InVivoPlus anti-mouse/human/rat/monkey/hamster/canine/bovine TGF-β
Product Details
The 1D11.16.8 monoclonal antibody reacts with mouse, human, rat, monkey, hamster, canine and bovine TGF-β (transforming growth factor beta) isoforms 1, 2 and 3. TGF-β is a multifunctional cytokine that regulates the proliferation of epithelial cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, neurons, lymphoid cells including T lymphocytes and NK cells, and other hematopoietic cell types. TGF-β also regulates the activities of activated macrophages and the development of regulatory T cells. Additionally, TGF-β plays roles in immune function, tissue remodeling and wound repair. TGF-β exists as five highly similar isoforms (TGF-β 1-5) with homologies of 70-80%. TGF-β1 is synthesized by the enzymatic cleavage of a long precursor TGF-β1 polypeptide encoded by the TGFB1 gene which yields the mature protein and the Latency Associated Peptide (LAP). The LAP and mature TGF-β1 non-covalently associate during secretion. TGF-β is ubiquitously expressed by many cell types including macrophages and platelets which express high levels of TGF-β. TGF-β signaling has been shown to plays roles in cancer, autoimmune diseases, asthma, heart disease, and diabetes. Its importance is illustrated by TGF-β knockout mice which show defects in hematopoiesis and endothelial differentiation, and die of overwhelming inflammation. The 1D11.16.8 monoclonal antibody is a neutralizing antibody.Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoPlus mouse IgG1 isotype control, unknown specificity |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
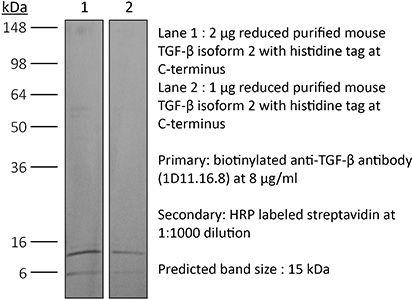
| Immunogen | Bovine TGFβ isoform 2 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo TGFβ neutralization in vitro TGFβ neutralization Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Aggregation* |
<5% Determined by SEC |
| Purity |
>95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107757 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests* |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
Additional Formats
Recommended Products
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Komai, T., et al. (2018). "Transforming Growth Factor-beta and Interleukin-10 Synergistically Regulate Humoral Immunity via Modulating Metabolic Signals" Front Immunol 9: 1364. PubMed
Inhibitory cytokines, such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and interleukin-10 (IL-10), are humoral factors involved in the suppressive function of regulatory T cells and play critical roles in maintaining immune homeostasis. However, TGF-beta and IL-10 also have pleiotropic effects and induce humoral immune responses depending on conditions, and thus their therapeutic application to autoimmune diseases remains limited. Here, we show that a combination of TGF-beta and IL-10, but not single cytokine, is required to suppress B cell activation induced by toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation. In in vivo analyses, the simultaneous presence of TGF-beta and IL-10 effectively suppressed TLR-mediated antigen-specific immune responses and ameliorated pathologies in imiquimod (TLR7 agonist)-induced lupus model and lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. Intriguingly, TGF-beta and IL-10 synergistically modulated transcriptional programs and suppressed cellular energetics of both glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation via inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)/S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) pathway in TLR-stimulated B cells. On the other hand, enhancement of mTOR signaling and mitochondrial biosynthesis in TLR-stimulated B cells counteracted the synergistic inhibitory effects. The inhibitory cytokine synergy of TGF-beta and IL-10 via suppression of energy metabolism was also observed in human TLR-stimulated B cells. There is increasing evidence supporting the importance of adequate metabolic signals in various immune cells to exert their immune function. In this study, we have shown that a previously unrecognized synergy of inhibitory cytokines regulates systemic humoral immune responses via modulating immunometabolism in B cells. Our findings indicate that inhibition of B cell metabolism mediated by two synergistic cytokines contributes to the induction of immune tolerance and could be a new therapeutic strategy for autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Clemente-Casares, X., et al. (2016). "Expanding antigen-specific regulatory networks to treat autoimmunity" Nature 530(7591): 434-440. PubMed
Regulatory T cells hold promise as targets for therapeutic intervention in autoimmunity, but approaches capable of expanding antigen-specific regulatory T cells in vivo are currently not available. Here we show that systemic delivery of nanoparticles coated with autoimmune-disease-relevant peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex class II (pMHCII) molecules triggers the generation and expansion of antigen-specific regulatory CD4(+) T cell type 1 (TR1)-like cells in different mouse models, including mice humanized with lymphocytes from patients, leading to resolution of established autoimmune phenomena. Ten pMHCII-based nanomedicines show similar biological effects, regardless of genetic background, prevalence of the cognate T-cell population or MHC restriction. These nanomedicines promote the differentiation of disease-primed autoreactive T cells into TR1-like cells, which in turn suppress autoantigen-loaded antigen-presenting cells and drive the differentiation of cognate B cells into disease-suppressing regulatory B cells, without compromising systemic immunity. pMHCII-based nanomedicines thus represent a new class of drugs, potentially useful for treating a broad spectrum of autoimmune conditions in a disease-specific manner.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Manlove, L. S., et al. (2015). "Adaptive Immunity to Leukemia Is Inhibited by Cross-Reactive Induced Regulatory T Cells" J Immunol . PubMed
BCR-ABL+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients have transient responses to current therapies. However, the fusion of BCR to ABL generates a potential leukemia-specific Ag that could be a target for immunotherapy. We demonstrate that the immune system can limit BCR-ABL+ leukemia progression although ultimately this immune response fails. To address how BCR-ABL+ leukemia escapes immune surveillance, we developed a peptide: MHC class II tetramer that labels endogenous BCR-ABL-specific CD4+ T cells. Naive mice harbored a small population of BCR-ABL-specific T cells that proliferated modestly upon immunization. The small number of naive BCR-ABL-specific T cells was due to negative selection in the thymus, which depleted BCR-ABL-specific T cells. Consistent with this observation, we saw that BCR-ABL-specific T cells were cross-reactive with an endogenous peptide derived from ABL. Despite this cross-reactivity, the remaining population of BCR-ABL reactive T cells proliferated upon immunization with the BCR-ABL fusion peptide and adjuvant. In response to BCR-ABL+ leukemia, BCR-ABL-specific T cells proliferated and converted into regulatory T (Treg) cells, a process that was dependent on cross-reactivity with self-antigen, TGF-beta1, and MHC class II Ag presentation by leukemic cells. Treg cells were critical for leukemia progression in C57BL/6 mice, as transient Treg cell ablation led to extended survival of leukemic mice. Thus, BCR-ABL+ leukemia actively suppresses antileukemia immune responses by converting cross-reactive leukemia-specific T cells into Treg cells.
