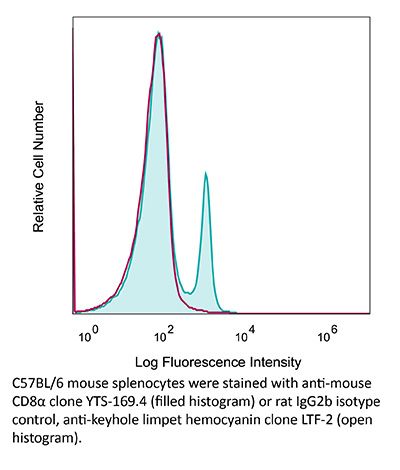
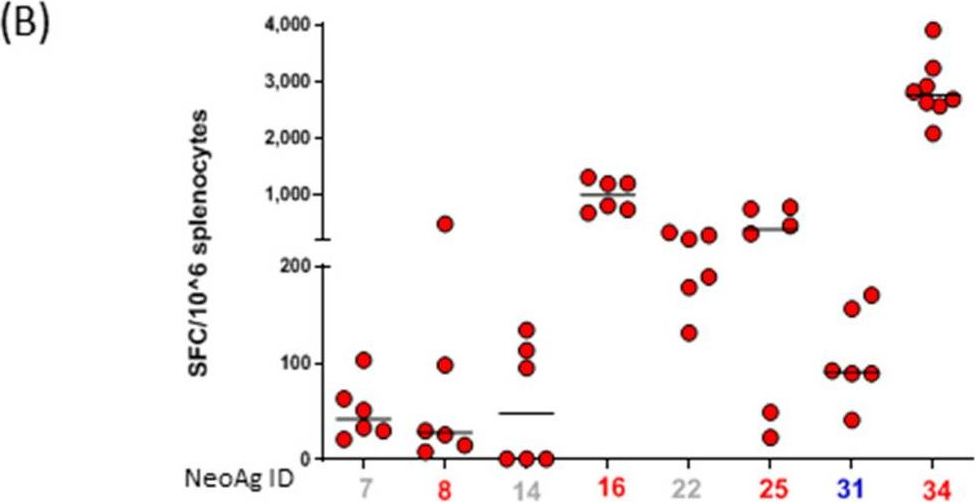
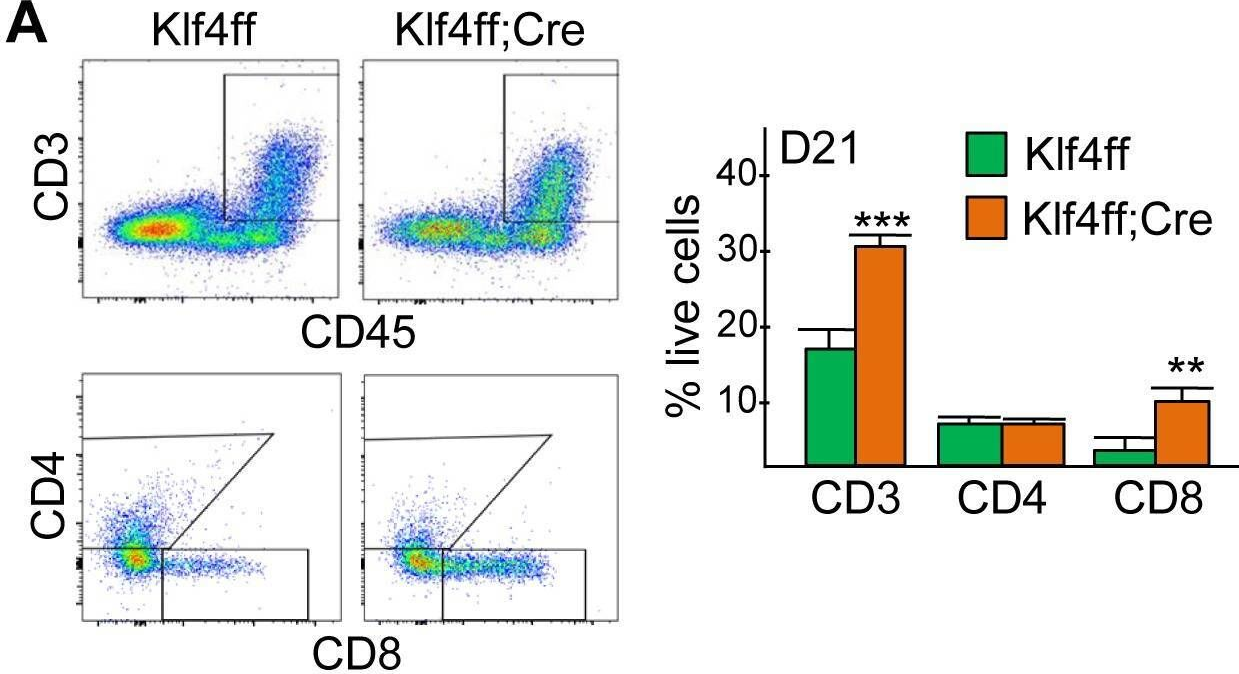
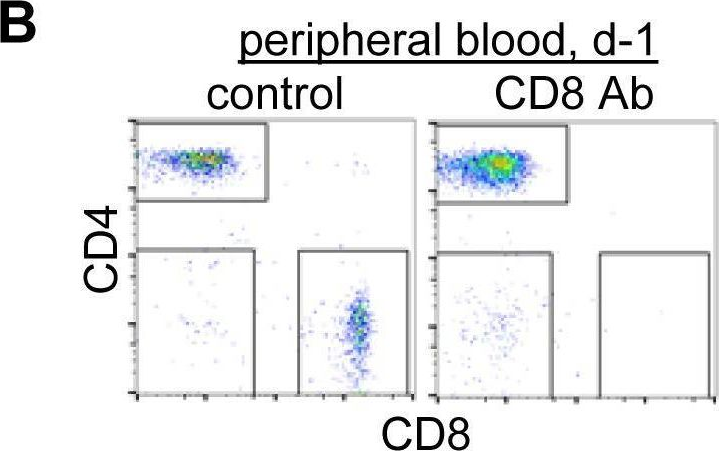
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD8α
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | CBA mouse thymocytes |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10950145 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Vashist, N., et al (2018). "Influenza-Activated ILC1s Contribute to Antiviral Immunity Partially Influenced by Differential GITR Expression" Front Immunol 9: 505.
