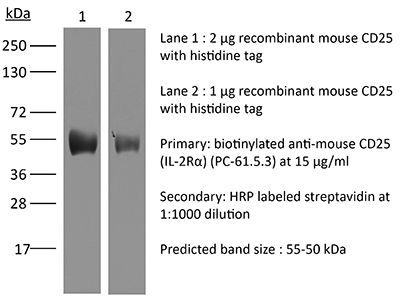
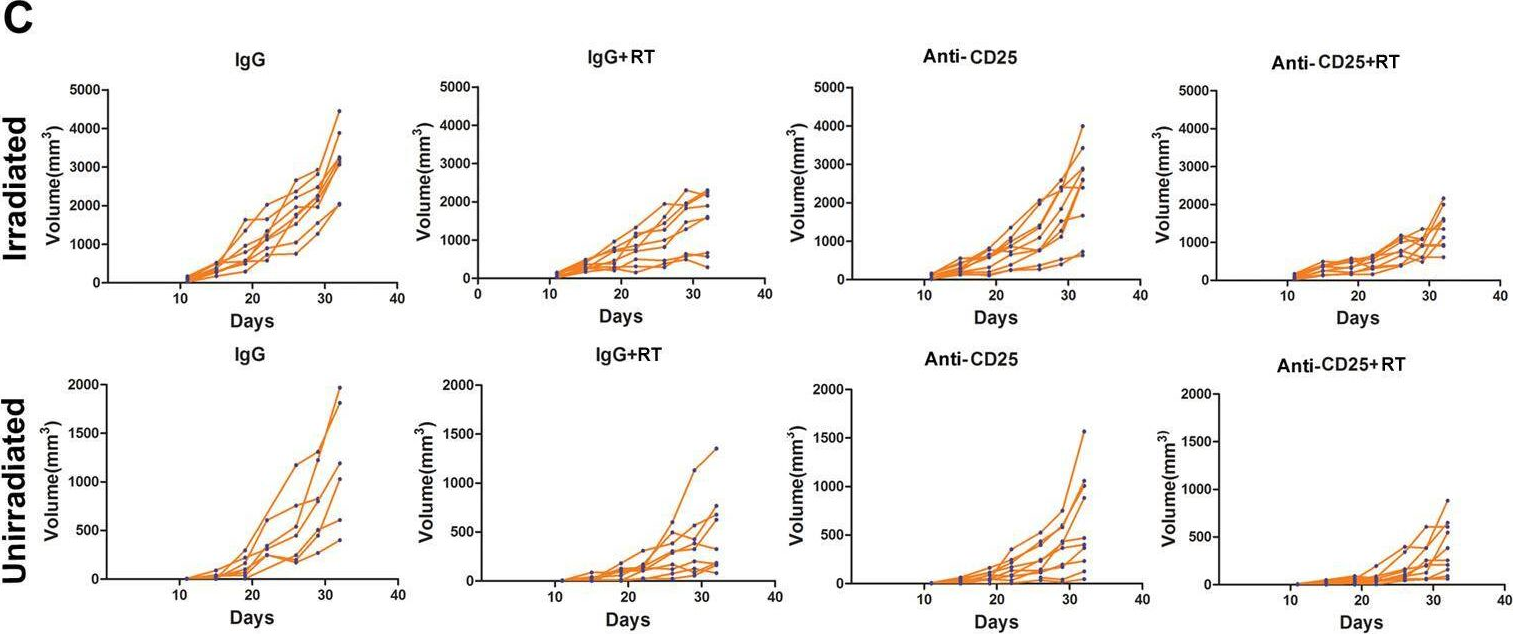
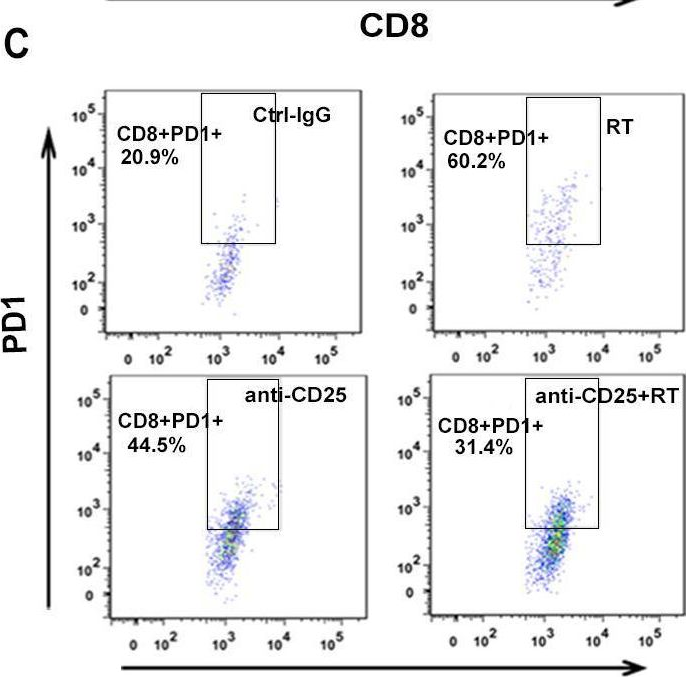
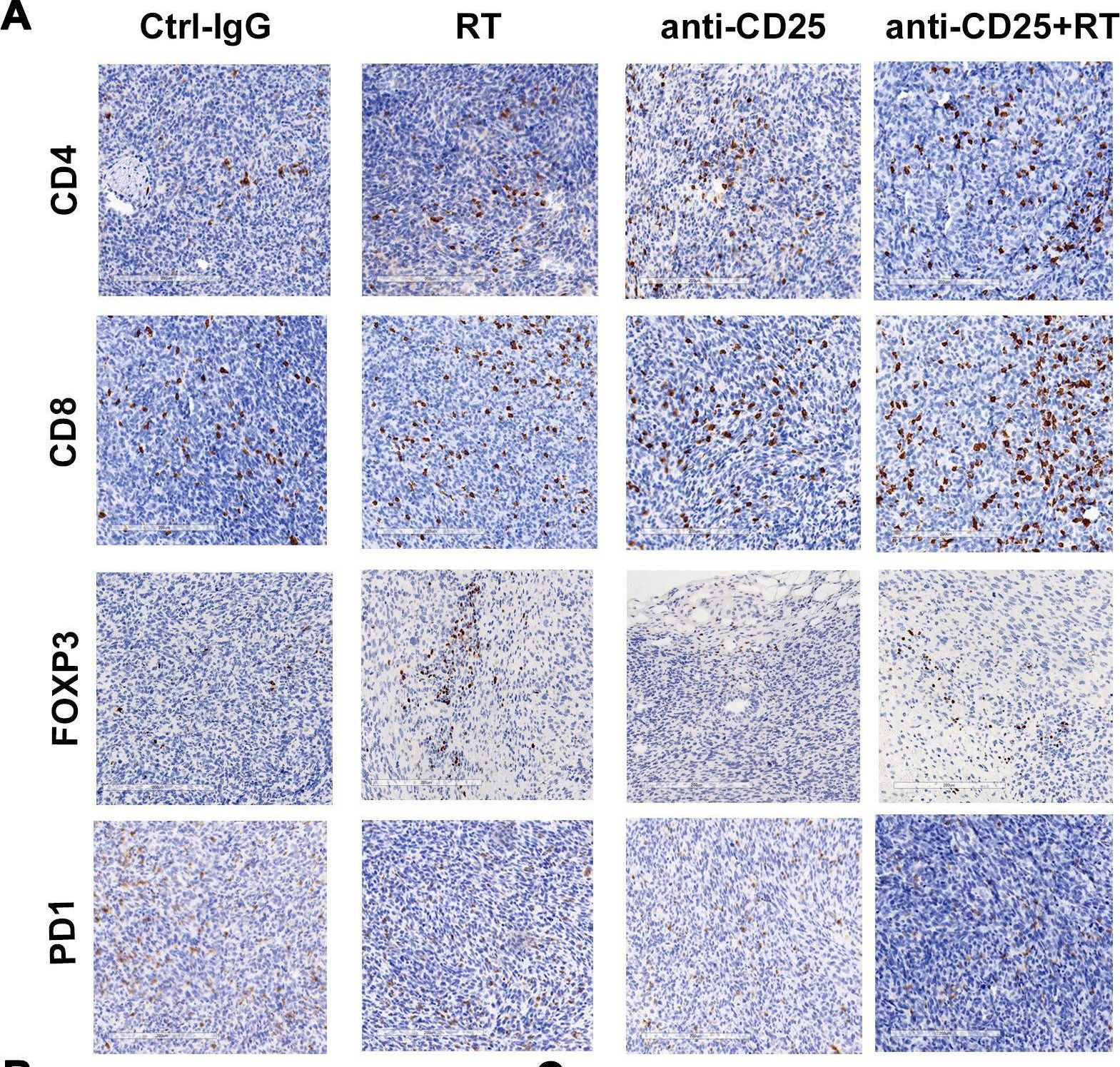
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD25 (IL-2Rα)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG1, λ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG1 isotype control, anti-horseradish peroxidase |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | IL-2-dependent cytolytic mouse T cell clone B6.1 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion Flow cytometry |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A High Salt |
| RRID | AB_1107619 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Goschl, L., et al (2018). "A T cell-specific deletion of HDAC1 protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis" J Autoimmun 86: 51-61.
PubMed
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a human neurodegenerative disease characterized by the invasion of autoreactive T cells from the periphery into the CNS. Application of pan-histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model for MS, suggesting that HDACi might be a potential therapeutic strategy for MS. However, the function of individual HDAC members in the pathogenesis of EAE is not known. In this study we report that mice with a T cell-specific deletion of HDAC1 (using the Cd4-Cre deleter strain; HDAC1-cKO) were completely resistant to EAE despite the ability of HDAC1cKO CD4(+) T cells to differentiate into Th17 cells. RNA sequencing revealed STAT1 as a prominent upstream regulator of differentially expressed genes in activated HDAC1-cKO CD4(+) T cells and this was accompanied by a strong increase in phosphorylated STAT1 (pSTAT1). This suggests that HDAC1 controls STAT1 activity in activated CD4(+) T cells. Increased pSTAT1 levels correlated with a reduced expression of the chemokine receptors Ccr4 and Ccr6, which are important for the migration of T cells into