in vitro TGFβ neutralization
Bodogai, M., et al. (2015). "Immunosuppressive and Prometastatic Functions of Myeloid-Derived Suppressive Cells Rely upon Education from Tumor-Associated B Cells" Cancer Res 75(17): 3456-3465. PubMed
Myeloid-derived suppressive cells (MDSC) have been reported to promote metastasis, but the loss of cancer-induced B cells/B regulatory cells (tBreg) can block metastasis despite MDSC expansion in cancer. Here, using multiple murine tumor models and human MDSC, we show that MDSC populations that expand in cancer have only partially primed regulatory function and limited prometastatic activity unless they are fully educated by tBregs. Cancer-induced tBregs directly activate the regulatory function of both the monocyte and granulocyte subpopulations of MDSC, relying, in part, on TgfbetaR1/TgfbetaR2 signaling. MDSC fully educated in this manner exhibit an increased production of reactive oxygen species and NO and more efficiently suppress CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells, thereby promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Thus, loss of tBregs or TgfbetaR deficiency in MDSC is sufficient to disable their suppressive function and to block metastasis. Overall, our data indicate that cancer-induced B cells/B regulatory cells are important regulators of the immunosuppressive and prometastatic functions of MDSC.
in vitro TGFβ neutralization
Choi, Y. S., et al. (2015). "LEF-1 and TCF-1 orchestrate TFH differentiation by regulating differentiation circuits upstream of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6" Nat Immunol 16(9): 980-990. PubMed
Follicular helper T cells (TFH cells) are specialized effector CD4(+) T cells that help B cells develop germinal centers (GCs) and memory. However, the transcription factors that regulate the differentiation of TFH cells remain incompletely understood. Here we report that selective loss of Lef1 or Tcf7 (which encode the transcription factor LEF-1 or TCF-1, respectively) resulted in TFH cell defects, while deletion of both Lef1 and Tcf7 severely impaired the differentiation of TFH cells and the formation of GCs. Forced expression of LEF-1 enhanced TFH differentiation. LEF-1 and TCF-1 coordinated such differentiation by two general mechanisms. First, they established the responsiveness of naive CD4(+) T cells to TFH cell signals. Second, they promoted early TFH differentiation via the multipronged approach of sustaining expression of the cytokine receptors IL-6Ralpha and gp130, enhancing expression of the costimulatory receptor ICOS and promoting expression of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Greco, S. H., et al. (2015). "TGF-beta Blockade Reduces Mortality and Metabolic Changes in a Validated Murine Model of Pancreatic Cancer Cachexia" PLoS One 10(7): e0132786. PubMed
Cancer cachexia is a debilitating condition characterized by a combination of anorexia, muscle wasting, weight loss, and malnutrition. This condition affects an overwhelming majority of patients with pancreatic cancer and is a primary cause of cancer-related death. However, few, if any, effective therapies exist for both treatment and prevention of this syndrome. In order to develop novel therapeutic strategies for pancreatic cancer cachexia, appropriate animal models are necessary. In this study, we developed and validated a syngeneic, metastatic, murine model of pancreatic cancer cachexia. Using our model, we investigated the ability of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) blockade to mitigate the metabolic changes associated with cachexia. We found that TGF-beta inhibition using the anti-TGF-beta antibody 1D11.16.8 significantly improved overall mortality, weight loss, fat mass, lean body mass, bone mineral density, and skeletal muscle proteolysis in mice harboring advanced pancreatic cancer. Other immunotherapeutic strategies we employed were not effective. Collectively, we validated a simplified but useful model of pancreatic cancer cachexia to investigate immunologic treatment strategies. In addition, we showed that TGF-beta inhibition can decrease the metabolic changes associated with cancer cachexia and improve overall survival.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Leon, B., et al. (2014). "FoxP3+ regulatory T cells promote influenza-specific Tfh responses by controlling IL-2 availability" Nat Commun 5: 3495. PubMed
Here, we test the role of FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) in controlling T follicular helper (Tfh) and germinal centre (GC) B-cell responses to influenza. In contrast to the idea that Tregs suppress T-cell responses, we find that Treg depletion severely reduces the Tfh cell response to influenza virus. Furthermore, Treg depletion prevents the accumulation of influenza-specific GCs. These effects are not due to alterations in TGFbeta availability or a precursor-progeny relationship between Tregs and Tfh cells, but are instead mediated by increased availability of IL-2, which suppresses the differentiation of Tfh cells and as a consequence, compromises the GC B response. Thus, Tregs promote influenza-specific GC responses by preventing excessive IL-2 signalling, which suppresses Tfh cell differentiation.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Li, W., et al. (2014). "Tgfbr2 disruption in postnatal smooth muscle impairs aortic wall homeostasis" J Clin Invest 124(2): 755-767. PubMed