PubMed
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) represent diversified subsets of effector cells as well as immune regulators of mucosal immunity and are classified into group 1 ILCs, group 2 ILCs, and group 3 ILCs. Group 1 ILCs encompass natural killer (NK) cells and non-NK ILCs (ILC1s) and mediate their functionality via the rapid production of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. The current knowledge of ILC1s mainly associates them to inflammatory processes. Much less is known about their regulation during infection and their capacity to interact with cells of the adaptive immune system. The present study dissected the role of ILC1s during early influenza A virus infection, thereby revealing their impact on the antiviral response. Exploiting in vitro and in vivo H1N1 infection systems, a cross-talk of ILC1s with cells of the innate and the adaptive immunity was demonstrated, which contributes to anti-influenza immunity. A novel association of ILC1 functionality and the expression of the glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) was observed, which hints toward a so far undescribed role of GITR in regulating ILC1 responsiveness. Overexpression of GITR inhibits IFN-gamma production by ILC1s, whereas partial reduction of GITR expression can reverse this effect, thereby regulating ILC1 functionality. These new insights into ILC1 biology define potential intervention targets to modulate the functional properties of ILC1s, thus contributing toward the development of new immune interventions against influenza.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Triplett, T. A., et al (2018). "Reversal of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated cancer immune suppression by systemic kynurenine depletion with a therapeutic enzyme" Nat Biotechnol 36(8): 758-764.
PubMed
Increased tryptophan (Trp) catabolism in the tumor microenvironment (TME) can mediate immune suppression by upregulation of interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) and/or ectopic expression of the predominantly liver-restricted enzyme tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). Whether these effects are due to Trp depletion in the TME or mediated by the accumulation of the IDO1 and/or TDO (hereafter referred to as IDO1/TDO) product kynurenine (Kyn) remains controversial. Here we show that administration of a pharmacologically optimized enzyme (PEGylated kynureninase; hereafter referred to as PEG-KYNase) that degrades Kyn into immunologically inert, nontoxic and readily cleared metabolites inhibits tumor growth. Enzyme treatment was associated with a marked increase in the tumor infiltration and proliferation of polyfunctional CD8(+) lymphocytes. We show that PEG-KYNase administration had substantial therapeutic effects when combined with approved checkpoint inhibitors or with a cancer vaccine for the treatment of large B16-F10 melanoma, 4T1 breast carcinoma or CT26 colon carcinoma tumors. PEG-KYNase mediated prolonged depletion of Kyn in the TME and reversed the modulatory effects of IDO1/TDO upregulation in the TME.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Li, Z., et al (2015). "Pre-treatment of allogeneic bone marrow recipients with the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 transiently enhances hematopoietic chimerism without promoting donor-specific skin allograft tolerance" Transpl Immunol 33(2): 125-129.
PubMed
Hematopoietic chimerism established by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is known to promote donor-specific organ allograft tolerance; however, clinical application is limited by the need for toxic host conditioning and “megadoses” of donor bone marrow cells. A potential solution to this problem has been suggested by the observation that recipient bone marrow mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 promotes chimerism in congenic bone marrow transplantation experiments in mice. Here we report that a single subcutaneous dose of 10mg/kg AMD3100 in recipient C57BL/6 mice was able to enhance hematopoietic chimerism when complete MHC-mismatched BALB/c donor bone marrow cells were transplanted 1h after drug dosing. However, levels of chimerism measured 30days post-transplantation were not sustained when mice were reexamined on day 90 post-transplantation. Moreover, transient chimerism induced by this protocol did not support robust donor-specific skin allograft tolerance. Using the same transient immunosuppression protocol, we confirmed that “megadoses” of donor bone marrow cells could induce durable chimerism associated with donor-specific skin allograft tolerance without AMD3100 pre-treatment. We conclude that in this protocol AMD3100 pretreatment may empty bone marrow niches that become reoccupied by allogeneic donor hematopoietic progenitor cells but not by true long-lived donor hematopoietic stem cells, resulting in short-lived chimerism and failure to support durable donor-specific allograft tolerance.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Burrack, K. S., et al (2015). "Myeloid Cell Arg1 Inhibits Control of Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection by Suppressing Antiviral T Cells" PLoS Pathog 11(10): e1005191.
PubMed
Arthritogenic alphaviruses, including Ross River virus (RRV) and chikungunya virus (CHIKV), are responsible for explosive epidemics involving millions of cases. These mosquito-transmitted viruses cause inflammation and injury in skeletal muscle and joint tissues that results in debilitating pain. We previously showed that arginase 1 (Arg1) was highly expressed in myeloid cells in the infected and inflamed musculoskeletal tissues of RRV- and CHIKV-infected mice, and specific deletion of Arg1 from myeloid cells resulted in enhanced viral control. Here, we show that Arg1, along with other genes associated with suppressive myeloid cells, is induced in PBMCs isolated from CHIKV-infected patients during the acute phase as well as the chronic phase, and that high Arg1 expression levels were associated with high viral loads and disease severity. Depletion of both CD4 and CD8 T cells from RRV-infected Arg1-deficient mice restored viral loads to levels detected in T cell-depleted wild-type mice. Moreover, Arg1-expressing myeloid cells inhibited virus-specific T cells in the inflamed and infected musculoskeletal tissues, but not lymphoid tissues, following RRV infection in mice, including suppression of interferon-gamma and CD69 expression. Collectively, these data enhance our understanding of the immune response following arthritogenic alphavirus infection and suggest that immunosuppressive myeloid cells may contribute to the duration or severity of these debilitating infections.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Carmi, Y., et al (2015). "Allogeneic IgG combined with dendritic cell stimuli induce antitumour T-cell immunity" Nature 521(7550): 99-104.