the CNS. Finally, EAE susceptibility was restored in WT:HDAC1-cKO mixed BM chimeric mice, indicating a cell-autonomous defect. Our data demonstrate a novel pathophysiological role for HDAC1 in EAE and provide evidence that selective inhibition of HDAC1 might be a promising strategy for the treatment of MS.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Clemente-Casares, X., et al (2016). "Expanding antigen-specific regulatory networks to treat autoimmunity" Nature 530(7591): 434-440.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells hold promise as targets for therapeutic intervention in autoimmunity, but approaches capable of expanding antigen-specific regulatory T cells in vivo are currently not available. Here we show that systemic delivery of nanoparticles coated with autoimmune-disease-relevant peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex class II (pMHCII) molecules triggers the generation and expansion of antigen-specific regulatory CD4(+) T cell type 1 (TR1)-like cells in different mouse models, including mice humanized with lymphocytes from patients, leading to resolution of established autoimmune phenomena. Ten pMHCII-based nanomedicines show similar biological effects, regardless of genetic background, prevalence of the cognate T-cell population or MHC restriction. These nanomedicines promote the differentiation of disease-primed autoreactive T cells into TR1-like cells, which in turn suppress autoantigen-loaded antigen-presenting cells and drive the differentiation of cognate B cells into disease-suppressing regulatory B cells, without compromising systemic immunity. pMHCII-based nanomedicines thus represent a new class of drugs, potentially useful for treating a broad spectrum of autoimmune conditions in a disease-specific manner.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Miller, M. L., et al (2015). "Spontaneous restoration of transplantation tolerance after acute rejection" Nat Commun 6: 7566.
