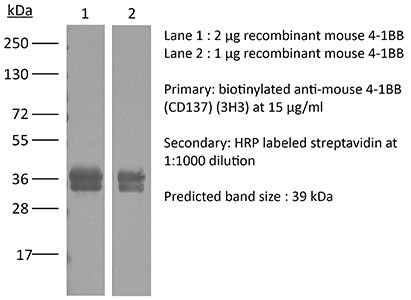
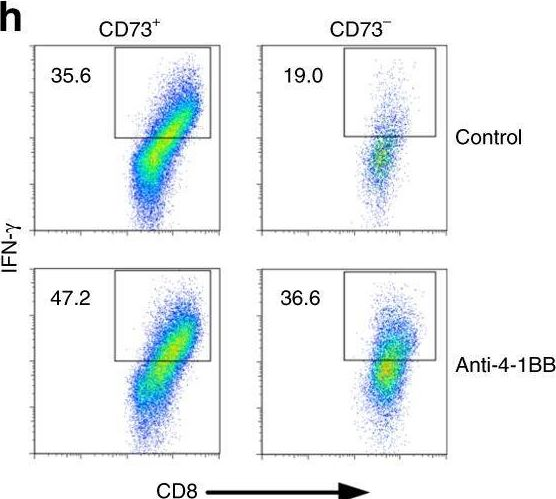
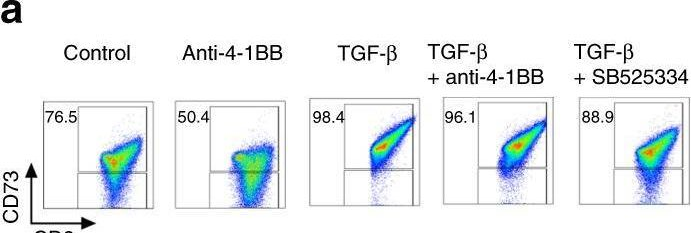
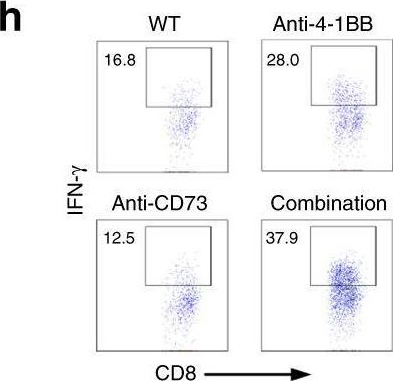
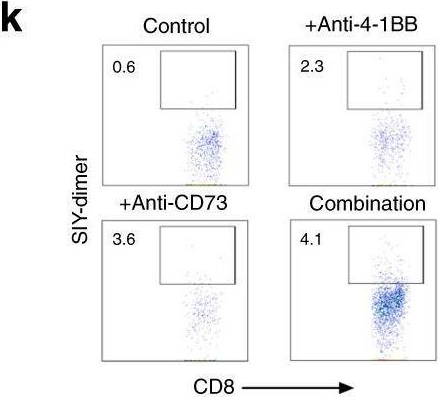
InVivoMAb anti-mouse 4-1BB (CD137)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse CD137 human Fc fusion protein |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo 4-1BB stimulation in vitro 4-1BB stimulation in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_2687721 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vitro Organoids/Organ-on-Chip
Arrizabalaga L, Russo-Cabrera JS, Belsúe V, Berraondo P, Melero I, Aranda F (2024). "Tumor slice culture system for ex vivo immunotherapy studies" Methods Cell Biol .
PubMed
Personalized immunotherapy is emerging as a promising approach for cancer treatment, aiming to harness the patient's own immune system to target and eliminate tumor cells. One key aspect of developing effective personalized immunotherapies is the utilization of tumor slices derived from individual patient tumors. Tumor slice models retain the complexity and heterogeneity of the original tumor microenvironment, including interactions with immune cells, stromal elements, and vasculature. These ex vivo models serve as valuable tools for studying tumor-immune interactions and for testing the efficacy of immunotherapeutic agents tailored to the specific characteristics of each patient's tumor. In this chapter, we set up a protocol for immunotherapy strategies in mouse models highlighting their translational potential to guide treatment decisions and improve therapeutic outcomes in cancer patients.
in vivo activation of 4-1BB
Qi, X., et al (2019). "Optimization of 4-1BB antibody for cancer immunotherapy by balancing agonistic strength with FcgammaR affinity" Nat Commun 10(1): 2141.