PubMed
Whereas cancers grow within host tissues and evade host immunity through immune-editing and immunosuppression, tumours are rarely transmissible between individuals. Much like transplanted allogeneic organs, allogeneic tumours are reliably rejected by host T cells, even when the tumour and host share the same major histocompatibility complex alleles, the most potent determinants of transplant rejection. How such tumour-eradicating immunity is initiated remains unknown, although elucidating this process could provide the basis for inducing similar responses against naturally arising tumours. Here we find that allogeneic tumour rejection is initiated in mice by naturally occurring tumour-binding IgG antibodies, which enable dendritic cells (DCs) to internalize tumour antigens and subsequently activate tumour-reactive T cells. We exploited this mechanism to treat autologous and autochthonous tumours successfully. Either systemic administration of DCs loaded with allogeneic-IgG-coated tumour cells or intratumoral injection of allogeneic IgG in combination with DC stimuli induced potent T-cell-mediated antitumour immune responses, resulting in tumour eradication in mouse models of melanoma, pancreas, lung and breast cancer. Moreover, this strategy led to eradication of distant tumours and metastases, as well as the injected primary tumours. To assess the clinical relevance of these findings, we studied antibodies and cells from patients with lung cancer. T cells from these patients responded vigorously to autologous tumour antigens after culture with allogeneic-IgG-loaded DCs, recapitulating our findings in mice. These results reveal that tumour-binding allogeneic IgG can induce powerful antitumour immunity that can be exploited for cancer immunotherapy.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Wensveen, F. M., et al (2015). "NK cells link obesity-induced adipose stress to inflammation and insulin resistance" Nat Immunol 16(4): 376-385.
PubMed
An important cause of obesity-induced insulin resistance is chronic systemic inflammation originating in visceral adipose tissue (VAT). VAT inflammation is associated with the accumulation of proinflammatory macrophages in adipose tissue, but the immunological signals that trigger their accumulation remain unknown. We found that a phenotypically distinct population of tissue-resident natural killer (NK) cells represented a crucial link between obesity-induced adipose stress and VAT inflammation. Obesity drove the upregulation of ligands of the NK cell-activating receptor NCR1 on adipocytes; this stimulated NK cell proliferation and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production, which in turn triggered the differentiation of proinflammatory macrophages and promoted insulin resistance. Deficiency of NK cells, NCR1 or IFN-gamma prevented the accumulation of proinflammatory macrophages in VAT and greatly ameliorated insulin sensitivity. Thus NK cells are key regulators of macrophage polarization and insulin resistance in response to obesity-induced adipocyte stress.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Krupnick, A. S., et al (2014). "Central memory CD8+ T lymphocytes mediate lung allograft acceptance" J Clin Invest 124(3): 1130-1143.
PubMed
Memory T lymphocytes are commonly viewed as a major barrier for long-term survival of organ allografts and are thought to accelerate rejection responses due to their rapid infiltration into allografts, low threshold for activation, and ability to produce inflammatory mediators. Because memory T cells are usually associated with rejection, preclinical protocols have been developed to target this population in transplant recipients. Here, using a murine model, we found that costimulatory blockade-mediated lung allograft acceptance depended on the rapid infiltration of the graft by central memory CD8+ T cells (CD44(hi)CD62L(hi)CCR7+). Chemokine receptor signaling and alloantigen recognition were required for trafficking of these memory T cells to lung allografts. Intravital 2-photon imaging revealed that CCR7 expression on CD8+ T cells was critical for formation of stable synapses with antigen-presenting cells, resulting in IFN-gamma production, which induced NO and downregulated alloimmune responses. Thus, we describe a critical role for CD8+ central memory T cells in lung allograft acceptance and highlight the need for tailored approaches for tolerance induction in the lung.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Pastille, E., et al (2014). "Transient ablation of regulatory T cells improves antitumor immunity in colitis-associated colon cancer" Cancer Res 74(16): 4258-4269.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Treg) are supportive to cancer development in most tissues, but their role in colitis-associated colon cancer (CAC) remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) Treg in a mouse model of CAC and in patients with colon cancer. These Treg were increased strongly in number in a mouse model of CAC and in the peripheral blood of patients with colon cancer, exhibiting an activated phenotype as defined by elevated expression of GARP, CD103, CTLA-4, and IL10, along with an increased suppressive effect on the proliferation and Th1 cytokine expression of CD4(+)CD25(-) responder T cells ex vivo. Transient ablation of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) Treg during tumor development in the CAC model suppressed tumor outgrowth and distribution, accompanied by an increased number of CD8(+)IFNgamma/granzyme B-producing effector T cells. Conversely, inactivation of IL10 in Treg did not elevate the antitumor response but instead further boosted tumor development. Our results establish a tumor-promoting function for Treg during CAC formation, but they also suggest that a selective, transient ablation of Treg can evoke antitumor responses, with implications for immunotherapeutic interventions in patients with CAC.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Dai, M., et al (2013). "Long-lasting complete regression of established mouse tumors by counteracting Th2 inflammation" J Immunother 36(4): 248-257.