TGF-beta is essential for vascular development; however, excess TGF-beta signaling promotes thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in multiple disorders, including Marfan syndrome. Since the pathology of TGF-beta overactivity manifests primarily within the arterial media, it is widely assumed that suppression of TGF-beta signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells will ameliorate aortic disease. We tested this hypothesis by conditional inactivation of Tgfbr2, which encodes the TGF-beta type II receptor, in smooth muscle cells of postweanling mice. Surprisingly, the thoracic aorta rapidly thickened, dilated, and dissected in these animals. Tgfbr2 disruption predictably decreased canonical Smad signaling, but unexpectedly increased MAPK signaling. Type II receptor-independent effects of TGF-beta and pathological responses by nonrecombined smooth muscle cells were excluded by serologic neutralization. Aortic disease was caused by a perturbed contractile apparatus in medial cells and growth factor production by adventitial cells, both of which resulted in maladaptive paracrine interactions between the vessel wall compartments. Treatment with rapamycin restored a quiescent smooth muscle phenotype and prevented dissection. Tgfbr2 disruption in smooth muscle cells also accelerated aneurysm growth in a murine model of Marfan syndrome. Our data indicate that basal TGF-beta signaling in smooth muscle promotes postnatal aortic wall homeostasis and impedes disease progression.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization, in vitro TGFβ neutralization
Worthington, J. J., et al. (2013). "Loss of the TGFbeta-activating integrin alphavbeta8 on dendritic cells protects mice from chronic intestinal parasitic infection via control of type 2 immunity" PLoS Pathog 9(10): e1003675. PubMed
Chronic intestinal parasite infection is a major global health problem, but mechanisms that promote chronicity are poorly understood. Here we describe a novel cellular and molecular pathway involved in the development of chronic intestinal parasite infection. We show that, early during development of chronic infection with the murine intestinal parasite Trichuris muris, TGFbeta signalling in CD4+ T-cells is induced and that antibody-mediated inhibition of TGFbeta function results in protection from infection. Mechanistically, we find that enhanced TGFbeta signalling in CD4+ T-cells during infection involves expression of the TGFbeta-activating integrin alphavbeta8 by dendritic cells (DCs), which we have previously shown is highly expressed by a subset of DCs in the intestine. Importantly, mice lacking integrin alphavbeta8 on DCs were completely resistant to chronic infection with T. muris, indicating an important functional role for integrin alphavbeta8-mediated TGFbeta activation in promoting chronic infection. Protection from infection was dependent on CD4+ T-cells, but appeared independent of Foxp3+ Tregs. Instead, mice lacking integrin alphavbeta8 expression on DCs displayed an early increase in production of the protective type 2 cytokine IL-13 by CD4+ T-cells, and inhibition of this increase by crossing mice to IL-4 knockout mice restored parasite infection. Our results therefore provide novel insights into how type 2 immunity is controlled in the intestine, and may help contribute to development of new therapies aimed at promoting expulsion of gut helminths.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Ring, S., et al. (2013). "Targeting of autoantigens to DEC205(+) dendritic cells in vivo suppresses experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice" J Immunol 191(6): 2938-2947. PubMed
The dendritic and epithelial cell receptor with a m.w. of 205 kDa (DEC205) is expressed by dendritic cells (DCs) and facilitates Ag presentation. After injection of Ags coupled to Abs specific for DEC205 into mice, Ag presentation occurs by nonactivated DCs, which leads to induction of regulatory T cells (Tregs). To test this system for tolerance induction in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE), we created single-chain fragment variables (scFv) specific for DEC205 and fused the scFv to the self-Ag myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG; scFv DEC:MOG). An anti-beta-galactosidase scFv:MOG fusion protein (scFv GL117:MOG) served as isotype control. After staining of DCs in vitro with purified scFv DEC:MOG, binding to DCs and colocalization with MHC class II was apparent, whereas isotype controls did not bind. We next injected scFv DEC:MOG into mice and observed elevated numbers of highly activated, IL-10-producing CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) Tregs (17% of CD4) in spleens, as compared with isotype controls and uninjected mice (12% of CD4). Furthermore, DCs isolated from scFv DEC:MOG-injected animals produced significantly increased levels of TGF-beta. Most importantly, when EAE was induced in scFv DEC:MOG-injected mice, 90% of the mice were protected from EAE, whereas all mice in the isotype controls (scFv GL117:MOG) experienced development of EAE. When applying scFv DEC:MOG to mice that had already experienced EAE symptoms, abrogation of the disease in 90% of the animals was apparent, whereas all animals in the control groups experienced development of severe EAE. Thus, these data indicate that targeting of MOG to “steady-state” DCs in vivo may provide a tool to prevent and to treat EAE by a DC/Treg-driven mechanism.
