InVivoMAb anti-mouse LAG-3
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG1 isotype control, anti-horseradish peroxidase |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CD223-Ig fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization in vitro LAG-3 neutralization Flow cytometry Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10949602 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization
Bauche, D., et al (2018). "LAG3(+) Regulatory T Cells Restrain Interleukin-23-Producing CX3CR1(+) Gut-Resident Macrophages during Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Driven Colitis" Immunity 49(2): 342-352 e345.
PubMed
Interleukin-22 (IL-22)-producing group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) maintains gut homeostasis but can also promote inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The regulation of ILC3-dependent colitis remains to be elucidated. Here we show that Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells (Treg cells) prevented ILC3-mediated colitis in an IL-10-independent manner. Treg cells inhibited IL-23 and IL-1beta production from intestinal-resident CX3CR1(+) macrophages but not CD103(+) dendritic cells. Moreover, Treg cells restrained ILC3 production of IL-22 through suppression of CX3CR1(+) macrophage production of IL-23 and IL-1beta. This suppression was contact dependent and was mediated by latent activation gene-3 (LAG-3)-an immune checkpoint receptor-expressed on Treg cells. Engagement of LAG-3 on MHC class II drove profound immunosuppression of CX3CR1(+) tissue-resident macrophages. Our study reveals that the health of the intestinal mucosa is maintained by an axis driven by Treg cells communication with resident macrophages that withhold inflammatory stimuli required for ILC3 function.
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Rouhani, S. J., et al (2015). "Roles of lymphatic endothelial cells expressing peripheral tissue antigens in CD4 T-cell tolerance induction" Nat Commun 6: 6771.
PubMed
Lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) directly express peripheral tissue antigens and induce CD8 T-cell deletional tolerance. LECs express MHC-II molecules, suggesting they might also tolerize CD4 T cells. We demonstrate that when beta-galactosidase (beta-gal) is expressed in LECs, beta-gal-specific CD8 T cells undergo deletion via the PD-1/PD-L1 and LAG-3/MHC-II pathways. In contrast, LECs do not present endogenous beta-gal in the context of MHC-II molecules to beta-gal-specific CD4 T cells. Lack of presentation is independent of antigen localization, as membrane-bound haemagglutinin and I-Ealpha are also not presented by MHC-II molecules. LECs express invariant chain and cathepsin L, but not H2-M, suggesting that they cannot load endogenous antigenic peptides onto MHC-II molecules. Importantly, LECs transfer beta-gal to dendritic cells, which subsequently present it to induce CD4 T-cell anergy. Therefore, LECs serve as an antigen reservoir for CD4 T-cell tolerance, and MHC-II molecules on LECs are used to induce CD8 T-cell tolerance via LAG-3.
in vitro LAG-3 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Erickson, J. J., et al (2014). "Programmed death-1 impairs secondary effector lung CD8(+) T cells during respiratory virus reinfection" J Immunol 193(10): 5108-5117.
PubMed
Reinfections with respiratory viruses are common and cause significant clinical illness, yet precise mechanisms governing this susceptibility are ill defined. Lung Ag-specific CD8(+) T cells (T(CD8)) are impaired during acute viral lower respiratory infection by the inhibitory receptor programmed death-1 (PD-1). To determine whether PD-1 contributes to recurrent infection, we first established a model of reinfection by challenging B cell-deficient mice with human metapneumovirus (HMPV) several weeks after primary infection, and found that HMPV replicated to high titers in the lungs. A robust secondary effector lung TCD8 response was generated during reinfection, but these cells were more impaired and more highly expressed the inhibitory receptors PD-1, LAG-3, and 2B4 than primary T(CD8). In vitro blockade demonstrated that PD-1 was the dominant inhibitory receptor early after reinfection. In vivo therapeutic PD-1 blockade during HMPV reinfection restored lung T(CD8) effector functions (i.e., degranulation and cytokine production) and enhanced viral clearance. PD-1 also limited the protective efficacy of HMPV epitope-specific peptide vaccination and impaired lung T(CD8) during heterotypic influenza virus challenge infection. Our results indicate that PD-1 signaling may contribute to respiratory virus reinfection and evasion of vaccine-elicited immune responses. These results have important implications for the design of effective vaccines against respiratory viruses.
