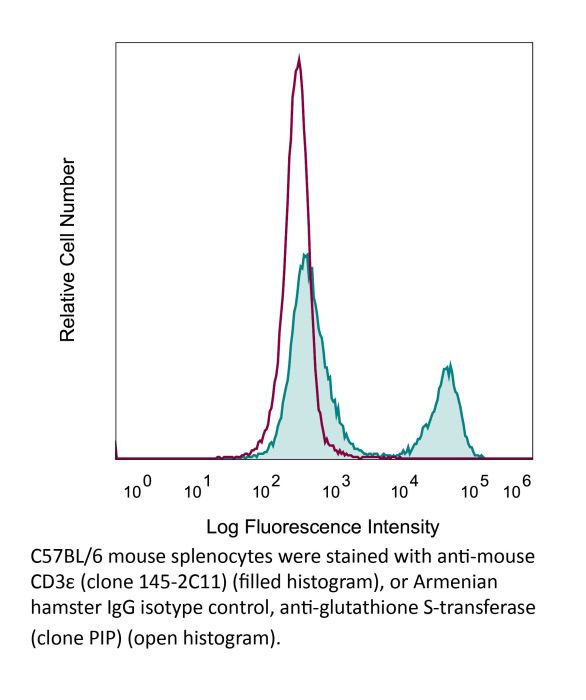
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD3ε
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Armenian Hamster IgG1 |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb polyclonal Armenian hamster IgG |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse BM10-37 cytotoxic T cells |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo T cell depletion in vitro T cell stimulation/activation Immunofluorescence Flow cytometry Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_1107634 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo T cell depletion
Glasner, A., et al (2018). "NKp46 Receptor-Mediated Interferon-gamma Production by Natural Killer Cells Increases Fibronectin 1 to Alter Tumor Architecture and Control Metastasis" Immunity 48(1): 107-119 e104.
PubMed
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphoid cells, and their presence within human tumors correlates with better prognosis. However, the mechanisms by which NK cells control tumors in vivo are unclear. Here, we used reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) imaging in humans and in mice to visualize tumor architecture in vivo. We demonstrated that signaling via the NK cell receptor NKp46 (human) and Ncr1 (mouse) induced interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) secretion from intratumoral NK cells. NKp46- and Ncr1-mediated IFN-gamma production led to the increased expression of the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin 1 (FN1) in the tumors, which altered primary tumor architecture and resulted in decreased metastases formation. Injection of IFN-gamma into tumor-bearing mice or transgenic overexpression of Ncr1 in NK cells in mice resulted in decreased metastasis formation. Thus, we have defined a mechanism of NK cell-mediated control of metastases in vivo that may help develop NK cell-dependent cancer therapies.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Lacher, S. M., et al (2018). "NF-kappaB inducing kinase (NIK) is an essential post-transcriptional regulator of T-cell activation affecting F-actin dynamics and TCR signaling" J Autoimmun 94: 110-121.
PubMed
NF-kappaB inducing kinase (NIK) is the key protein of the non-canonical NF-kappaB pathway and is important for the development of lymph nodes and other secondary immune organs. We elucidated the specific role of NIK in T cells using T-cell specific NIK-deficient (NIK(DeltaT)) mice. Despite showing normal development of lymphoid organs, NIK(DeltaT) mice were resistant to induction of CNS autoimmunity. T cells from NIK(DeltaT) mice were deficient in late priming, failed to up-regulate T-bet and to transmigrate into the CNS. Proteomic analysis of activated NIK(-/-) T cells showed de-regulated expression of proteins involved in the formation of the immunological synapse: in particular, proteins involved in cytoskeleton dynamics. In line with this we found that NIK-deficient T cells were hampered in phosphorylation of Zap70, LAT, AKT, ERK1/2 and PLCgamma upon TCR engagement. Hence, our data disclose a hitherto unknown function of NIK in T-cell priming and differentiation.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Wendland, K., et al (2018). "Retinoic Acid Signaling in Thymic Epithelial Cells Regulates Thymopoiesis" J Immunol 201(2): 524-532.
PubMed
Despite the essential role of thymic epithelial cells (TEC) in T cell development, the signals regulating TEC differentiation and homeostasis remain incompletely understood. In this study, we show a key in vivo role for the vitamin A metabolite, retinoic acid (RA), in TEC homeostasis. In the absence of RA signaling in TEC, cortical TEC (cTEC) and CD80(lo)MHC class II(lo) medullary TEC displayed subset-specific alterations in gene expression, which in cTEC included genes involved in epithelial proliferation, development, and differentiation. Mice whose TEC were unable to respond to RA showed increased cTEC proliferation, an accumulation of stem cell Ag-1(hi) cTEC, and, in early life, a decrease in medullary TEC numbers. These alterations resulted in reduced thymic cellularity in early life, a reduction in CD4 single-positive and CD8 single-positive numbers in both young and adult mice, and enhanced peripheral CD8(+) T cell survival upon TCR stimulation. Collectively, our results identify RA as a regulator of TEC homeostasis that is essential for TEC function and normal thymopoiesis.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Ron-Harel, N., et al (2016). "Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Proteome Remodeling Promote One-Carbon Metabolism for T Cell Activation" Cell Metab 24(1): 104-117.
