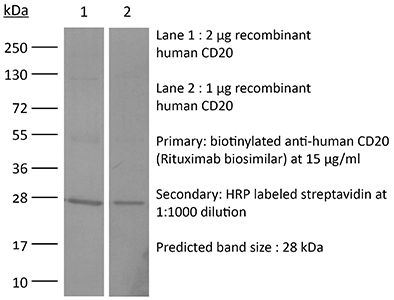
InVivoSIM anti-human CD20 (Rituximab Biosimilar)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Human IgG1 |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb human IgG1 isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Human lymphoblastoid cell line SB |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo functional assay in vitro functional assay in vitro CD20+ cell depletion (ADCC assay) Flow Cytometry ELISA Western Blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2894729 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro CD20+ cell depletion (ADCC assay)
Berjis A, Muthumani D, Aguilar OA, Pomp O, Johnson O, Finck AV, Engel NW, Chen L, Plachta N, Scholler J, Lanier LL, June CH, Sheppard NC (2024). "Pretreatment with IL-15 and IL-18 rescues natural killer cells from granzyme B-mediated apoptosis after
PubMed
Human natural killer (NK) cell-based therapies are under assessment for treating various cancers, but cryopreservation reduces both the recovery and function of NK cells, thereby limiting their therapeutic feasibility. Using cryopreservation protocols optimized for T cells, here we find that ~75% of NK cells die within 24 h post-thaw, with the remaining cells displaying reduced cytotoxicity. Using CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing and confocal microscopy, we find that cryopreserved NK cells largely die via apoptosis initiated by leakage of granzyme B from cytotoxic vesicles. Pretreatment of NK cells with a combination of Interleukins-15 (IL-15) and IL-18 prior to cryopreservation improves NK cell recovery to ~90-100% and enables equal tumour control in a xenograft model of disseminated Raji cell lymphoma compared to non-cryopreserved NK cells. The mechanism of IL-15 and IL-18-induced protection incorporates two mechanisms: a transient reduction in intracellular granzyme B levels via degranulation, and the induction of antiapoptotic genes.
in vitro CD20+ cell depletion (ADCC assay)
Lee DH, Ahn H, Sim HI, Choi E, Choi S, Jo Y, Yun B, Song HK, Oh SJ, Denda-Nagai K, Park CS, Irimura T, Park Y, Jin HS (2023). "A CRISPR activation screen identifies MUC-21 as critical for resistance to NK and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity" J Exp Clin
PubMed
Background: Immunotherapy has significantly advanced cancer treatments, but many patients do not respond to it, partly due to immunosuppressive mechanisms used by tumor cells. These cells employ immunosuppressive ligands to evade detection and elimination by the immune system. Therefore, the discovery and characterization of novel immunosuppressive ligands that facilitate immune evasion are crucial for developing more potent anti-cancer therapies. Methods: We conducted gain-of-function screens using a CRISPRa (CRISPR activation) library that covered the entire human transmembrane sub-genome to identify surface molecules capable of hindering NK-mediated cytotoxicity. The immunosuppressive role and mechanism of MUC21 were validated using NK and T cell mediated cytotoxicity assays. Bioinformatics tools were employed to assess the clinical implications of mucin-21 (MUC21) in cancer cell immunity. Results: Our genetic screens revealed that MUC21 expression on cancer cell surfaces inhibits both the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, but not affecting complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Additionally, MUC21 expression hinders T cell activation by impeding antigen recognition, thereby diminishing the effectiveness of the immune checkpoint inhibitor, anti-PD-L1. Moreover, MUC21 expression suppress the antitumor function of both CAR-T cells and CAR-NK cells. Mechanistically, MUC21 facilitates immune evasion by creating steric hindrance, preventing interactions between cancer and immune cells. Bioinformatics analysis revealed elevated MUC21 expression in lung cancer, which correlated with reduced infiltration and activation of cytotoxic immune cells. Intriguingly, MUC21 expression was higher in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tumors that were non-responsive to anti-PD-(L)1 treatment compared to responsive tumors. Conclusions: These findings indicate that surface MUC21 serves as a potent immunosuppressive ligand, shielding cancer cells from NK and CD8+T cell attacks. This suggests that inhibiting MUC21 could be a promising strategy to improve cancer immunotherapy.