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization
McGray, A. J., et al (2014). "Immunotherapy-induced CD8+ T cells instigate immune suppression in the tumor" Mol Ther 22(1): 206-218.
PubMed
Despite clear evidence of immunogenicity, cancer vaccines only provide a modest clinical benefit. To evaluate the mechanisms that limit tumor regression following vaccination, we have investigated the weak efficacy of a highly immunogenic experimental vaccine using a murine melanoma model. We discovered that the tumor adapts rapidly to the immune attack instigated by tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in the first few days following vaccination, resulting in the upregulation of a complex set of biological networks, including multiple immunosuppressive processes. This rapid adaptation acts to prevent sustained local immune attack, despite continued infiltration by increasing numbers of tumor-specific T cells. Combining vaccination with adoptive transfer of tumor-specific T cells produced complete regression of the treated tumors but did not prevent the adaptive immunosuppression. In fact, the adaptive immunosuppressive pathways were more highly induced in regressing tumors, commensurate with the enhanced level of immune attack. Examination of tumor infiltrating T-cell functionality revealed that the adaptive immunosuppression leads to a progressive loss in T-cell function, even in tumors that are regressing. These novel observations that T cells produced by therapeutic intervention can instigate a rapid adaptive immunosuppressive response within the tumor have important implications for clinical implementation of immunotherapies.
in vitro LAG-3 neutralization
Verhagen, J. and D. C. Wraith (2014). "Blockade of LFA-1 augments in vitro differentiation of antigen-induced Foxp3(+) Treg cells" J Immunol Methods 414: 58-64.
PubMed
Adoptive transfer of antigen-specific, in vitro-induced Foxp3(+) Treg (iTreg) cells protects against autoimmune disease. To generate antigen-specific iTreg cells at high purity, however, remains a challenge. Whereas polyclonal T cell stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibody yields Foxp3(+) iTreg cells at a purity of 90-95%, antigen-induced iTreg cells typically do not exceed a purity of 65-75%, even in a TCR-transgenic model. In a similar vein to thymic Treg cell selection, iTreg cell differentiation is influenced not only by antigen recognition and the availability of TGF-beta but also by co-factors including costimulation and adhesion molecules. In this study, we demonstrate that blockade of the T cell integrin Leukocyte Function-associated Antigen-1 (LFA-1) during antigen-mediated iTreg cell differentiation augments Foxp3 induction, leading to approximately 90% purity of Foxp3(+) iTreg cells. This increased efficacy not only boosts the yield of Foxp3(+) iTreg cells, it also reduces contamination with activated effector T cells, thus improving the safety of adoptive transfer immunotherapy.
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization
in vitro LAG-3 neutralization
Durham, N. M., et al (2014). "Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 (LAG-3) modulates the ability of CD4 T-cells to be suppressed in vivo" PLoS One 9(11): e109080.
PubMed
Lymphocyte Activation Gene – 3 (LAG-3) is an immune checkpoint molecule that regulates both T-cell activation and homeostasis. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying LAG-3’s function are generally unknown. Using a model in which LAG-3 blockade or absence reliably augmented homeostatic proliferation in vivo, we found that IL-2 and STAT5 are critical for LAG-3 function. Similarly, LAG-3 blockade was ineffective in the absence of regulatory T-cells (Treg), suggesting an important role for LAG-3 in either the responsiveness of conventional T-cells (Tconv) to regulation, or a relative defect in the ability of LAG-3 KO regulatory T-cells (Treg) to suppress the proliferation of Tconv. In this model, LAG-3 KO Treg suppressed proliferation in a manner fairly similar to wild-type (WT) Treg, but LAG-3 KO Tconv were relatively resistant to suppression. Further studies also identified a role for LAG-3 in the induction/expansion of Treg. Finally, we found that LAG-3 blockade (or knockout) led to a relative skewing of naive CD4 T-cells toward a TH1 phenotype both in vitro and in in vivo. Together, these data suggest that LAG-3 expression on Tconv cells makes them more susceptible to Treg based suppression, and also regulates the development of a TH1 T-cell response.
in vivo LAG-3 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Goding, S. R., et al (2013). "Restoring immune function of tumor-specific CD4+ T cells during recurrence of melanoma" J Immunol 190(9): 4899-4909.
