InVivoMAb anti-mouse IL-23 (p19)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG1 isotype control, anti-horseradish peroxidase |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Insect cell-expressed, recombinant mouse IL-23 heterodimer |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo IL-23p19 neutralization Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_2754551 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo IL-23p19 neutralization
Calcinotto, A., et al (2018). "IL-23 secreted by myeloid cells drives castration-resistant prostate cancer" Nature 559(7714): 363-369.
PubMed
Patients with prostate cancer frequently show resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy, a condition known as castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Acquiring a better understanding of the mechanisms that control the development of CRPC remains an unmet clinical need. The well-established dependency of cancer cells on the tumour microenvironment indicates that the microenvironment might control the emergence of CRPC. Here we identify IL-23 produced by myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) as a driver of CRPC in mice and patients with CRPC. Mechanistically, IL-23 secreted by MDSCs can activate the androgen receptor pathway in prostate tumour cells, promoting cell survival and proliferation in androgen-deprived conditions. Intra-tumour MDSC infiltration and IL-23 concentration are increased in blood and tumour samples from patients with CRPC. Antibody-mediated inactivation of IL-23 restored sensitivity to androgen-deprivation therapy in mice. Taken together, these results reveal that MDSCs promote CRPC by acting in a non-cell autonomous manner. Treatments that block IL-23 can oppose MDSC-mediated resistance to castration in prostate cancer and synergize with standard therapies.
in vivo IL-23p19 neutralization
Coffelt, S. B., et al (2015). "IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis" Nature 522(7556): 345-348.
PubMed
Metastatic disease remains the primary cause of death for patients with breast cancer. The different steps of the metastatic cascade rely on reciprocal interactions between cancer cells and their microenvironment. Within this local microenvironment and in distant organs, immune cells and their mediators are known to facilitate metastasis formation. However, the precise contribution of tumour-induced systemic inflammation to metastasis and the mechanisms regulating systemic inflammation are poorly understood. Here we show that tumours maximize their chance of metastasizing by evoking a systemic inflammatory cascade in mouse models of spontaneous breast cancer metastasis. We mechanistically demonstrate that interleukin (IL)-1beta elicits IL-17 expression from gamma delta (gammadelta) T cells, resulting in systemic, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-dependent expansion and polarization of neutrophils in mice bearing mammary tumours. Tumour-induced neutrophils acquire the ability to suppress cytotoxic T lymphocytes carrying the CD8 antigen, which limit the establishment of metastases. Neutralization of IL-17 or G-CSF and absence of gammadelta T cells prevents neutrophil accumulation and downregulates the T-cell-suppressive phenotype of neutrophils. Moreover, the absence of gammadelta T cells or neutrophils profoundly reduces pulmonary and lymph node metastases without influencing primary tumour progression. Our data indicate that targeting this novel cancer-cell-initiated domino effect within the immune system–the gammadelta T cell/IL-17/neutrophil axis–represents a new strategy to inhibit metastatic disease.
in vivo IL-23p19 neutralization
Krause, P., et al (2015). "IL-10-producing intestinal macrophages prevent excessive antibacterial innate immunity by limiting IL-23 synthesis" Nat Commun 6: 7055.
PubMed
Innate immune responses are regulated in the intestine to prevent excessive inflammation. Here we show that a subset of mouse colonic macrophages constitutively produce the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. In mice infected with Citrobacter rodentium, a model for enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in humans, these macrophages are required to prevent intestinal pathology. IL-23 is significantly increased in infected mice with a myeloid cell-specific deletion of IL-10, and the addition of IL-10 reduces IL-23 production by intestinal macrophages. Furthermore, blockade of IL-23 leads to reduced mortality in the context of macrophage IL-10 deficiency. Transcriptome and other analyses indicate that IL-10-expressing macrophages receive an autocrine IL-10 signal. Interestingly, only transfer of the IL-10 positive macrophages could rescue IL-10-deficient infected mice. Therefore, these data indicate a pivotal role for intestinal macrophages that constitutively produce IL-10, in controlling excessive innate immune activation and preventing tissue damage after an acute bacterial infection.
in vivo IL-23p19 neutralization
Wang, X., et al (2013). "High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)-Toll-like receptor (TLR)4-interleukin (IL)-23-IL-17A axis in drug-induced damage-associated lethal hepatitis: Interaction of gammadelta T cells with macrophages" Hepatology 57(1): 373-384.
