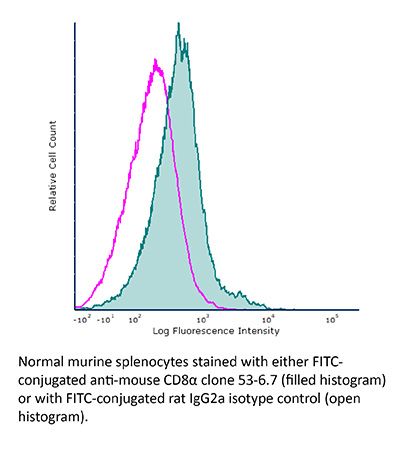
FlowMAb FITC anti-mouse CD8α
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | FlowMAb FITC rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Conjugation | FITC |
| Excitation Source | Blue 488 nm |
| Excitation Max | 494 nm |
| Emission Max | 518 nm |
| Immunogen | Mouse Spleen Cells or Thymocyte Membranes |
| Reported Applications |
Immunofluorescence Flow cytometry |
| Protocol Information | It is recommended that the reagent be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. |
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/ml |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 6.5 Contains 0.09% Sodium Azide |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G. Conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate under optimal conditions. |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
Flow Cytometry
Wang, W., et al. (2018). "RIP1 Kinase Drives Macrophage-Mediated Adaptive Immune Tolerance in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancer Cell 34(5): 757-774 e757.
PubMed
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is characterized by immune tolerance and immunotherapeutic resistance. We discovered upregulation of receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1 (RIP1) in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in PDA. To study its role in oncogenic progression, we developed a selective small-molecule RIP1 inhibitor with high in vivo exposure. Targeting RIP1 reprogrammed TAMs toward an MHCII(hi)TNFalpha(+)IFNgamma(+) immunogenic phenotype in a STAT1-dependent manner. RIP1 inhibition in TAMs resulted in cytotoxic T cell activation and T helper cell differentiation toward a mixed Th1/Th17 phenotype, leading to tumor immunity in mice and in organotypic models of human PDA. Targeting RIP1 synergized with PD1-and inducible co-stimulator-based immunotherapies. Tumor-promoting effects of RIP1 were independent of its co-association with RIP3. Collectively, our work describes RIP1 as a checkpoint kinase governing tumor immunity.
Immunofluorescence
Finisguerra, V., et al. (2015). "MET is required for the recruitment of anti-tumoural neutrophils" Nature 522(7556): 349-353.
PubMed
Mutations or amplification of the MET proto-oncogene are involved in the pathogenesis of several tumours, which rely on the constitutive engagement of this pathway for their growth and survival. However, MET is expressed not only by cancer cells but also by tumour-associated stromal cells, although its precise role in this compartment is not well characterized. Here we show that MET is required for neutrophil chemoattraction and cytotoxicity in response to its ligand hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Met deletion in mouse neutrophils enhances tumour growth and metastasis. This phenotype correlates with reduced neutrophil infiltration to both the primary tumour and metastatic sites. Similarly, Met is necessary for neutrophil transudation during colitis, skin rash or peritonitis. Mechanistically, Met is induced by tumour-derived tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha or other inflammatory stimuli in both mouse and human neutrophils. This induction is instrumental for neutrophil transmigration across an activated endothelium and for inducible nitric oxide synthase production upon HGF stimulation. Consequently, HGF/MET-dependent nitric oxide release by neutrophils promotes cancer cell killing, which abates tumour growth and metastasis. After systemic administration of a MET kinase inhibitor, we prove that the therapeutic benefit of MET targeting in cancer cells is partly countered by the pro-tumoural effect arising from MET blockade in neutrophils. Our work identifies an unprecedented role of MET in neutrophils, suggests a potential ‘Achilles’ heel’ of MET-targeted therapies in cancer, and supports the rationale for evaluating anti-MET drugs in certain inflammatory diseases.
Flow Cytometry
Uddin, M. N., et al. (2014). "TNF-alpha-dependent hematopoiesis following Bcl11b deletion in T cells restricts metastatic melanoma" J Immunol 192(4): 1946-1953.