PubMed
Recurrent solid malignancies are often refractory to standard therapies. Although adoptive T cell transfer may benefit select individuals, the majority of patients succumb to their disease. To address this important clinical dilemma, we developed a mouse melanoma model in which initial regression of advanced disease was followed by tumor recurrence. During recurrence, Foxp3(+) tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells became PD-1(+) and represented >60% of the tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells in the host. Concomitantly, tumor-specific CD4(+) T effector cells showed traits of chronic exhaustion, as evidenced by their high expression of the PD-1, TIM-3, 2B4, TIGIT, and LAG-3 inhibitory molecules. Although blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway with anti-PD-L1 Abs or depletion of tumor-specific regulatory T cells (Tregs) alone failed to reverse tumor recurrence, the combination of PD-L1 blockade with tumor-specific Treg depletion effectively mediated disease regression. Furthermore, blockade with a combination of anti-PD-L1 and anti-LAG-3 Abs overcame the requirement to deplete tumor-specific Tregs. In contrast, successful treatment of primary melanoma with adoptive cell therapy required only Treg depletion or Ab therapy, underscoring the differences in the characteristics of treatment between primary and relapsing cancer. These data highlight the need for preclinical development of combined immunotherapy approaches specifically targeting recurrent disease.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Identification of anti-TIM-3 based checkpoint inhibitor combinations with activity in immunotherapy refractory melanoma models.
In J Immunother Cancer on 18 August 2025 by Phadke, M. S., Li, J., et al.
PubMed
A significant percentage of melanomas are refractory to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) monotherapies and combinations. As there are currently no effective second-line therapies available for ICI-resistant patients, we sought to identify novel checkpoint inhibitor combinations for future clinical evaluation.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Combination immunotherapy targeting LAG-3, PD-1 and STING suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma as monitored by LAG-3 targeted PET imaging.
In Biomark Res on 12 August 2025 by Quan, Z., Gao, Y., et al.
PubMed
The low response rate of anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) requires the development of combination immunotherapy strategies to improve their efficacy. This study aimed to use LAG-3-targeted PET imaging to monitor the efficacy of anti-PD-1 mAb, a stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonist, and anti-LAG-3 mAb, both individually and in combination. Furthermore, we evaluated the potential of a triple immunotherapy regimen (anti-PD-1 mAb, STING agonist, and anti-LAG-3 mAb) to improve HCC treatment.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Development of PVTX-405 as a potent and highly selective molecular glue degrader of IKZF2 for cancer immunotherapy.
In Nat Commun on 1 May 2025 by Chen, Z., Dhruv, H., et al.
