InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD172a (SIRPα)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG1 isotype control, anti-horseradish peroxidase |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse brain membrane protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo SIRPα blocking In vitro SIRPα blocking Western blot Immunoprecipitation Flow cytometry |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2819049 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo SIRPα blocking
in vitro SIRPα blocking
Yanagita, T., et al (2017). "Anti-SIRPalpha antibodies as a potential new tool for cancer immunotherapy" JCI Insight 2(1): e89140.
PubMed
Tumor cells are thought to evade immune surveillance through interaction with immune cells. Much recent attention has focused on the modification of immune responses as a basis for new cancer treatments. SIRPalpha is an Ig superfamily protein that inhibits phagocytosis in macrophages upon interaction with its ligand CD47 expressed on the surface of target cells. Here, we show that SIRPalpha is highly expressed in human renal cell carcinoma and melanoma. Furthermore, an anti-SIRPalpha Ab that blocks the interaction with CD47 markedly suppressed tumor formation by renal cell carcinoma or melanoma cells in immunocompetent syngeneic mice. This inhibitory effect of the Ab appeared to be mediated by dual mechanisms: direct induction of Ab-dependent cellular phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages and blockade of CD47-SIRPalpha signaling that negatively regulates such phagocytosis. The antitumor effect of the Ab was greatly attenuated by selective depletion not only of macrophages but also of NK cells or CD8(+) T cells. In addition, the anti-SIRPalpha Ab also enhances the inhibitory effects of Abs against CD20 and programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) on tumor formation in mice injected with SIRPalpha-nonexpressing tumor cells. Anti-SIRPalpha Abs thus warrant further study as a potential new therapy for a broad range of cancers.
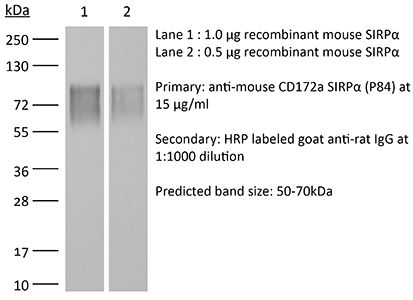
Western Blot
Immunoprecipitation
Flow Cytometry
Koskinen, C., et al (2013). "Lack of CD47 impairs bone cell differentiation and results in an osteopenic phenotype in vivo due to impaired signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) signaling" J Biol Chem 288(41): 29333-29344.
PubMed
Here, we investigated whether the cell surface glycoprotein CD47 was required for normal formation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts and to maintain normal bone formation activity in vitro and in vivo. In parathyroid hormone or 1alpha,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 (D3)-stimulated bone marrow cultures (BMC) from CD47(-/-) mice, we found a strongly reduced formation of multinuclear tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)(+) osteoclasts, associated with reduced expression of osteoclastogenic genes (nfatc1, Oscar, Trap/Acp, ctr, catK, and dc-stamp). The production of M-CSF and RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappabeta ligand) was reduced in CD47(-/-) BMC, as compared with CD47(+/+) BMC. The stromal cell phenotype in CD47(-/-) BMC involved a blunted expression of the osteoblast-associated genes osterix, Alp/Akp1, and alpha-1-collagen, and reduced mineral deposition, as compared with that in CD47(+/+) BMC. CD47 is a ligand for SIRPalpha (signal regulatory protein alpha), which showed strongly reduced tyrosine phosphorylation in CD47(-/-) bone marrow stromal cells. In addition, stromal cells lacking the signaling SIRPalpha cytoplasmic domain also had a defect in osteogenic differentiation, and both CD47(-/-) and non-signaling SIRPalpha mutant stromal cells showed a markedly reduced ability to support osteoclastogenesis in wild-type bone marrow macrophages, demonstrating that CD47-induced SIRPalpha signaling is critical for stromal cell support of osteoclast formation. In vivo, femoral bones of 18- or 28-week-old CD47(-/-) mice showed significantly reduced osteoclast and osteoblast numbers and exhibited an osteopenic bone phenotype. In conclusion, lack of CD47 strongly impairs SIRPalpha-dependent osteoblast differentiation, deteriorate bone formation, and cause reduced formation of osteoclasts.
in vivo SIRPα blocking
Teraoka, Y., et al (2013). "Expression of recipient CD47 on rat insulinoma cell xenografts prevents macrophage-mediated rejection through SIRPalpha inhibitory signaling in mice" PLoS One 8(3): e58359.
PubMed
We have previously proven that the interspecies incompatibility of CD47 is responsible for in vitro phagocytosis of xenogeneic cells by host macrophages. Utilizing an in vivo model in the present study, we investigated whether genetically engineered expression of mouse CD47 in rat insulinoma cells (INS-1E) could inhibit macrophage-mediated xenograft rejection. INS-1E cells transfected with the pRc/CMV-mouse CD47 vector (mCD47-INS-1E) induced SIRPalpha-tyrosine phosphorylation in mouse macrophages in vitro, whereas cells transfected with the control vector (cont-INS-1E) did not. When these cells were injected into the peritoneal cavity of streptozotocin-induced diabetic Rag2(-/-)gamma chain (-/-) mice, which lack T, B, and NK cells, the expression of mouse CD47 on the INS-1E cells markedly reduced the susceptibility of these cells to phagocytosis by macrophages. Moreover, these mice became normoglycemic after receiving mCD47-INS-1E, whereas the mice that received cont-INS-1E failed to achieve normoglycemia. Furthermore, injection of an anti-mouse SIRPalpha blocking monoclonal antibody into the mouse recipients of mCD47-INS-1E cells prevented achievement of normoglycemia. These results demonstrate that interspecies incompatibility of CD47 significantly contributes to in vivo rejection of xenogeneic cells by macrophages. Thus, genetic induction of the expression of recipient CD47 on xenogeneic donor cells could provide inhibitory signals to recipient macrophages via SIPRalpha; this constitutes a novel approach for preventing macrophage-mediated xenograft rejection.
Western Blot
Zen, K., et al (2013). "Inflammation-induced proteolytic processing of the SIRPalpha cytoplasmic ITIM in neutrophils propagates a proinflammatory state" Nat Commun 4: 2436.
PubMed
Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha), an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)-containing receptor, is an essential negative regulator of leukocyte inflammatory responses. Here we report that SIRPalpha cytoplasmic signalling ITIMs in neutrophils are cleaved during active inflammation and that the loss of SIRPalpha ITIMs enhances the polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) inflammatory response. Using human leukocytes and two inflammatory models in mice, we show that the cleavage of SIRPalpha ITIMs in PMNs but not monocytes occurs at the post-acute stage of inflammation and correlates with increased PMN recruitment to inflammatory loci. Enhanced transmigration of PMNs and PMN-associated tissue damage are confirmed in mutant mice expressing SIRPalpha but lacking the ITIMs. Moreover, the loss of SIRPalpha ITIMs in PMNs during colitis is blocked by an anti-interleukin-17 (IL-17) antibody. These results demonstrate a SIRPalpha-based mechanism that dynamically regulates PMN inflammatory responses by generating a CD47-binding but non-signalling SIRPalpha ‘decoy’.
in vitro SIRPα blocking
Lundberg, P., et al (2007). "Osteoclast formation is strongly reduced both in vivo and in vitro in the absence of CD47/SIRPalpha-interaction" Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352(2): 444-448.
PubMed
Physical interaction between the cell surface receptors CD47 and signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) was reported to regulate cell migration, phagocytosis, cytokine production, and macrophage fusion. However, it is unclear if the CD47/SIRPalpha-interaction can also regulate macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-stimulated formation of osteoclasts. Here, we show that functional blocking antibodies to either CD47 or SIRPalpha strongly reduced formation of multinucleated tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)+ osteoclasts in cultures of murine hematopoietic cells, stimulated in vitro by M-CSF and RANKL. In addition, the numbers of osteoclasts formed in M-CSF/RANKL-stimulated bone marrow macrophage cultures from CD47-/- mice were strongly reduced, and bones of CD47-/- mice exhibited significantly reduced osteoclast numbers, as compared with wild-type controls. We conclude that the CD47/SIRPalpha interaction is important for M-CSF/RANKL-stimulated osteoclast formation both in vivo and in vitro, and that absence of CD47 results in decreased numbers of osteoclasts in CD47-/- mice.
in vitro SIRPα blocking
Oldenborg, P. A., et al (2001). "CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) regulates Fcgamma and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis" J Exp Med 193(7): 855-862.
