 by Liu, W. C., Wei, Y. H., et al.
PubMed
Posttranscriptional modifications are involved in cancer progression. However, the function and regulatory mechanism of mRNA acetylation modification remains largely unknown. Here, we discover an unexpected role of N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) RNA acetyltransferase NAT10 in reshaping the tumor immune microenvironment. By analyzing patients' data, we find that NAT10 is upregulated in tumor tissues, and negatively correlated with immune cell infiltration and overall survival. Loss of tumoral NAT10 enhances tumor-specific cellular immune response and suppresses tumor growth. Mechanistically, MYC is identified as a key downstream target of NAT10 via enhancing mRNA ac4C modification. Inhibition of NAT10 blocks the MYC/CDK2/DNMT1 pathway, enhances double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) formation, which triggers type I interferon response and improves tumor specific CD8+ T cell response in vivo. More importantly, the inhibition of NAT10, using either small molecule inhibitor (Remodelin) or PEI/PC7A/siNAT10 nanoparticles, synergize PD-1 blockade in elevating anti-tumor immune response and repressing tumor progression. Our findings thus uncover the crucial role of tumor-intrinsic NAT10 in tumor immune microenvironment, which represents a promising target for enhancing cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In vivo armed macrophages curb liver metastasis through tumor-reactive T-cell rejuvenation.
In Nat Commun on 11 April 2025 by Notaro, M., Borghetti, M., et al.
PubMed
Despite recent progress in cancer treatment, liver metastases persist as an unmet clinical need. Here, we show that arming liver and tumor-associated macrophages in vivo to co-express tumor antigens (TAs), IFNα, and IL-12 unleashes robust anti-tumor immune responses, leading to the regression of liver metastases. Mechanistically, in vivo armed macrophages expand tumor reactive CD8+ T cells, which acquire features of progenitor exhausted T cells and kill cancer cells independently of CD4+ T cell help. IFNα and IL-12 produced by armed macrophages reprogram antigen presenting cells and rewire cellular interactions, rescuing tumor reactive T cell functions. In vivo armed macrophages trigger anti-tumor immunity in distinct liver metastasis mouse models of colorectal cancer and melanoma, expressing either surrogate tumor antigens, naturally occurring neoantigens or tumor-associated antigens. Altogether, our findings support the translational potential of in vivo armed liver macrophages to expand and rejuvenate tumor reactive T cells for the treatment of liver metastases.
-
-
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
High baseline levels of PD-L1 reduce the heterogeneity of immune checkpoint signature and sensitize anti-PD1 therapy in lung and colorectal cancers.
In Cell Death Dis on 4 March 2025 by Fan, P., Qi, Z., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy only induces durable responses in a subset of cancer patients. The underlying mechanisms of such selective efficacy remain largely unknown. By analyzing the expression profiles of immune checkpoint molecules in different statuses of murine tumors, we found that tumor progression generally randomly upregulated multiple immune checkpoints, thus increased the Heterogeneity of Immune checkpoint Signature (HIS) and resulted in immunotherapeutic resistance. Interestingly, overexpressing one pivotal immune checkpoint in a tumor hindered the upregulation of a majority of other immune checkpoint genes during tumor progression via suppressing interferon γ, resulting in HIS-low. Indeed, PD-L1 high-expression sensitized baseline large tumors to anti-PD1 therapy without altering the sensitivity of baseline small tumors. In line with these preclinical results, a retrospective analysis of a phase III study involving patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) revealed that PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥ 50% more reliably predicted therapeutic response in NSCLC patients with baseline tumor volume (BTV)-large compared to patients with BTV-small. Notably, TPS combined with BTV significantly improved the predictive accuracy. Collectively, the data suggest that HIS reflects the dynamic features of tumor immune evasion and dictates the selective efficacy of ICB in a tumor size-dependent manner, providing a potential novel strategy to improve precision ICB. These findings highlight the application of ICB to earlier stages of cancer patients. The integration of PD-L1 with BTV may immediately improve patient stratification and prediction performance in the clinic.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Ultra-high dose rate radiotherapy overcomes radioresistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
In Signal Transduct Target Ther on 3 March 2025 by Li, H. S., Tang, R., et al.