in vitro functional assay
Jarvi NL, Balu-Iyer SV (2023). "A mechanistic marker-based screening tool to predict clinical immunogenicity of biologics" Commun Med (Lond) 3(1):174.
PubMed
Background: The efficacy and safety of therapeutic proteins are undermined by immunogenicity driven by anti-drug antibodies. Immunogenicity risk assessment is critically necessary during drug development, but current methods lack predictive power and mechanistic insight into antigen uptake and processing leading to immune response. A key mechanistic step in T-cell-dependent immune responses is the migration of mature dendritic cells to T-cell areas of lymphoid compartments, and this phenomenon is most pronounced in the immune response toward subcutaneously delivered proteins. Methods: The migratory potential of monocyte-derived dendritic cells is proposed to be a mechanistic marker for immunogenicity screening. Following exposure to therapeutic protein in vitro, dendritic cells are analyzed for changes in activation markers (CD40 and IL-12) in combination with levels of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 to represent migratory potential. Then a transwell assay captures the intensity of dendritic cell migration in the presence of a gradient of therapeutic protein and chemokine ligands. Results: Here, we show that an increased ability of the therapeutic protein to induce dendritic cell migration along a gradient of chemokine CCL21 and CXCL12 predicts higher immunogenic potential. Expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells, in combination with activation markers CD40 and IL-12, strongly correlates with clinical anti-drug antibody incidence. Conclusions: Mechanistic understanding of processes driving immunogenicity led to the development of a predictive tool for immunogenicity risk assessment of therapeutic proteins. These predictive markers could be adapted for immunogenicity screening of other biological modalities.
in vitro functional assay
in vivo functional assay
Curreri AM, Kim J, Dunne M, Angsantikul P, Goetz M, Gao Y, Mitragotri S (2023). "Deep Eutectic Solvents for Subcutaneous Delivery of Protein Therapeutics" Adv Sci (Weinh) 10(7):e2205389.
PubMed
Proteins are among the most common therapeutics for the treatment of diabetes, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and metabolic diseases, among others. Despite their common use, current protein therapies, most of which are injectables, have several limitations. Large proteins such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) suffer from poor absorption after subcutaneous injections, thus forcing their administration by intravenous injections. Even small proteins such as insulin suffer from slow pharmacokinetics which poses limitations in effective management of diabetes. Here, a deep eutectic-based delivery strategy is used to offer a generalized approach for improving protein absorption after subcutaneous injections. The lead formulation enhances absorption of mAbs after subcutaneous injections by ≈200%. The same composition also improves systemic absorption of subcutaneously injected insulin faster than Humalog, the current gold-standard of rapid acting insulin. Mechanistic studies reveal that the beneficial effect of deep eutectics on subcutaneous absorption is mediated by their ability to reduce the interactions of proteins with the subcutaneous matrix, especially collagen. Studies also confirm that these deep eutectics are safe for subcutaneous injections. Deep eutectic-based formulations described here open new possibilities for subcutaneous injections of therapeutic proteins.
in vitro functional assay
Müller T, Tasser C, Tesar M, Fucek I, Schniegler-Mattox U, Koch J, Ellwanger K (2023). "Selection of bispecific antibodies with optimal developability using FcRn‑Ph‑HPLC as an optimized FcRn affinity chromatography method" MAbs 15(1):2245519.