PubMed
Acetaminophen overdose causes acute liver inflammation with neutrophil infiltration; however, the mechanism of damage-associated inflammation has not been elucidated. In this study we found that the HMGB1-TLR4-IL-23-IL-17A axis played a crucial role in acetaminophen-induced infiltration of neutrophils and liver injury. Notably, interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-23 significantly increased after acetaminophen challenge. A neutralizing antibody against IL-17A attenuated the recruitment of neutrophils, accompanied by reduced liver injury. Only IL-17A(+) CD3(+) gammadelta T cell receptor (TCR)(+) cells were significantly increased in the liver, and depletion of gammadelta T cells, but not CD4(+) T cells or natural killer (NK)T cells significantly reduced IL-17A production, attenuated liver injury, and decreased the number of neutrophils in the liver. Furthermore, a neutralizing IL-23 p19 antibody or p40-deficiency significantly decreased the levels of IL-17A and infiltration of neutrophils. After in vitro stimulation, the percentage of IL-17A-producing gammadelta T cells and the levels of supernatant IL-17A from total hepatic lymphocytes or purified gammadelta T cells markedly increased in the presence with IL-23. Importantly, IL-23 and IL-17A were reduced after inhibition of macrophages and could not be induced in Toll-like receptor TLR4(-/-) mice after acetaminophen challenge. Meanwhile, serum high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), a damage-associated molecule released from necrotic hepatocytes, increased after acetaminophen challenge, and the HMGB1 inhibitor glycyrrhizin markedly reduced the production of IL-23 and IL-17A and the recruitment of hepatic neutrophils. HMGB1 stimulated the production of IL-23 by TLR4(+/+) but not by TLR4(-/-) macrophages. CONCLUSION: The HMGB1-TLR4-IL-23 pathway in macrophages makes the generation of IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells, which mediates neutrophil infiltration and damage-induced liver inflammation.
in vivo IL-23p19 neutralization
Wakita, D., et al (2010). "Tumor-infiltrating IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells support the progression of tumor by promoting angiogenesis" Eur J Immunol 40(7): 1927-1937.
PubMed
Based on the evidence that IL-17 is a key cytokine involved in various inflammatory diseases, we explored the critical role of IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells for tumor development in tumor-bearing mouse model. IL-17(-/-) mice exhibited a significant reduction of tumor growth, concomitantly with the decrease of vascular density at lesion area, indicating a pro-tumor property of IL-17. Among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), gammadelta T cells were the major cellular source of IL-17. Analysis of TCR repertoires in TIL-gammadelta T cells showed that circulating gammadelta T cells, but not skin resident Vgamma5(+)gammadelta T cells, produced IL-17. Neutralizing antibodies against IL-23, IL-6, and TGF-beta, which were produced within the tumor microenvironment, inhibited the induction of IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells. IL-17 production by tumor-infiltrating gammadelta T cells was blocked by anti-gammadeltaTCR or anti-NKG2D antibodies, indicating that these ligands, expressed within the tumor microenvironment, are involved in gammadelta T-cell activation. The IL-17-producing TIL-gammadelta T cells exhibited reduced levels of perforin mRNA expression, but increased levels of COX-2 mRNA expression. Together, our findings support the novel concept that IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells, generated in response to tumor microenvironment, act as tumor-promoting cells by inducing angiogenesis.
Western Blot
Ivanov, S., et al (2007). "Functional relevance of the IL-23-IL-17 axis in lungs in vivo" Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 36(4): 442-451.