PubMed
40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.”}” data-sheets-userformat=”{“2″:14851,”3”:{“1″:0},”4”:{“1″:2,”2″:16777215},”12″:0,”14”:{“1″:2,”2″:1521491},”15″:”Roboto, sans-serif”,”16″:12}”>Mice with intraperitoneal ID8 ovarian carcinoma or subcutaneous SW1 melanoma were injected with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to CD137PD-1CTLA4 7-15 days after tumor initiation. Survival of mice with ID8 tumors tripled and >40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Bivas-Benita, M., et al (2013). "Airway CD8(+) T cells induced by pulmonary DNA immunization mediate protective anti-viral immunity" Mucosal Immunol 6(1): 156-166.
PubMed
Vaccination strategies for protection against a number of respiratory pathogens must induce T-cell populations in both the pulmonary airways and peripheral lymphoid organs. In this study, we show that pulmonary immunization using plasmid DNA formulated with the polymer polyethyleneimine (PEI-DNA) induced antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells in the airways that persisted long after antigen local clearance. The persistence of the cells was not mediated by local lymphocyte proliferation or persistent antigen presentation within the lung or airways. These vaccine-induced CD8(+) T cells effectively mediated protective immunity against respiratory challenges with vaccinia virus and influenza virus. Moreover, this protection was not dependent upon the recruitment of T cells from peripheral sites. These findings demonstrate that pulmonary immunization with PEI-DNA is an efficient approach for inducing robust pulmonary CD8(+) T-cell populations that are effective at protecting against respiratory pathogens.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Sledzinska, A., et al (2013). "TGF-beta signalling is required for CD4(+) T cell homeostasis but dispensable for regulatory T cell function" PLoS Biol 11(10): e1001674.
PubMed
TGF-beta is widely held to be critical for the maintenance and function of regulatory T (T(reg)) cells and thus peripheral tolerance. This is highlighted by constitutive ablation of TGF-beta receptor (TR) during thymic development in mice, which leads to a lethal autoimmune syndrome. Here we describe that TGF-beta-driven peripheral tolerance is not regulated by TGF-beta signalling on mature CD4(+) T cells. Inducible TR2 ablation specifically on CD4(+) T cells did not result in a lethal autoinflammation. Transfer of these TR2-deficient CD4(+) T cells to lymphopenic recipients resulted in colitis, but not overt autoimmunity. In contrast, thymic ablation of TR2 in combination with lymphopenia led to lethal multi-organ inflammation. Interestingly, deletion of TR2 on mature CD4(+) T cells does not result in the collapse of the T(reg) cell population as observed in constitutive models. Instead, a pronounced enlargement of both regulatory and effector memory T cell pools was observed. This expansion is cell-intrinsic and seems to be caused by increased T cell receptor sensitivity independently of common gamma chain-dependent cytokine signals. The expression of Foxp3 and other regulatory T cells markers was not dependent on TGF-beta signalling and the TR2-deficient T(reg) cells retained their suppressive function both in vitro and in vivo. In summary, absence of TGF-beta signalling on mature CD4(+) T cells is not responsible for breakdown of peripheral tolerance, but rather controls homeostasis of mature T cells in adult mice.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Krieg, C., et al (2010). "Improved IL-2 immunotherapy by selective stimulation of IL-2 receptors on lymphocytes and endothelial cells" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(26): 11906-11911.
PubMed
IL-2 immunotherapy is an attractive treatment option for certain metastatic cancers. However, administration of IL-2 to patients can lead, by ill-defined mechanisms, to toxic adverse effects including severe pulmonary edema. Here, we show that IL-2-induced pulmonary edema is caused by direct interaction of IL-2 with functional IL-2 receptors (IL-2R) on lung endothelial cells in vivo. Treatment of mice with high-dose IL-2 led to efficient expansion of effector immune cells expressing high levels of IL-2Rbetagamma, including CD8(+) T cells and natural killer cells, which resulted in a considerable antitumor response against s.c. and pulmonary B16 melanoma nodules. However, high-dose IL-2 treatment also affected immune cell lineage marker-negative CD31(+) pulmonary endothelial cells via binding to functional alphabetagamma IL-2Rs, expressed at low to intermediate levels on these cells, thus causing pulmonary edema. Notably, IL-2-mediated pulmonary edema was abrogated by a blocking antibody to IL-2Ralpha (CD25), genetic disruption of CD25, or the use of IL-2Rbetagamma-directed IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes, thereby interfering with IL-2 binding to IL-2Ralphabetagamma(+) pulmonary endothelial cells. Moreover, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes led to vigorous activation of IL-2Rbetagamma(+) effector immune cells, which generated a dramatic antitumor response. Thus, IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complexes might improve current strategies of IL-2-based tumor immunotherapy.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Shariff, H., et al (2010). "Intermittent antibody-based combination therapy removes alloantibodies and achieves indefinite heart transplant survival in presensitized recipients" Transplantation 90(3): 270-278.
PubMed
BACKGROUND: It is well established that primed/memory T cells play a critical role in heart transplant rejection. This contributes to the challenges faced in the transplant clinic because current treatments that are efficient in controlling naive T cell alloresponses have limited efficacy on primed T cell responders. METHODS: Fully MHC-mismatched heart transplantation was performed from BALB/c to C57BL/6 mice presensitized with BALB/c splenocytes 14 days pretransplantation. A combination therapy comprising CD70-, CD154-, and CD8-specific antibodies (Abs) was administered at day 0 and 4 posttransplantation with rapamycin on days 0 to 4. RESULTS: The Ab combination therapy extended heart transplant survival in presensitized recipients from median survival time 8 days (MST) to MST 78 days. A decrease in the number of splenic interferon-gamma-secreting cells measured by ELISpot assay was seen in the treated group compared with the untreated controls. However, graft-infiltrating CD8+ and CD4+ T cells persisted despite treatment and the number of intragraft CD4+ T cells increased at day 30 posttransplantation. When an additional “rescue therapy” comprising the same Abs was readministered at days 30, 60, and 90 posttransplantation, T cell infiltration was reduced and indefinite graft survival was observed. Furthermore, rescue therapy resulted in gradual decrease in titer and, by day 90 posttransplantation, the complete loss of the preexisting, donor-specific Abs. CONCLUSION: We conclude that our Ab combination therapy extends allograft survival in presensitized recipients. When combined with intermittent Ab-mediated rescue therapy, this results in indefinite allograft survival and a loss of the preexisting, donor-specific Abs from the circulation.
in vivo CD8+ T cell depletion
Kish, D. D., et al (2009). "CD8 T cells producing IL-17 and IFN-gamma initiate the innate immune response required for responses to antigen skin challenge" J Immunol 182(10): 5949-5959.