PubMed
A challenge when developing therapeutic antibodies is the identification of candidates with favorable pharmacokinetics (PK) early in development. A key determinant of immunoglobulin (IgG) serum half‑life in vivo is the efficiency of pH-dependent binding to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). Numerous studies have proposed techniques to assess FcRn binding of IgG-based therapeutics in vitro, enabling prediction of serum half-life prior to clinical assessment. FcRn high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) assays FcRn binding of therapeutic IgGs across a pH gradient, allowing the correlation of IgG column retention time to the half‑life of a therapeutic IgG in vivo. However, as FcRn retention time cannot be directly compared to an in vivo parameter, modifications to FcRn-HPLC are required to enable interpretation of the data within a physiological context, to provide more accurate estimations of serum half-life. This study presents an important modification to this method, FcRn-pH-HPLC, which reproducibly measures FcRn dissociation pH, allowing correlation with previously established half-lives of therapeutic antibodies. Furthermore, the influence of incorporating various antibody modifications, binding modules, and their orientations within IgGs and bispecifics on FcRn dissociation pH was evaluated using antibodies from the redirected optimized cell killing (ROCK®) platform. Target and effector antigen-binding domain sequences, their presentation format and orientation within a bispecific antibody alter FcRn retention; tested Fc domain modifications and incorporating stabilizing disulfide bonds had minimal effect. This study may inform the generation of mono-, bi- and multi-specific antibodies with tailored half-lives based on FcRn binding properties in vitro, to differentiate antibody-based therapeutic candidates with optimal developability.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
In vivo perturb-seq of cancer and microenvironment cells dissects oncologic drivers and radiotherapy responses in glioblastoma.
In Genome Biol on 7 October 2024 by Liu, S. J., Zou, C., et al.
PubMed
Genetic perturbation screens with single-cell readouts have enabled rich phenotyping of gene function and regulatory networks. These approaches have been challenging in vivo, especially in adult disease models such as cancer, which include mixtures of malignant and microenvironment cells. Glioblastoma (GBM) is a fatal cancer, and methods of systematically interrogating gene function and therapeutic targets in vivo, especially in combination with standard of care treatment such as radiotherapy, are lacking.
-
-
Pretreatment with IL-15 and IL-18 rescues natural killer cells from granzyme B-mediated apoptosis after cryopreservation.
In Nat Commun on 10 May 2024 by Berjis, A., Muthumani, D., et al.
PubMed
Human natural killer (NK) cell-based therapies are under assessment for treating various cancers, but cryopreservation reduces both the recovery and function of NK cells, thereby limiting their therapeutic feasibility. Using cryopreservation protocols optimized for T cells, here we find that ~75% of NK cells die within 24 h post-thaw, with the remaining cells displaying reduced cytotoxicity. Using CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing and confocal microscopy, we find that cryopreserved NK cells largely die via apoptosis initiated by leakage of granzyme B from cytotoxic vesicles. Pretreatment of NK cells with a combination of Interleukins-15 (IL-15) and IL-18 prior to cryopreservation improves NK cell recovery to ~90-100% and enables equal tumour control in a xenograft model of disseminated Raji cell lymphoma compared to non-cryopreserved NK cells. The mechanism of IL-15 and IL-18-induced protection incorporates two mechanisms: a transient reduction in intracellular granzyme B levels via degranulation, and the induction of antiapoptotic genes.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A mechanistic marker-based screening tool to predict clinical immunogenicity of biologics.
In Commun Med (Lond) on 8 December 2023 by Jarvi, N. L., Balu-Iyer, S. V., et al.
PubMed
The efficacy and safety of therapeutic proteins are undermined by immunogenicity driven by anti-drug antibodies. Immunogenicity risk assessment is critically necessary during drug development, but current methods lack predictive power and mechanistic insight into antigen uptake and processing leading to immune response. A key mechanistic step in T-cell-dependent immune responses is the migration of mature dendritic cells to T-cell areas of lymphoid compartments, and this phenomenon is most pronounced in the immune response toward subcutaneously delivered proteins.
-