PubMed
Costimulation of T cell responses with monoclonal antibody agonists (mAb-AG) targeting 4-1BB showed robust anti-tumor activity in preclinical models, but their clinical development was hampered by low efficacy (Utomilumab) or severe liver toxicity (Urelumab). Here we show that isotype and intrinsic agonistic strength co-determine the efficacy and toxicity of anti-4-1BB mAb-AG. While intrinsically strong agonistic anti-4-1BB can activate 4-1BB in the absence of FcgammaRs, weak agonistic antibodies rely on FcgammaRs to activate 4-1BB. All FcgammaRs can crosslink anti-41BB antibodies to strengthen co-stimulation, but activating FcgammaR-induced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity compromises anti-tumor immunity by deleting 4-1BB(+) cells. This suggests balancing agonistic activity with the strength of FcgammaR interaction as a strategy to engineer 4-1BB mAb-AG with optimal therapeutic performance. As a proof of this concept, we have developed LVGN6051, a humanized 4-1BB mAb-AG that shows high anti-tumor efficacy in the absence of liver toxicity in a mouse model of cancer immunotherapy.
in vitro 4-1BB stimulation
Giardino Torchia, M. L., et al (2015). "c-IAP ubiquitin protein ligase activity is required for 4-1BB signaling and CD8(+) memory T-cell survival" Eur J Immunol 45(9): 2672-2682.
PubMed
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (c-IAP) 1 and 2 are widely expressed ubiquitin protein ligases that regulate a variety of cellular functions, including the sensitivity of T cells to costimulation. 4-1BB is a TNF receptor family member that signals via a complex that includes TRAF family members and the c-IAPs to upregulate NF-kappaB and ERK, and has been implicated in memory T-cell survival. Here, we show that effector and memory T cells from mice expressing a dominant negative E3-inactive c-IAP2 (c-IAP2(H570A) ) have impaired signaling downstream of 4-1BB. When infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, unlike mice in which c-IAPs were acutely downregulated by c-IAP antagonists, the primary response of c-IAP2(H570A) mice was normal. However, the number of antigen-specific CD8(+) but not CD4(+) T cells declined more rapidly and to a greater extent in c-IAP2(H570A) mice than in WT controls. Studies with T-cell adoptive transfer demonstrated that the enhanced decay of memory cells was T-cell intrinsic. Thus, c-IAP E3 activity is required for 4-1BB coreceptor signaling and maintenance of CD8(+) T-cell memory.
in vivo 4-1BB stimulation
Guillerey, C., et al (2015). "Immunosurveillance and therapy of multiple myeloma are CD226 dependent" J Clin Invest 125(5): 2077-2089.
PubMed
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an age-dependent hematological malignancy. Evaluation of immune interactions that drive MM relies on in vitro experiments that do not reflect the complex cellular stroma involved in MM pathogenesis. Here we used Vk*MYC transgenic mice, which spontaneously develop MM, and demonstrated that the immune system plays a critical role in the control of MM progression and the response to treatment. We monitored Vk*MYC mice that had been crossed with Cd226 mutant mice over a period of 3 years and found that CD226 limits spontaneous MM development. The CD226-dependent anti-myeloma immune response against transplanted Vk*MYC MM cells was mediated both by NK and CD8+ T cells through perforin and IFN-gamma pathways. Moreover, CD226 expression was required for optimal antimyeloma efficacy of cyclophosphamide (CTX) and bortezomib (Btz), which are both standardly used to manage MM in patients. Activation of costimulatory receptor CD137 with mAb (4-1BB) exerted strong antimyeloma activity, while inhibition of coinhibitory receptors PD-1 and CTLA-4 had no effect. Taken together, the results of this study provide in vivo evidence that CD226 is important for MM immunosurveillance and indicate that specific immune components should be targeted for optimal MM treatment efficacy. As progressive immunosuppression associates with MM development, strategies aimed to increase immune functions may have important therapeutic implications in MM.
in vivo 4-1BB stimulation
Kobayashi, T., et al (2015). "NKT cell-targeted vaccination plus anti-4-1BB antibody generates persistent CD8 T cell immunity against B cell lymphoma" Oncoimmunology 4(3): e990793.
PubMed
Harnessing the immune adjuvant properties of natural killer T (NKT) cells is an effective strategy to generate anticancer immunity. The objective of this study was to increase the potency and durability of vaccine-induced immunity against B cell lymphoma by combining alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer)-loaded tumor cell vaccination with an agonistic antibody targeting the immune checkpoint molecule 4-1BB (CD137). We observed potent synergy when combining vaccination and anti-4-1BB antibody treatment resulting in significantly enhanced survival of mice harboring Emu-myc tumors, including complete eradication of lymphoma in over 50% of mice. Tumor-free survival required interferon gamma (IFNgamma)-dependent expansion of CD8+ T cells and was associated with 4-1BB-mediated differentiation of KLRG1+ effector CD8+ T cells. ‘Cured’ mice were also resistant to lymphoma re-challenge 80 days later indicating successful generation of immunological memory. Overall, our results demonstrate that therapeutic anticancer vaccination against B cell lymphoma using an NKT cell ligand can be boosted by subsequent co-stimulation through 4-1BB leading to a sustainable immune response that may enhance outcomes to conventional treatment.
in vivo 4-1BB stimulation
Tewalt, E. F., et al (2012). "Lymphatic endothelial cells induce tolerance via PD-L1 and lack of costimulation leading to high-level PD-1 expression on CD8 T cells" Blood 120(24): 4772-4782.