PubMed
Naive T cell stimulation activates anabolic metabolism to fuel the transition from quiescence to growth and proliferation. Here we show that naive CD4(+) T cell activation induces a unique program of mitochondrial biogenesis and remodeling. Using mass spectrometry, we quantified protein dynamics during T cell activation. We identified substantial remodeling of the mitochondrial proteome over the first 24 hr of T cell activation to generate mitochondria with a distinct metabolic signature, with one-carbon metabolism as the most induced pathway. Salvage pathways and mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism, fed by serine, contribute to purine and thymidine synthesis to enable T cell proliferation and survival. Genetic inhibition of the mitochondrial serine catabolic enzyme SHMT2 impaired T cell survival in culture and antigen-specific T cell abundance in vivo. Thus, during T cell activation, mitochondrial proteome remodeling generates specialized mitochondria with enhanced one-carbon metabolism that is critical for T cell activation and survival.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Gu, A. D., et al (2015). "A critical role for transcription factor Smad4 in T cell function that is independent of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling" Immunity 42(1): 68-79.
PubMed
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) suppresses T cell function to maintain self-tolerance and to promote tumor immune evasion. Yet how Smad4, a transcription factor component of TGF-beta signaling, regulates T cell function remains unclear. Here we have demonstrated an essential role for Smad4 in promoting T cell function during autoimmunity and anti-tumor immunity. Smad4 deletion rescued the lethal autoimmunity resulting from transforming growth factor-beta receptor (TGF-betaR) deletion and compromised T-cell-mediated tumor rejection. Although Smad4 was dispensable for T cell generation, homeostasis, and effector function, it was essential for T cell proliferation after activation in vitro and in vivo. The transcription factor Myc was identified to mediate Smad4-controlled T cell proliferation. This study thus reveals a requirement of Smad4 for T-cell-mediated autoimmunity and tumor rejection, which is beyond the current paradigm. It highlights a TGF-betaR-independent role for Smad4 in promoting T cell function, autoimmunity, and anti-tumor immunity.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Awe, O., et al (2015). "PU.1 Expression in T Follicular Helper Cells Limits CD40L-Dependent Germinal Center B Cell Development" J Immunol .
PubMed
PU.1 is an ETS family transcription factor that is important for the development of multiple hematopoietic cell lineages. Previous work demonstrated a critical role for PU.1 in promoting Th9 development and in limiting Th2 cytokine production. Whether PU.1 has functions in other Th lineages is not clear. In this study, we examined the effects of ectopic expression of PU.1 in CD4+ T cells and observed decreased expression of genes involved with the function of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, including Il21 and Tnfsf5 (encoding CD40L). T cells from conditional mutant mice that lack expression of PU.1 in T cells (Sfpi1lck-/-) demonstrated increased production of CD40L and IL-21 in vitro. Following adjuvant-dependent or adjuvant-independent immunization, we observed that Sfpi1lck-/- mice had increased numbers of Tfh cells, increased germinal center B cells (GCB cells), and increased Ab production in vivo. This correlated with increased expression of IL-21 and CD40L in Tfh cells from Sfpi1lck-/- mice compared with control mice. Finally, although blockade of IL-21 did not affect GCB cells in Sfpi1lck-/- mice, anti-CD40L treatment of immunized Sfpi1lck-/- mice decreased GCB cell numbers and Ag-specific Ig concentrations. Together, these data indicate an inhibitory role for PU.1 in the function of Tfh cells, germinal centers, and Tfh-dependent humoral immunity.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Xu, H., et al (2015). "Regulation of bifurcating B cell trajectories by mutual antagonism between transcription factors IRF4 and IRF8" Nat Immunol .
PubMed
Upon recognition of antigen, B cells undertake a bifurcated response in which some cells rapidly differentiate into plasmablasts while others undergo affinity maturation in germinal centers (GCs). Here we identified a double-negative feedback loop between the transcription factors IRF4 and IRF8 that regulated the initial developmental bifurcation of activated B cells as well as the GC response. IRF8 dampened signaling via the B cell antigen receptor (BCR), facilitated antigen-specific interaction with helper T cells, and promoted antibody affinity maturation while antagonizing IRF4-driven differentiation of plasmablasts. Genomic analysis revealed concentration-dependent actions of IRF4 and IRF8 in regulating distinct gene-expression programs. Stochastic modeling suggested that the double-negative feedback was sufficient to initiate bifurcation of the B cell developmental trajectories.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Huang, Y., et al (2015). "CRK proteins selectively regulate T cell migration into inflamed tissues" J Clin Invest 125(3): 1019-1032.
PubMed
Effector T cell migration into inflamed sites greatly exacerbates tissue destruction and disease severity in inflammatory diseases, including graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). T cell migration into such sites depends heavily on regulated adhesion and migration, but the signaling pathways that coordinate these functions downstream of chemokine receptors are largely unknown. Using conditional knockout mice, we found that T cells lacking the adaptor proteins CRK and CRK-like (CRKL) exhibit reduced integrin-dependent adhesion, chemotaxis, and diapedesis. Moreover, these two closely related proteins exhibited substantial functional redundancy, as ectopic expression of either protein rescued defects in T cells lacking both CRK and CRKL. We determined that CRK proteins coordinate with the RAP guanine nucleotide exchange factor C3G and the adhesion docking molecule CASL to activate the integrin regulatory GTPase RAP1. CRK proteins were required for effector T cell trafficking into sites of inflammation, but not for migration to lymphoid organs. In a murine bone marrow transplantation model, the differential migration of CRK/CRKL-deficient T cells resulted in efficient graft-versus-leukemia responses with minimal GVHD. Together, the results from our studies show that CRK family proteins selectively regulate T cell adhesion and migration at effector sites and suggest that these proteins have potential as therapeutic targets for preventing GVHD.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Immunofluorescence
Kim, Y. U., et al (2015). "Regulation of autoimmune germinal center reactions in lupus-prone BXD2 mice by follicular helper T cells" PLoS One 10(3): e0120294.