PubMed
It is known that interleukin (IL)-23, an IL-12-family cytokine, can be released by certain antigen-presenting cells in response to bacterial pathogens. Recent in vitro studies indicate that this cytokine stimulates a unique subset of CD4 cells, the T helper cell (Th)17 subset, to produce and release the proinflammatory cytokine IL-17. However, it has not been known whether this is an action of IL-23 per se that has bearing for the early innate response in lungs in vivo and whether there is an IL-23-responsive population of IL-17-producing CD4 cells in the bronchoalveolar space. We now present evidence that IL-23 can be involved in the early innate response to both gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial products in the lungs: Recombinant IL-23 protein per se accumulates inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar space in part via endogenous production of IL-17, and this IL-17 production occurs locally in IL-23-responsive CD4 cells. This IL-17 response to IL-23 occurs without any pronounced impact on Th1/Th2 polarization. Moreover, recombinant IL-23 protein increases the local MMP-9 activity, which is generated by neutrophils mainly. CD4 cells in the lungs may thus respond to IL-23 from antigen-presenting cells exposed to gram-negative and gram-positive pathogens and thereby reinforce the early innate response. These findings support that IL-23 and IL-17 form a functionally relevant “immunological axis” in the lungs in vivo.
Product Citations
-
Synergistic exacerbation of oral mucositis caused by IL-23 deficiency and oral Candida albicans exposure.
In MBio on 8 October 2025 by Dillon, J. T., Hickey, M. T., et al.
PubMed
Targeted head and neck irradiation (HNI) used for cancer therapy causes mucosal damage and immune dysregulation, leaving cancer patients highly susceptible to infections of the oral mucosa. Oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC) is an opportunistic infection caused by Candida albicans, a commensal fungus found in up to 80% of the population at any given time. High colonization levels of C. albicans are known to worsen damage caused by HNI. The interleukin-23 (IL-23)-T-helper 17 (Th17) axis is a central and non-redundant mediator of immunity to OPC, and anti-cytokine biologics targeting IL-23 have come into widespread clinical use for treating various autoimmune conditions. Here, we sought to understand the consequences of IL-23 deficiency in the setting of HNI, taking advantage of a mouse model of radiation-induced oral mucositis (OM) which we combined with fungal infection. Surprisingly, mice lacking IL-23 did not show increased signs of injury to the oral mucosa when subjected to HNI. However, in mice subjected to HNI and exposed to oral C. albicans, damage to the oral mucosa was markedly exacerbated, accompanied by substantially increased fungal susceptibility when IL-23 was absent. Thus, IL-23-driven control of fungal infections is needed to mitigate susceptibility to OM in the high proportion of individuals who carry C. albicans in the mouth.IMPORTANCEIL-23 plays key roles in expanding the T-helper 17 (Th17) cell subset during differentiation and promoting expression of cytokines, including the subset-defining cytokine IL-17 (IL-17A). While the effector cytokines produced by Th17 cells are required for host defense against extracellular microbes, especially Candida albicans, these can also be pathogenic during inflammatory and autoimmune disorders including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, among others. While IL-23 and IL-17 are similarly required for protection against oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC), they can exert divergent functions in other forms of immune-mediated inflammation; for example, anti-IL-17 blockade or Il17ra gene deficiency is linked to inflammatory bowel disease, whereas loss of IL-23 is protective in this setting. We previously showed that head and neck irradiation (HNI) induces IL-17 expression in oral tissue and that IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) signaling is required for resistance against mucosal damage and OPC. In contrast, we show here that loss of IL-23 does not affect oral mucosal injury caused by HNI. However, lack of IL-23 magnifies HNI-induced susceptibility to OPC due to insufficient levels of antimicrobial peptides. Clinically, these findings suggest that patients receiving treatments that target IL-23 may not need to discontinue therapy should they require HNI, but that screening for oral C. albicans may be useful to help limit the risk of developing severe OM and its attendant adverse events.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
HPV16 E6 and E7 expressing cancer cells suppress the antitumor immune response by upregulating KLF2-mediated IL-23 expression in macrophages.
In J Immunother Cancer on 19 August 2025 by Prins, R., Fernandez, D. J., et al.
PubMed
Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) positive cancers have a tumor environment that induces antigen-presenting cells to increase IL-23 expression. Unclear is if HPV16 E6/E7 oncoproteins expressed in these cancers play a role in upregulating interleukin (IL)-23 in the tumor microenvironment (TME), and how this cytokine impacts the antitumor cytotoxic T-cell response in HPV16+ cancer.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
MrgprA3 neurons drive cutaneous immunity against helminths through selective control of myeloid-derived IL-33.
In Nat Immunol on 1 November 2024 by Inclan-Rico, J. M., Napuri, C. M., et al.
PubMed
Skin uses interdependent cellular networks for barrier integrity and host immunity, but most underlying mechanisms remain obscure. Herein, we demonstrate that the human parasitic helminth Schistosoma mansoni inhibited pruritus evoked by itch-sensing afferents bearing the Mas-related G-protein-coupled receptor A3 (MrgprA3) in mice. MrgprA3 neurons controlled interleukin (IL)-17+ γδ T cell expansion, epidermal hyperplasia and host resistance against S. mansoni through shaping cytokine expression in cutaneous antigen-presenting cells. MrgprA3 neuron activation downregulated IL-33 but induced IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor in macrophages and type 2 conventional dendritic cells partially through the neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide. Macrophages exposed to MrgprA3-derived secretions or bearing cell-intrinsic IL-33 deletion showed increased chromatin accessibility at multiple inflammatory cytokine loci, promoting IL-17/IL-23-dependent changes to the epidermis and anti-helminth resistance. This study reveals a previously unrecognized intercellular communication mechanism wherein itch-inducing MrgprA3 neurons initiate host immunity against skin-invasive parasites by directing cytokine expression patterns in myeloid antigen-presenting cell subsets.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Distinctive CD39+CD9+ lung interstitial macrophages suppress IL-23/Th17-mediated neutrophilic asthma by inhibiting NETosis.
In Nat Commun on 4 October 2024 by Han, S., Kim, B., et al.
PubMed
The IL-23-Th17 axis is responsible for neutrophilic inflammation in various inflammatory diseases. Here, we discover a potential pathway to inhibit neutrophilic asthma. In our neutrophil-dominant asthma (NDA) model, single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies a subpopulation of CD39+CD9+ interstitial macrophages (IMs) suppressed by IL-23 in NDA conditions but increased by an IL-23 inhibitor αIL-23p19. Adoptively transferred CD39+CD9+ IMs suppress neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis), a representative phenotype of NDA, and also Th17 cell activation and neutrophilic inflammation. CD39+CD9+ IMs first attach to neutrophils in a CD9-dependent manner, and then remove ATP near neutrophils that contribute to NETosis in a CD39-dependent manner. Transcriptomic data from asthmatic patients finally show decreased CD39+CD9+ IMs in severe asthma than mild/moderate asthma. Our results suggest that CD39+CD9+ IMs function as a potent negative regulator of neutrophilic inflammation by suppressing NETosis in the IL-23-Th17 axis and can thus serve as a potential therapeutic target for IL-23-Th17-mediated neutrophilic asthma.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Post-immunotherapy CTLA-4 Ig treatment improves antitumor efficacy.
In Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A on 2 July 2024 by Mok, S., Ağaç Çobanoğlu, D., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint therapies (ICT) improve overall survival of patients with cancer but may cause immune-related adverse events (irAEs) such as myocarditis. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 immunoglobulin fusion protein (CTLA-4 Ig), an inhibitor of T cell costimulation through CD28, reverses irAEs in animal models. However, concerns exist about potentially compromising antitumor response of ICT. In mouse tumor models, we administered CTLA-4 Ig 1) concomitantly with ICT or 2) after ICT completion. Concomitant treatment reduced antitumor efficacy, while post-ICT administration improved efficacy without affecting frequency and function of CD8 T cells. The improved response was independent of the ICT used, whether CTLA-4 or PD-1 blockade. The frequency of Tregs was significantly decreased with CTLA-4 Ig. The resulting increased CD8/Treg ratio potentially underlies the enhanced efficacy of ICT followed by CTLA-4 Ig. This paradoxical mechanism shows that a CTLA-4 Ig regimen shown to reduce irAE severity does not compromise antitumor efficacy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
ZEB1 shapes AML immunological niches, suppressing CD8 T cell activity while fostering Th17 cell expansion.
In Cell Rep on 27 February 2024 by Bassani, B., Simonetti, G., et al.