PubMed
Lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) induce peripheral tolerance by direct presentation to CD8 T cells (T(CD8)). We demonstrate that LECs mediate deletion only via programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) ligand 1, despite expressing ligands for the CD160, B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator, and lymphocyte activation gene-3 inhibitory pathways. LECs induce activation and proliferation of T(CD8), but lack of costimulation through 4-1BB leads to rapid high-level expression of PD-1, which in turn inhibits up-regulation of the high-affinity IL-2 receptor that is necessary for T(CD8) survival. Rescue of tyrosinase-specific T(CD8) by interference with PD-1 or provision of costimulation results in autoimmune vitiligo, demonstrating that LECs are significant, albeit suboptimal, antigen-presenting cells. Because LECs express numerous peripheral tissue antigens, lack of costimulation coupled to rapid high-level up-regulation of inhibitory receptors may be generally important in systemic peripheral tolerance.
in vivo 4-1BB stimulation
Verbrugge, I., et al (2012). "Radiotherapy increases the permissiveness of established mammary tumors to rejection by immunomodulatory antibodies" Cancer Res 72(13): 3163-3174.
PubMed
It is becoming increasingly evident that radiotherapy may benefit from coincident or subsequent immunotherapy. In this study, we examined whether the antitumor effects of radiotherapy, in established triple-negative breast tumors could be enhanced with combinations of clinically relevant monoclonal antibodies (mAb), designed to stimulate immunity [anti-(alpha)-CD137, alpha-CD40] or relieve immunosuppression [alpha-programmed death (PD)-1]. While the concomitant targeting of the costimulatory molecules CD137 and CD40 enhanced the antitumor effects of radiotherapy and promoted the rejection of subcutaneous BALB/c-derived 4T1.2 tumors, this novel combination was noncurative in mice bearing established C57BL/6-derived AT-3 tumors. We identified PD-1 signaling within the AT-3 tumors as a critical limiting factor to the therapeutic efficacy of alpha-CD137 therapy, alone and in combination with radiotherapy. Strikingly, all mice bearing established orthotopic AT-3 mammary tumors were cured when alpha-CD137 and alpha-PD-1 mAbs were combined with single- or low-dose fractionated radiotherapy. CD8+ T cells were essential for curative responses to this combinatorial regime. Interestingly, CD137 expression on tumor-associated CD8+ T cells was largely restricted to a subset that highly expressed PD-1. These CD137+PD-1High CD8+ T cells, persisted in irradiated AT-3 tumors, expressed Tim-3, granzyme B and Ki67 and produced IFN-gamma ex vivo in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin stimulation. Notably, radiotherapy did not deplete, but enriched tumors of functionally active, tumor-specific effector cells. Collectively, these data show that concomitant targeting of immunostimulatory and inhibitory checkpoints with immunomodulatory mAbs can enhance the curative capacity of radiotherapy in established breast malignancy.
in vivo 4-1BB stimulation
Vezys, V., et al (2011). "4-1BB signaling synergizes with programmed death ligand 1 blockade to augment CD8 T cell responses during chronic viral infection" J Immunol 187(4): 1634-1642.
PubMed
Previous studies have identified the inhibitory role that the programmed death 1 (PD-1) pathway plays during chronic infection. Blockade of this pathway results in rescue of viral-specific CD8 T cells, as well as reduction of viral loads in mice chronically infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). We tested the effect of combining PD ligand 1 (PD-L1) blockade with an agonistic regimen that induces 4-1BB costimulation during chronic LCMV infection. There is a boosting effect in the rescue of LCMV-specific CD8 T cell responses after dual treatment with PD-L1 blockade and 4-1BB agonistic Abs when the amount and timing of 4-1BB costimulation are carefully controlled. When PD-L1-blocking Abs are given together with a single low dose of anti-4-1BB agonistic Abs, there is an enhanced and stable expansion of viral-specific CD8 T cells. Conversely, when blocking Abs to PD-L1 are given with a repetitive high dose of anti-4-1BB, there is an initial synergistic expansion of viral-specific CD8 T cells by day 7, followed by dramatic apoptosis by day 14. Viral control paralleled CD8 T cell kinetics after dual treatment. By day 7 posttreatment, viral titers were lower in both of the combined regimens (compared with PD-L1 blockade alone). However, whereas the high dose of anti-4-1BB plus PD-L1 blockade resulted in rebound of viral titers to original levels, the low dose of anti-4-1BB plus PD-L1 blockade resulted in a stable reduction of viral loads. These findings demonstrate the importance of carefully manipulating the balance between activating and inhibitory signals to enhance T cell responses during chronic infection.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
Enrichment of decidual CD11c + CD8 + T cells with altered immune function in early pregnancy loss.
In Nat Commun on 21 July 2025 by Guo, L., Guo, A., et al.