in vitro TGFβ neutralization
Tai, N., et al. (2013). "TLR9 deficiency promotes CD73 expression in T cells and diabetes protection in nonobese diabetic mice" J Immunol 191(6): 2926-2937. PubMed
TLR9-deficient (TLR9(-)/(-)) NOD mice develop a significantly reduced incidence of diabetes. This study was to investigate the molecular mechanisms of the protective role of TLR9 deficiency. Through gene screening and confirmation by both mRNA and protein expression, we found a significant increase in CD73-expressing immune cells from peripheral lymphoid tissues in TLR9(-)/(-) NOD mice. The elevated frequency of CD73-expressing immune cells seemed to be specific for TLR9 deficiency and was MyD88 independent. Moreover, the increased frequency of CD73 expression was limited to the NOD background. Increased frequency of CD73 expression was also associated with lower levels of proinflammatory cytokines and more anti-inflammatory cytokine production in CD4(+) T cells in TLR9(-)/(-) NOD mice. Purified CD73(+)CD4(+) T cells showed stronger immunosuppressive function in vitro and delayed diabetes development in vivo. The immunosuppression appeared to be mediated by TGF-beta. In addition, elevated frequency of CD73-expressing cells was associated with improved beta cell function. Our observations were further confirmed by protection from diabetes with similar alterations in CD73 in the NY8.3 TCR NOD mouse model crossed with TLR9(-)/(-) mice and by the use of a TLR9 inhibitor in NOD mice. Our novel findings suggest an important immune-regulatory role of CD73 in regulation of diabetes development and may offer a new therapeutic strategy for specific intervention to prevent type 1 diabetes.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Kurkjian, C., et al. (2012). "Alveolar macrophages in neonatal mice are inherently unresponsive to Pneumocystis murina infection" Infect Immun 80(8): 2835-2846. PubMed
Pneumocystis pneumonia was first diagnosed in malnourished children and has more recently been found in children with upper respiratory symptoms. We previously reported that there is a significant delay in the immune response in newborn mice infected with Pneumocystis compared to adults (Garvy BA, Harmsen AG, Infect. Immun. 64:3987-3992, 1996, and Garvy BA, Qureshi M, J. Immunol. 165:6480-6486, 2000). This delay is characterized by the failure of neonatal lungs to upregulate proinflammatory cytokines and attract T cells into the alveoli. Here, we report that regardless of the age at which we infected the mice, they failed to mount an inflammatory response in the alveolar spaces until they were 21 days of age or older. Anti-inflammatory cytokines had some role in dampening inflammation, since interleukin-10 (IL-10)-deficient pups cleared Pneumocystis faster than wild-type pups and the neutralization of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) with specific antibody enhanced T cell migration into the lungs at later time points. However, the clearance kinetics were similar to those of control pups, suggesting that there is an intrinsic deficiency in the ability of innate immunity to control Pneumocystis. We found, using an adoptive transfer strategy, that the lung environment contributes to association of Pneumocystis organisms with alveolar macrophages, implying no intrinsic deficiency in the binding of Pneumocystis by neonatal macrophages. Using both in vivo and in vitro assays, we found that Pneumocystis organisms were less able to stimulate translocation of NF-kappaB to the nucleus of alveolar macrophages from neonatal mice. These data indicate that there is an early unresponsiveness of neonatal alveolar macrophages to Pneumocystis infection that is both intrinsic and related to the immunosuppressive environment found in neonatal lungs.
in vivo TGFβ neutralization
Garidou, L., et al. (2012). "Therapeutic blockade of transforming growth factor beta fails to promote clearance of a persistent viral infection" J Virol 86(13): 7060-7071. PubMed
Persistent viral infections often overburden the immune system and are a major cause of disease in humans. During many persistent infections, antiviral T cells are maintained in a state of immune exhaustion characterized by diminished effector and helper functions. In mammalian systems, an extensive immune regulatory network exists to limit unwanted, potentially fatal immunopathology by inducing T cell exhaustion. However, this regulatory network at times overprotects the host and fosters viral persistence by severely dampening adaptive immune responsiveness. Importantly, recent studies have shown that T cell exhaustion is mediated in part by host immunoregulatory pathways (e.g., programmed death 1 [PD-1], interleukin 10 [IL-10]) and that therapeutic blockade of these pathways either before or during persistent infection can promote viral clearance. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) is another immunosuppressive cytokine known to impede both self- and tumor-specific T cells, but its role in regulating antiviral immunity is not entirely understood. In this study, we inhibited TGF-beta with three potent antagonists to determine whether neutralization of this regulatory molecule is a viable approach to control a persistent viral infection. Our results revealed that these inhibitors modestly elevate the number of antiviral T cells following infection with a persistent variant of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) but have no impact on viral clearance. These data suggest that therapeutic neutralization of TGF-beta is not an efficacious means to promote clearance of a persistent viral infection.
- Cancer Research,
TGF-β Type I Receptor Signaling in Melanoma Liver Metastases Increases Metastatic Outgrowth.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 12 May 2023 by Marvin, D. L., Dijkstra, J., et al.