PubMed
BXD2 mice spontaneously develop autoantibodies and subsequent glomerulonephritis, offering a useful animal model to study autoimmune lupus. Although initial studies showed a critical contribution of IL-17 and Th17 cells in mediating autoimmune B cell responses in BXD2 mice, the role of follicular helper T (Tfh) cells remains incompletely understood. We found that both the frequency of Th17 cells and the levels of IL-17 in circulation in BXD2 mice were comparable to those of wild-type. By contrast, the frequency of PD-1+ CXCR5+ Tfh cells was significantly increased in BXD2 mice compared with wild-type mice, while the frequency of PD-1+ CXCR5+ Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T (Tfr) cells was reduced in the former group. The frequency of Tfh cells rather than that of Th17 cells was positively correlated with the frequency of germinal center B cells as well as the levels of autoantibodies to dsDNA. More importantly, CXCR5+ CD4+ T cells isolated from BXD2 mice induced the production of IgG from naive B cells in an IL-21-dependent manner, while CCR6+ CD4+ T cells failed to do so. These results together demonstrate that Tfh cells rather than Th17 cells contribute to the autoimmune germinal center reactions in BXD2 mice.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Liu, H., et al (2015). "The Immune Adaptor SLP-76 Binds to SUMO-RANGAP1 at Nuclear Pore Complex Filaments to Regulate Nuclear Import of Transcription Factors in T Cells" Mol Cell 59(5): 840-849.
PubMed
While immune cell adaptors regulate proximal T cell signaling, direct regulation of the nuclear pore complex (NPC) has not been reported. NPC has cytoplasmic filaments composed of RanGAP1 and RanBP2 with the potential to interact with cytoplasmic mediators. Here, we show that the immune cell adaptor SLP-76 binds directly to SUMO-RanGAP1 of cytoplasmic fibrils of the NPC, and that this interaction is needed for optimal NFATc1 and NF-kappaB p65 nuclear entry in T cells. Transmission electron microscopy showed anti-SLP-76 cytoplasmic labeling of the majority of NPCs in anti-CD3 activated T cells. Further, SUMO-RanGAP1 bound to the N-terminal lysine 56 of SLP-76 where the interaction was needed for optimal RanGAP1-NPC localization and GAP exchange activity. While the SLP-76-RanGAP1 (K56E) mutant had no effect on proximal signaling, it impaired NF-ATc1 and p65/RelA nuclear entry and in vivo responses to OVA peptide. Overall, we have identified SLP-76 as a direct regulator of nuclear pore function in T cells.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Flow Cytometry
Tang, W., et al (2014). "The oncoprotein and transcriptional regulator Bcl-3 governs plasticity and pathogenicity of autoimmune T cells" Immunity 41(4): 555-566.
PubMed
Bcl-3 is an atypical member of the IkappaB family that modulates transcription in the nucleus via association with p50 (NF-kappaB1) or p52 (NF-kappaB2) homodimers. Despite evidence attesting to the overall physiologic importance of Bcl-3, little is known about its cell-specific functions or mechanisms. Here we demonstrate a T-cell-intrinsic function of Bcl-3 in autoimmunity. Bcl-3-deficient T cells failed to induce disease in T cell transfer-induced colitis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. The protection against disease correlated with a decrease in Th1 cells that produced the cytokines IFN-gamma and GM-CSF and an increase in Th17 cells. Although differentiation into Th1 cells was not impaired in the absence of Bcl-3, differentiated Th1 cells converted to less-pathogenic Th17-like cells, in part via mechanisms involving expression of the RORgammat transcription factor. Thus, Bcl-3 constrained Th1 cell plasticity and promoted pathogenicity by blocking conversion to Th17-like cells, revealing a unique type of regulation that shapes adaptive immunity.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Rabenstein, H., et al (2014). "Differential kinetics of antigen dependency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells" J Immunol 192(8): 3507-3517.
PubMed
Ag recognition via the TCR is necessary for the expansion of specific T cells that then contribute to adaptive immunity as effector and memory cells. Because CD4+ and CD8+ T cells differ in terms of their priming APCs and MHC ligands we compared their requirements of Ag persistence during their expansion phase side by side. Proliferation and effector differentiation of TCR transgenic and polyclonal mouse T cells were thus analyzed after transient and continuous TCR signals. Following equally strong stimulation, CD4+ T cell proliferation depended on prolonged Ag presence, whereas CD8+ T cells were able to divide and differentiate into effector cells despite discontinued Ag presentation. CD4+ T cell proliferation was neither affected by Th lineage or memory differentiation nor blocked by coinhibitory signals or missing inflammatory stimuli. Continued CD8+ T cell proliferation was truly independent of self-peptide/MHC-derived signals. The subset divergence was also illustrated by surprisingly broad transcriptional differences supporting a stronger propensity of CD8+ T cells to programmed expansion. These T cell data indicate an intrinsic difference between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells regarding the processing of TCR signals for proliferation. We also found that the presentation of a MHC class II-restricted peptide is more efficiently prolonged by dendritic cell activation in vivo than a class I bound one. In summary, our data demonstrate that CD4+ T cells require continuous stimulation for clonal expansion, whereas CD8+ T cells can divide following a much shorter TCR signal.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Vegran, F., et al (2014). "The transcription factor IRF1 dictates the IL-21-dependent anticancer functions of TH9 cells" Nat Immunol 15(8): 758-766.