PubMed
Early pregnancy loss (EPL) is closely associated with imbalances in the maternal-foetal immune microenvironment. Here we identify CD11c + CD8 + T cells, an unconventional cytotoxic T cell subset, as significantly enriched and activated in EPL cases. These cells contribute to immune dysregulation and inhibit trophoblast invasion through secreting granzyme B, perforin, CD107a, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. Furthermore, we present an effective early prediction model for EPL, based on cytokine and cytotoxic molecule profiles of CD11c + CD8 + T cells in maternal serum, collected 12-16 days post-embryo transfer. Functional assays reveal that IFN-γ triggers trophoblast pyroptosis via the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway, impairing trophoblast invasion. In vivo validation using abortion-prone mice and an anti-4-1BB antibody-induced model of CD11c + CD8 + T cell activation confirms increased embryo resorption and reduced trophoblast infiltration. These findings highlight the role of dysregulated CD11c + CD8 + T cells at the maternal-foetal interface in EPL, and suggest their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for EPL-management.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Systemic 4-1BB stimulation augments extrafollicular memory B cell formation and recall responses during Plasmodium infection.
In Cell Rep on 22 April 2025 by Calôba, C., Sturtz, A. J., et al.
PubMed
T-dependent germinal center (GC) output, comprising plasma cells and memory B cells (MBCs), is crucial for clearance of Plasmodium infection and protection against reinfection. In this study, we examine the effect of an agonistic antibody targeting 4-1BB (CD137) during experimental malaria. We show that exogenous 4-1BB stimulation, despite delaying the effector GC response, surprisingly enhances humoral memory recall and protection from reinfection. Single-cell RNA and assay for transposase-accessible chromatin (ATAC) sequencing of MBCs from mice receiving 4-1BB stimulation reveal populations with distinct transcriptional signatures and a chromatin landscape indicative of superior recall and proliferative potential. Importantly, our results indicate that the effects of 4-1BB stimulation are dependent on interleukin (IL)-9R signaling in B cells but independent of parasite load during primary infection. Our study proposes an immunomodulatory approach to enhance the quality of the MBC pool, providing superior protection during infection and vaccination, particularly in the context of malaria.
-
-
Single-cell and chromatin accessibility profiling reveals regulatory programs of pathogenic Th2 cells in allergic asthma.
In Nat Commun on 15 March 2025 by Khan, M., Alteneder, M., et al.
PubMed
Lung pathogenic T helper type 2 (pTh2) cells are important in mediating allergic asthma, but fundamental questions remain regarding their heterogeneity and epigenetic regulation. Here we investigate immune regulation in allergic asthma by single-cell RNA sequencing in mice challenged with house dust mite, in the presence and absence of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) function. Our analyses indicate two distinct highly proinflammatory subsets of lung pTh2 cells and pinpoint thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and Tumour Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily (TNFRSF) members as important drivers to generate pTh2 cells in vitro. Using our in vitro model, we uncover how signalling via TSLP and a TNFRSF member shapes chromatin accessibility at the type 2 cytokine gene loci by modulating HDAC1 repressive function. In summary, we have generated insights into pTh2 cell biology and establish an in vitro model for investigating pTh2 cells that proves useful for discovering molecular mechanisms involved in pTh2-mediated allergic asthma.
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Neoadjuvant anti-4-1BB confers protection against spontaneous metastasis through low-affinity intratumor CD8+T cells in triple-negative breast cancer
In bioRxiv on 2 February 2025 by Lim, B. J. W., Liu, M., et al.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Effective cancer immunotherapy combining mRNA-encoded bispecific antibodies that induce polyclonal T cell engagement and PD-L1-dependent 4-1BB costimulation.
In Front Immunol on 21 January 2025 by Hangiu, O., Navarro, R., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized cancer therapy, but many patients fail to respond or develop resistance, often due to reduced T cell activity. Costimulation via 4-1BB has emerged as a promising approach to enhance the effector function of antigen-primed T cells. Bispecific T cell-engaging (TCE) antibodies are an effective way to provide tumor-specific T cell receptor-mediated signaling to tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. mRNA-based delivery of bispecific antibodies, offer a novel approach to enhance tumor-specific immune responses while minimizing adverse effects.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Developing an Effective Therapeutic HPV Vaccine to Eradicate Large Tumors by Genetically Fusing Xcl1 and Incorporating IL-9 as Molecular Adjuvants.
In Vaccines (Basel) on 9 January 2025 by Sun, Z., Wu, Z., et al.
PubMed
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a prevalent infection affecting both men and women, leading to various cytological lesions. Therapeutic vaccines mount a HPV-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte response, thus clearing HPV-infected cells. However, no therapeutic vaccines targeting HPV are currently approved for clinical treatment due to limited efficacy. Our goal is to develop a vaccine that can effectively eliminate tumors caused by HPV.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Photothermal therapy co-localized with CD137 agonism improves survival in an SM1 melanoma model without hepatotoxicity.
In Nanomedicine (Lond) on 3 September 2024 by Medina, J. A., Ledezma, D. K., et al.