PubMed
Effector CD8 T cell recruitment into the skin in response to Ag challenge requires prior CXCL1/KC-directed neutrophil infiltration. Mechanisms inducing CXCL1 production and the dynamics of neutrophil-CD8 T cell interactions during elicitation of Ag-specific responses in the skin were investigated. CXCL1 and CXCL2/MIP-2 were produced within 3-6 h of Ag challenge at 10-fold higher levels in skin challenge sites of Ag-sensitized vs nonsensitized mice. In the challenge sites of sensitized mice this production decreased at 6-9 h postchallenge to near the levels observed in skin challenge sites of nonsensitized mice but rose to a second peak 12 h after challenge. The elevated early neutrophil chemoattractant production at 3-6 h after skin challenge of sensitized animals required both IFN-gamma and IL-17, produced by distinct populations of Ag-primed CD8 T cells in response to Ag challenge. Although induced by the Ag-primed CD8 T cells, the early CXCL1 and CXCL2 production was accompanied by neutrophil but not CD8 T cell infiltration into the skin Ag challenge site. Infiltration of the CD8 T cells into the challenge site was not observed until 18-24 h after challenge. These results demonstrate an intricate series of early interactions between Ag-specific and innate immune components that regulate the sequential infiltration of neutrophils and then effector T cells into the skin to mediate an immune response.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
NOTCH1 reverses immune suppression in small cell lung cancer through reactivation of STING.
In J Clin Invest on 16 September 2025 by Kim, Y. S., Nabet, B. Y., et al.
PubMed
Downregulation of antigen presentation and lack of immune infiltration are defining features of small cell lung cancer (SCLC), limiting response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). While a high-MHC class I, immune-inflamed subset benefits from ICB, underlying mechanisms of immune response in SCLC have yet to be elucidated. Here we show that in the IMpower133 clinical trial, high, but not low, NOTCH1 expression was significantly associated with longer survival with the addition of ICB to chemotherapy among approximately 80% of SCLC patients with NE-enriched tumors (ASCL1-enriched, HR 0.39, P = 0.0012; NEUROD1-enriched, HR 0.44, P = 0.024). Overexpression or pharmacologic activation of NOTCH1 in ASCL1 and NEUROD1 SCLC cell lines dramatically upregulated MHC class I through epigenetic reactivation of STING. In syngeneic mouse models, Notch1 activation reprogrammed SCLC tumors from immune-excluded to immune-inflamed, facilitating durable, complete responses with ICB combined with a STING agonist. STING1 expression was significantly enriched in high- compared with low-NOTCH1-expressing tumors in IMpower133, validating our proposed mechanism. Our data reveal a previously undiscovered role for NOTCH1 as a critical driver of SCLC immunogenicity and a potential predictive biomarker for ICB in SCLC. NOTCH1 activation may be a therapeutic strategy to unleash antitumor immune responses in SCLC and other neuroendocrine cancers in which NOTCH1 is typically suppressed.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Selective Alanine Transporter Utilization Is a Therapeutic Vulnerability in ARID1A-Mutant Ovarian Cancer.
In Cancer Res on 15 September 2025 by Nie, H., Liao, L., et al.
PubMed
Subunits of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex are altered in ∼20% of human cancers. Exemplifying the alterations is the ARID1A mutation that occurs in ∼50% of ovarian clear-cell carcinoma (OCCC), a disease with limited therapeutic options. In this study, we showed that ARID1A mutations create a dependence on alanine by regulating alanine transporters to increase intracellular alanine levels. ARID1A directly repressed the alanine importer SLC38A2 and simultaneously promoted the alanine exporter SLC7A8. ARID1A inactivation increased alanine utilization predominantly in protein synthesis and passively through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Indeed, ARID1A-mutant OCCCs were hypersensitive to the inhibition of SLC38A2. In addition, SLC38A2 inhibition enhanced chimeric antigen receptor T-cell assault in vitro and synergized with immune checkpoint blockade using an anti-PD-L1 antibody in a genetically engineered mouse model of OCCC driven by conditional Arid1a inactivation in a CD8+ T-cell-dependent manner. These findings suggest that targeting alanine transport alone or in combination with immunotherapy may represent an effective therapeutic strategy for ARID1A-mutant cancers.
-
-
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Enhancing immunotherapy efficacy in NSCLC through the combined use of phenelzine and Akkermansia muciniphila to regulate gut microbial metabolite 5-HIAA.
In J Immunother Cancer on 10 September 2025 by Sun, S., Wang, L., et al.
PubMed
Improving the efficacy of anti-programmed death 1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy remains a major challenge for cancer immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Gut microbial metabolites can influence immunotherapy efficacy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Identification of anti-TIM-3 based checkpoint inhibitor combinations with activity in immunotherapy refractory melanoma models.
In J Immunother Cancer on 18 August 2025 by Phadke, M. S., Li, J., et al.
PubMed
A significant percentage of melanomas are refractory to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) monotherapies and combinations. As there are currently no effective second-line therapies available for ICI-resistant patients, we sought to identify novel checkpoint inhibitor combinations for future clinical evaluation.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
TIM3+ breast cancer cells license immune evasion during micrometastasis outbreak.