PubMed
The TH9 subset of helper T cells was initially shown to contribute to the induction of autoimmune and allergic diseases, but subsequent evidence has suggested that these cells also exert antitumor activities. However, the molecular events that account for their effector properties are elusive. Here we found that the transcription factor IRF1 enhanced the effector function of TH9 cells and dictated their anticancer properties. Under TH9-skewing conditions, interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) induced phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT1 and subsequent expression of IRF1, which bound to the promoters of Il9 and Il21 and enhanced secretion of the cytokines IL-9 and IL-21 from TH9 cells. Furthermore, IL-1beta-induced TH9 cells exerted potent anticancer functions in an IRF1- and IL-21-dependent manner. Our findings thus identify IRF1 as a target for controlling the function of TH9 cells.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Bertin, S., et al (2014). "The ion channel TRPV1 regulates the activation and proinflammatory properties of CD4(+) T cells" Nat Immunol 15(11): 1055-1063.
PubMed
TRPV1 is a Ca(2+)-permeable channel studied mostly as a pain receptor in sensory neurons. However, its role in other cell types is poorly understood. Here we found that TRPV1 was functionally expressed in CD4(+) T cells, where it acted as a non-store-operated Ca(2+) channel and contributed to T cell antigen receptor (TCR)-induced Ca(2+) influx, TCR signaling and T cell activation. In models of T cell-mediated colitis, TRPV1 promoted colitogenic T cell responses and intestinal inflammation. Furthermore, genetic and pharmacological inhibition of TRPV1 in human CD4(+) T cells recapitulated the phenotype of mouse Trpv1(-/-) CD4(+) T cells. Our findings suggest that inhibition of TRPV1 could represent a new therapeutic strategy for restraining proinflammatory T cell responses.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Berger, H., et al (2013). "SOCS3 transactivation by PPARgamma prevents IL-17-driven cancer growth" Cancer Res 73(12): 3578-3590.
PubMed
Activation of the transcription factor PPARgamma by the n-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is implicated in controlling proinflammatory cytokine secretion, but the intracellular signaling pathways engaged by PPARgamma are incompletely characterized. Here, we identify the adapter-encoding gene SOCS3 as a critical transcriptional target of PPARgamma. SOCS3 promoter binding and gene transactivation by PPARgamma was associated with a repression in differentiation of proinflammatory T-helper (TH)17 cells. Accordingly, TH17 cells induced in vitro displayed increased SOCS3 expression and diminished capacity to produce interleukin (IL)-17 following activation of PPARgamma by DHA. Furthermore, naive CD4 T cells derived from mice fed a DHA-enriched diet displayed less capability to differentiate into TH17 cells. In two different mouse models of cancer, DHA prevented tumor outgrowth and angiogenesis in an IL-17-dependent manner. Altogether, our results uncover a novel molecular pathway by which PPARgamma-induced SOCS3 expression prevents IL-17-mediated cancer growth.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Sledzinska, A., et al (2013). "TGF-beta signalling is required for CD4(+) T cell homeostasis but dispensable for regulatory T cell function" PLoS Biol 11(10): e1001674.
PubMed
TGF-beta is widely held to be critical for the maintenance and function of regulatory T (T(reg)) cells and thus peripheral tolerance. This is highlighted by constitutive ablation of TGF-beta receptor (TR) during thymic development in mice, which leads to a lethal autoimmune syndrome. Here we describe that TGF-beta-driven peripheral tolerance is not regulated by TGF-beta signalling on mature CD4(+) T cells. Inducible TR2 ablation specifically on CD4(+) T cells did not result in a lethal autoinflammation. Transfer of these TR2-deficient CD4(+) T cells to lymphopenic recipients resulted in colitis, but not overt autoimmunity. In contrast, thymic ablation of TR2 in combination with lymphopenia led to lethal multi-organ inflammation. Interestingly, deletion of TR2 on mature CD4(+) T cells does not result in the collapse of the T(reg) cell population as observed in constitutive models. Instead, a pronounced enlargement of both regulatory and effector memory T cell pools was observed. This expansion is cell-intrinsic and seems to be caused by increased T cell receptor sensitivity independently of common gamma chain-dependent cytokine signals. The expression of Foxp3 and other regulatory T cells markers was not dependent on TGF-beta signalling and the TR2-deficient T(reg) cells retained their suppressive function both in vitro and in vivo. In summary, absence of TGF-beta signalling on mature CD4(+) T cells is not responsible for breakdown of peripheral tolerance, but rather controls homeostasis of mature T cells in adult mice.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Goswami, R., et al (2012). "STAT6-dependent regulation of Th9 development" J Immunol 188(3): 968-975.
PubMed
Th cell effector subsets develop in response to specific cytokine environments. The development of a particular cytokine-secreting pattern requires an integration of signals that may promote the development of opposing pathways. A recent example of this paradigm is the IL-9-secreting Th9 cell that develops in response to TGF-beta and IL-4, cytokines that, in isolation, promote the development of inducible regulatory T cells and Th2 cells, respectively. To determine how the balance of these factors results in priming for IL-9 secretion, we examined the effects of each pathway on transcription factors that regulate Th cell differentiation. We demonstrated that TGF-beta induces the PU.1-encoding Sfpi1 locus and that this is independent of IL-4-induced STAT6 activation. IL-4-activated STAT6 is required for repressing the expression of T-bet and Foxp3 in Th9 cells, transcription factors that inhibit IL-9 production, and STAT6 is required for the induction of IRF4, which promotes Th9 development. These data established a transcription factor network that regulates IL-9 and demonstrated how combinations of cytokine signals generate cytokine-secreting potential by altering the expression of a panel of transcription factors.
in vivo T cell depletion
Peng, B., et al (2009). "Anti-CD3 antibodies modulate anti-factor VIII immune responses in hemophilia A mice after factor VIII plasmid-mediated gene therapy" Blood 114(20): 4373-4382.