PubMed
Transplantation is a cure for end-stage organ failure but, in the absence of pharmacological immunosuppression, allogeneic organs are acutely rejected. Such rejection invariably results in allosensitization and accelerated rejection of secondary donor-matched grafts. Transplantation tolerance can be induced in animals and a subset of humans, and enables long-term acceptance of allografts without maintenance immunosuppression. However, graft rejection can occur long after a state of transplantation tolerance has been acquired. When such an allograft is rejected, it has been assumed that the same rules of allosensitization apply as to non-tolerant hosts and that immunological tolerance is permanently lost. Using a mouse model of cardiac transplantation, we show that when Listeria monocytogenes infection precipitates acute rejection, thus abrogating transplantation tolerance, the donor-specific tolerant state re-emerges, allowing spontaneous acceptance of a donor-matched second transplant. These data demonstrate a setting in which the memory of allograft tolerance dominates over the memory of transplant rejection.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Christensen, A. D., et al (2015). "Depletion of regulatory T cells in a hapten-induced inflammation model results in prolonged and increased inflammation driven by T cells" Clin Exp Immunol 179(3): 485-499.
PubMed
Regulatory T cells (Tregs ) are known to play an immunosuppressive role in the response of contact hypersensitivity (CHS), but neither the dynamics of Tregs during the CHS response nor the exaggerated inflammatory response after depletion of Tregs has been characterized in detail. In this study we show that the number of Tregs in the challenged tissue peak at the same time as the ear-swelling reaches its maximum on day 1 after challenge, whereas the number of Tregs in the draining lymph nodes peaks at day 2. As expected, depletion of Tregs by injection of a monoclonal antibody to CD25 prior to sensitization led to a prolonged and sustained inflammatory response which was dependent upon CD8 T cells, and co-stimulatory blockade with cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4-immunoglobulin (CTLA-4-Ig) suppressed the exaggerated inflammation. In contrast, blockade of the interleukin (IL)-10-receptor (IL-10R) did not further increase the exaggerated inflammatory response in the Treg -depleted mice. In the absence of Tregs , the response changed from a mainly acute reaction with heavy infiltration of neutrophils to a sustained response with more chronic characteristics (fewer neutrophils and dominated by macrophages). Furthermore, depletion of Tregs enhanced the release of cytokines and chemokines locally in the inflamed ear and augmented serum levels of the systemic inflammatory mediators serum amyloid (SAP) and haptoglobin early in the response.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Deligne, C., et al (2015). "Anti-CD20 therapy induces a memory Th1 response through the IFN-gamma/IL-12 axis and prevents protumor regulatory T-cell expansion in mice" Leukemia 29(4): 947-957.
PubMed
The long-lasting clinical response by lymphoma patients to anti-CD20 therapy has been attributed to the induction of an anti-tumor adaptive immunity. We previously demonstrated that a CD4-dependent mechanism is responsible for the long-term protection of CD20(+) tumor-bearing mice by anti-CD20 treatment. Here, we compare tumor immunity in tumor-bearing animals that did or did not receive anti-CD20 treatment. Splenic CD4(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) expanded substantially in untreated mice that exhibited then a reduced survival, whereas Tregs depletion led to long-term survival of the animals, suggesting the establishment of a Treg-dependent immunosuppressive environment after tumor injection. Strikingly, anti-CD20 therapy reversed the initial expansion of Tregs, and was accompanied by a marked increase in the number of Th1 cells, with no detectable change in Th2 and Th17 cell numbers. Interleukin-12 serum level was also increased by the anti-CD20 treatment, and activated myeloid dendritic cells producing interleukin-12 could be detected in lymph nodes of treated animals, while interferon-gamma blockade strongly reduced survival. Also, CD4(+) effector memory T cells were evidenced in surviving animals, and the transfer of CD4(+) T cells induced long-term protection. Thus, anti-CD20 therapy promotes strong anti-tumor adaptive immunity, opposes Treg expansion and inhibits tumor cells from maintaining an immunosuppressive environment.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Glatigny, S., et al (2015). "Integrin alpha L controls the homing of regulatory T cells during CNS autoimmunity in the absence of integrin alpha 4" Sci Rep 5: 7834.
PubMed
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), results from an autoimmune attack of the central nervous system (CNS) by effector T helper (Th) 1 and Th17 cells. Regulatory T cells (Treg) can control effector T cells and limit the progression of CNS autoimmunity. Integrin alpha 4 (Itga4) is critical for the entry of Th1 but not Th17 cells into the CNS during EAE. Whether Itga4 controls the homing of Tregs in the CNS and whether Tregs can limit Th17-mediated EAE has, however, not been addressed. Through selective elimination of Itga4 in Foxp3-expressing cells, we show here that Tregs can suppress Th17-mediated EAE and enter into the CNS independently of Itga4. Furthermore, similarly to Th17 cells and in contrast to Th1 cells, Tregs depend on LFA-1 for their entry into the CNS in the absence of Itga4. Therefore, these data suggest that the efficacy of Itga4 neutralization on MS progression may be associated with the prevention of Th1 cells and the maintenance of Tregs migration into the CNS.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Park, H. J., et al (2015). "PD-1 upregulated on regulatory T cells during chronic virus infection enhances the suppression of CD8+ T cell immune response via the interaction with PD-L1 expressed on CD8+ T cells" J Immunol 194(12): 5801-5811.
PubMed
Regulatory T (Treg) cells act as terminators of T cell immuniy during acute phase of viral infection; however, their role and suppressive mechanism in chronic viral infection are not completely understood. In this study, we compared the phenotype and function of Treg cells during acute or chronic infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Chronic infection, unlike acute infection, led to a large expansion of Treg cells and their upregulation of programmed death-1 (PD-1). Treg cells from chronically infected mice (chronic Treg cells) displayed greater suppressive capacity for inhibiting both CD8(+) and CD4(+) T cell proliferation and subsequent cytokine production than those from naive or acutely infected mice. A contact between Treg and CD8(+) T cells was necessary for the potent suppression of CD8(+) T cell immune response. More importantly, the suppression required cell-specific expression and interaction of PD-1 on chronic Treg cells and PD-1 ligand on CD8(+) T cells. Our study defines PD-1 upregulated on Treg cells and its interaction with PD-1 ligand on effector T cells as one cause for the potent T cell suppression and proposes the role of PD-1 on Treg cells, in addition to that on exhausted T cells, during chronic viral infection.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Allam, A., et al (2014). "Dual function of CD70 in viral infection: modulator of early cytokine responses and activator of adaptive responses" J Immunol 193(2): 871-878.