PubMed
Despite advances in treatment for metastatic melanoma patients, patients with liver metastasis have an unfavorable prognosis. A better understanding of the development of liver metastasis is needed. The multifunctional cytokine Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β) plays various roles in melanoma tumors and metastasis, affecting both tumor cells and cells from the surrounding tumor microenvironment. To study the role of TGF-β in melanoma liver metastasis, we created a model to activate or repress the TGF-β receptor pathway in vitro and in vivo in an inducible manner. For this, we engineered B16F10 melanoma cells to have inducible ectopic expression of a constitutively active (ca) or kinase-inactive (ki) TGF-β receptor I, also termed activin receptor-like kinase (ALK5). In vitro, stimulation with TGF-β signaling and ectopic caALK5 expression reduced B16F10 cell proliferation and migration. Contrasting results were found in vivo; sustained caALK5 expression in B16F10 cells in vivo increased the metastatic outgrowth in liver. Blocking microenvironmental TGF-β did not affect metastatic liver outgrowth of both control and caALK5 expressing B16F10 cells. Upon characterizing the tumor microenvironment of control and caALk5 expressing B16F10 tumors, we observed reduced (cytotoxic) T cell presence and infiltration, as well as an increase in bone marrow-derived macrophages in caALK5 expressing B16F10 tumors. This suggests that caALK5 expression in B16F10 cells induces changes in the tumor microenvironment. A comparison of newly synthesized secreted proteins upon caALK5 expression by B16F10 cells revealed increased secretion of matrix remodeling proteins. Our results show that TGF-β receptor activation in B16F10 melanoma cells can increase metastatic outgrowth in liver in vivo, possibly through remodeling of the tumor microenvironment leading to altered infiltration of immune cells. These results provide insights in the role of TGF-β signaling in B16F10 liver metastasis and could have implications regarding the use of TGF-β inhibitors for the treatment of melanoma patients with liver metastasis.
- Cancer Research,
- Immunology and Microbiology
Combined mitoxantrone and anti-TGFβ treatment with PD-1 blockade enhances antitumor immunity by remodelling the tumor immune landscape in neuroblastoma.
In Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR on 17 November 2022 by Lucarini, V., Melaiu, O., et al.
PubMed
Poor infiltration of functioning T cells renders tumors unresponsive to checkpoint-blocking immunotherapies. Here, we identified a combinatorial in situ immunomodulation strategy based on the administration of selected immunogenic drugs and immunotherapy to sensitize poorly T-cell-infiltrated neuroblastoma (NB) to the host antitumor immune response. 975A2 and 9464D NB cell lines derived from spontaneous tumors of TH-MYCN transgenic mice were employed to study drug combinations able of enhancing the antitumor immune response using in vivo and ex vivo approaches. Migration of immune cells towards drug-treated murine-derived organotypic tumor spheroids (MDOTS) were assessed by microfluidic devices. Activation status of immune cells co-cultured with drug-treated MDOTS was evaluated by flow cytometry analysis. The effect of drug treatment on the immune content of subcutaneous or orthotopic tumors was comprehensively analyzed by flow-cytometry, immunohistochemistry and multiplex immunofluorescence. The chemokine array assay was used to detect soluble factors released into the tumor microenvironment. Patient-derived organotypic tumor spheroids (PDOTS) were generated from human NB specimens. Migration and activation status of autologous immune cells to drug-treated PDOTS were performed. We found that treatment with low-doses of mitoxantrone (MTX) recalled immune cells and promoted CD8+ T and NK cell activation in MDOTS when combined with TGFβ and PD-1 blockade. This combined immunotherapy strategy curbed NB growth resulting in the enrichment of a variety of both lymphoid and myeloid immune cells, especially intratumoral dendritic cells (DC) and IFNγ- and granzyme B-expressing CD8+ T cells and NK cells. A concomitant production of inflammatory chemokines involved in remodelling the tumor immune landscape was also detected. Interestingly, this treatment induced immune cell recruitment against PDOTS and activation of CD8+ T cells and NK cells. Combined treatment with low-dose of MTX and anti-TGFβ treatment with PD-1 blockade improves antitumor immunity by remodelling the tumor immune landscape and overcoming the immunosuppressive microenvironment of aggressive NB. © 2022. The Author(s).
- Mus musculus (House mouse)
Latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 3 controls adipogenesis.
In Matrix Biology : Journal of the International Society for Matrix Biology on 1 September 2022 by Singh, K., Sachan, N., et al.
PubMed
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) is released from cells as part of a trimeric latent complex consisting of TGFβ, the TGFβ propeptides, and either a latent TGFβ binding protein (LTBP) or glycoprotein-A repetitions predominant (GARP) protein. LTBP1 and 3 modulate latent TGFβ function with respect to secretion, matrix localization, and activation and, therefore, are vital for the proper function of the cytokine in a number of tissues. TGFβ modulates stem cell differentiation into adipocytes (adipogenesis), but the potential role of LTBPs in this process has not been studied. We observed that 72 h post adipogenesis initiation Ltbp1, 2, and 4 expression levels decrease by 74-84%, whereas Ltbp3 expression levels remain constant during adipogenesis. We found that LTBP3 silencing in C3H/10T1/2 cells reduced adipogenesis, as measured by the percentage of cells with lipid vesicles and the expression of the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). Lentiviral mediated expression of an Ltbp3 mRNA resistant to siRNA targeting rescued the phenotype, validating siRNA specificity. Knockdown (KD) of Ltbp3 expression in 3T3-L1, M2, and primary bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) indicated a similar requirement for Ltbp3. Epididymal and inguinal white adipose tissue fat pad weights of Ltbp3-/- mice were reduced by 62% and 57%, respectively, compared to wild-type mice. Inhibition of adipogenic differentiation upon LTBP3 loss is mediated by TGFβ, as TGFβ neutralizing antibody and TGFβ receptor I kinase blockade rescue the LTBP3 KD phenotype. These results indicate that LTBP3 has a TGFβ-dependent function in adipogenesis both in vitro and possibly in vivo. SIGNIFICANCE: Understanding the control of mesenchymal stem cell fate is crucial for the potential use of these cells for regenerative medicine. Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Latent Transforming Growth Factor β Binding Protein 3 Controls Adipogenesis
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 10 July 2022 by Singh, K., Sachan, N., et al.