PubMed
One major obstacle in gene therapy is the generation of immune responses directed against transgene product. Five consecutive anti-CD3 treatments concomitant with factor VIII (FVIII) plasmid injection prevented the formation of inhibitory antibodies against FVIII and achieved persistent, therapeutic levels of FVIII gene expression in treated hemophilia A mice. Repeated plasmid gene transfer is applicable in tolerized mice without eliciting immune responses. Anti-CD3 treatment significantly depleted both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, whereas increased transforming growth factor-beta levels in plasma and the frequency of both CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ and CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the initial few weeks after treatment. Although prior depletion of CD4+CD25+ cells did not abrogate tolerance induction, adoptive transfer of CD4+ cells from tolerized mice at 6 weeks after treatment protected recipient mice from anti-FVIII immune responses. Anti-CD3-treated mice mounted immune responses against both T-dependent and T-independent neo-antigens, indicating that anti-CD3 did not hamper the immune systems in the long term. Concomitant FVIII plasmid + anti-CD3 treatment induced long-term tolerance specific to FVIII via a mechanism involving the increase in transforming growth factor-beta levels and the generation of adaptive FVIII-specific CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells at the periphery. Furthermore, anti-CD3 can reduce the titers of preexisting anti-FVIII inhibitory antibodies in hemophilia A mice.
in vitro T cell stimulation/activation
Dardalhon, V., et al (2008). "IL-4 inhibits TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-beta, generates IL-9+ IL-10+ Foxp3(-) effector T cells" Nat Immunol 9(12): 1347-1355.
PubMed
Transcription factor Foxp3 is critical for generating regulatory T cells (T(reg) cells). Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) induces Foxp3 and suppressive T(reg) cells from naive T cells, whereas interleukin 6 (IL-6) inhibits the generation of inducible T(reg) cells. Here we show that IL-4 blocked the generation of TGF-beta-induced Foxp3(+) T(reg) cells and instead induced a population of T helper cells that produced IL-9 and IL-10. The IL-9(+)IL-10(+) T cells demonstrated no regulatory properties despite producing abundant IL-10. Adoptive transfer of IL-9(+)IL-10(+) T cells into recombination-activating gene 1-deficient mice induced colitis and peripheral neuritis, the severity of which was aggravated if the IL-9(+)IL-10(+) T cells were transferred with CD45RB(hi) CD4(+) effector T cells. Thus IL-9(+)IL-10(+) T cells lack suppressive function and constitute a distinct population of helper-effector T cells that promote tissue inflammation.
Product Citations
-
A glucose kinase-independent HK2 activity prevents TNF-induced cell death by phosphorylating RIPK1.
In Nat Commun on 13 November 2025 by Zou, T., Liu, R., et al.
PubMed
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced RIPK1-mediated cell death is implicated in various human diseases. However, the mechanisms RIPK1-mediated cell death is regulated by metabolic processes remain unclear. Here, we identify hexokinase 2 (HK2), a critical regulator of glycolysis, as a suppressor of TNF-induced RIPK1 kinase-dependent cell death through its non-metabolic function. HK2 inhibits RIPK1 kinase activity through constitutively phosphorylation at serine 32 of RIPK1. Inhibition of RIPK1 S32-phosphorylation results in RIPK1 kinase activation and subsequent cell death in response to TNFα stimulation. We further show that HK2 is elevated under pathological conditions including liver ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) via the transcriptional factor HMGA1. Moreover, the upregulation of HK2 in the liver confers protection against liver IR injury mediated by RIPK1 kinase, while depleting HK2 in HCC cells enhances TNFα-induced cell death and synergistically improves the efficacy of anti-PD1 therapy in an HCC model. Thus, the findings reveal a potential therapeutic avenue for RIPK1-related diseases through manipulating HK2 non-metabolic function.
-
-
Cell Biology
IRF7 drives macrophages to kill bacteria and improves septic outcomes via autophagy.
In JCI Insight on 10 November 2025 by Chen, G., Li, K., et al.
PubMed
Sepsis contributes substantially to mortality rates worldwide, yet clinical trials that have focused on its underlying pathogenesis have failed to demonstrate benefits. Recently, enhancing self-defense has been regarded as an emerging therapeutic approach. Autophagy is a self-defense mechanism that protects septic mice, but its regulatory factor is still unknown. Moreover, the role of interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) in sepsis has been debated. Here, we showed that Irf7 deficiency increased mortality during polymicrobial sepsis. Furthermore, IRF7 drove macrophages to protect against sepsis. Mechanistically, IRF7 is a transcription factor that upregulates the expression of autophagy-related genes responsible for autophagosome formation and autolysosome maturation, induces autophagic killing of bacteria, and ultimately reduces septic organ injury. Recombinant adeno-associated virus 9-Irf7-mediated IRF7 overexpression promoted the autophagic clearance of pathogens and improved sepsis outcomes, which may be the mechanism underlying the observed improvement in bacterial clearance. These findings provide evidence that IRF7 is the underlying regulatory factor that drives autophagy to eliminate pathogens in macrophages during sepsis. Collectively, IRF7 overexpression represents a potential host-directed therapeutic strategy for preclinical sepsis models, operating independently of antibiotic mechanisms.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
Temporal and context-dependent requirements for the transcription factor Foxp3 expression in regulatory T cells.