PubMed
IKZF2 (Helios) is a transcription factor that is selectively expressed by Tregs and is essential for preserving the function and stability of Tregs in the tumor microenvironment (TME), where it suppresses the anti-tumor immune response. Targeted IKZF2 degradation by small molecules represents a promising strategy for the development of a new class of cancer immunotherapy. Herein, we describe the discovery of PVTX-405, a potent, effective, highly selective, and orally efficacious IKZF2 molecular glue degrader. PVTX-405 degrades IKZF2 (DC50 = 0.7 nM and Dmax = 91%) while sparing other CRBN neo-substrates. Degradation of IKZF2 by PVTX-405 increases production of inflammatory cytokine IL-2 and reduces the suppressive activity of Tregs, leading to an increase in Teff cell proliferation. Once-daily oral administration of PVTX-405 as single agent significantly delays the growth of MC38 tumors in a syngeneic tumor model using humanized CRBN mice. PVTX-405 in combination with anti-PD1 or anti-LAG3 significantly increases animal survival compared to anti-PD1 or anti-LAG3 alone. Together, these results demonstrate that PVTX-405 is a promising IKZF2 degrader for clinical development for the treatment of human cancers.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
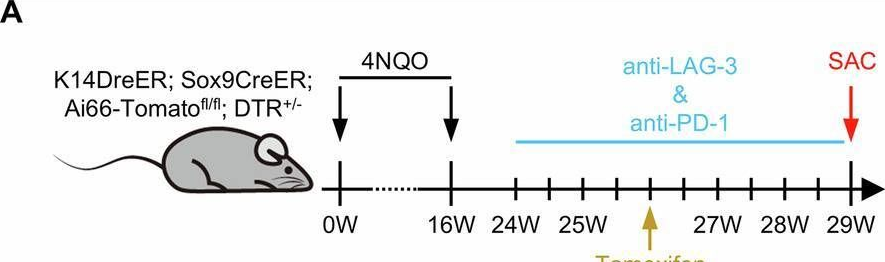
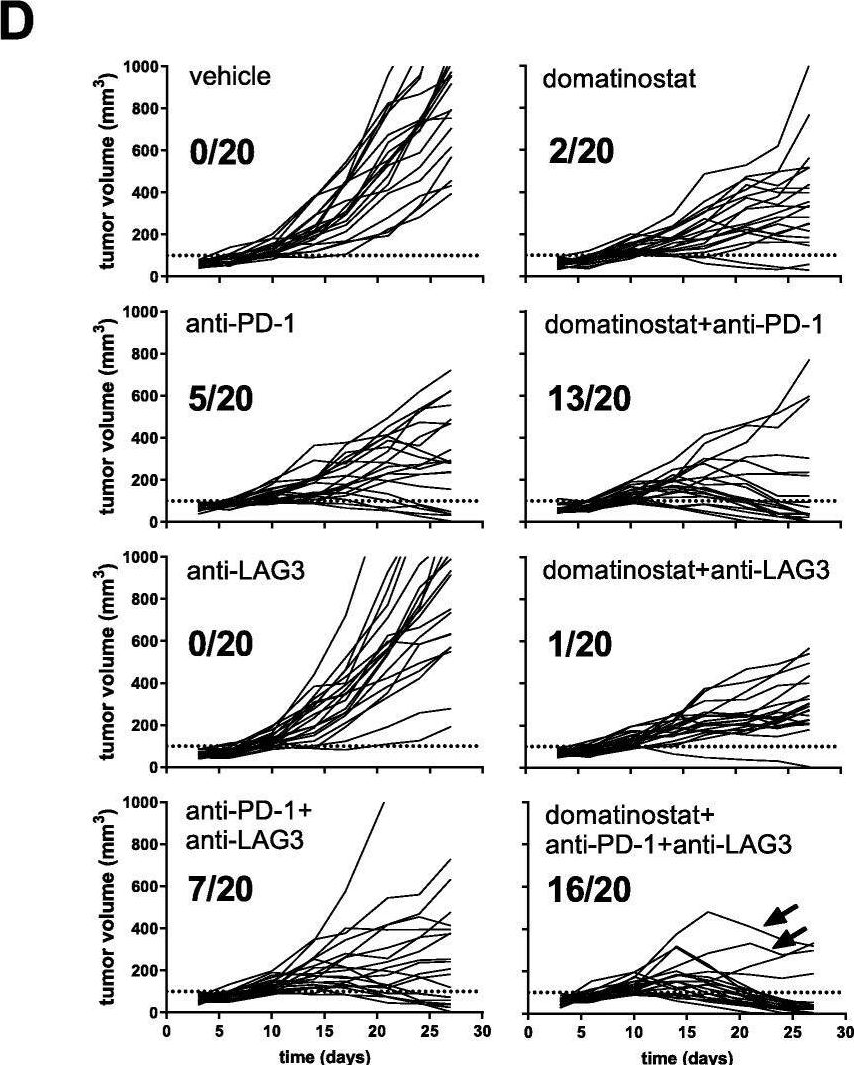
Resistance to anti-LAG-3 plus anti-PD-1 therapy in head and neck cancer is mediated by Sox9+ tumor cells interaction with Fpr1+ neutrophils.