PubMed
The role of the TNF family member CD70 in adaptive T cell responses has been intensively studied, but its function in innate responses is still under investigation. In this study, we show that CD70 inhibits the early innate response to murine CMV (MCMV) but is essential for the optimal generation of virus-specific CD8 T cells. CD70(-/-) mice reacted to MCMV infection with a robust type I IFN and proinflammatory cytokine response. This response was sufficient for initial control of MCMV, although at later time points, CD70(-/-) mice became more susceptible to MCMV infection. The heightened cytokine response during the early phase of MCMV infection in CD70(-/-) mice was paralleled by a reduction in regulatory T cells (Treg). Treg from naive CD70(-/-) mice were not as efficient at suppressing T cell proliferation compared with Treg from naive wild-type mice, and depletion of Treg during MCMV infection in Foxp3-diphtheria toxin receptor mice or in wild-type mice recapitulated the phenotype observed in CD70(-/-) mice. Our study demonstrates that although CD70 is required for the activation of the antiviral adaptive response, it has a regulatory role in early cytokine responses to viruses such as MCMV, possibly through maintenance of Treg survival and function.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Sarraj, B., et al (2014). "Impaired selectin-dependent leukocyte recruitment induces T-cell exhaustion and prevents chronic allograft vasculopathy and rejection" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(33): 12145-12150.
PubMed
Selectin-selectin ligand interactions mediate the initial steps in leukocyte migration, an integral part of immune responses. Fucosyltransferase-VII (FucT-VII), encoded by Fut7, is essential for biosynthesis of selectin ligands. In an established model of cardiac allograft vasculopathy and chronic rejection, Fut7(-/-) recipients exhibited long-term graft survival with minimal vasculopathy compared with WT controls. Graft survival was associated with CD4 T-cell exhaustion in the periphery, characterized by impaired effector cytokine production, defective proliferation, increased expression of inhibitory receptors programmed death-1 (PD-1) and T cell Ig- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (Tim-3), low levels of IL-7Ralpha on CD4 T cells, and reduced migration of polyfunctional CD4 memory T cells to the allograft. Blocking PD-1 triggered rejection only in Fut7(-/-) recipients, whereas depleting regulatory T cells had no effect in either Fut7(-/-) or WT recipients. Adoptive transfer experiments confirmed that this CD4 T cell-exhausted phenotype is seen primarily in Fut7(-/-) CD4 T cells. These data suggest that impaired leukocyte recruitment is a novel mechanism leading to CD4 T-cell exhaustion. Our experimental system serves as an excellent model to study CD4 T-cell exhaustion as a dominant mechanism of transplant tolerance. Further, targeting FucT-VII may serve as a promising strategy to prevent chronic allograft rejection and promote tolerance.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Richter, K., et al (2013). "Macrophage and T cell produced IL-10 promotes viral chronicity" PLoS Pathog 9(11): e1003735.
PubMed
Chronic viral infections lead to CD8(+) T cell exhaustion, characterized by impaired cytokine secretion. Presence of the immune-regulatory cytokine IL-10 promotes chronicity of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV) Clone 13 infection, while absence of IL-10/IL-10R signaling early during infection results in viral clearance and higher percentages and numbers of antiviral, cytokine producing T cells. IL-10 is produced by several cell types during LCMV infection but it is currently unclear which cellular sources are responsible for induction of viral chronicity. Here, we demonstrate that although dendritic cells produce IL-10 and overall IL-10 mRNA levels decrease significantly in absence of CD11c(+) cells, absence of IL-10 produced by CD11c(+) cells failed to improve the LCMV-specific T cell response and control of LCMV infection. Similarly, NK cell specific IL-10 deficiency had no positive impact on the LCMV-specific T cell response or viral control, even though high percentages of NK cells produced IL-10 at early time points after infection. Interestingly, we found markedly improved T cell responses and clearance of normally chronic LCMV Clone 13 infection when either myeloid cells or T cells lacked IL-10 production and mice depleted of monocytes/macrophages or CD4(+) T cells exhibited reduced overall levels of IL-10 mRNA. These data suggest that the decision whether LCMV infection becomes chronic or can be cleared critically depends on early CD4(+) T cell and monocyte/macrophage produced IL-10.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Flow Cytometry
Locatelli, G., et al (2012). "Primary oligodendrocyte death does not elicit anti-CNS immunity" Nat Neurosci 15(4): 543-550.
PubMed
Anti-myelin immunity is commonly thought to drive multiple sclerosis, yet the initial trigger of this autoreactivity remains elusive. One of the proposed factors for initiating this disease is the primary death of oligodendrocytes. To specifically test such oligodendrocyte death as a trigger for anti-CNS immunity, we inducibly killed oligodendrocytes in an in vivo mouse model. Strong microglia-macrophage activation followed oligodendrocyte death, and myelin components in draining lymph nodes made CNS antigens available to lymphocytes. However, even conditions favoring autoimmunity-bystander activation, removal of regulatory T cells, presence of myelin-reactive T cells and application of demyelinating antibodies-did not result in the development of CNS inflammation after oligodendrocyte death. In addition, this lack of reactivity was not mediated by enhanced myelin-specific tolerance. Thus, in contrast with previously reported impairments of oligodendrocyte physiology, diffuse oligodendrocyte death alone or in conjunction with immune activation does not trigger anti-CNS immunity.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Tang, S., et al (2012). "Increased CD8+ T-cell function following castration and immunization is countered by parallel expansion of regulatory T cells" Cancer Res 72(8): 1975-1985.
PubMed
Although androgen ablation therapy is effective in treating primary prostate cancers, a significant number of patients develop incurable castration-resistant disease. Recent studies have suggested a potential synergy between vaccination and androgen ablation, yet the enhanced T-cell function is transient. Using a defined tumor antigen model, UV-8101-RE, we found that concomitant castration significantly increased the frequency and function of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells early after the immunization of wild-type mice. However, at a late time point after immunization, effector function was reduced to the same level as noncastrated mice and was accompanied by a concomitant amplification in CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells (Treg) following immunization. We investigated whether Treg expansion occurred following castration of prostate tumor-bearing mice. In the prostate-specific Pten(-/-) mouse model of prostate cancer, we observed an accelerated Treg expansion in mice bearing the castration-resistant endogenous prostate tumor, which prevented effector responses to UV-8101-RE. Treg depletion together with castration elicited a strong CD8(+) T-cell response to UV-8101-RE in Pten(-/-) mice and rescued effector function in castrated and immunized wild-type mice. In addition, Treg expansion in Pten(-/-) mice was prevented by in vivo interleukin (IL)-2 blockade suggesting that increased IL-2 generated by castration and immunization promotes Treg expansion. Our findings therefore suggest that although effector responses are augmented by castration, the concomitant expansion of Tregs is one mechanism responsible for only transient immune potentiation after androgen ablation.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Mohamadzadeh, M., et al (2011). "Regulation of induced colonic inflammation by Lactobacillus acidophilus deficient in lipoteichoic acid" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108 Suppl 1: 4623-4630.