PubMed
Aim: We investigate combining Prussian Blue nanoparticles (PBNPs), as photothermal therapy (PTT) agents, with agonistic CD137 antibodies (αCD137) on a single nanoparticle platform to deliver non-toxic, anti-tumor efficacy in SM1 murine melanoma.Methods: We electrostatically coated PBNPs with αCD137 (αCD137-PBNPs) and quantified their physicochemical characteristics, photothermal and co-stimulatory capabilities. Next, we tested the efficacy and hepatotoxicity of PTT using αCD137-PBNPs (αCD137-PBNP-PTT) in SM1 tumor-bearing mice.Results: The αCD137-PBNPs retained both the photothermal and agonistic properties of the PBNPs and αCD137, respectively. In vivo, SM1 tumor-bearing mice treated with αCD137-PBNP-PTT exhibited a significantly higher survival rate (50%) without hepatotoxicity, compared with control treatments.Conclusion: These data suggest the potential utility of co-localizing PBNP-PTT with αCD137-based agonism as a novel combination nanomedicine.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Human/mouse CD137 agonist, JNU-0921, effectively shrinks tumors through enhancing the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells in cis and in trans.
In Sci Adv on 23 August 2024 by Liu, L., Chen, F., et al.
PubMed
Agonistic antibodies against CD137 have been demonstrated to completely regress established tumors through activating T cell immunity. Unfortunately, current CD137 antibodies failed to benefit patients with cancer. Moreover, their antitumor mechanisms in vivo remain to be determined. Here, we report the development of a small molecular CD137 agonist, JNU-0921. JNU-0921 effectively activates both human and mouse CD137 through direct binding their extracellular domains to induce oligomerization and signaling and effectively shrinks tumors in vivo. Mechanistically, JNU-0921 enhances effector and memory function of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (CTLs) and alleviates their exhaustion. JNU-0921 also skews polarization of helper T cells toward T helper 1 type and enhances their activity to boost CTL function. Meanwhile, JNU-0921 attenuates the inhibitory function of regulatory T cells on CTLs. Our current work shows that JNU-0921 shrinks tumors by enhancing the cytotoxicity of CTLs in cis and in trans and sheds light on strategy for developing CD137 small molecular agonists.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Therapeutic potential of co-signaling receptor modulation in hepatitis B.
In Cell on 25 July 2024 by Andreata, F., Laura, C., et al.
PubMed
Reversing CD8+ T cell dysfunction is crucial in treating chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, yet specific molecular targets remain unclear. Our study analyzed co-signaling receptors during hepatocellular priming and traced the trajectory and fate of dysfunctional HBV-specific CD8+ T cells. Early on, these cells upregulate PD-1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, OX40, 4-1BB, and ICOS. While blocking co-inhibitory receptors had minimal effect, activating 4-1BB and OX40 converted them into antiviral effectors. Prolonged stimulation led to a self-renewing, long-lived, heterogeneous population with a unique transcriptional profile. This includes dysfunctional progenitor/stem-like (TSL) cells and two distinct dysfunctional tissue-resident memory (TRM) populations. While 4-1BB expression is ubiquitously maintained, OX40 expression is limited to TSL. In chronic settings, only 4-1BB stimulation conferred antiviral activity. In HBeAg+ chronic patients, 4-1BB activation showed the highest potential to rejuvenate dysfunctional CD8+ T cells. Targeting all dysfunctional T cells, rather than only stem-like precursors, holds promise for treating chronic HBV infection.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
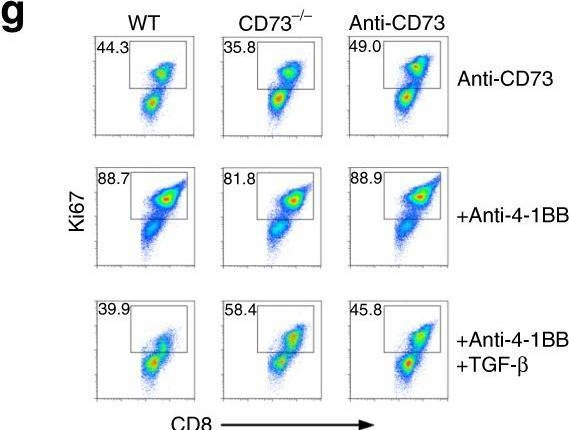
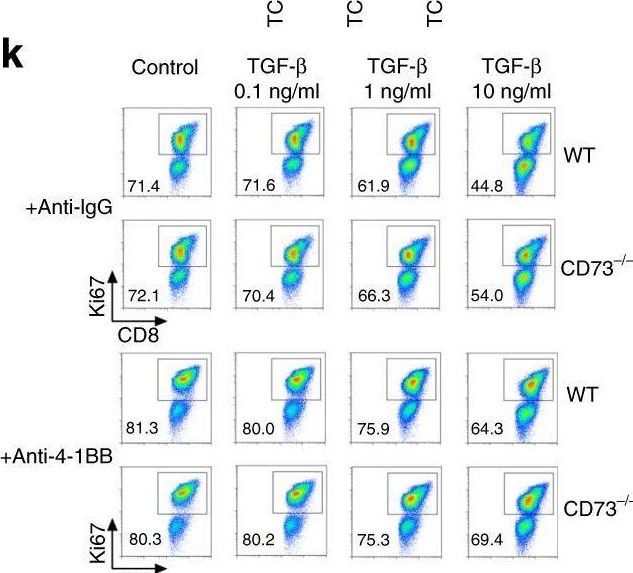
Short-term cultured tumor fragments to study immunotherapy combinations based on CD137 (4-1BB) agonism.
In Oncoimmunology on 11 July 2024 by Eguren-Santamaria, I., Rodriguez, I., et al.
PubMed
Biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy are an unmet medical need. The group of Daniela Thommen at the NKI recently reported on novel methodologies based on short-term cultures of patient-derived tumor fragments whose cytokine concentrations in the supernatants and activation markers on infiltrating T cells were associated with clinical response to PD-1 blockade. We set up a similar culture technology with tumor-derived fragments using mouse tumors transplanted into syngeneic immunocompetent mice to test an agonist anti-CD137 mAb and its combinations with anti-PD-1 and/or anti-TGF-β. Increases in IFNγ concentrations in the tissue culture supernatants were detected upon in-culture activation with the anti-CD137 and anti-PD-1 mAb combinations or concanavalin A as a positive control. No other cytokine from a wide array was informative of stimulation with these mAbs. Interestingly, increases in Ki67 and other activation markers were substantiated in lymphocytes from cell suspensions gathered at the end of 72 h cultures. In mice bearing bilateral tumors in which one was excised prior to in vivo anti-CD137 + anti-PD-1 treatment to perform the fragment culture evaluation, no association was found between IFNγ production from the fragments and the in vivo therapeutic outcome in the non-resected contralateral tumors. The experimental system permitted freezing and thawing of the fragments with similar functional outcomes. Using a series of patient-derived tumor fragments from excised solid malignancies, we showed IFNγ production in a fraction of the studied cases, that was conserved in frozen/thawed fragments. The small tumor fragment culture technique seems suitable to preclinically explore immunotherapy combinations.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Genetics
Glucose-driven histone lactylation promotes the immunosuppressive activity of monocyte-derived macrophages in glioblastoma.
In Immunity on 14 May 2024 by De Leo, A., Ugolini, A., et al.
PubMed
Immunosuppressive macrophages restrict anti-cancer immunity in glioblastoma (GBM). Here, we studied the contribution of microglia (MGs) and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) to immunosuppression and mechanisms underlying their regulatory function. MDMs outnumbered MGs at late tumor stages and suppressed T cell activity. Molecular and functional analysis identified a population of glycolytic MDM expressing GLUT1 with potent immunosuppressive activity. GBM-derived factors promoted high glycolysis, lactate, and interleukin-10 (IL-10) production in MDMs. Inhibition of glycolysis or lactate production in MDMs impaired IL-10 expression and T cell suppression. Mechanistically, intracellular lactate-driven histone lactylation promoted IL-10 expression, which was required to suppress T cell activity. GLUT1 expression on MDMs was induced downstream of tumor-derived factors that activated the PERK-ATF4 axis. PERK deletion in MDM abrogated histone lactylation, led to the accumulation of intratumoral T cells and tumor growth delay, and, in combination with immunotherapy, blocked GBM progression. Thus, PERK-driven glucose metabolism promotes MDM immunosuppressive activity via histone lactylation.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
Preclinical characterization and phase 1 results of ADG106 in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
In Cell Rep Med on 20 February 2024 by Ma, Y., Luo, F., et al.
PubMed
ADG106, a ligand-blocking agonistic antibody targeting CD137 (4-1BB), exhibits promising results in preclinical studies, demonstrating tumor suppression in various animal models and showing a balanced profile between safety and efficacy. This phase 1 study enrolls 62 patients with advanced malignancies, revealing favorable tolerability up to the 5.0 mg/kg dose level. Dose-limiting toxicity occurs in only one patient (6.3%) at 10.0 mg/kg, resulting in grade 4 neutropenia. The most frequent treatment-related adverse events include leukopenia (22.6%), neutropenia (22.6%), elevated alanine aminotransferase (22.6%), rash (21.0%), itching (17.7%), and elevated aspartate aminotransferase (17.7%). The overall disease control rates are 47.1% for advanced solid tumors and 54.5% for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Circulating biomarkers suggest target engagement by ADG106 and immune modulation of circulating T, B, and natural killer cells and cytokines interferon γ and interleukin-6, which may affect the probability of clinical efficacy. ADG106 has a manageable safety profile and preliminary anti-tumor efficacy in patients with advanced cancers (this study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03802955).
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Human Metapneumovirus Reinfection in Aged Mice Recapitulates Increased Disease Severity in Elderly Humans Infected with Human Metapneumovirus.
In Immunohorizons on 1 June 2023 by Parks, O. B., Eddens, T., et al.