In Cancer Cell on 11 August 2025 by Rozalén, C., Sangrador, I., et al.
PubMed
In metastasis, the dynamics of tumor-immune interactions during micrometastasis remain unclear. Identifying the vulnerabilities of micrometastases before outbreaking into macrometastases can reveal therapeutic opportunities for metastasis. Here, we report a function of T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM3) in tumor cells during micrometastasis using breast cancer (BC) metastasis mouse models. TIM3 is highly upregulated in micrometastases, promoting survival, stemness, and immune escape. TIM3+ tumor cells are specifically selected during early seeding of micrometastasis. Mechanistically, TIM3 increases β-catenin/interleukin-1β (IL-1β) signaling, leading to stemness and immune-evasion by inducing immunosuppressive γδ T cells and reducing CD8 T cells during micrometastasis. Clinical data confirm increased TIM3+ tumor cells in BC metastasis and TIM3+ tumor cells as a biomarker of poor outcome in BC patients. (Neo)adjuvant TIM3 blockade reduces the metastatic seeding and incidence in preclinical models. These findings unveil a specific mechanism of micrometastasis immune-evasion and the potential use of TIM3 blockade for subclinical metastasis.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Augment proteasome inhibitor efficacy activates CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity in breast cancer.
In Cell Rep Med on 15 July 2025 by Tang, D., Lin, S., et al.
PubMed
Although three proteasome inhibitors are used for liquid tumor treatment, their effectiveness against solid tumors remains inadequate. To address this issue, we employ a drug combination strategy and discover that ammonium tetrathiomolybdate (TM) and AMD3100 can sensitize solid cancer cell lines to proteasome inhibitors. Mechanistically, we find that TM and AMD3100 reduce proteasome activity by decreasing the protein level of PSMB5. This reduction occurs through the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation. Notably, our in vivo studies reveal that drug combinations retard tumor growth dependent on CD8+ T cells. The combination of bortezomib with TM or AMD3100 induces cancer cell antigen presentation and the production of CCL5, which together stimulate the recruitment and generation of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. This study identifies synergistic lethal pairs that enhance the effectiveness of bortezomib-centered therapy for breast cancer treatment in a way relied on intact immune system.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Tumor-intrinsic ENO1 inhibition promotes antitumor immune response and facilitates the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in bladder cancer.
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 15 July 2025 by Shen, C., Liu, J., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, yet understanding immunotherapy resistance mechanisms remains challenging. Here, a CRISPR cas9 screening in vivo and an RNA-sequencing for clinical immunotherapy resistance BC samples identified enolase 1 (ENO1) as a potent regulator of anti-PD-L1 treatment efficacy. Investigation of clinical BC samples demonstrated a correlation between ENO1 overexpression and immune evasion in BC, evidenced by reduced CD8+ T cell infiltration and resistance to anti-PD-L1 therapy. Increased CD8+ T cell infiltration and function were indicative of antitumor immunity, which was elicited by ENO1 knockdown, which also suppressed carcinogenesis. Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrated that wild-type (WT) and ENO1 knockout (KO) tumors have different immune cell compositions with the latter preferring an immunostimulatory microenvironment. Mechanistically, ENO1 regulated CD8+ T cell function and tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) polarization via the SPP1-ITGA4/ITGB1 pathway in the TME. Importantly, genetic and pharmacological inhibition of ENO1 sensitizes tumors to anti-tumor immunity and synergizes with anti-PD-L1 therapy. The results highlight tumor-intrinsic ENO1 as a critical regulator of tumor immune evasion in BC. Targeting ENO1 enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade therapy by promoting antitumor immunity.
-
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Oligodendrocyte-derived IL-33 regulates self-reactive CD8+ T cells in CNS autoimmunity.
In J Exp Med on 7 July 2025 by Fonta, N., Page, N., et al.
PubMed
In chronic inflammatory disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), tissue-resident self-reactive T cells perpetuate disease. The specific tissue factors governing the persistence and continuous differentiation of these cells remain undefined but could represent attractive therapeutic targets. In a model of chronic CNS autoimmunity, we find that oligodendrocyte-derived IL-33, an alarmin, is key for locally regulating the pathogenicity of self-reactive CD8+ T cells. The selective ablation of IL-33 from neo-self-antigen-expressing oligodendrocytes mitigates CNS disease. In this context, fewer self-reactive CD8+ T cells persist in the inflamed CNS, and the remaining cells are impaired in generating TCF-1low effector cells. Importantly, interventional IL-33 blockade by locally administered somatic gene therapy reduces T cell infiltrates and improves the disease course. Our study identifies oligodendrocyte-derived IL-33 as a druggable tissue factor regulating the differentiation and survival of self-reactive CD8+ T cells in the inflamed CNS. This finding introduces tissue factors as a novel category of immune targets for treating chronic CNS autoimmune diseases.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Activated T Cells Break Tumor Immunosuppression by Macrophage Reeducation.
In Cancer Discov on 3 July 2025 by Trotta, R., Rivis, S., et al.
PubMed
In this study, we observe that in human and murine melanomas, T-cell activation abates hematopoietic prostaglandin-D2 synthase (HPGDS) transcription in tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) through TNFα signaling. Mechanistically, HPGDS installs a prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) autocrine loop in TAMs via DP1 and DP2 activation that sustains their protumoral phenotype and promotes paracrine inhibition of CD8+ T cells via a PGD2-DP1 axis. Genetic or pharmacologic HPGDS targeting induces antitumoral features in TAMs and favors CD8+ T-cell recruitment, activation, and cytotoxicity, altogether sensitizing tumors to αPD1. Conversely, HPGDS overexpression in TAMs or systemic TNFα blockade sustains a protumoral environment and αPD1 resistance, preventing the downregulation of HPGDS by T cells. Congruently, patients and mice resistant to αPD1 fail to suppress HPGDS in TAMs, reinforcing the evidence that circumventing HPGDS is necessary for efficient αPD1 treatment. Overall, we disclose a mechanism whereby T-cell activation controls the innate immune system, and we suggest HPGDS/PGD2 targeting to overcome immunotherapy resistance.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Ex vivo engineering of phagocytic signals in breast cancer cells for a whole tumor cell-based vaccine.