PubMed
Radiotherapy (RT) resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) significantly hampers local control and patient prognosis. This study investigated the efficacy and molecular mechanisms of high-energy X-ray-based ultra-high dose rate radiotherapy (UHDR-RT) in overcoming RT resistance. The established RT-resistant HNSCC cell lines and animal models were subjected to UHDR-RT or conventional RT (Conv-RT) via a high-power rhodotron accelerator. Cellular assays assessed the malignant phenotype, viability, and degree of DNA damage, whereas in vivo evaluations focused on tumor proliferation and the tumor immune microenvironment (TiME). Transcriptome sequencing and Olink proteomics were employed to explore the underlying mechanisms involved. In vitro experiments indicated that UHDR-RT suppressed radioresistant cell proliferation and invasion, while promoting apoptosis and exacerbating DNA damage. In contrast, its efficacy in radiosensitive cells was comparable to that of Conv-RT. In vivo studies using patient-derived xenograft nude mice models demonstrated that UHDR-RT only partially reversed RT resistance. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of C57BL/6J mice models revealed the predominant role of TiME modulating in reversing radioresistance. Immunofluorescence and flow cytometry confirmed increased CD8+ T cells and an increased M1/M2 macrophage ratio post-UHDR-RT. Mechanistically, UHDR-RT activated CD8+ T cells, which stimulated M1 macrophages through paracrine IFN-γ signaling, thereby enhancing TiME activation. Furthermore, the activated M1 macrophages secreted CXCL9, which in turn reactivated CD8+ T cells, forming a feedforward loop that amplified TiME activation. This study elucidates the dual role of UHDR-RT in directly inducing DNA damage and modulating the TiME, highlighting its potential in treating radioresistant HNSCC.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Single-cell data-driven design of armed oncolytic virus to boost cooperative innate-adaptive immunity against cancer.
In Mol Ther on 5 February 2025 by Zhao, J., Wang, H., et al.
PubMed
Oncolytic viruses have been considered promising cancer immunotherapies. However, oncovirotherapy agents impart durable responses in only a subset of cancer patients. Thus, exploring the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the heterogeneous responses in patients can provide guidance to develop more effective oncolytic virus therapies. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis of tumors responsive and non-responsive to oncovirotherapy revealed signatures of the tumor immune microenvironment associated with immune response. Thus, we designed and constructed an armed oncolytic virus, OV-5A, that expressed five genes with non-redundant functions. OV-5A treatment exhibits robust immune response against various tumors in multiple mouse models, peripheral blood mononuclear cell -patient-derived xenograft models, organoid-immune cell co-culture systems, and patient tissue sections by activating a cooperative innate-adaptive immune response against tumor cells. scRNA-seq analysis of complete responders and partial responders to OV-5A treatment guided the design of combination therapy of OV-5A. This data-driven approach paves an innovative way to rationalize the design of oncolytic virus and multi-agent combination therapies.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Targeting the oncogenic m6A demethylase FTO suppresses tumourigenesis and potentiates immune response in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Gut on 10 December 2024 by Chen, A., Zhang, V. X., et al.
PubMed
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO), an eraser of N6-methyadenosine (m6A), plays oncogenic roles in various cancers. However, its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is unclear. Furthermore, small extracellular vesicles (sEVs, or exosomes) are critical mediators of tumourigenesis and metastasis, but the relationship between FTO-mediated m6A modification and sEVs in HCC is unknown.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
EHMT1/2 Inhibition Promotes Regression of Therapy-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Tumors in a CD8 T-cell-Dependent Manner.
In Mol Cancer Res on 3 December 2024 by Nguyen, L. L., Watson, Z. L., et al.
PubMed
Poly ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) are first-line maintenance therapy for ovarian cancer and an alternative therapy for several other cancer types. However, PARPi-resistance is rising, and there is currently an unmet need to combat PARPi-resistant tumors. Here, we created an immunocompetent, PARPi-resistant mouse model to test the efficacy of combinatory PARPi and euchromatic histone methyltransferase 1/2 inhibitor (EHMTi) in the treatment of PARPi-resistant ovarian cancer. We discovered that inhibition of EHMT1/2 resensitizes cells to PARPi. Markedly, we show that single EHMTi and combinatory EHMTi/PARPi significantly reduced PARPi-resistant tumor burden and that this reduction is partially dependent on CD8 T cells. Altogether, our results show a low-toxicity drug that effectively treats PARPi-resistant ovarian cancer in an immune-dependent manner, supporting its entry into clinical development and potential incorporation of immunotherapy. Implications: Targeting the epigenome of therapy-resistant ovarian cancer induces an antitumor response mediated in part through an antitumor immune response.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
CDC7 Inhibition Potentiates Antitumor Efficacy of PARP Inhibitor in Advanced Ovarian Cancer.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 December 2024 by Liu, S., Deng, P., et al.
PubMed
Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) have demonstrated remarkable clinical efficacy in treating ovarian cancer (OV) with BRCA1/2 mutations. However, drug resistance inevitably limits their clinical applications and there is an urgent need for improved therapeutic strategies to enhance the clinical utility of PARPi, such as Olaparib. Here, compelling evidence indicates that sensitivity of PARPi is associated with cell cycle dysfunction. Through high-throughput drug screening with a cell cycle kinase inhibitor library, XL413, a potent cell division cycle 7 (CDC7) inhibitor, is identified which can synergistically enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of Olaparib. Mechanistically, the combined administration of XL413 and Olaparib demonstrates considerable DNA damage and DNA replication stress, leading to increased sensitivity to Olaparib. Additionally, a robust type-I interferon response is triggered through the induction of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway. Using murine syngeneic tumor models, the combination treatment further demonstrates enhanced antitumor immunity, resulting in tumor regression. Collectively, this study presents an effective treatment strategy for patients with advanced OV by combining CDC7 inhibitors (CDC7i) and PARPi, offering a promising therapeutic approach for patients with limited response to PARPi.