In Nat Commun on 28 April 2025 by Wang, X., Cheng, M., et al.
PubMed
Relatlimab and nivolumab combination therapy shows significant efficacy in treating various types of cancer. Current research on the molecular mechanisms of this treatment is abundant, but in-depth investigations into post-treatment resistance remain notably lacking. In this study, we identify significant enrichment of SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (Sox9)+ tumor cells in resistant samples using single cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) in a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) mouse model. In addition, Sox9 directly regulates the expression of annexin A1 (Anxa1), mediating apoptosis of formyl peptide receptor 1 (Fpr1)+ neutrophils through the Anxa1-Fpr1 axis, which promotes mitochondrial fission, inhibits mitophagy by downregulating BCL2/adenovirus E1B interacting protein 3 (Bnip3) expression and ultimately prevents the accumulation of neutrophils in tumor tissues. The reduction of Fpr1+ neutrophils impairs the infiltration and tumor cell-killing ability of cytotoxic Cd8 T and γδT cells within the tumor microenvironment, thereby leading to the development of resistance to the combination therapy. We further validate these findings using various transgenic mouse models. Overall, this study comprehensively explains the mechanisms underlying resistance to the anti-LAG-3 plus anti-PD-1 combination therapy and identifies potential therapeutic targets to overcome this resistance.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Inhibitors of oncogenic Kras specifically prime CTLA4 blockade to transcriptionally reprogram Tregs and overcome resistance to suppress pancreas cancer
In bioRxiv on 4 March 2025 by Mahadevan, K. K., Maldonado, A. S., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Coordinated macrophage and T cell interactions mediate response to checkpoint blockade in colorectal cancer
In bioRxiv on 17 February 2025 by Mestrallet, G., Brown, M., et al.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Combined KRAS Inhibition and Immune Therapy Generates Durable Complete Responses in an Autochthonous PDAC Model.
In Cancer Discov on 13 January 2025 by Liu, Y., Han, J., et al.
PubMed
Clinically available KRAS* inhibitors and IO agents alleviated the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in PDAC. Profound tumor regression and prolonged survival in an autochthonous PDAC model provide a compelling rationale for combining KRAS* inhibition with IO agents targeting multiple arms of the immunity cycle to combat PDAC.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
Combined Autophagy Inhibition and Dendritic Cell Recruitment Induces Antitumor Immunity and Enhances Immune Checkpoint Blockade Sensitivity in Pancreatic Cancer.
In Cancer Res on 16 December 2024 by Oyama, K., Nakata, K., et al.
PubMed
The effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors is extremely limited in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) due to the suppressive tumor immune microenvironment. Autophagy, which has been shown to play a role in antitumor immunity, has been proposed as a therapeutic target for PDAC. In this study, single-cell RNA sequencing of autophagy-deficient murine PDAC tumors revealed that autophagy inhibition in cancer cells induced dendritic cell (DC) activation. Analysis of human PDAC tumors substantiated a negative correlation between autophagy and DC activation signatures. Mechanistically, autophagy inhibition increased the intracellular accumulation of tumor antigens, which could activate DCs. Administration of chloroquine, an autophagy inhibitor, in combination with Flt3 ligand-induced DC infiltration inhibited tumor growth and increased tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes. However, autophagy inhibition in cancer cells also induced CD8+ T-cell exhaustion with high expression of immune checkpoint LAG3. A triple-therapy comprising chloroquine, Flt3 ligand, and an anti-LAG3 antibody markedly reduced tumor growth in orthotopic syngeneic PDAC mouse models. Thus, targeting autophagy in cancer cells and activating DCs sensitize PDAC tumors to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, warranting further development of this treatment approach to overcome immunosuppression in pancreatic cancer. Significance: Inhibiting autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells enhances intracellular accumulation of tumor antigens to induce dendritic cell activation and synergizes with immunotherapy to markedly inhibit the growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Therapeutic potential of co-signaling receptor modulation in hepatitis B.