PubMed
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) is released from cells as part of a trimeric latent complex consisting of TGFβ, the TGFβ propeptides, and either a latent TGFβ binding protein (LTBP) or glycoprotein-A repetitions predominant (GARP) protein. LTBP1 and 3 modulate latent TGFβ function with respect to secretion, matrix localization, and activation and, therefore, are vital for the proper function of the cytokine in a number of tissues. TGFβ modulates stem cell differentiation into adipocytes (adipogenesis), but the potential role of LTBPs in this process has not been studied. We observed that 72 h post adipogenesis initiation Ltbp1 , 2 , and 4 expression levels decrease by 74-84%, whereas Ltbp3 expression levels remain constant during adipogenesis. We found that LTBP3 silencing in C3H/10T1/2 cells reduced adipogenesis, as measured by the percentage of cells with lipid vesicles and the expression of the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). Lentiviral mediated expression of an Ltbp3 mRNA resistant to siRNA targeting rescued the phenotype, validating siRNA specificity. Knockdown (KD) of Ltbp3 expression in 3T3-L1, M2, and primary bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) indicated a similar requirement for Ltbp3 . Epididymal and inguinal white adipose tissue fat pad weights of Ltbp3 -/- mice were reduced by 62% and 57%, respectively, compared to wild-type mice. Inhibition of adipogenic differentiation upon LTBP3 loss is mediated by TGFβ, as TGFβ neutralizing antibody and TGFβ receptor I kinase blockade rescue the LTBP3 KD phenotype. These results indicate that LTBP3 has a TGFβ-dependent function in adipogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. h4>Significance/h4> Understanding the control of mesenchymal stem cell fate is crucial for the potential use of these cells for regenerative medicine. h4>Highlights/h4> Latent TGFβ binding protein 3 (LTBP3) is required for adipogenesis LTBP3 mediates TGFβ levels in adipogenesis Loss of LTBP3 results in enhanced rather than decreased levels of active TGFβ
- Immunology and Microbiology
Identification of a Broadly Fibrogenic Macrophage Subset Induced by Type 3 Inflammation in Human and Murine Liver and Lung Fibrosis
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 2 July 2022 by Fabre, T., Barron, A. M. S., et al.
PubMed
Macrophages are central orchestrators of the tissue response to injury, with distinct macrophage activation states playing key roles in the progression and resolution of fibrosis. Identifying the unique fibrogenic macrophages that are found in human fibrotic tissues could lead to new and more effective treatments for fibrosis. Here we used human liver and lung single cell RNA sequencing datasets to identify a unique subset of CD9 + TREM2 + macrophages expressing SPP1, GPNMB, FABP5, and CD63 with strong pro-fibrotic activity. This population was validated across orthogonal techniques, species and tissues. These macrophages were enriched at the outside edges of scarring adjacent to activated mesenchymal cells, and in the fibrotic niche across species and organs. Neutrophils producing the type 3 cytokines GM-CSF and IL-17A, and expressing MMP9, which participates in the activation of TGF-β1, clustered with these scar-associated macrophages. Using in vitro primary human cell assays, we determined that GM-CSF, IL-17A and TGF-β1 drive the differentiation of these scar-associated macrophages, and that co-culture of monocyte-derived macrophages with hepatic stellate cells and TGF-β1 augmented type 1 collagen deposition. In vivo blockade of GM-CSF, IL-17A or TGF-β1 with small or large molecules reduced scar-associated macrophage expansion and fibrosis in multiple models of hepatic and pulmonary fibrosis. Our work demonstrates that a specific scar-associated macrophage population is linked with fibrosis across species and tissues. It further provides a strategy for unbiased discovery, triage and preclinical validation of therapeutic targets within this fibrogenic macrophage population.
- Endocrinology and Physiology
Lysyl oxidase regulation and protein aldehydes in the injured newborn lung.
In American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology on 1 February 2022 by Zhong, Y., Mahoney, R. C., et al.
PubMed
During newborn lung injury, excessive activity of lysyl oxidases (LOXs) disrupts extracellular matrix (ECM) formation. Previous studies indicate that TGFβ activation in the O2-injured mouse pup lung increases lysyl oxidase (LOX) expression. But how TGFβ regulates this, and whether the LOXs generate excess pulmonary aldehydes are unknown. First, we determined that O2-mediated lung injury increases LOX protein expression in TGFβ-stimulated pup lung interstitial fibroblasts. This regulation appeared to be direct; this is because TGFβ treatment also increased LOX protein expression in isolated pup lung fibroblasts. Then using a fibroblast cell line, we determined that TGFβ stimulates LOX expression at a transcriptional level via Smad2/3-dependent signaling. LOX is translated as a pro-protein that requires secretion and extracellular cleavage before assuming amine oxidase activity and, in some cells, reuptake with nuclear localization. We found that pro-LOX is processed in the newborn mouse pup lung. Also, O2-mediated injury was determined to increase pro-LOX secretion and nuclear LOX immunoreactivity particularly in areas populated with interstitial fibroblasts and exhibiting malformed ECM. Then, using molecular probes, we detected increased aldehyde levels in vivo in O2-injured pup lungs, which mapped to areas of increased pro-LOX secretion in lung sections. Increased activity of LOXs plays a critical role in the aldehyde generation; an inhibitor of LOXs prevented the elevation of aldehydes in the O2-injured pup lung. These results reveal new mechanisms of TGFβ and LOX in newborn lung disease and suggest that aldehyde-reactive probes might have utility in sensing the activation of LOXs in vivo during lung injury.