PubMed
In autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), circulating red blood cells (RBCs) opsonized with autoantibody are recognized by macrophage Fcgamma and complement receptors. This triggers phagocytosis and elimination of RBCs from the circulation by splenic macrophages. We recently found that CD47 on unopsonized RBCs binds macrophage signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha), generating a negative signal that prevents phagocytosis of the unopsonized RBCs. We show here that clearance and phagocytosis of opsonized RBCs is also regulated by CD47-SIRPalpha. The inhibition generated by CD47-SIRPalpha interaction is strongly attenuated but not absent in mice with only residual activity of the phosphatase Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-1, suggesting that most SIRPalpha signaling in this system is mediated by SHP-1 phosphatase activity. The macrophage phagocytic response is controlled by an integration of the inhibitory SIRPalpha signal with prophagocytic signals such as from Fcgamma and complement receptor activation. Thus, augmentation of inhibitory CD47-SIRPalpha signaling may prevent or attenuate RBC clearance in AIHA.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Loss of NR2F6 Protects from Salmonella Typhimurium Infection.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 October 2025 by Woelk, J., Pfeifhofer-Obermair, C., et al.
PubMed
Nuclear receptors regulate key functions of mononuclear phagocytes and are critical components of the innate immune system, acting as regulators of organ health and disease. In healthy mice, the loss of the nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 alters tissue-resident macrophage populations in the liver, lung, and spleen. In response to Salmonella Typhimurium infection, Nr2f6-deficient mice exhibit improved clinical outcomes, characterized by reduced weight loss, bacterial loads in the spleen and liver, and decreased plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines. Despite unchanged basal iron metabolism in the spleen and liver, iron regulatory proteins and the interleukin (IL)-6-hepcidin axis are altered in Nr2f6-deficient mice during Salmonella infection, reducing hypoferremia. Transcriptomic analysis of splenic red pulp macrophages reveals significant alterations of phagocytosis-related genes, including upregulation of signal-regulatory protein alpha (Sirpa). In vitro, phagocytosis of red blood cells, regulated by the inhibitory CD47-Sirpα axis, and Salmonella Typhimurium phagocytosis are significantly impaired in Nr2f6-deficient splenic macrophages. Blocking Sirpα in vitro restores the phagocytic activity of Nr2f6-deficient macrophages to wild-type levels. In vivo, Salmonella Typhimurium loads are partially increased post-infection in anti-Sirpα treated Nr2f6-deficient mice. These findings uncover a previously unrecognized role of NR2F6 in host-pathogen interactions, positioning it as a potential therapeutic target for infectious diseases.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
SIRPα blockade therapy potentiates immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1+ myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Death Dis on 16 June 2025 by Huang, D., Xu, M., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are pivotal cell populations involved in the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). However, there has been little success in large-scale clinical trials of myeloid cell modulators. We aim to investigate potential molecular targets for TIMs and disclose the underlying mechanism. Using mass cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), we analyzed 24 spontaneous HCC tissues from mouse. Orthotopic and subcutaneous tumor models were established with or without anti-SIRPα antibody treatment. Patient-derived tumor xenografts model (PDX) was used to identify the CD47-SIRPα axis blocked therapy. In 24 murine spontaneous HCC tissues, we observed that the proportion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plus macrophages accounts for 40-90% of TIMs and SIRPα was highly expressed in TIMs, especially in macrophages and MDSCs. Through in vivo experiments, we showed that anti-SIRPα therapy inhibited tumor growth, accompanied by increased CD8+ T cells infiltration and decreased TIMs including MDSCs and macrophages. We found that anti-SIRPα inhibited immunosuppressive function, migration and PD-L1 expression of myeloid cells. In a series of in vivo experiments, we demonstrated the anti-tumor and immune-active effect of SIRPα-blocked therapy. Mechanistically, anti-SIRPα inhibited the immunosuppressive function and PD-L1 expression of TIMs through downregulating PI3K/AKT signaling in myeloid cells. At last, anti-SIRPα enhanced the antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 therapy in orthotopic and spontaneous murine models. Together, SIRPα blocked therapy reversed the immunosuppressive TIME, which provides a promising therapeutic rationale for increasing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in treating HCC.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Western Blotting