In Cell on 25 July 2024 by Andreata, F., Laura, C., et al.
PubMed
Reversing CD8+ T cell dysfunction is crucial in treating chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, yet specific molecular targets remain unclear. Our study analyzed co-signaling receptors during hepatocellular priming and traced the trajectory and fate of dysfunctional HBV-specific CD8+ T cells. Early on, these cells upregulate PD-1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, OX40, 4-1BB, and ICOS. While blocking co-inhibitory receptors had minimal effect, activating 4-1BB and OX40 converted them into antiviral effectors. Prolonged stimulation led to a self-renewing, long-lived, heterogeneous population with a unique transcriptional profile. This includes dysfunctional progenitor/stem-like (TSL) cells and two distinct dysfunctional tissue-resident memory (TRM) populations. While 4-1BB expression is ubiquitously maintained, OX40 expression is limited to TSL. In chronic settings, only 4-1BB stimulation conferred antiviral activity. In HBeAg+ chronic patients, 4-1BB activation showed the highest potential to rejuvenate dysfunctional CD8+ T cells. Targeting all dysfunctional T cells, rather than only stem-like precursors, holds promise for treating chronic HBV infection.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The diversity of inhibitory receptor co-expression patterns of exhausted CD8+ T cells in oropharyngeal carcinoma.
In iScience on 17 May 2024 by Rao, Y., Qiu, K., et al.
PubMed
Exhausted CD8+ T cells (Texs) are characterized by the expression of various inhibitory receptors (IRs), whereas the functional attributes of these co-expressed IRs remain limited. Here, we systematically characterized the diversity of IR co-expression patterns in Texs from both human oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) tissues and syngeneic OPSCC model. Nearly 60% of the Texs population co-expressed two or more IRs, and the number of co-expressed IRs was positively associated with superior exhaustion and cytotoxicity phenotypes. In OPSCC patients, programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) blockade significantly enhanced PDCD1-based co-expression with other IR genes, whereas dual blockades of PD-1 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) significantly upregulated CTLA4-based co-expression with other IR genes. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that highly diverse IR co-expression is a leading feature of Texs and represents their functional states, which might provide essential clues for the rational selection of immune checkpoint inhibitors in treating OPSCC.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Combining toll-like receptor agonists with immune checkpoint blockade affects antitumor vaccine efficacy.
In J Immunother Cancer on 3 May 2024 by Jeon, D., Hill, E., et al.
PubMed
T cell checkpoint receptors are expressed when T cells are activated, and modulation of the expression or signaling of these receptors can alter the function of T cells and their antitumor efficacy. We previously found that T cells activated with cognate antigen had increases in the expression of PD-1, and this was attenuated in the presence of multiple toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, notably TLR3 plus TLR9. In the current report, we sought to investigate whether combining TLR agonists with immune checkpoint blockade can further augment vaccine-mediated T cell antitumor immunity in murine tumor models.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Targeting TIGIT for cancer immunotherapy: recent advances and future directions.
In Biomark Res on 16 January 2024 by Zhang, P., Liu, X., et al.
PubMed
As a newly identified checkpoint, T cell immunoreceptor with immunoglobulin and tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) domain (TIGIT) is highly expressed on CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). TIGIT has been associated with NK cell exhaustion in vivo and in individuals with various cancers. It not only modulates NK cell survival but also mediates T cell exhaustion. As the primary ligand of TIGIT in humans, CD155 may be the main target for immunotherapy due to its interaction with TIGIT. It has been found that the anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) treatment response in cancer immunotherapy is correlated with CD155 but not TIGIT. Anti-TIGIT alone and in combination with anti-PD-1 agents have been tested for cancer immunotherapy. Although two clinical studies on advanced lung cancer had positive results, the TIGIT-targeted antibody, tiragolumab, recently failed in two new trials. In this review, we highlight the current developments on TIGIT for cancer immunotherapy and discuss the characteristics and functions of TIGIT.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Noninvasive Monitoring of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer by Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 PET Imaging of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes.