PubMed
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a leading cause of respiratory infection in adults >65 y. Nearly all children worldwide are seropositive for HMPV by age 5 y, but reinfections occur throughout life, and there is no licensed vaccine. Recurrent HMPV infection is mild and self-resolving in immunocompetent individuals. However, elderly individuals develop severe respiratory disease on HMPV reinfection that leads to a high risk for morbidity and mortality. In this study, we developed a mouse model to mirror HMPV reinfection in elderly humans. C57BL/6J mice were infected with HMPV at 6-7 wk old, aged in-house, and rechallenged with high-dose virus at 70 wk. Aged rechallenged mice had profound weight loss similar to primary infected mice, increased lung histopathology, and accumulated cytotoxic CD8+CD44+CD62L-CD69+CD103+ memory cells despite having undetectable lung virus titer. When aged mice 14 mo postinfection (p.i.) or young mice 5 wk p.i. were restimulated with HMPV cognate Ag to mimic epitope vaccination, aged mice had an impaired CD8+ memory response. Convalescent serum transfer from young naive or 5 wk p.i. mice into aged mice on day of infection did not protect. Aged mice vaccinated with UV-inactivated HMPV also exhibited diminished protection and poor CD8+ memory response compared with young mice. These results suggest aged individuals with HMPV reinfection have a dysregulated CD8+ memory T cell response that fails to protect and exacerbates disease. Moreover, aged mice exhibited a poor memory response to either epitope peptide or UV-inactivated vaccination, suggesting that aged CD8+ T cell dysfunction presents a barrier to effective vaccination strategies.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Dendritic cell therapy augments antitumor immunity triggered by CDK4/6 inhibition and immune checkpoint blockade by unleashing systemic CD4 T-cell responses.
In J Immunother Cancer on 1 May 2023 by Kumar, A., Ramani, V., et al.
PubMed
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) combined with endocrine therapy are a mainstay treatment for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. While their principal mechanism is inhibition of cancer cell proliferation, preclinical and clinical evidence suggests that CDK4/6i can also promote antitumor T-cell responses. However, this pro-immunogenic property is yet to be successfully harnessed in the clinic, as combining CDK4/6i with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) has not shown a definitive benefit in patients.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
Synergistic effects of combined immunotherapy strategies in a model of multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Rep Med on 18 April 2023 by Ochoa, M. C., Sánchez-Gregorio, S., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint-inhibitor combinations are the best therapeutic option for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, but improvements in efficacy are needed to improve response rates. We develop a multifocal HCC model to test immunotherapies by introducing c-myc using hydrodynamic gene transfer along with CRISPR-Cas9-mediated disruption of p53 in mouse hepatocytes. Additionally, induced co-expression of luciferase, EGFP, and the melanosomal antigen gp100 facilitates studies on the underlying immunological mechanisms. We show that treatment of the mice with a combination of anti-CTLA-4 + anti-PD1 mAbs results in partial clearance of the tumor with an improvement in survival. However, the addition of either recombinant IL-2 or an anti-CD137 mAb markedly improves both outcomes in these mice. Combining tumor-specific adoptive T cell therapy to the aCTLA-4/aPD1/rIL2 or aCTLA-4/aPD1/aCD137 regimens enhances efficacy in a synergistic manner. As shown by multiplex tissue immunofluorescence and intravital microscopy, combined immunotherapy treatments enhance T cell infiltration and the intratumoral performance of T lymphocytes.
-
-
-
Immunocytochemistry-immunofluorescence
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Synergistic effects of combined immunotherapy strategies in a model of multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Rep Med on 18 April 2023 by Ochoa, M. C., Sánchez-Gregorio, S., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint-inhibitor combinations are the best therapeutic option for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, but improvements in efficacy are needed to improve response rates. We develop a multifocal HCC model to test immunotherapies by introducing c-myc using hydrodynamic gene transfer along with CRISPR-Cas9-mediated disruption of p53 in mouse hepatocytes. Additionally, induced co-expression of luciferase, EGFP, and the melanosomal antigen gp100 facilitates studies on the underlying immunological mechanisms. We show that treatment of the mice with a combination of anti-CTLA-4 + anti-PD1 mAbs results in partial clearance of the tumor with an improvement in survival. However, the addition of either recombinant IL-2 or an anti-CD137 mAb markedly improves both outcomes in these mice. Combining tumor-specific adoptive T cell therapy to the aCTLA-4/aPD1/rIL2 or aCTLA-4/aPD1/aCD137 regimens enhances efficacy in a synergistic manner. As shown by multiplex tissue immunofluorescence and intravital microscopy, combined immunotherapy treatments enhance T cell infiltration and the intratumoral performance of T lymphocytes.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Synergistic effects of combined immunotherapy strategies in a model of multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma.
In Cell Rep Med on 18 April 2023 by Ochoa, M. C., Sánchez-Gregorio, S., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint-inhibitor combinations are the best therapeutic option for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, but improvements in efficacy are needed to improve response rates. We develop a multifocal HCC model to test immunotherapies by introducing c-myc using hydrodynamic gene transfer along with CRISPR-Cas9-mediated disruption of p53 in mouse hepatocytes. Additionally, induced co-expression of luciferase, EGFP, and the melanosomal antigen gp100 facilitates studies on the underlying immunological mechanisms. We show that treatment of the mice with a combination of anti-CTLA-4 + anti-PD1 mAbs results in partial clearance of the tumor with an improvement in survival. However, the addition of either recombinant IL-2 or an anti-CD137 mAb markedly improves both outcomes in these mice. Combining tumor-specific adoptive T cell therapy to the aCTLA-4/aPD1/rIL2 or aCTLA-4/aPD1/aCD137 regimens enhances efficacy in a synergistic manner. As shown by multiplex tissue immunofluorescence and intravital microscopy, combined immunotherapy treatments enhance T cell infiltration and the intratumoral performance of T lymphocytes.