-
-
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Probiotics and their metabolite spermidine enhance IFN-γ+CD4+ T cell immunity to inhibit hepatitis B virus.
In Cell Rep Med on 19 November 2024 by Wang, T., Fan, Y., et al.
PubMed
The therapeutic potential of commensal microbes and their metabolites is promising in the functional cure of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which is defined as hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) loss. Here, using both specific-pathogen-free and germ-free mice, we report that probiotics significantly promote the decline of HBsAg and inhibit HBV replication by enhancing intestinal homeostasis and provoking intrahepatic interferon (IFN)-γ+CD4+ T cell immune response. Depletion of CD4+ T cells or blockage of IFN-γ abolishes probiotics-mediated HBV inhibition. Specifically, probiotics-derived spermidine accumulates in the gut and transports to the liver, where it exhibits a similar anti-HBV effect. Mechanistically, spermidine enhances IFN-γ+CD4+ T cell immunity by autophagy. Strikingly, administration of probiotics in HBV patients reveals a preliminary trend to accelerate the decline of serum HBsAg. In conclusion, probiotics and their derived spermidine promote HBV clearance via autophagy-enhanced IFN-γ+CD4+ T cell immunity, highlighting the therapeutic potential of probiotics and spermidine for the functional cure of HBV patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Egfl6 promotes ovarian cancer progression by enhancing the immunosuppressive functions of tumor-associated myeloid cells.
In J Clin Invest on 1 November 2024 by Hamze Sinno, S., Imperatore, J. A., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) play a critical role in resistance to immunotherapy. In this study, we identified epidermal growth factor-like 6 (Egfl6) as a regulator of myeloid cell functions. Our analyses indicated that Egfl6, via binding with β3 integrins and activation of p38 and SYK signaling, acts as a chemotactic factor for myeloid cell migration and promotes their differentiation toward an immunosuppressive state. In syngeneic mouse models of ovarian cancer (OvCa), tumor expression of Egfl6 increased the intratumoral accumulation of polymorphonuclear (PMN) MDSCs and TAMs and their expression of immunosuppressive factors, including CXCL2, IL-10, and PD-L1. Consistent with this, in an immune 'hot' tumor model, Egfl6 expression eliminated response to anti-PD-L1 therapy, while Egfl6 neutralizing antibody decreased the accumulation of tumor-infiltrating CD206+ TAMs and PMN-MDSCs and restored the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy. Supporting a role in human tumors, in human OvCa tissue samples, areas of high EGFL6 expression colocalized with myeloid cell infiltration. scRNA-Seq analyses revealed a correlation between EGFL6 and immune cell expression of immunosuppressive factors. Our data provide mechanistic insights into the oncoimmunologic functions of EGFL6 in mediating tumor immune suppression and identified EGFL6 as a potential therapeutic target to enhance immunotherapy in patients with OvCa.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
SIN3B Loss Heats up Cold Tumor Microenvironment to Boost Immunotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 November 2024 by Zhang, Z., Tang, Y., et al.
PubMed
Despite progress significant advances in immunotherapy for some solid tumors, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains unresponsive poorly responsive to such interventions, largely due to its highly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) with limited CD8+ T cell infiltration. This study explores the role of the epigenetic factor Sin3B in the PDAC TME. Using murine PDAC models, we found that tumor cell-intrinsic Sin3B loss reshapes the TME, increasing CD8+ T cell infiltration and cytotoxicity, thus impeding tumor progression and enhancing sensitivity to anti-PD1 treatment. Sin3B-deficient tumor cells exhibited amplified CXCL9/10 secretion in response to Interferon-gamma (IFNγ), creating a positive feedback loop via the CXCL9/10-CXCR3 axis, thereby intensifying the anti-tumor immune response against PDAC. Mechanistically, extensive epigenetic regulation is uncovered by Sin3B loss, particularly enhanced H3K27Ac distribution on genes related to immune responses in PDAC cells. Consistent with the murine model findings, analysis of human PDAC samples revealed a significant inverse correlation between SIN3B levels and both CD8+ T cell infiltration and CXCL9/10 expression. Notebly, PDAC patients with lower SIN3B expression showed a more favorable response to anti-PD1 therapy. The findings suggest that targeting SIN3B can enhance cytotoxic T cell infiltration into the tumor site and improve immunotherapy efficacy in PDAC, offering potential avenues for therapeutic biomarker or target in this challenging disease.
-