In J Nucl Med on 2 January 2024 by Quan, Z., Han, Z., et al.
PubMed
Although immunotherapy has revolutionized the entire cancer treatment landscape, small fractions of patients respond to immunotherapy. Early identification of responders may improve patient management during immunotherapy. In this study, we evaluated a PET approach for monitoring immunotherapy in lung cancer by imaging the upregulation of lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3)-expressing (LAG-3+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Methods: We synthesized a LAG-3-targeted molecular imaging probe, [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 and performed a series of in vitro and in vivo assays to test its specificity. Next, [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 PET was used to monitor immunotherapy in murine lung cancer-bearing mice and in humanized mouse models for assessing clinical translational potential, with confirmation by immunostaining and flow cytometry analysis. Results: [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 PET could noninvasively detect intertumoral differences in LAG-3+ TIL levels in different tumor models. Importantly, in Lewis lung carcinoma tumor models treated with an agonist of a stimulator of interferon genes, [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 PET also detected an immunophenotyping transition of the tumor from "cold" to "hot" before changes in tumor size. Meanwhile, animals carrying "hot" tumor showed more significant tumor inhibition and longer survival than those carrying "cold" tumor. [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 PET also showed markedly higher tumor uptake in immune system-humanized mice carrying human non-small cell lung cancer than immunodeficient models. Conclusion: [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 PET could be used to noninvasively monitor the early response to immunotherapy by imaging LAG-3+ TILs in lung cancer. [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-C25 PET also exhibited excellent translational potential, with great significance for the precise management of lung cancer patients receiving immunotherapy.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Intestinal microbiota-specific Th17 cells possess regulatory properties and suppress effector T cells via c-MAF and IL-10.
In Immunity on 12 December 2023 by Brockmann, L., Tran, A., et al.
PubMed
Commensal microbes induce cytokine-producing effector tissue-resident CD4+ T cells, but the function of these T cells in mucosal homeostasis is not well understood. Here, we report that commensal-specific intestinal Th17 cells possess an anti-inflammatory phenotype marked by expression of interleukin (IL)-10 and co-inhibitory receptors. The anti-inflammatory phenotype of gut-resident commensal-specific Th17 cells was driven by the transcription factor c-MAF. IL-10-producing commensal-specific Th17 cells were heterogeneous and derived from a TCF1+ gut-resident progenitor Th17 cell population. Th17 cells acquired IL-10 expression and anti-inflammatory phenotype in the small-intestinal lamina propria. IL-10 production by CD4+ T cells and IL-10 signaling in intestinal macrophages drove IL-10 expression by commensal-specific Th17 cells. Intestinal commensal-specific Th17 cells possessed immunoregulatory functions and curbed effector T cell activity in vitro and in vivo in an IL-10-dependent and c-MAF-dependent manner. Our results suggest that tissue-resident commensal-specific Th17 cells perform regulatory functions in mucosal homeostasis.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Differential requirements for CD4+ T cells in the efficacy of the anti-PD-1+LAG-3 and anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 combinations in melanoma flank and brain metastasis models.
In J Immunother Cancer on 6 December 2023 by Phadke, M. S., Li, J., et al.
PubMed
Although the anti-PD-1+LAG-3 and the anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 combinations are effective in advanced melanoma, it remains unclear whether their mechanisms of action overlap.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Kruppel-like factor 2+ CD4 T cells avert microbiota-induced intestinal inflammation.
In Cell Rep on 28 November 2023 by Shao, T. Y., Jiang, T. T., et al.