PubMed
Imbalance in the regulatory immune mechanisms that control intestinal cellular and bacterial homeostasis may lead to induction of the detrimental inflammatory signals characterized in humans as inflammatory bowel disease. Induction of proinflammatory cytokines (i.e., IL-12) induced by dendritic cells (DCs) expressing pattern recognition receptors may skew naive T cells to T helper 1 polarization, which is strongly implicated in mucosal autoimmunity. Recent studies show the ability of probiotic microbes to treat and prevent numerous intestinal disorders, including Clostridium difficile-induced colitis. To study the molecular mechanisms involved in the induction and repression of intestinal inflammation, the phosphoglycerol transferase gene that plays a key role in lipoteichoic acid (LTA) biosynthesis in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM (NCK56) was deleted. The data show that the L. acidophilus LTA-negative in LTA (NCK2025) not only down-regulated IL-12 and TNFalpha but also significantly enhanced IL-10 in DCs and controlled the regulation of costimulatory DC functions, resulting in their inability to induce CD4(+) T-cell activation. Moreover, treatment of mice with NCK2025 compared with NCK56 significantly mitigated dextran sulfate sodium and CD4(+)CD45RB(high)T cell-induced colitis and effectively ameliorated dextran sulfate sodium-established colitis through a mechanism that involves IL-10 and CD4(+)FoxP3(+) T regulatory cells to dampen exaggerated mucosal inflammation. Directed alteration of cell surface components of L. acidophilus NCFM establishes a potential strategy for the treatment of inflammatory intestinal disorders.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
Akins, E. J., et al (2010). "In situ vaccination combined with androgen ablation and regulatory T-cell depletion reduces castration-resistant tumor burden in prostate-specific pten knockout mice" Cancer Res 70(9): 3473-3482.
PubMed
There is no effective treatment for prostate cancer arising after androgen ablation. Previous studies have analyzed the short-term effects of androgen ablation on the immune system and suggest an abatement of immune suppression by hormone removal. Because castration-resistant disease can arise years after treatment, it is crucial to determine the duration of immune potentiation by castration. Because immunotherapeutic efficacy is determined by the balance of immune cell subsets and their location within the tumor, we assessed the acute and chronic effect of androgen ablation on the localization of T-cell subsets within castration-resistant murine prostate cancer. We observed a transient increase in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell numbers at the residual tumor after androgen ablation. More than 2 months later, regulatory T cells (Treg) were increasingly found within prostate epithelium, whereas CTLs, which were evenly distributed before androgen ablation, became sequestered within stroma. Anti-CD25 antibody administration along with castration enhanced CTL access to cancerous glands but did not increase effector function. Intraprostatic injection of LIGHT-expressing tumor cells increased the proportion of CD8+ T cells with functional capacity within the cancerous gland. In addition, Treg depletion within the tumor was enhanced. Together, these manipulations significantly reduced castration-resistant tumor burden. Thus, our results indicate that immune modulations, which prevent Treg accumulation and augment effector cell infiltration of prostatic epithelium, may be effective in reducing tumor burden or preventing tumor recurrence after androgen ablation therapy.
in vivo regulatory T cell depletion
D’Alessio, F. R., et al (2009). "CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs resolve experimental lung injury in mice and are present in humans with acute lung injury" J Clin Invest 119(10): 2898-2913.
PubMed
Acute lung injury (ALI) is characterized by rapid alveolar injury, inflammation, cytokine induction, and neutrophil accumulation. Although early events in the pathogenesis of ALI have been defined, the mechanisms underlying resolution are unknown. As a model of ALI, we administered intratracheal (i.t.) LPS to mice and observed peak lung injury 4 days after the challenge, with resolution by day 10. Numbers of alveolar lymphocytes increased as injury resolved. To examine the role of lymphocytes in this response, lymphocyte-deficient Rag-1-/- and C57BL/6 WT mice were exposed to i.t. LPS. The extent of injury was similar between the groups of mice through day 4, but recovery was markedly impaired in the Rag-1-/- mice. Adoptive transfer studies revealed that infusion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs as late as 24 hours after i.t. LPS normalized resolution in Rag-1-/- mice. Similarly, Treg depletion in WT mice delayed recovery. Treg transfer into i.t. LPS-exposed Rag-1-/- mice also corrected the elevated levels of alveolar proinflammatory cytokines and increased the diminished levels of alveolar TGF-beta and neutrophil apoptosis. Mechanistically, Treg-mediated resolution of lung injury was abrogated by TGF-beta inhibition. Moreover, BAL of patients with ALI revealed dynamic changes in CD3+CD4+CD25hiCD127loFoxp3+ cells. These results indicate that Tregs modify innate immune responses during resolution of lung injury and suggest potential targets for treating ALI, for which there are no specific therapies currently available.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Antigen choice determines vaccine-induced generation of immunogenic versus tolerogenic dendritic cells that are marked by differential expression of pancreatic enzymes.
In The Journal of Immunology on 1 April 2013 by Farkas, A. M., Marvel, D. M., et al.
PubMed
Dendritic cells (DC) elicit immunity to pathogens and tumors while simultaneously preserving tolerance to self. Efficacious cancer vaccines have been a challenge because they are based on tumor Ags, some of which are self-Ags and thus subject to self-tolerance. One such Ag is the tumor-associated mucin MUC1. Preclinical testing of MUC1 vaccines revealed existence of peripheral tolerance to MUC1 that compromises their efficacy. To identify mechanisms that act early postvaccination and might predict vaccine outcome, we immunized human MUC1 transgenic mice (MUC1.Tg) i.v. with a MUC1 peptide vaccine against which they generate weak immunity and wild-type (WT) mice that respond strongly to the same peptide. We analyzed differences in splenic DC phenotype and function between the two mouse strains at 24 and 72 h postvaccination and also performed unbiased total gene expression analysis of the spleen. Compared to WT, MUC1.Tg spleens had significantly fewer DC, and they exhibited significantly lower expression of costimulatory molecules, decreased motility, and preferential priming of Ag-specific Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. This tolerogenic DC phenotype and function was marked by a new putative biomarker revealed by the microarray: a cohort of pancreatic enzymes (trypsin, carboxypeptidase, elastase, and others) not previously reported in DC. These enzymes were strongly upregulated in the splenic DC from vaccinated WT mice and suppressed in the splenic DC of vaccinated MUC1.Tg mice. Suppression of the enzymes was dependent on regulatory T cells and on signaling through the IL-10R and correlated with global downregulation of DC immunostimulatory phenotype and function.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
COVID-19
CD25 modulation enhances broadly neutralizing antibody response of SARS-CoV-2 subunit vaccine.