In Nat Immunol on 1 November 2025 by Hu, W., Dolsten, G. A., et al.
PubMed
Regulatory T (Treg) cells, expressing the transcription factor Foxp3, are obligatory gatekeepers of immune responsiveness, yet the mechanisms by which Foxp3 governs the Treg transcriptional network remain incompletely understood. Using a novel chemogenetic system of inducible Foxp3 protein degradation in vivo, we found that while Foxp3 was indispensable for the establishment of transcriptional and functional programs of newly generated Treg cells, Foxp3 loss in mature Treg cells resulted in minimal functional and transcriptional changes under steady state. This resilience of the Foxp3-dependent program in mature Treg cells was acquired over an unexpectedly long timescale; however, in settings of severe inflammation, Foxp3 loss led to a pronounced perturbation of Treg cell transcriptome and fitness. Furthermore, tumoral Treg cells were uniquely sensitive to Foxp3 degradation, which led to impairment in their suppressive function and tumor shrinkage in the absence of pronounced adverse effects. These studies demonstrate a context-dependent differential requirement for Foxp3 for Treg transcriptional and functional programs.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Heme and iron toxicity in the aged spleen impairs T cell immunity through iron deprivation.
In Nat Aging on 1 November 2025 by Ezuz, D., Ombashe, H., et al.
PubMed
Mechanisms of T cell aging involve cell-intrinsic alterations and interactions with immune and stromal cells. Here we found that splenic T cells exhibit greater functional decline than lymph node T cells within the same aged mouse, prompting investigation into how the aged spleen contributes to T cell aging. Proteomic analysis revealed increased expression of heme detoxification in aged spleen-derived lymphocytes. Exposure to the heme- and iron-rich aged splenic microenvironment induced aging phenotypes in young T cells, including reduced proliferation and CD39 upregulation. T cells survived this hostile niche by maintaining a low labile iron pool, at least in part, via IRP2 downregulation to resist ferroptosis but failed to induce sufficient iron uptake for activation. Iron supplementation enhanced antigen-specific T cell responses in aged mice. This study identifies the aged spleen as a source of hemolytic signals that systemically impair T cell function, underscoring a trade-off between T cell survival and function and implicating iron metabolism in immune aging.
-
-
Spatiotemporal dynamics of the cardioimmune niche during lesion repair.
In Nat Cardiovasc Res on 1 November 2025 by Chan, A., Greiner, J., et al.
PubMed
The heart is one of the least regenerative organs in humans, and ischemic heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. Understanding the cellular and molecular processes that occur during cardiac wound healing is an essential prerequisite to reducing health burden and improving cardiac function after myocardial tissue damage. Here, by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing with high-resolution spatial transcriptomics, we reconstruct the spatiotemporal dynamics of the fibrotic niches after cardiac injury in adult mice. We reveal a complex multicellular network that regulates cardiac repair, including fibroblast proliferation silencing by Trem2high macrophages to prevent excessive fibrosis. We further discovered a rare population of progenitor-like cardiomyocytes after lesion, promoted by myeloid and lymphoid niche signals. Culturing non-regenerative mouse cardiomyocytes or human heart tissue with these niche factors reactivated progenitor gene expression and cell cycle activity. In summary, this spatiotemporal atlas provides valuable insights into the heterocellular interactions that control cardiac repair.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Combination LIGHT overexpression and checkpoint blockade disrupts the tumor immune environment impacting colorectal liver metastases.
In Sci Adv on 10 October 2025 by Keenan, B. P., Qiao, G., et al.
PubMed
Colorectal cancer and liver metastases are a leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Overexpression of the immunostimulatory cytokine TNFSF14/LIGHT associates with improved survival and correlates with increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients and a clinically relevant model of colorectal liver metastases. We demonstrate that LIGHT monotherapy activates T cells, but also induces T cell exhaustion and the recruitment of immunosuppressive elements. As colorectal liver metastases exhibit high levels of CTLA-4 expression, we combined LIGHT overexpression with anti-CTLA-4, leading to complete tumor control. The combination functions by homing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, inducing tumor antigen-specific T cells, and reversing T cell exhaustion. Whereas both LIGHT overexpression and anti-CTLA-4 increase tumor-promoting macrophages, the combination eliminates this population. The ability of LIGHT overexpression combined with CTLA-4 inhibition to reverse T cell exhaustion and myeloid cell suppression is supported by analysis of complementary patient cohorts and has strong clinical relevance, especially given that liver metastases contribute to immunotherapy resistance across various cancer types.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
TAGAP restrains myeloid and T cell activation in inflammatory bowel disease.
In Front Immunol on 8 October 2025 by Lin, R. C., Shao, Z., et al.
PubMed
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by chronic, relapsing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Genetic factors, including variants in T-cell activation Rho GTPase-activating protein (TAGAP), contribute to disease susceptibility and severity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Protocol for the coculture of murine vaginal epithelial organoids and T cells to induce resident memory CD8 T cell differentiation.
In STAR Protoc on 19 September 2025 by Ramprashad, J. C., Lin, Y., et al.
PubMed
Inducing robust resident memory T cell (TRM) establishment in mucosal tissues could enhance immunotherapy and vaccine efficacy. However, the factors influencing TRM formation are not fully understood. We present a protocol to coculture murine effector CD8 T cells with epithelial organoids, which serve as a reductionist model for investigating TRM differentiation in vitro. We describe steps for naive CD8 T cell activation, coculture of T cells with vaginal epithelial organoids (VEOs), and analysis of T cell phenotypes via flow cytometry. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Ulibarri et al.1.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Systemic metabolic changes in acute and chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection.