In BMC Cancer on 1 July 2025 by Martí-Díaz, R., Sánchez-del-Campo, L., et al.
PubMed
Today, cell therapies are constantly evolving and providing new options for cancer patients. These therapies are mostly based on the inoculation of immune cells extracted from a person's own tumor; however, some studies using whole tumor cell-based vaccines are approaching the level of maturity required for clinical use. Although these latest therapies will have to be developed further and adapted to overcome many ethical barriers, there is no doubt that therapeutic cancer vaccines are the next frontier of immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
STAT5 and STAT3 balance shapes dendritic cell function and tumour immunity.
In Nature on 1 July 2025 by Zhou, J., Tison, K., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) has transformed cancer therapy1,2. The efficacy of immunotherapy depends on dendritic cell-mediated tumour antigen presentation, T cell priming and activation3,4. However, the relationship between the key transcription factors in dendritic cells and ICB efficacy remains unknown. Here we found that ICB reprograms the interplay between the STAT3 and STAT5 transcriptional pathways in dendritic cells, thereby activating T cell immunity and enabling ICB efficacy. Mechanistically, STAT3 restrained the JAK2 and STAT5 transcriptional pathway, determining the fate of dendritic cell function. As STAT3 is often activated in the tumour microenvironment5, we developed two distinct PROTAC (proteolysis-targeting chimera) degraders of STAT3, SD-36 and SD-2301. STAT3 degraders effectively degraded STAT3 in dendritic cells and reprogrammed the dendritic cell-transcriptional network towards immunogenicity. Furthermore, STAT3 degrader monotherapy was efficacious in treatment of advanced tumours and ICB-resistant tumours without toxicity in mice. Thus, the crosstalk between STAT3 and STAT5 transcriptional pathways determines the dendritic cell phenotype in the tumour microenvironment and STAT3 degraders hold promise for cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
IL-2 immunotherapy rescues irradiation-induced T cell exhaustion in mouse colon cancer.
In iScience on 20 June 2025 by Yong, C. S. M., Telarovic, I., et al.
PubMed
Radiotherapy (RT) can stimulate anti-cancer T cell responses, and cytokines, notably interleukin-2 (IL-2), are necessary for optimal T cell function and memory. However, timing and IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) bias of IL-2 signals are ill-defined. Using image-guided RT in a mouse colon cancer model, we observed single high-dose (20 Gy) RT transiently upregulated IL-2Rα (CD25) on effector CD8+ T cells, facilitating the use of CD25-biased IL-2 immunotherapy. Timed administration of CD25-biased IL-2 treatment after RT favored intratumoral expansion of CD8+ T cells over regulatory T cells, which resulted in comparable anti-tumor effects as with RT plus IL-2Rβ (CD122)-biased IL-2 immunotherapy. Moreover, intratumoral CD8+ T cells of animals receiving combined IL-2R-biased IL-2 and RT showed reduced markers of exhaustion. These combination treatments affected both primary irradiated and distant non-irradiated tumors and achieved durable responses. We demonstrate that timed IL-2R subunit-biased IL-2 immunotherapy synergizes with single high-dose RT to achieve potent anti-cancer immunity.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Biologically targeted dual adaptive and innate nano-Immunotherapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma treatment.
In Mol Cancer on 18 June 2025 by Au, K. M., Li, S., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapy treatments have significantly improved metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treatment outcomes. Despite recent advancements, the rates of durable response to immunotherapy remain low, and the toxicity profiles of treatment continue to be high. To address these challenges, we report the development of a human carbonic anhydrase-IX (hCA-9)-targeted multifunctional immunotherapy nanoparticles (MINPs) aimed at improving treatment efficacy and reducing toxicity. We hypothesized that these MINPs will facilitate the recognition and elimination of hCA-9-expressing tumor cells by both adaptive immune cells (cytotoxic CD8+ T cells) and innate immune cells (natural killer (NK) cells).
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
GPX4 knockdown suppresses M2 macrophage polarization in gastric cancer by modulating kynurenine metabolism.
In Theranostics on 14 May 2025 by Xu, J., Weng, C., et al.
PubMed
Background: Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), an important factor regulating redox homeostasis, plays an important role in tumor microenvironment and progression. However, the role of GPX4 in gastric cancer (GC) is unclear. Methods: Spectral flow cytometry and multiplex immunohistochemistry were employed to assess the correlation between GPX4 expression and immune cell infiltration. Metabolomics analysis of conditioned media from GPX4 knockdown NUGC3 cells identified metabolic alterations. Additionally, both in vitro and in vivo functional studies were conducted to elucidate the mechanistic role of GPX4 in regulating the tumor microenvironment and progression. Results: Knockdown of GPX4 in GC cells inhibited tumor growth, enhanced CD8+ T cell infiltration, and suppressed the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) toward the pro-tumor M2 phenotype. Multiplex immunohistochemistry revealed a positive correlation between GPX4 expression and M2 macrophage infiltration in clinical samples from patients with GC. Metabolomics revealed that GPX4 knockdown regulate kynurenine metabolism pathway. Furthermore, mechanistic studies reveal that GPX4 silencing elevates lipid peroxidation, triggering the conversion of KYNU ubiquitin chain modifications from K48 to K63. Such ubiquitination remodeling stabilizes KYNU expression (a key kynurenine-metabolizing enzyme), reduces kynurenine accumulation, and ultimately reprograms TAM polarization to enhance antitumor immunity. We also identified that the K96 and K163 sites are important for KYNU's modification by K48 and K63 ubiquitin chains. Conclusion: Our study not only affirm the role of GPx4 in GC progression but also highlight it as a promising target for reshaping the immune microenvironment.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Palmitoylation prevents B7-H4 lysosomal degradation sustaining tumor immune evasion.