In Commun Biol on 17 February 2026 by Li, F., Yu, X., et al.
PubMed
The primary aim of COVID-19 vaccine development is to induce highly efficient broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) against circulating and emergent SARS-CoV-2 variants. Rapid and sustained germinal center (GC) responses at an early stage are crucial to produce bNAbs. However, the mechanisms underlying the formation of early GC responses and strategies to effectively promote these responses remain to be further investigated. In this study, we found that the combination of anti-CD25 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) with the COVID-19 subunit vaccine significantly enhances cross-reactive neutralizing antibody responses in mice. Modulation of CD25 at different time points before and after vaccination resulted in varying effects on the GC response, with day 0 being the most effective in assisting the vaccine to induce a stronger GC response. This enhancement is achieved by rapidly inhibiting regulatory T (Treg) cells in draining lymph nodes, an effect observed not only in antigen-specific subsets but also across the bulk lymphocyte population-thereby creating a pro-immune microenvironment that facilitates the induction of an effective early GC response. This leads to the generation of more antigen-recognizing B cells and significantly increases both the potency and breadth of neutralizing antibody responses. Our findings propose a strategy to enhance vaccine efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 and other hypervariable pathogens by effectively promoting the development of early and robust GC responses.
-
-
Colonic Engyodontium fungus triggers neutrophil antimicrobial activity to suppress Lactobacillus johnsonii-derived glutamic acid-maintained Tregs.
In J Clin Invest on 17 February 2026 by Wang, X., Sun, H., et al.
PubMed
Isolating commensal fungi from mouse intestines has been challenging, limiting our understanding of their role in intestinal immune homeostasis and diseases. Using an Fc fusion protein of the C-type lectin Dectin-2, we successfully purified the commensal Ascomycota fungus Engyodontium sp. from mouse feces. Engyodontium enhances the antimicrobial activity of colonic neutrophils via CARD9 pathway, and exacerbates colitis by impairing the colonization of intestinal Lactobacillus johnsonii (L. johnsonii) WXY strain. L. johnsonii produces high levels of L-glutamic acid by expressing the glutaminase-encoding gene glsA to facilitate Treg expansion via enhancing IL-2 receptor signaling. Patients with Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis harbored increased Engyodontium and decreased L. johnsonii abundance. Engyodontium directly induced calprotectin in human colonic neutrophils, and CD patients exhibited lower levels of L-glutamic acid which also promoted human Treg expansion. These findings highlight the Engyodontium-calprotectin axis against the Lactobacillus-glutamate-Treg cascade to aggravate colitis, suggesting commensal Engyodontium-triggered signaling as a therapeutic target for mucosal inflammatory diseases.
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
A CD25-chemokine receptor complex initiates noncanonical IL-2 signaling.
In J Biol Chem on 1 January 2026 by Lee, H., Kim, S. H. J., et al.
PubMed
An antimouse CD25 antibody, PC61, induces a complex formed by the interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent association of CD25 with CCR7 and an alternative IL-2 signaling pathway that results in integrin activation in CD4+CD25HiFoxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs). Here, we used structure-based design together with combinatorial screening to identify a human IL-2 mutant (IL-2(E52K)) that disrupts CD25-CCR7 complex formation while retaining the full CD25 affinity of the parent molecule. An anti-human CD25 (hCD25), 7G7B6, drove formation of IL-2-dependent hCD25-CCR7, CD25-CXCR4, and CD25-CCR5 complexes and induced integrin activation in hCD25-expressing IL-2Rα+ YT-1 cells, Jurkat T cells, and primary Tregs. IL-2(E52K) failed to support activation in CCR5Lo Jurkat T cells and primary Tregs. In contrast, IL-2(E52K) supported activation in CCR5Hi IL-2Rα+ YT-1 cells, which was blocked by the CCR5-specific antagonist, maraviroc. Heparan sulfate (HS), a physiological ligand of IL-2, induced IL-2-dependent CD25-CCR7 association, and IL-2(E52K) failed to support HS-induced CD25-CCR7 complex formation and integrin activation in Jurkat cells. Both HS and 7G7B6 did not block canonical IL-2 signaling. CD122 was present in the 7G7B6-induced CCR7-CD25 complex. CD122 forms a heterodimer with CD132 (the common γ chain) that triggers canonical IL-2 signaling. Thus, both anti-CD25 antibody and HS require formation of a chemokine receptor-CD25 complex to initiate alternative IL-2 signaling. In addition, our findings suggest that alternative and canonical IL-2 signaling receptors can be incorporated into the same multiprotein assembly, allowing for a single complex to mediate divergent effects on downstream signaling.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CYP4X1/sEH-Dependent Endocannabinoid Metabolism Drives Fibroblast-Mediated Immunosuppression to Limit Immunotherapy in Colon Cancer.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 January 2026 by Mo, M., Chen, X., et al.
PubMed
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 4X1 and soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), the key enzymes responsible for endocannabinoid oxidative metabolism, have been implicated in inflammation and cancer. However, the precise role of CYP4X1 and sEH in tumor immune evasion is poorly understood. Here, it is elucidated that CYP4X1/sEH-dependent endocannabinoid metabolism governs immune evasion in colon cancer by promoting the infiltration of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and impairing CD8+ T cell effector function. Mechanistically, CYP4X1/sEH-derived 14,15-EET-EA upregulates PD-L1, CXCL12, and TGF-β in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) via the GPR119-Gs/β-arrestin 2 signaling axis. Importantly, targeted regulation of the CYP4X1/sEH-GPR119 axis enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy. Moreover, CYP4X1 and sEH levels jointly predict prognosis and immune infiltration in human colon cancer. Together, this study highlights that CYP4X1/sEH-dependent endocannabinoid metabolism controls CAF-mediated immune evasion, and targeting the CYP4X1/sEH-14,15-EET-EA-GPR119 axis represents a promising therapeutic strategy for improving anti-PD-1 therapy in colon cancer.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
αTIGIT-IL2 achieves tumor regression by promoting tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cell fragility in mouse models.