PubMed
Intestinal colonization by antigenically foreign microbes necessitates expanded peripheral immune tolerance. Here we show commensal microbiota prime expansion of CD4 T cells unified by the Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) transcriptional regulator and an essential role for KLF2+ CD4 cells in averting microbiota-driven intestinal inflammation. CD4 cells with commensal specificity in secondary lymphoid organs and intestinal tissues are enriched for KLF2 expression, and distinct from FOXP3+ regulatory T cells or other differentiation lineages. Mice with conditional KLF2 deficiency in T cells develop spontaneous rectal prolapse and intestinal inflammation, phenotypes overturned by eliminating microbiota or reconstituting with donor KLF2+ cells. Activated KLF2+ cells selectively produce IL-10, and eliminating IL-10 overrides their suppressive function in vitro and protection against intestinal inflammation in vivo. Together with reduced KLF2+ CD4 cell accumulation in Crohn's disease, a necessity for the KLF2+ subpopulation of T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells in sustaining commensal tolerance is demonstrated.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Reciprocal transmission of activating and inhibitory signals and cell fate in regenerating T cells.
In Cell Rep on 31 October 2023 by Wang, P. H., Washburn, R. S., et al.
PubMed
The ability of activated progenitor T cells to self-renew while producing differentiated effector cell descendants may underlie immunological memory and persistent responses to ongoing infection. The nature of stem-like T cells responding to cancer and during treatment with immunotherapy is not clear. The subcellular organization of dividing progenitor CD8+ T cells from mice challenged with syngeneic tumors is examined here. Three-dimensional microscopy reveals an activating hub composed of polarized CD3, CD28, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity at the putative immunological synapse with an inhibitory hub composed of polarized PD-1 and CD73 at the opposite pole of mitotic blasts. Progenitor T cells from untreated and inhibitory checkpoint blockade-treated mice yield a differentiated TCF1- daughter cell, which inherits the PI3K activation hub, alongside a discordantly fated, self-renewing TCF1+ sister cell. Dynamic organization of opposite activating and inhibitory signaling poles in mitotic lymphocytes may account for the enigmatic durability of specific immunity.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Autophagy inhibition in pancreatic cancer cells synergizes with immunotherapy via DC activation due to increased antigenicity and adjuvanticity
In Research Square on 18 October 2023 by Nakata, K., Oyama, K., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Defining the mechanisms of action and resistance to the anti-PD-1+LAG-3 and anti-PD-1+CTLA-4 combinations in melanoma flank and brain models
In bioRxiv on 16 April 2023 by Phadke, M. S., Li, J., et al.
-
-
A Pilot Study to Develop Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration Mouse Model.
In Cerebellum on 2 February 2023 by Faure, F., Yshii, L., et al.
PubMed
Modeling paraneoplastic neurological diseases to understand the immune mechanisms leading to neuronal death is a major challenge given the rarity and terminal access of patients' autopsies. Here, we present a pilot study aiming at modeling paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration with Yo autoantibodies (Yo-PCD). Female mice were implanted with an ovarian carcinoma cell line expressing CDR2 and CDR2L, the known antigens recognized by anti-Yo antibodies. To boost the immune response, we also immunized the mice by injecting antigens with diverse adjuvants and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ataxia and gait instability were assessed in treated mice as well as autoantibody levels, Purkinje cell density, and immune infiltration in the cerebellum. We observed the production of anti-Yo antibodies in the CSF and serum of all immunized mice. Brain immunoreaction varied depending on the site of implantation of the tumor, with subcutaneous administration leading to a massive infiltration of immune cells in the meningeal spaces, choroid plexus, and cerebellar parenchyma. However, we did not observe massive Purkinje cell death nor any motor impairments in any of the experimental groups. Self-sustained neuro-inflammation might require a longer time to build up in our model. Unusual tumor antigen presentation and/or intrinsic, species-specific factors required for pro-inflammatory engagement in the brain may also constitute strong limitations to achieve massive recruitment of antigen-specific T-cells and killing of antigen-expressing neurons in this mouse model.