-
-
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
mRNAs encoding IL-12 and a decoy-resistant variant of IL-18 synergize to engineer T cells for efficacious intratumoral adoptive immunotherapy.
In Cell Rep Med on 17 March 2023 by Olivera, I., Bolaños, E., et al.
PubMed
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) gene transfer enhances the therapeutic potency of adoptive T cell therapies. We previously reported that transient engineering of tumor-specific CD8 T cells with IL-12 mRNA enhanced their systemic therapeutic efficacy when delivered intratumorally. Here, we mix T cells engineered with mRNAs to express either single-chain IL-12 (scIL-12) or an IL-18 decoy-resistant variant (DRIL18) that is not functionally hampered by IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP). These mRNA-engineered T cell mixtures are repeatedly injected into mouse tumors. Pmel-1 T cell receptor (TCR)-transgenic T cells electroporated with scIL-12 or DRIL18 mRNAs exert powerful therapeutic effects in local and distant melanoma lesions. These effects are associated with T cell metabolic fitness, enhanced miR-155 control on immunosuppressive target genes, enhanced expression of various cytokines, and changes in the glycosylation profile of surface proteins, enabling adhesiveness to E-selectin. Efficacy of this intratumoral immunotherapeutic strategy is recapitulated in cultures of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells on IL-12 and DRIL18 mRNA electroporation.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
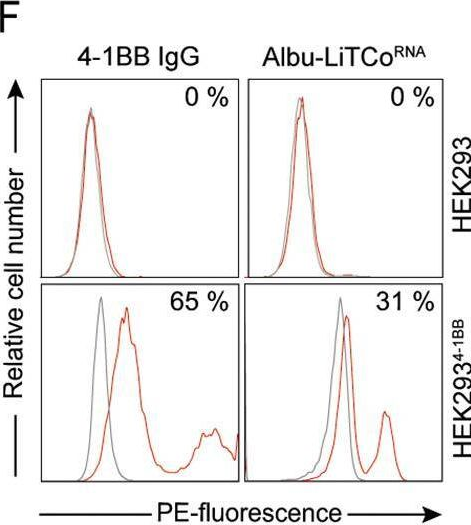
Tumor targeted 4-1BB agonist antibody-albumin fusions with high affinity to FcRn induce anti-tumor immunity without toxicity.
In iScience on 16 September 2022 by Hangiu, O., Compte, M., et al.
PubMed
Costimulation of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes by anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) has shown anti-tumor activity in human trials, but can be associated with significant off-tumor toxicities involving FcγR interactions. Here, we introduce albumin-fused mouse and human bispecific antibodies with clinically favorable pharmacokinetics designed to confine 4-1BB costimulation to the tumor microenvironment. These Fc-free 4-1BB agonists consist of an EGFR-specific VHH antibody, a 4-1BB-specific scFv, and a human albumin sequence engineered for high FcRn binding connected in tandem (LiTCo-Albu). We demonstrate in vitro cognate target engagement, EGFR-specific costimulatory activity, and FcRn-driven cellular recycling similar to non-fused FcRn high-binding albumin. The mouse LiTCo-Albu exhibited a prolonged circulatory half-life and in vivo tumor inhibition, with no indication of 4-1BB mAb-associated toxicity. Furthermore, we show a greater therapeutic effect when used in combination with PD-1-blocking mAbs. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of tumor-specific LiTCo-Albu antibodies for safe and effective costimulatory strategies in cancer immunotherapy.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Optimal CD8+ T cell effector function requires costimulation-induced RNA-binding proteins that reprogram the transcript isoform landscape.
In Nat Commun on 20 June 2022 by Karginov, T. A., Menoret, A., et al.
PubMed
Boosting T cell activation through costimulation directs defense against cancer and viral infections. Despite multiple studies targeting costimulation in clinical trials, the increased potency and reprogramming of T cells endowed by costimulation is poorly understood. Canonical dogma states that transcription mediates T cell activation. Here, we show that the spliceosome, controlling post-transcriptional alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation, is the most enriched pathway in T cells after CD134/CD137 costimulation. Costimulation of CD8+ T cells significantly increases expression of 29 RNA-binding proteins while RNA-seq uncovers over 1000 differential alternative splicing and polyadenylation events. Using in vivo mouse and in vitro human models, we demonstrate that RNA-binding protein Tardbp is required for effector cytokine production, CD8+ T cell clonal expansion, and isoform regulation after costimulation. The prospect of immune response optimization through reprogramming of mRNA isoform production offered herein opens new avenues for experimentally and therapeutically tuning the activities of T cells.
-