In Nat Commun on 17 October 2025 by Wang, T., Xu, Y., et al.
PubMed
Administration of IL-2 may promote the suppressive function and proliferation of Treg cells that cause immune tolerance in patients with cancer, which causes low-dose IL-2 to fail in achieving an optimal anti-tumor effect. Here, we designed an immunocytokine by fusing IL-2 and an anti-TIGIT monoclonal antibody, named αTIGIT-IL2, that targets Treg cells and promotes their fragility in the tumor milieu. These fragile-like Treg cells show impaired suppressive function and high IFN-γ production, triggering an immune-reactive tumor microenvironment. Such inflammation leads to the recruitment and functional reprogramming of intratumoral neutrophils, improving cross-talk between neutrophils and CD8+ T cells and enhancing the antitumor ability of CD8+ T cells. Combination therapy with αTIGIT-IL2 and PD-1 blocker could eliminate triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) tumors resistant to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. These findings provide the basis for developing a new generation of immunocytokines that target Treg cells and promote their fragility in the tumor milieu, resulting in robust antitumor immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells Restrain Th1 Response Shielding the Brain from Lethal Inflammatory Damage during Cryptococcal Meningoencephalitis
In Research Square on 30 July 2025 by Olszewski, M., Li, H., et al.
-
-
-
Cardiovascular biology
Myocardial transcriptomic and proteomic landscapes across the menopausal continuum in a murine model of chemically induced accelerated ovarian failure.
In Physiol Genomics on 1 July 2025 by Lopez-Pier, M. A., Marino, V. A., et al.
PubMed
Risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in women increases with the menopausal transition. Using a chemical model (4-vinylcyclohexene diepoxide; VCD) of accelerated ovarian failure, we previously demonstrated that menopausal females are more susceptible to CVD compared with peri- or premenopausal females like humans. Yet, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying this shift in CVD susceptibility across the pre- to peri- to menopause continuum remain understudied. In this work using the VCD mouse model, we phenotyped cellular and molecular signatures from hearts at each hormonally distinct stage that included transcriptomic, proteomic, and cell biological analyses. The transcriptional profile of premenopausal hearts clustered separately from perimenopausal and menopausal hearts, which clustered more similarly. Proteomics also revealed hormonal clustering; perimenopausal hearts grouped more closely with premenopausal than menopausal hearts. Both proteomes and transcriptomes showed similar trends in genes associated with atherothrombosis, contractility, and impaired nuclear signaling between pre-, peri-, and menopausal murine hearts. Further analysis of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) showed hormone-dependent shifts in the phosphoproteome and acetylome. To further interrogate these findings, we triggered pathological remodeling using angiotensin II (Ang II). Phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling and histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity were found to be dependent on hormonal status and Ang II stimulation. Finally, knockdown of anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells (Treg) exacerbated Ang II-dependent fibrosis implicating HDAC-mediated epigenetic suppression of Treg activity. Taken together, we demonstrated unique cellular and molecular profiles underlying the cardiac phenotype of pre-, peri-, and menopausal mice supporting the necessity to study CVD in females across the hormonal transition.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Cycling and perimenopausal females are protected from cardiovascular disease (CVD) whereas menopausal females are more susceptible to CVD and other pathological sequalae. The cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying loss of CVD protection across the pre- to peri- to menopause transition remain understudied. Using the murine 4-vinylcyclohexene diepoxide (VCD) model of menopause we highlight cellular and molecular signatures from hearts at each hormonally distinct stage that included transcriptomic, proteomic, and cell biological analyses.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Inhibitors of oncogenic Kras specifically prime CTLA4 blockade to transcriptionally reprogram Tregs and overcome resistance to suppress pancreas cancer
In bioRxiv on 4 March 2025 by Mahadevan, K. K., Maldonado, A. S., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A novel HVEM-Fc recombinant protein for lung cancer immunotherapy.
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 20 February 2025 by Yao, Y., Li, B., et al.
PubMed
The ubiquitously expressed transmembrane protein, Herpesvirus Entry Mediator (HVEM), functions as a molecular switch, capable of both activating and inhibiting the immune response depending on its interacting ligands. HVEM-Fc is a novel recombinant fusion protein with the potential to eradicate tumor cells.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
HSCs and Tregs cooperate to preserve extramedullary hematopoiesis under chronic inflammation
In bioRxiv on 8 February 2025 by Kuzmina, M., Grusanovic, S., et al.
-
-
A CD25-CCR7 complex initiates non-canonical IL-2 signaling
In bioRxiv on 4 February 2025 by Kim, S. H. J., Lee, H., et al.
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Sorafenib Promotes Treg Cell Differentiation To Compromise Its Efficacy via VEGFR/AKT/Foxo1 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
In Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol on 2 January 2025 by Shen, Y., Wang, H., et al.
PubMed
Sora is the first-line drug for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, acquired resistance to Sora treatment largely hinders its therapeutic efficacy, and the mechanisms underlying Sora resistance remain poorly understood. Here, we revealed a new mechanism by which Sora promotes the differentiation of regulatory T (Treg) cells to suppress the immune response in the HCC tumor microenvironment (TME) and induce Sora resistance.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Pathobiont-induced suppressive immune imprints thwart T cell vaccine responses.
In Nat Commun on 16 December 2024 by Hajam, I. A., Tsai, C. M., et al.