In Mol Metab on 1 September 2025 by Bartman, C. R., Hou, S., et al.
PubMed
Viral infection of cells leads to metabolic changes, but how viral infection changes whole-body and tissue metabolism in vivo has not been comprehensively studied. In particular, it is unknown how metabolism might be differentially affected by an acute infection that the immune system can successfully clear compared to a chronic persistent infection.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
Upstream open reading frame translation enhances immunogenic peptide presentation in mitotically arrested cancer cells.
In Nat Commun on 27 August 2025 by Kowar, A., Becker, J. P., et al.
PubMed
Mitosis is a critical phase of the cell cycle and a vulnerable point where cancer cells can be disrupted, causing cell death and inhibiting tumor growth. Challenges such as drug resistance persist in clinical applications. During mitosis, mRNA translation is generally downregulated, while non-canonical translation of specific transcripts continues. Here, we show that mitotic cancer cells redistribute ribosomes toward the 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) and beginning of the coding sequence (CDS), enhancing translation of thousands of upstream open reading frames (uORFs) and upstream overlapping open reading frames (uoORFs). This mitotic induction of uORF/uoORF enriches human leukocyte antigen (HLA) presentation of non-canonical peptides on the surface of cancer cells after mitotic inhibitor treatment. Functional assays indicate these epitopes provoke cancer-cell killing by T cells. Our findings highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting uORF/uoORF-derived epitopes with mitotic inhibitors to enhance immune recognition and tumor cell elimination.
-
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Cancer Research
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
Tumor-infiltrating nociceptor neurons promote immunosuppression.
In Sci Signal on 5 August 2025 by Restaino, A. C., Ahmadi, M., et al.
PubMed
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) released from tumors recruit nociceptor neurons to the tumor bed. Here, we found that ablating these neurons in mouse models of head and neck carcinoma and melanoma reduced the infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Moreover, sEV-deficient tumors failed to develop in mice lacking nociceptor neurons. We investigated the interplay between tumor-infiltrating nociceptors and immune cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and melanoma. Upon exposure to cancer-derived sEVs, mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons secreted increased amounts of substance P, IL-6, and injury-associated neuronal markers. Patient-derived sEVs sensitized DRG neurons to capsaicin, implying enhanced nociceptor responsiveness. Furthermore, nociceptors cultured with sEVs induced an immunosuppressed state in CD8+ T cells. Incubation with conditioned medium from cocultures of neurons and cancer cells resulted in increased expression of markers of MDSCs and suppressive function in primary bone marrow cells, and the combination of neuron-conditioned medium and cancer sEVs promoted checkpoint receptor expression on T cells. Together, these findings reveal that nociceptor neurons facilitate CD8+ T cell exhaustion and bolster MDSC infiltration into HNSCC and melanoma. Consequently, targeting nociceptors may provide a strategy to disrupt detrimental neuroimmune cross-talk in cancer and potentiate antitumor immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Antimalarial Drug Artemotil Promotes Induction of Type 1 Regulatory T Cells.
In Inflammation on 1 August 2025 by Madan, U., Awasthi, A., et al.
PubMed
Artemisinin and its derivatives, used as front-line anti-malarial drugs, exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. They were found to suppress the generation and function of Th1 and Th17 cells while promoting the generation of Foxp3 + regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, the specific role of Artemotil (β-arteether) in modulating the generation and functions of CD4 + T cells, particularly Type 1 regulatory T cells (Tr1), remains to be explored. Tr1 cells are one of the key cell types that are essential for regulating inflammatory response through IL-10. In this study, we report that Artemotil selectively promotes generation of Tr1 cells induced by IL-27 by upregulating signature genes of Tr1 cells, such as c-Maf, AhR, prdm1, IRF-1, and Batf, while inhibiting the Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells generation. We found that co-administration of Artemotil with anti-CD3 antibody increases the induction of IL-10 and frequency of Tr1 cells while suppressing Th1 and Th17 cells in vivo. Artemotil suppresses T-cell-induced enteropathy and alleviates the signs of colitis associated with the increased frequencies of Tr1 cells. Taken together, our data suggest that Artemotil provides protection in T-cell-mediated colitis by increasing the expansion of Tr1 cells and inhibiting the generation of Th1 and Th17 cells.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
Testosterone Suppresses IL-17 Expression by Targeting RORγt Functions.
In Eur J Immunol on 1 August 2025 by Binayke, A., Dalal, R., et al.
PubMed
Th17 cells play a crucial role in autoimmune disease pathogenesis. However, the mechanisms behind the sex differences in immune responses, particularly women's higher susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, remain unclear. This study investigated the role of testosterone in modulating the IL-17 response. IL-17 levels and IL-17-expressing cells were compared between males and females, and testosterone's effect on Th17 differentiation was evaluated. In an imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model, testosterone supplementation reduced psoriasis severity in female mice, whereas castration of male mice exacerbated psoriasis. Testosterone inhibited both in vitro Th17 differentiation and in vivo IL-17 expression, correlating with reduced psoriasis severity. Molecular studies indicated that testosterone is an inverse agonist of related orphan receptor gamma (RORγt), a key transcription factor for IL-17 expression. These findings offer mechanistic insights into how testosterone limits tissue inflammation in psoriasis and suggest a basis for developing novel testosterone derivatives to target RORγt and suppress Th17-mediated inflammation.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
BLIMP1 negatively regulates IL-2 signaling in T cells.
In Sci Adv on 18 July 2025 by Roy, S., Ren, M., et al.