PubMed
Using several tumor models, we demonstrate that mice deficient in Bcl11b in T cells, although having reduced numbers of T cells in the peripheral lymphoid organs, developed significantly less tumors compared with wild-type mice. Bcl11b(-/-) CD4(+) T cells, with elevated TNF-alpha levels, but not the Bcl11b(-/-) CD8(+) T cells, were required for the reduced tumor burden, as were NK1.1(+) cells, found in increased numbers in Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice. Among NK1.1(+) cells, the NK cell population was predominant in number and was the only population displaying elevated granzyme B levels and increased degranulation, although not increased proliferation. Although the number of myeloid-derived suppressor cells was increased in the lungs with metastatic tumors of Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice, their arginase-1 levels were severely reduced. The increase in NK cell and myeloid-derived suppressor cell numbers was associated with increased bone marrow and splenic hematopoiesis. Finally, the reduced tumor burden, increased numbers of NK cells in the lung, and increased hematopoiesis in Bcl11b(F/F)/CD4-Cre mice were all dependent on TNF-alpha. Moreover, TNF-alpha treatment of wild-type mice also reduced the tumor burden and increased hematopoiesis and the numbers and activity of NK cells in the lung. In vitro treatment with TNF-alpha of lineage-negative hematopoietic progenitors increased NK and myeloid differentiation, further supporting a role of TNF-alpha in promoting hematopoiesis. These studies reveal a novel role for TNF-alpha in the antitumor immune response, specifically in stimulating hematopoiesis and increasing the numbers and activity of NK cells.
Flow Cytometry
Walsh, K. B., et al. (2014). "Animal model of respiratory syncytial virus: CD8+ T cells cause a cytokine storm that is chemically tractable by sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor agonist therapy" J Virol 88(11): 6281-6293.
PubMed
The cytokine storm is an intensified, dysregulated, tissue-injurious inflammatory response driven by cytokine and immune cell components. The cytokine storm during influenza virus infection, whereby the amplified innate immune response is primarily responsible for pulmonary damage, has been well characterized. Now we describe a novel event where virus-specific T cells induce a cytokine storm. The paramyxovirus pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) is a model of human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV). Unexpectedly, when C57BL/6 mice were infected with PVM, the innate inflammatory response was undetectable until day 5 postinfection, at which time CD8(+) T cells infiltrated into the lung, initiating a cytokine storm by their production of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Administration of an immunomodulatory sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 (S1P1R) agonist significantly inhibited PVM-elicited cytokine storm by blunting the PVM-specific CD8(+) T cell response, resulting in diminished pulmonary disease and enhanced survival. IMPORTANCE: A dysregulated overly exuberant immune response, termed a “cytokine storm,” accompanies virus-induced acute respiratory diseases (VARV), is primarily responsible for the accompanying high morbidity and mortality, and can be controlled therapeutically in influenza virus infection of mice and ferrets by administration of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor (S1P1R) agonists. Here, two novel findings are recorded. First, in contrast to influenza infection, where the cytokine storm is initiated early by the innate immune system, for pneumonia virus of mice (PVM), a model of RSV, the cytokine storm is initiated late in infection by the adaptive immune response: specifically, by virus-specific CD8 T cells via their release of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. Blockading these cytokines with neutralizing antibodies blunts the cytokine storm and protects the host. Second, PVM infection is controlled by administration of an S1P1R agonist.
Immunofluorescence
Schwager, K., et al. (2013). "The immunocytokine L19-IL2 eradicates cancer when used in combination with CTLA-4 blockade or with L19-TNF" J Invest Dermatol 133(3): 751-758.