PubMed
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression is influenced by immune suppression induced by leukemia cells. ZEB1, a critical transcription factor in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, demonstrates immune regulatory functions in AML. Silencing ZEB1 in leukemic cells reduces engraftment and extramedullary disease in immune-competent mice, activating CD8 T lymphocytes and limiting Th17 cell expansion. ZEB1 in AML cells directly promotes Th17 cell development that, in turn, creates a self-sustaining loop and a pro-invasive phenotype, favoring transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), interleukin-23 (IL-23), and SOCS2 gene transcription. In bone marrow biopsies from AML patients, immunohistochemistry shows a direct correlation between ZEB1 and Th17. Also, the analysis of ZEB1 expression in larger datasets identifies two distinct AML groups, ZEB1high and ZEB1low, each with specific immunological and molecular traits. ZEB1high patients exhibit increased IL-17, SOCS2, and TGF-β pathways and a negative association with overall survival. This unveils ZEB1's dual role in AML, entwining pro-tumoral and immune regulatory capacities in AML blasts.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
MrgprA3 neurons selectively control myeloid-derived cytokines for IL-17 dependent cutaneous immunity.
In Research Square on 30 November 2023 by Herbert, D., Inclan-Rico, J., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
-
Deciphering the mechanism of Peptostreptococcus anaerobius-induced chemoresistance in colorectal cancer: the important roles of MDSC recruitment and EMT activation.
In Front Immunol on 2 October 2023 by Gu, J., Lv, X., et al.
PubMed
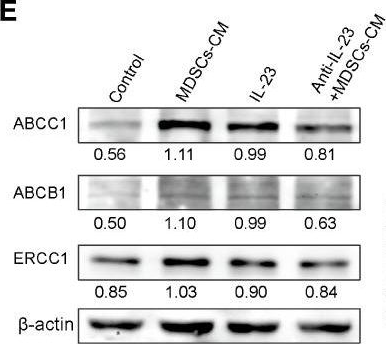
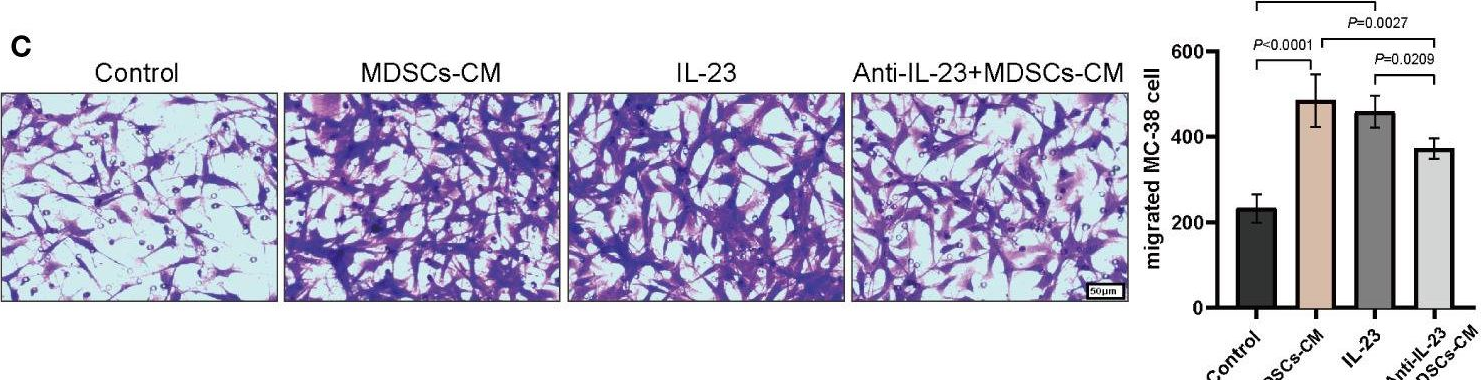
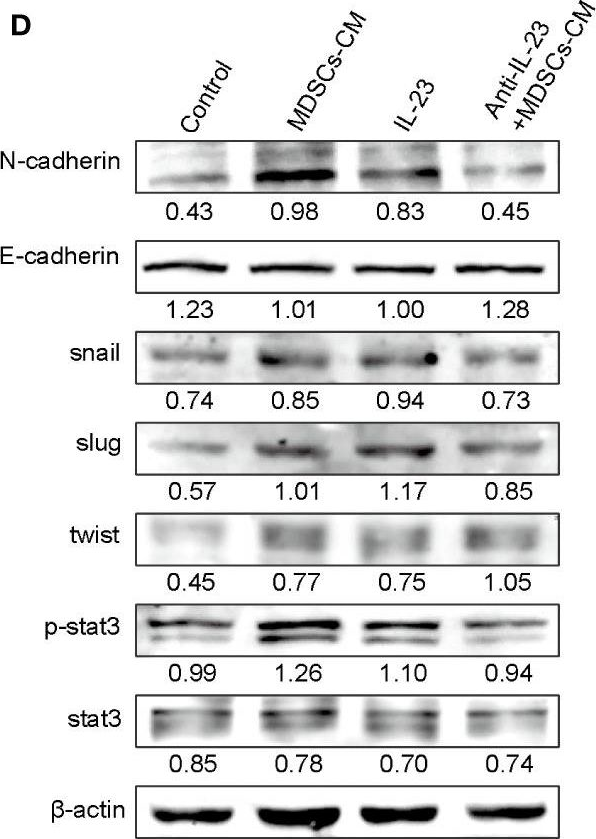
Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (P. anaerobius, PA) in intestinal flora of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) are associated with poor prognosis. Studies have shown that P. anaerobius could promote colorectal carcinogenesis and progression, but whether P. anaerobius could induce chemoresistance of colorectal cancer has not been clarified. Here, both in vitro and in vivo experiments showed that P. anaerobius specifically colonized the CRC lesion and enhanced chemoresistance of colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin by recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) into the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, this study revealed that it was the increased secretion of IL-23 by MDSCs that subsequently facilitated the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of tumor cells to induce chemoresistance of CRC by activating the Stat3-EMT pathway. Our results highlight that targeting P. anaerobius might be a novel therapeutic strategy to overcome chemoresistance in the treatment of CRC.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The enteric nervous system relays psychological stress to intestinal inflammation.