SIRPα blockade therapy potentiates immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1+ myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Death Dis on 16 June 2025 by Huang, D., Xu, M., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are pivotal cell populations involved in the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). However, there has been little success in large-scale clinical trials of myeloid cell modulators. We aim to investigate potential molecular targets for TIMs and disclose the underlying mechanism. Using mass cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), we analyzed 24 spontaneous HCC tissues from mouse. Orthotopic and subcutaneous tumor models were established with or without anti-SIRPα antibody treatment. Patient-derived tumor xenografts model (PDX) was used to identify the CD47-SIRPα axis blocked therapy. In 24 murine spontaneous HCC tissues, we observed that the proportion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plus macrophages accounts for 40-90% of TIMs and SIRPα was highly expressed in TIMs, especially in macrophages and MDSCs. Through in vivo experiments, we showed that anti-SIRPα therapy inhibited tumor growth, accompanied by increased CD8+ T cells infiltration and decreased TIMs including MDSCs and macrophages. We found that anti-SIRPα inhibited immunosuppressive function, migration and PD-L1 expression of myeloid cells. In a series of in vivo experiments, we demonstrated the anti-tumor and immune-active effect of SIRPα-blocked therapy. Mechanistically, anti-SIRPα inhibited the immunosuppressive function and PD-L1 expression of TIMs through downregulating PI3K/AKT signaling in myeloid cells. At last, anti-SIRPα enhanced the antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 therapy in orthotopic and spontaneous murine models. Together, SIRPα blocked therapy reversed the immunosuppressive TIME, which provides a promising therapeutic rationale for increasing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in treating HCC.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
SIRPα blockade therapy potentiates immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1+ myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Death Dis on 16 June 2025 by Huang, D., Xu, M., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are pivotal cell populations involved in the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). However, there has been little success in large-scale clinical trials of myeloid cell modulators. We aim to investigate potential molecular targets for TIMs and disclose the underlying mechanism. Using mass cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), we analyzed 24 spontaneous HCC tissues from mouse. Orthotopic and subcutaneous tumor models were established with or without anti-SIRPα antibody treatment. Patient-derived tumor xenografts model (PDX) was used to identify the CD47-SIRPα axis blocked therapy. In 24 murine spontaneous HCC tissues, we observed that the proportion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plus macrophages accounts for 40-90% of TIMs and SIRPα was highly expressed in TIMs, especially in macrophages and MDSCs. Through in vivo experiments, we showed that anti-SIRPα therapy inhibited tumor growth, accompanied by increased CD8+ T cells infiltration and decreased TIMs including MDSCs and macrophages. We found that anti-SIRPα inhibited immunosuppressive function, migration and PD-L1 expression of myeloid cells. In a series of in vivo experiments, we demonstrated the anti-tumor and immune-active effect of SIRPα-blocked therapy. Mechanistically, anti-SIRPα inhibited the immunosuppressive function and PD-L1 expression of TIMs through downregulating PI3K/AKT signaling in myeloid cells. At last, anti-SIRPα enhanced the antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 therapy in orthotopic and spontaneous murine models. Together, SIRPα blocked therapy reversed the immunosuppressive TIME, which provides a promising therapeutic rationale for increasing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in treating HCC.