PubMed
Pathobionts have evolved many strategies to coexist with the host, but how immune evasion mechanisms contribute to the difficulty of developing vaccines against pathobionts is unclear. Meanwhile, Staphylococcus aureus (SA) has resisted human vaccine development to date. Here we show that prior SA exposure induces non-protective CD4+ T cell imprints, leading to the blunting of protective IsdB vaccine responses. Mechanistically, these SA-experienced CD4+ T cells express IL-10, which is further amplified by vaccination and impedes vaccine protection by binding with IL-10Rα on CD4+ T cell and inhibit IL-17A production. IL-10 also mediates cross-suppression of IsdB and sdrE multi-antigen vaccine. By contrast, the inefficiency of SA IsdB, IsdA and MntC vaccines can be overcome by co-treatment with adjuvants that promote IL-17A and IFN-γ responses. We thus propose that IL-10 secreting, SA-experienced CD4+ T cell imprints represent a staphylococcal immune escaping mechanism that needs to be taken into consideration for future vaccine development.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Blockade of CCR5+ T Cell Accumulation in the Tumor Microenvironment Optimizes Anti-TGF-β/PD-L1 Bispecific Antibody.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 November 2024 by Yi, M., Li, T., et al.
PubMed
In the previous studies, anti-TGF-β/PD-L1 bispecific antibody YM101 is demonstrated, with superior efficacy to anti-PD-L1 monotherapy in multiple tumor models. However, YM101 therapy can not achieve complete regression in most tumor-bearing mice, suggesting the presence of other immunosuppressive elements in the tumor microenvironment (TME) beyond TGF-β and PD-L1. Thoroughly exploring the TME is imperative to pave the way for the successful translation of anti-TGF-β/PD-L1 BsAb into clinical practice. In this work, scRNA-seq is employed to comprehensively profile the TME changes induced by YM101. The scRNA-seq analysis reveals an increase in immune cell populations associated with antitumor immunity and enhances cell-killing pathways. However, the analysis also uncovers the presence of immunosuppressive CCR5+ T cells in the TME after YM101 treatment. To overcome this hurdle, YM101 is combined with Maraviroc, a widely used CCR5 antagonist for treating HIV infection, suppressing CCR5+ T cell accumulation, and optimizing the immune response. Mechanistically, YM101-induced neutrophil activation recruits immunosuppressive CCR5+ T cells via CCR5 ligand secretion, creating a feedback loop that diminishes the antitumor response. Maraviroc then cleared these infiltrating cells and offset YM101-mediated immunosuppressive effects, further unleashing the antitumor immunity. These findings suggest selectively targeting CCR5 signaling with Maraviroc represents a promising and strategic approach to enhance YM101 efficacy.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
An injectable subcutaneous colon-specific immune niche for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
In Nat Biomed Eng on 1 October 2024 by Au, K. M., Wilson, J. E., et al.
PubMed
As a chronic autoinflammatory condition, ulcerative colitis is often managed via systemic immunosuppressants. Here we show, in three mouse models of established ulcerative colitis, that a subcutaneously injected colon-specific immunosuppressive niche consisting of colon epithelial cells, decellularized colon extracellular matrix and nanofibres functionalized with programmed death-ligand 1, CD86, a peptide mimic of transforming growth factor-beta 1, and the immunosuppressive small-molecule leflunomide, induced intestinal immunotolerance and reduced inflammation in the animals' lower gastrointestinal tract. The bioengineered colon-specific niche triggered autoreactive T cell anergy and polarized pro-inflammatory macrophages via multiple immunosuppressive pathways, and prevented the infiltration of immune cells into the colon's lamina propria, promoting the recovery of epithelial damage. The bioengineered niche also prevented colitis-associated colorectal cancer and eliminated immune-related colitis triggered by kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint blockade.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
IL-34 empowers regulatory T cells with novel non-canonical function to safeguard brain barrier integrity during neuro-inflammation
In bioRxiv on 13 September 2024 by Van Hoecke, L., Verreycken, J., et al.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
p40 homodimers bridge ischemic tissue inflammation and heterologous alloimmunity in mice via IL-15 transpresentation.
In J Clin Invest on 25 January 2024 by Tsuda, H., Keslar, K. S., et al.
PubMed
Virus-induced memory T cells often express functional cross-reactivity, or heterologous immunity, to other viruses and to allogeneic MHC molecules that is an important component of pathogenic responses to allogeneic transplants. During immune responses, antigen-reactive naive and central memory T cells proliferate in secondary lymphoid organs to achieve sufficient cell numbers to effectively respond, whereas effector memory T cell proliferation occurs directly within the peripheral inflammatory microenvironment. Mechanisms driving heterologous memory T cell proliferation and effector function expression within peripheral tissues remain poorly understood. Here, we dissected proliferation of heterologous donor-reactive memory CD8+ T cells and their effector functions following infiltration into heart allografts with low or high intensities of ischemic inflammation. Proliferation within both ischemic conditions required p40 homodimer-induced IL-15 transpresentation by graft DCs, but expression of effector functions mediating acute allograft injury occurred only in high-ischemic allografts. Transcriptional responses of heterologous donor-reactive memory CD8+ T cells were distinct from donor antigen-primed memory CD8+ T cells during early activation in allografts and at graft rejection. Overall, the results provide insights into mechanisms driving heterologous effector memory CD8+ T cell proliferation and the separation between proliferation and effector function that is dependent on the intensity of inflammation within the tissue microenvironment.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
An Injectable Subcutaneous Colon-Specific Immune Niche For The Treatment Of Ulcerative Colitis
In bioRxiv on 4 October 2023 by Au, K. M., Wilson, J. E., et al.
-
-
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Intestinal microbiota controls graft-versus-host disease independent of donor-host genetic disparity.
In Immunity on 8 August 2023 by Koyama, M., Hippe, D. S., et al.
PubMed
Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) remains a major limitation of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT), and severe intestinal manifestation is the major cause of early mortality. Intestinal microbiota control MHC class II (MHC-II) expression by ileal intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) that promote GVHD. Here, we demonstrated that genetically identical mice of differing vendor origins had markedly different intestinal microbiota and ileal MHC-II expression, resulting in discordant GVHD severity. We utilized cohousing and antibiotic treatment to characterize the bacterial taxa positively and negatively associated with MHC-II expression. A large proportion of bacterial MHC-II inducers were vancomycin sensitive, and peri-transplant oral vancomycin administration attenuated CD4+ T cell-mediated GVHD. We identified a similar relationship between pre-transplant microbes, HLA class II expression, and both GVHD and mortality in a large clinical SCT cohort. These data highlight therapeutically tractable mechanisms by which pre-transplant microbial taxa contribute to GVHD independently of genetic disparity.
-