In Nat Commun on 8 May 2025 by Yan, Y., Yu, J., et al.
PubMed
B7-H4 functions as an immune checkpoint in the tumor microenvironment (TME). However, the post-translational modification (PTM) of B7-H4 and its translational potential in cancer remains incompletely understood. We find that ZDHHC3, a zinc finger DHHC-type palmitoyltransferase, palmitoylates B7-H4 at Cys130 in breast cancer cells, preventing its lysosomal degradation and sustaining B7-H4-mediated immunosuppression. Knockdown of ZDHHC3 in tumors results in robust anti-tumor immunity and reduces tumor progression in murine models. Moreover, abemaciclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, primes lysosome activation and promotes lysosomal degradation of B7-H4 independently of the tumor cell cycle. Treatment with abemaciclib results in T cell activation and mitigates B7-H4-mediated immune suppression via inducing B7-H4 degradation in preclinical tumor models. Thus, B7-H4 palmitoylation is an important PTM controlling B7-H4 protein stability and abemaciclib may be repurposed to promote B7-H4 degradation, thereby treating patients with B7-H4 expressing tumors.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
T-cell-derived IFN-γ suppresses T follicular helper cell differentiation and antibody responses.
In EMBO J on 1 May 2025 by Sala, E., Nelli, M., et al.
PubMed
CD4+ T cells play a critical role in antiviral humoral and cellular immune responses. We have previously reported that subcutaneous lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (s.c. LCMV) infection is characterized by a stark compartmentalization of CD4+ T cells, leading to strong TH1 cell polarization but virtually absent T follicular helper (TFH) cells, key drivers of humoral immunity. Here, we investigate the mechanisms responsible for this impaired TFH differentiation. We show that T-bet+ cells induced by LCMV infection encompass a TH1 cell subset expressing granzyme B (GzmB), and a Tcf-1+ cell subset that retains the potential for TFH differentiation without expressing mature TFH markers. Notably, IFN-γ blockade enables full differentiation of Tcf-1+ cells into TFH cells, formation of germinal centers, and increased antibody production. Suppression of TFH cells by IFN-γ is not directly mediated by CD4+ T cells but rather involves another cell type, likely dendritic cells (DCs). Our study provides novel insights into the mechanisms underlying early CD4+ T-cell polarization and humoral responses to viruses, with the potential to facilitate the development of effective vaccine strategies.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Activating the CXCR3/CXCL10 pathway overrides tumor immune suppression by enhancing immune trafficking and effector cell priming in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
In bioRxiv on 28 April 2025 by Shinn, C. K., Saddawi-Konefka, R., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Cholangiocarcinoma PDHA1 succinylation suppresses macrophage antigen presentation via alpha-ketoglutaric acid accumulation.
In Nat Commun on 3 April 2025 by Zhang, N., Sun, L., et al.
PubMed
Gemcitabine combined with cisplatin is the first-line chemotherapy for advanced cholangiocarcinoma, but drug resistance remains a challenge, leading to unsatisfactory therapeutic effect. Here, we elucidate the possibility of chemotherapy regimens sensitized by inhibiting succinylation in patients with cholangiocarcinoma from the perspective of post-translational modification. Our omics analysis reveals that succinylation of PDHA1 lysine 83, a key enzyme in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, alters PDH enzyme activity, modulates metabolic flux, and leads to alpha-ketoglutaric acid accumulation in the tumor microenvironment. This process activates the OXGR1 receptor on macrophages, triggering MAPK signaling and inhibiting MHC-II antigen presentation, which promotes immune escape and tumor progression. Moreover, we show that inhibiting PDHA1 succinylation with CPI-613 enhances the efficacy of gemcitabine and cisplatin. Targeting PDHA1 succinylation may be a promising strategy to improve treatment outcomes in cholangiocarcinoma and warrants further clinical exploration.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
KLF2 inhibition expands tumor-resident T cells and enhances tumor immunity
In Research Square on 13 March 2025 by Gilboa, E., Gupta, V., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
VCP downstream metabolite glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) inhibits CD8+T cells function in the HCC microenvironment.
In Signal Transduct Target Ther on 24 January 2025 by Cheng, C., Zha, Q., et al.
PubMed
CD8+T cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME) are often functionally impaired, which limits their ability to mount effective anti-tumor responses. However, the molecular mechanisms behind this dysfunction remain incompletely understood. Here, we identified valosin-containing protein (VCP) as a key regulator of CD8+T cells suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Our findings reveal that VCP suppresses the activation, expansion, and cytotoxic capacity of CD8+T cells both in vitro and in vivo, significantly contributing to the immunosuppressive nature of the TME. Mechanistically, VCP stabilizes the expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like protein (GPD1L), leading to the accumulation of glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P), a downstream metabolite of GPD1L. The accumulated G3P diffuses into the TME and directly interacts with SRC-family tyrosine kinase LCK, a critical component of the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway in CD8+T cells. This interaction heightens the phosphorylation of Tyr505, a key inhibitory residue, ultimately reducing LCK activity and impairing downstream TCR signaling. Consequently, CD8+T cells lose their functional capacity, diminishing their ability to fight against HCC. Importantly, we demonstrated that targeting VCP in combination with anti-PD1 therapy significantly suppresses HCC tumor growth and restores the anti-tumor function of CD8+T cells, suggesting synergistic therapeutic potential. These findings highlight a previously unrecognized mechanism involving VCP and G3P in suppressing T-cell-mediated immunity in the TME, positioning VCP as a promising upstream target for enhancing immunotherapy in HCC.
-