-
-
-
Immunohistochemistry
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
SIRPα blockade therapy potentiates immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1+ myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Death Dis on 16 June 2025 by Huang, D., Xu, M., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are pivotal cell populations involved in the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). However, there has been little success in large-scale clinical trials of myeloid cell modulators. We aim to investigate potential molecular targets for TIMs and disclose the underlying mechanism. Using mass cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), we analyzed 24 spontaneous HCC tissues from mouse. Orthotopic and subcutaneous tumor models were established with or without anti-SIRPα antibody treatment. Patient-derived tumor xenografts model (PDX) was used to identify the CD47-SIRPα axis blocked therapy. In 24 murine spontaneous HCC tissues, we observed that the proportion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plus macrophages accounts for 40-90% of TIMs and SIRPα was highly expressed in TIMs, especially in macrophages and MDSCs. Through in vivo experiments, we showed that anti-SIRPα therapy inhibited tumor growth, accompanied by increased CD8+ T cells infiltration and decreased TIMs including MDSCs and macrophages. We found that anti-SIRPα inhibited immunosuppressive function, migration and PD-L1 expression of myeloid cells. In a series of in vivo experiments, we demonstrated the anti-tumor and immune-active effect of SIRPα-blocked therapy. Mechanistically, anti-SIRPα inhibited the immunosuppressive function and PD-L1 expression of TIMs through downregulating PI3K/AKT signaling in myeloid cells. At last, anti-SIRPα enhanced the antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 therapy in orthotopic and spontaneous murine models. Together, SIRPα blocked therapy reversed the immunosuppressive TIME, which provides a promising therapeutic rationale for increasing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in treating HCC.
-
-
-
Immunocytochemistry-immunofluorescence
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
SIRPα blockade therapy potentiates immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1+ myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Death Dis on 16 June 2025 by Huang, D., Xu, M., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are pivotal cell populations involved in the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). However, there has been little success in large-scale clinical trials of myeloid cell modulators. We aim to investigate potential molecular targets for TIMs and disclose the underlying mechanism. Using mass cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), we analyzed 24 spontaneous HCC tissues from mouse. Orthotopic and subcutaneous tumor models were established with or without anti-SIRPα antibody treatment. Patient-derived tumor xenografts model (PDX) was used to identify the CD47-SIRPα axis blocked therapy. In 24 murine spontaneous HCC tissues, we observed that the proportion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plus macrophages accounts for 40-90% of TIMs and SIRPα was highly expressed in TIMs, especially in macrophages and MDSCs. Through in vivo experiments, we showed that anti-SIRPα therapy inhibited tumor growth, accompanied by increased CD8+ T cells infiltration and decreased TIMs including MDSCs and macrophages. We found that anti-SIRPα inhibited immunosuppressive function, migration and PD-L1 expression of myeloid cells. In a series of in vivo experiments, we demonstrated the anti-tumor and immune-active effect of SIRPα-blocked therapy. Mechanistically, anti-SIRPα inhibited the immunosuppressive function and PD-L1 expression of TIMs through downregulating PI3K/AKT signaling in myeloid cells. At last, anti-SIRPα enhanced the antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 therapy in orthotopic and spontaneous murine models. Together, SIRPα blocked therapy reversed the immunosuppressive TIME, which provides a promising therapeutic rationale for increasing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in treating HCC.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cell Biology
-
Cancer Research
SIRPα blockade therapy potentiates immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1+ myeloid cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Death Dis on 16 June 2025 by Huang, D., Xu, M., et al.
PubMed
Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells (TIMs) are pivotal cell populations involved in the immunosuppressive tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). However, there has been little success in large-scale clinical trials of myeloid cell modulators. We aim to investigate potential molecular targets for TIMs and disclose the underlying mechanism. Using mass cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF), we analyzed 24 spontaneous HCC tissues from mouse. Orthotopic and subcutaneous tumor models were established with or without anti-SIRPα antibody treatment. Patient-derived tumor xenografts model (PDX) was used to identify the CD47-SIRPα axis blocked therapy. In 24 murine spontaneous HCC tissues, we observed that the proportion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plus macrophages accounts for 40-90% of TIMs and SIRPα was highly expressed in TIMs, especially in macrophages and MDSCs. Through in vivo experiments, we showed that anti-SIRPα therapy inhibited tumor growth, accompanied by increased CD8+ T cells infiltration and decreased TIMs including MDSCs and macrophages. We found that anti-SIRPα inhibited immunosuppressive function, migration and PD-L1 expression of myeloid cells. In a series of in vivo experiments, we demonstrated the anti-tumor and immune-active effect of SIRPα-blocked therapy. Mechanistically, anti-SIRPα inhibited the immunosuppressive function and PD-L1 expression of TIMs through downregulating PI3K/AKT signaling in myeloid cells. At last, anti-SIRPα enhanced the antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 therapy in orthotopic and spontaneous murine models. Together, SIRPα blocked therapy reversed the immunosuppressive TIME, which provides a promising therapeutic rationale for increasing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in treating HCC.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Targeting HDAC6 improves anti-CD47 immunotherapy.
