Catalog #CP069
RecombiMAb anti-mouse LPAM-1 (Integrin α4β7)
Clone
DATK32-CP069
Isotype
Mouse IgG2a, kappa
(switched from rat IgG2a, kappa)
(switched from rat IgG2a, kappa)
You may also be interested in:
Product Description
The DATK32-CP069 monoclonal antibody is a recombinant, chimeric version of the original DATK32 antibody. The variable domain sequences are identical but the constant region sequences have been switched from rat IgG2a, κ to mouse IgG2a, κ for use in murine models. Species-matched chimeric antibodies exhibit regulated effector functions—including Fc receptor binding and complement activation—and result in less immunogenicity and formation of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) than xenogenic antibodies in animal models. The highly controlled sequence and lack of genetic drift in recombinant antibodies provide more reliable and reproducible results over hybridoma derived antibodies.
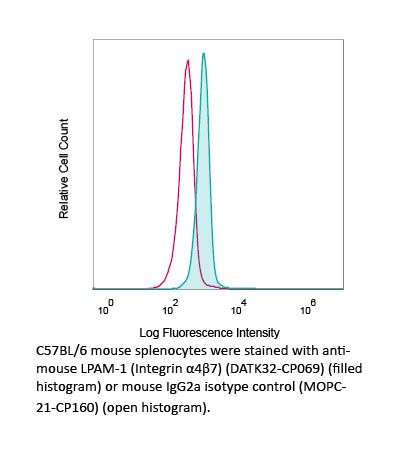
The DATK32 monoclonal antibody reacts with mouse LPAM-1 also known as integrin alpha 4 beta 7. The 130 kDa integrin β7 chain associates with the 150 kDa integrin α4 (CD49d) chain to form LPAM-1, a member of the Ig superfamily. LPAM-1 is expressed by peripheral lymphocytes, small subsets of thymocytes, and bone marrow progenitors. LPAM-1 binds VCAM-1 (CD106), MAdCAM-1, and fibronectin and facilitates lymphocyte adhesion and migration to the intestine and associated lymphoid tissues. The DATK32 antibody has been reported to block LPAM-1-mediated cell adhesion in vivo.
The DATK32 monoclonal antibody reacts with mouse LPAM-1 also known as integrin alpha 4 beta 7. The 130 kDa integrin β7 chain associates with the 150 kDa integrin α4 (CD49d) chain to form LPAM-1, a member of the Ig superfamily. LPAM-1 is expressed by peripheral lymphocytes, small subsets of thymocytes, and bone marrow progenitors. LPAM-1 binds VCAM-1 (CD106), MAdCAM-1, and fibronectin and facilitates lymphocyte adhesion and migration to the intestine and associated lymphoid tissues. The DATK32 antibody has been reported to block LPAM-1-mediated cell adhesion in vivo.
Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb mouse IgG2a isotype control, unknown specificity |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | TK1 cells |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo Integrin α4β7 neutralization Flow cytometry For information on in vivo applications, please contact technicalservice@bioxcell.com |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from HEK293 cell supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |