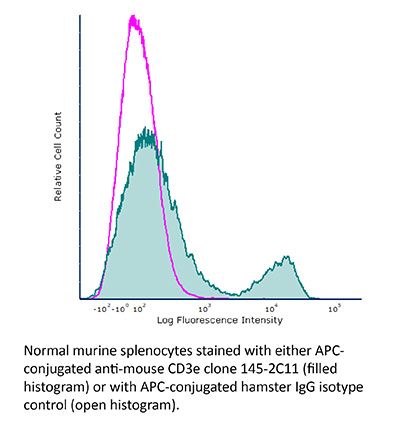
FlowMAb APC anti-mouse CD3ε
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Armenian Hamster IgG1 |
|---|---|
| Conjugation | APC |
| Excitation Source | Red 627-640 nm |
| Excitation Max | 651 nm |
| Emission Max | 660 nm |
| Immunogen | Mouse BM10-37 cytotoxic T cells |
| Reported Applications |
Immunofluorescence Flow cytometry |
| Protocol Information | It is recommended that the reagent be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. |
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/ml |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains 0.09% Sodium Azide |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A. Conjugated with allophycocyanin under optimal conditions. |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
Immunofluorescence
Kim, Y. U., et al. (2015). "Regulation of autoimmune germinal center reactions in lupus-prone BXD2 mice by follicular helper T cells" PLoS One 10(3): e0120294.
PubMed
BXD2 mice spontaneously develop autoantibodies and subsequent glomerulonephritis, offering a useful animal model to study autoimmune lupus. Although initial studies showed a critical contribution of IL-17 and Th17 cells in mediating autoimmune B cell responses in BXD2 mice, the role of follicular helper T (Tfh) cells remains incompletely understood. We found that both the frequency of Th17 cells and the levels of IL-17 in circulation in BXD2 mice were comparable to those of wild-type. By contrast, the frequency of PD-1+ CXCR5+ Tfh cells was significantly increased in BXD2 mice compared with wild-type mice, while the frequency of PD-1+ CXCR5+ Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T (Tfr) cells was reduced in the former group. The frequency of Tfh cells rather than that of Th17 cells was positively correlated with the frequency of germinal center B cells as well as the levels of autoantibodies to dsDNA. More importantly, CXCR5+ CD4+ T cells isolated from BXD2 mice induced the production of IgG from naive B cells in an IL-21-dependent manner, while CCR6+ CD4+ T cells failed to do so. These results together demonstrate that Tfh cells rather than Th17 cells contribute to the autoimmune germinal center reactions in BXD2 mice.
Flow Cytometry
Tang, W., et al. (2014). "The oncoprotein and transcriptional regulator Bcl-3 governs plasticity and pathogenicity of autoimmune T cells" Immunity 41(4): 555-566.
PubMed
Bcl-3 is an atypical member of the IkappaB family that modulates transcription in the nucleus via association with p50 (NF-kappaB1) or p52 (NF-kappaB2) homodimers. Despite evidence attesting to the overall physiologic importance of Bcl-3, little is known about its cell-specific functions or mechanisms. Here we demonstrate a T-cell-intrinsic function of Bcl-3 in autoimmunity. Bcl-3-deficient T cells failed to induce disease in T cell transfer-induced colitis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. The protection against disease correlated with a decrease in Th1 cells that produced the cytokines IFN-gamma and GM-CSF and an increase in Th17 cells. Although differentiation into Th1 cells was not impaired in the absence of Bcl-3, differentiated Th1 cells converted to less-pathogenic Th17-like cells, in part via mechanisms involving expression of the RORgammat transcription factor. Thus, Bcl-3 constrained Th1 cell plasticity and promoted pathogenicity by blocking conversion to Th17-like cells, revealing a unique type of regulation that shapes adaptive immunity.