- Cancer Research,
- Immunology and Microbiology
Myeloid cell subsets that express latency-associated peptide promote cancer growth by modulating T cells.
In IScience on 19 November 2021 by Gabriely, G., Ma, D., et al.
PubMed
Myeloid suppressor cells promote tumor growth by a variety of mechanisms which are not fully characterized. We identified myeloid cells (MCs) expressing the latency-associated peptide (LAP) of TGF-β on their surface and LAPHi MCs that stimulate Foxp3+ Tregs while inhibiting effector T cell proliferation and function. Blocking TGF-β inhibits the tolerogenic ability of LAPHi MCs. Furthermore, adoptive transfer of LAPHi MCs promotes Treg accumulation and tumor growth in vivo. Conversely, anti-LAP antibody, which reduces LAPHi MCs, slows cancer progression. Single-cell RNA-Seq analysis on tumor-derived immune cells revealed LAPHi dominated cell subsets with distinct immunosuppressive signatures, including those with high levels of MHCII and PD-L1 genes. Analogous to mice, LAP is expressed on myeloid suppressor cells in humans, and these cells are increased in glioma patients. Thus, our results identify a previously unknown function by which LAPHi MCs promote tumor growth and offer therapeutic intervention to target these cells in cancer.© 2021 The Authors.
- Cancer Research
Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Functional Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFβ) Activity and Benefit of TGFβ Inhibition in Irradiated Intracranial Tumors.
In International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics on 1 February 2021 by Gonzàlez-Juncà, A., Reiners, O., et al.
PubMed
Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) promotes cell survival by endorsing DNA damage repair and mediates an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Thus, TGFβ activation in response to radiation therapy is potentially targetable because it opposes therapeutic control. Strategies to assess this potential in the clinic are needed. We evaluated positron emission tomography (PET) to image 89Zr -fresolimumab, a humanized TGFβ neutralizing monoclonal antibody, as a means to detect TGFβ activation in intracranial tumor models. Pathway activity of TGFβ was validated by immunodetection of phosphorylated SMAD2 and the TGFβ target, tenascin. The contribution of TGFβ to radiation response was assessed by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of mice bearing intracranial murine tumor models GL261 and SB28 glioblastoma and brain-adapted 4T1 breast cancer (4T1-BrA) treated with TGFβ neutralizing monoclonal antibody, 1D11, and/or focal radiation (10 Gy). 89Zr-fresolimumab PET imaging detected engineered, physiological, and radiation-induced TGFβ activation, which was confirmed by immunostaining of biological markers. GL261 glioblastoma tumors had a greater PET signal compared with similar-sized SB28 glioblastoma tumors, whereas the widespread PET signal of 4T1-BrA intracranial tumors was consistent with their highly dispersed histologic distribution. Survival of mice bearing intracranial tumors treated with 1D11 neutralizing antibody alone was similar to that of mice treated with control antibody, whereas 1D11 improved survival when given in combination with focal radiation. The extent of survival benefit of a combination of radiation and 1D11 was associated with the degree of TGFβ activity detected by PET. This study demonstrates that 89Zr-fresolimumab PET imaging detects radiation-induced TGFβ activation in tumors. Functional imaging indicated a range of TGFβ activity in intracranial tumors, but TGFβ blockade provided survival benefit only in the context of radiation treatment. This study provides further evidence that radiation-induced TGFβ activity opposes therapeutic response to radiation. Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- Mus musculus (House mouse)
Aggressive Mammary Cancers Lacking Lymphocytic Infiltration Arise in Irradiated Mice and Can Be Prevented by Dietary Intervention.
In Cancer Immunology Research on 1 February 2020 by Omene, C., Ma, L., et al.
PubMed
Because the incidence of breast cancer increases decades after ionizing radiation exposure, aging has been implicated in the evolution of the tumor microenvironment and tumor progression. Here, we investigated radiation-induced carcinogenesis using a model in which the mammary glands of 10-month-old BALB/c mice were transplanted with Trp53-null mammary tissue 3 days after exposure to low doses of sparsely ionizing γ-radiation or densely ionizing particle radiation. Mammary transplants in aged, irradiated hosts gave rise to significantly more tumors that grew more rapidly than those in sham-irradiated mice, with the most pronounced effects seen in mice irradiated with densely ionizing particle radiation. Tumor transcriptomes identified a characteristic immune signature of these aggressive cancers. Consistent with this, fast-growing tumors exhibited an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment with few infiltrating lymphocytes, abundant immunosuppressive myeloid cells, and high COX-2 and TGFβ. Only irradiated hosts gave rise to tumors lacking cytotoxic CD8+ lymphocytes (defined here as immune desert), which also occurred in younger irradiated hosts. These data suggest that host irradiation may promote immunosuppression. To test this, young chimera mice were fed chow containing a honeybee-derived compound with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE). CAPE prevented the detrimental effects of host irradiation on tumor growth rate, immune signature, and immunosuppression. These data indicated that low-dose radiation, particularly densely ionizing exposure of aged mice, promoted more aggressive cancers by suppressing antitumor immunity. Dietary intervention with a nontoxic immunomodulatory agent could prevent systemic effects of radiation that fuel carcinogenesis, supporting the potential of this strategy for cancer prevention. ©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
- Immunology and Microbiology
Serum Amyloid A Proteins Induce Pathogenic Th17 Cells and Promote Inflammatory Disease.