PubMed
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) regulates immune homeostasis by fine-tuning the balance between effector and regulatory T (Treg) cells. To identify regulators of IL-2 signaling, we performed genome-wide CRISPR-knockout screening in IL-2-dependent cells derived from a patient with adult T cell leukemia (ATL) and found enrichment of single guide RNAs targeting PRDM1, which encodes B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1 (BLIMP1). BLIMP1 inhibits IL-2 production by T cells; however, its role in IL-2 signaling remains unknown. Here, we show that overexpressing Prdm1 down-regulated IL-2 signaling, whereas Prdm1-deficiency enhanced IL-2 signaling in mouse CD4+ T cells and Treg cells with augmented IL-2 signaling in T cells from influenza-infected mice and during adoptive T cell transfer-induced colitis. Deleting PRDM1 in human CD4+ T cells and Treg cells also increased IL-2 signaling. Furthermore, CD4+ T cells from patients with ATL expressed less BLIMP1 and had enhanced IL-2 signaling, whereas overexpressing PRDM1 in ATL cells suppressed IL-2 signaling. Thus, BLIMP1 inhibits IL-2 signaling during normal and pathophysiological responses, suggesting that manipulating BLIMP1 could have therapeutic potential.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Hepatitis B virus promotes liver cancer by modulating the immune response to environmental carcinogens.
In Nat Commun on 27 June 2025 by Huang, M., Wang, D., et al.
PubMed
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is associated with hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Considering that most HBV-infected individuals remain asymptomatic, the mechanism linking HBV to hepatitis and HCC remains uncertain. Herein, we demonstrate that HBV alone does not cause liver inflammation or cancer. Instead, HBV alters the chronic inflammation induced by chemical carcinogens to promote liver carcinogenesis. Long-term HBV genome expression in mouse liver increases liver inflammation and cancer propensity caused by a carcinogen, diethylnitrosamine (DEN). HBV plus DEN-activated interleukin-33 (IL-33)/regulatory T cell axis is required for liver carcinogenesis. Pitavastatin, an IL-33 inhibitor, suppresses HBV plus DEN-induced liver cancer. IL-33 is markedly elevated in HBV+ hepatitis patients, and pitavastatin use significantly correlates with reduced risk of hepatitis and its associated HCC in patients. Collectively, our findings reveal that environmental carcinogens are the link between HBV and HCC risk, creating a window of opportunity for cancer prevention in HBV carriers.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Intermittent fasting exacerbates colon inflammation by promoting Th17 cell differentiation through inhibition of gut microbiota-derived indoleacrylic acid.
In World J Gastroenterol on 14 June 2025 by Fu, R., Zhang, P., et al.
PubMed
Intermittent fasting (IF), particularly time-restricted feeding (TRF), is increasingly popular has gained popularity for weight loss, yet management, but its effects impact on gut health remain unclear. Remains inadequately understood. This study explores how investigated the effects of TRF effects on intestinal health and explored the underlying mechanisms.
-
-
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Pluripotent stem cell–derived extracellular vesicles for systemic immune modulation in diabetes therapy
In Research Square on 10 June 2025 by Li, S., Zarubova, J., et al.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
Dual Ribosome Profiling reveals metabolic limitations of cancer and stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment.
In Nat Commun on 19 May 2025 by Aviles-Huerta, D., Del Pizzo, R., et al.
PubMed
The tumor microenvironment (TME) influences cancer cell metabolism and survival. However, how immune and stromal cells respond to metabolic stress in vivo, and how nutrient limitations affect therapy, remains poorly understood. Here, we introduce Dual Ribosome Profiling (DualRP) to simultaneously monitor translation and ribosome stalling in multiple tumor cell populations. DualRP reveals that cancer-fibroblast interactions trigger an inflammatory program that reduces amino acid shortages during glucose starvation. In immunocompetent mice, we show that serine and glycine are essential for optimal T cell function and that their deficiency impairs T cell fitness. Importantly, immune checkpoint blockade therapy imposes amino acid restrictions specifically in T cells, demonstrating that therapies create distinct metabolic demands across TME cell types. By mapping codon-resolved ribosome stalling in a cell‑type‑specific manner, DualRP uncovers metabolic crosstalk that shapes translational programs. DualRP thus offers a powerful, innovative approach for dissecting tumor cell metabolic interplay and guiding combined metabolic-immunotherapeutic strategies.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
Temporal and Context-Dependent Requirements for the Transcription Factor Foxp3 Expression in Regulatory T Cells
In Research Square on 14 May 2025 by Rudensky, A., Hu, W., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Gene Therapy with Enterovirus 3 C Protease: A Promising Strategy for Various Solid Tumors.
In Nat Commun on 8 May 2025 by Yang, X., Li, W., et al.
PubMed
Current cancer gene therapies rely primarily on antitumor immunity, but the exploration of alternative mRNA cargoes for direct antitumor effects is crucial to expand cancer gene therapies. Here we show that lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) carrying mRNA encoding a viral 3 C protease can efficiently suppress tumors by selectively inducing tumor cell apoptosis. In various solid tumor models, intracranial injection of LNPs carrying mRNA encoding the 3 C protease (3C-LNPs) significantly inhibits tumor growth and prolongs survival in glioblastoma models. Similarly, subcutaneous injection reduces tumor volume and inhibits angiogenesis in a breast cancer model, while intravenous injection inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis and prolongs survival in hepatocellular carcinoma models. Mass spectrometry and cleavage site prediction assays identify heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1) as the main target degraded by the 3 C protease. This study suggests that viral protease mRNA could be a promising broad-spectrum antitumor therapeutic.
-