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 27 February 2024 by Gracia-Hernandez, M., Yende, A. S., et al.
PubMed
Cancer cells can overexpress CD47, an innate immune checkpoint that prevents phagocytosis upon interaction with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) expressed in macrophages and other myeloid cells. Several clinical trials have reported that CD47 blockade reduces tumor growth in hematological malignancies. However, CD47 blockade has shown modest results in solid tumors, including melanoma. Our group has demonstrated that histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors (HDAC6is) have immunomodulatory properties, such as controlling macrophage phenotype and inflammatory properties. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms controlling these processes are not fully understood. In this study, we evaluated the role of HDAC6 in regulating the CD47/SIRPα axis and phagocytosis in macrophages.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CD47 halts Ptpn6-deficient neutrophils from provoking lethal inflammation.
In Sci Adv on 6 January 2023 by Mazgaeen, L., Yorek, M. S., et al.
PubMed
Mice with SHP1 proteins, which have a single amino acid substitution from tyrosine-208 residue to asparagine (hereafter Ptpn6spin mice), develop an autoinflammatory disease with inflamed footpads. Genetic crosses to study CD47 function in Ptpn6spin mice bred Ptpn6spin × Cd47-/- mice that were not born at the expected Mendelian ratio. Ptpn6spin bone marrow cells, when transferred into lethally irradiated Cd47-deficient mice, caused marked weight loss and subsequent death. At a cellular level, Ptpn6-deficient neutrophils promoted weight loss and death of the lethally irradiated Cd47-/- recipients. We posited that leakage of gut microbiota promotes morbidity and mortality in Cd47-/- mice receiving Ptpn6spin cells. Colonic cell death and gut leakage were substantially increased in the diseased Cd47-/- mice. Last, IL-1 blockade using anakinra rescued the morbidity and mortality observed in the diseased Cd47-/- mice. These data together demonstrate a protective role for CD47 in tempering pathogenic neutrophils in the Ptpn6spin mice.
-
-
CD47-SIRPα axis blockade in NASH promotes necroptotic hepatocyte clearance by liver macrophages and decreases hepatic fibrosis.
In Sci Transl Med on 23 November 2022 by Shi, H., Wang, X., et al.
PubMed
Necroptosis contributes to hepatocyte death in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), but the fate and roles of necroptotic hepatocytes (necHCs) in NASH remain unknown. We show here that the accumulation of necHCs in human and mouse NASH liver is associated with an up-regulation of the "don't-eat-me" ligand CD47 on necHCs, but not on apoptotic hepatocytes, and an increase in the CD47 receptor SIRPα on liver macrophages, consistent with impaired macrophage-mediated clearance of necHCs. In vitro, necHC clearance by primary liver macrophages was enhanced by treatment with either anti-CD47 or anti-SIRPα. In a proof-of-concept mouse model of inducible hepatocyte necroptosis, anti-CD47 antibody treatment increased necHC uptake by liver macrophages and inhibited markers of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, which is responsible for liver fibrogenesis. Treatment of two mouse models of diet-induced NASH with anti-CD47, anti-SIRPα, or AAV8-H1-shCD47 to silence CD47 in hepatocytes increased the uptake of necHC by liver macrophages and decreased markers of HSC activation and liver fibrosis. Anti-SIRPα treatment avoided the adverse effect of anemia found in anti-CD47-treated mice. These findings provide evidence that impaired clearance of necHCs by liver macrophages due to CD47-SIRPα up-regulation contributes to fibrotic NASH, and suggest therapeutic blockade of the CD47-SIRPα axis as a strategy to decrease the accumulation of necHCs in NASH liver and dampen the progression of hepatic fibrosis.