PubMed
Systemic high-dose IL2 promotes long-term survival in a subset of metastatic melanoma patients, but this treatment is accompanied by severe toxicities. The immunocytokine L19-IL2, in which IL2 is fused to the human L19 antibody capable of selective accumulation on tumor neovasculature, has recently shown encouraging clinical activity in patients with metastatic melanoma. In this study, we have investigated the therapeutic performance of L19-IL2, administered systemically in combination with a murine anti-CTLA-4 antibody or with a second clinical-stage immunocytokine (L19-TNF) in two syngeneic immunocompetent mouse models of cancer. We observed complete tumor eradications when L19-IL2 was used in combination with CTLA-4 blockade. Interestingly, mice cured from F9 tumors developed new lesions when rechallenged with tumor cells after therapy, whereas mice cured from CT26 tumors were resistant to tumor rechallenge. Similarly, L19-IL2 induced complete remissions when administered in a single intratumoral injection in combination with L19-TNF, whereas the two components did not lead to cures when administered as single agents. These findings provide a rationale for combination trials in melanoma, as the individual therapeutic agents have been extensively studied in clinical trials, and the antigen recognized by the L19 antibody has an identical sequence in mouse and man.
Flow Cytometry
Cyktor, J. C., et al. (2013). "Clonal expansions of CD8+ T cells with IL-10 secreting capacity occur during chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection" PLoS One 8(3): e58612.
PubMed
The exact role of CD8(+) T cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection has been heavily debated, yet it is generally accepted that CD8(+) T cells contribute to protection against Mtb. In this study, however, we show that the Mtb-susceptible CBA/J mouse strain accumulates large numbers of CD8(+) T cells in the lung as infection progresses, and that these cells display a dysfunctional and immunosuppressive phenotype (PD-1(+), Tim-3(+), CD122(+)). CD8(+) T cell expansions from the lungs of Mtb-infected CBA/J mice were also capable of secreting the immunosuppressive cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), although in vivo CD8(+) T cell depletion did not significantly alter Mtb burden. Further analysis revealed that pulmonary CD8(+) T cells from Mtb-infected CBA/J mice were clonally expanded, preferentially expressing T cell receptor (TcR) Vbeta chain 8 (8.2, 8.3) or Vbeta 14. Although Vbeta8(+) CD8(+) T cells were responsible for the majority of IL-10 production, in vivo depletion of Vbeta8(+) did not significantly change the outcome of Mtb infection, which we hypothesize was a consequence of their dual IL-10/IFN-gamma secreting profiles. Our data demonstrate that IL-10-secreting CD8(+) T cells can arise during chronic Mtb infection, although the significance of this T cell population in tuberculosis pathogenesis remains unclear.
Flow Cytometry
Hafalla, J. C., et al. (2012). "The CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways independently regulate host resistance to Plasmodium-induced acute immune pathology" PLoS Pathog 8(2): e1002504.
PubMed
The balance between pro-inflammatory and regulatory immune responses in determining optimal T cell activation is vital for the successful resolution of microbial infections. This balance is maintained in part by the negative regulators of T cell activation, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L, which dampen effector responses during chronic infections. However, their role in acute infections, such as malaria, remains less clear. In this study, we determined the contribution of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L to the regulation of T cell responses during Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA)-induced experimental cerebral malaria (ECM) in susceptible (C57BL/6) and resistant (BALB/c) mice. We found that the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T cells correlates with the extent of pro-inflammatory responses induced during PbA infection, being higher in C57BL/6 than in BALB/c mice. Thus, ECM develops despite high levels of expression of these inhibitory receptors. However, antibody-mediated blockade of either the CTLA-4 or PD-1/PD-L1, but not the PD-1/PD-L2, pathways during PbA-infection in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice resulted in higher levels of T cell activation, enhanced IFN-gamma production, increased intravascular arrest of both parasitised erythrocytes and CD8(+) T cells to the brain, and augmented incidence of ECM. Thus, in ECM-resistant BALB/c mice, CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 represent essential, independent and non-redundant pathways for maintaining T cell homeostasis during a virulent malaria infection. Moreover, neutralisation of IFN-gamma or depletion of CD8(+) T cells during PbA infection was shown to reverse the pathologic effects of regulatory pathway blockade, highlighting that the aetiology of ECM in the BALB/c mice is similar to that in C57BL/6 mice. In summary, our results underscore the differential and complex regulation that governs immune responses to malaria parasites.