In Cell on 22 June 2023 by Schneider, K. M., Blank, N., et al.
PubMed
Mental health profoundly impacts inflammatory responses in the body. This is particularly apparent in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), in which psychological stress is associated with exacerbated disease flares. Here, we discover a critical role for the enteric nervous system (ENS) in mediating the aggravating effect of chronic stress on intestinal inflammation. We find that chronically elevated levels of glucocorticoids drive the generation of an inflammatory subset of enteric glia that promotes monocyte- and TNF-mediated inflammation via CSF1. Additionally, glucocorticoids cause transcriptional immaturity in enteric neurons, acetylcholine deficiency, and dysmotility via TGF-β2. We verify the connection between the psychological state, intestinal inflammation, and dysmotility in three cohorts of IBD patients. Together, these findings offer a mechanistic explanation for the impact of the brain on peripheral inflammation, define the ENS as a relay between psychological stress and gut inflammation, and suggest that stress management could serve as a valuable component of IBD care.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Microbiota instruct IL-17A-producing innate lymphoid cells to promote skin inflammation in cutaneous leishmaniasis.
In PLoS Pathog on 1 October 2021 by Singh, T. P., Carvalho, A. M., et al.
PubMed
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) comprise a heterogeneous population of immune cells that maintain barrier function and can initiate a protective or pathological immune response upon infection. Here we show the involvement of IL-17A-producing ILCs in microbiota-driven immunopathology in cutaneous leishmaniasis. IL-17A-producing ILCs were RORγt+ and were enriched in Leishmania major infected skin, and topical colonization with Staphylococcus epidermidis before L. major infection exacerbated the skin inflammatory responses and IL-17A-producing RORγt+ ILC accumulation without impacting type 1 immune responses. IL-17A responses in ILCs were directed by Batf3 dependent CD103+ dendritic cells and IL-23. Moreover, experiments using Rag1-/- mice established that IL-17A+ ILCs were sufficient in driving the inflammatory responses as depletion of ILCs or neutralization of IL-17A diminished the microbiota mediated immunopathology. Taken together, this study indicates that the skin microbiota promotes RORγt+ IL-17A-producing ILCs, which augment the skin inflammation in cutaneous leishmaniasis.
-