In Cell on 9 January 2020 by Lee, J. Y., Hall, J. A., et al.
PubMed
Lymphoid cells that produce interleukin (IL)-17 cytokines protect barrier tissues from pathogenic microbes but are also prominent effectors of inflammation and autoimmune disease. T helper 17 (Th17) cells, defined by RORγt-dependent production of IL-17A and IL-17F, exert homeostatic functions in the gut upon microbiota-directed differentiation from naive CD4+ T cells. In the non-pathogenic setting, their cytokine production is regulated by serum amyloid A proteins (SAA1 and SAA2) secreted by adjacent intestinal epithelial cells. However, Th17 cell behaviors vary markedly according to their environment. Here, we show that SAAs additionally direct a pathogenic pro-inflammatory Th17 cell differentiation program, acting directly on T cells in collaboration with STAT3-activating cytokines. Using loss- and gain-of-function mouse models, we show that SAA1, SAA2, and SAA3 have distinct systemic and local functions in promoting Th17-mediated inflammatory diseases. These studies suggest that T cell signaling pathways modulated by the SAAs may be attractive targets for anti-inflammatory therapies. Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- Cancer Research,
- Genetics,
- Immunology and Microbiology
Immune checkpoint blockade combined with IL-6 and TGF-β inhibition improves the therapeutic outcome of mRNA-based immunotherapy.
In International Journal of Cancer on 1 August 2018 by Bialkowski, L., Van der Jeught, K., et al.
PubMed
Improved understanding of cancer immunology has provided insight into the phenomenon of frequent tumor recurrence after initially successful immunotherapy. A delicate balance exists between the capacity of the immune system to control tumor growth and various resistance mechanisms that arise to avoid or even counteract the host's immune system. These resistance mechanisms include but are not limited to (i) adaptive expression of inhibitory checkpoint molecules in response to the proinflammatory environment and (ii) amplification of cancer stem cells, a small fraction of tumor cells possessing the capacity for self-renewal and mediating treatment resistance and formation of metastases after long periods of clinical remission. Several individual therapeutic agents have so far been developed to revert T-cell exhaustion or disrupt the cross-talk between cancer stem cells and the tumor-promoting microenvironment. Here, we demonstrate that a three-arm combination therapy-consisting of an mRNA-based vaccine to induce antigen-specific T-cell responses, monoclonal antibodies blocking inhibitory checkpoint molecules (PD-1, TIM-3, LAG-3), and antibodies targeting IL-6 and TGF-β-improves the therapeutic outcome in subcutaneous TC-1 tumors and significantly prolongs survival of treated mice. Our findings point to a need for a rational development of multidimensional anticancer therapies, aiming at the induction of tumor-specific immunity and simultaneously targeting multiple resistance mechanisms. © 2018 UICC.
Metastatic cancers promote cachexia through ZIP14 upregulation in skeletal muscle.
In Nature Medicine on 1 June 2018 by Wang, G., Biswas, A. K., et al.
PubMed
Patients with metastatic cancer experience a severe loss of skeletal muscle mass and function known as cachexia. Cachexia is associated with poor prognosis and accelerated death in patients with cancer, yet its underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here, we identify the metal-ion transporter ZRT- and IRT-like protein 14 (ZIP14) as a critical mediator of cancer-induced cachexia. ZIP14 is upregulated in cachectic muscles of mice and in patients with metastatic cancer and can be induced by TNF-α and TGF-β cytokines. Strikingly, germline ablation or muscle-specific depletion of Zip14 markedly reduces muscle atrophy in metastatic cancer models. We find that ZIP14-mediated zinc uptake in muscle progenitor cells represses the expression of MyoD and Mef2c and blocks muscle-cell differentiation. Importantly, ZIP14-mediated zinc accumulation in differentiated muscle cells induces myosin heavy chain loss. These results highlight a previously unrecognized role for altered zinc homeostasis in metastatic cancer-induced muscle wasting and implicate ZIP14 as a therapeutic target for its treatment.
- Immunology and Microbiology
Fibroblastic reticular cells from lymph nodes attenuate T cell expansion by producing nitric oxide.
In PLoS ONE on 24 November 2011 by Siegert, S., Huang, H. Y., et al.
PubMed
Adaptive immune responses are initiated when T cells encounter antigen on dendritic cells (DC) in T zones of secondary lymphoid organs. T zones contain a 3-dimensional scaffold of fibroblastic reticular cells (FRC) but currently it is unclear how FRC influence T cell activation. Here we report that FRC lines and ex vivo FRC inhibit T cell proliferation but not differentiation. FRC share this feature with fibroblasts from non-lymphoid tissues as well as mesenchymal stromal cells. We identified FRC as strong source of nitric oxide (NO) thereby directly dampening T cell expansion as well as reducing the T cell priming capacity of DC. The expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was up-regulated in a subset of FRC by both DC-signals as well as interferon-γ produced by primed CD8+ T cells. Importantly, iNOS expression was induced during viral infection in vivo in both LN FRC and DC. As a consequence, the primary T cell response was found to be exaggerated in Inos(-/-) mice. Our findings highlight that in addition to their established positive roles in T cell responses FRC and DC cooperate in a negative feedback loop to attenuate T cell expansion during acute inflammation.