InVivoMAb anti-mouse IL-9
Product Details
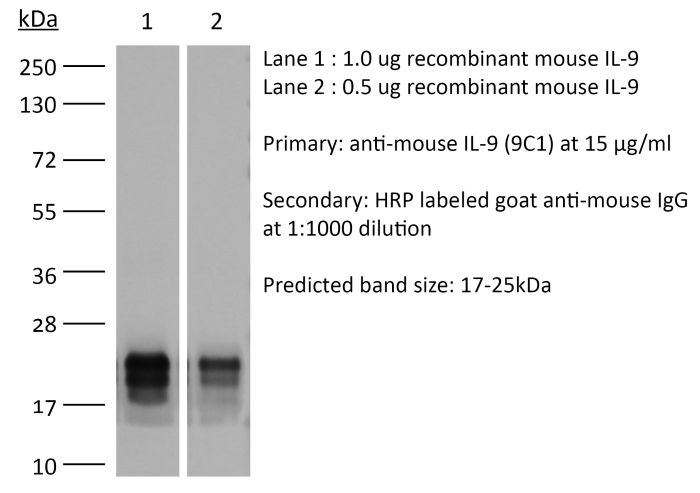
The 9C1 monoclonal antibody reacts with mouse IL-9, a pleiotropic cytokine expressed by Th9 cells, Th2 cells, Th17 cells, regulatory T cells, NKT cells, ILC2s, and mast cells. IL-9 promotes mast cell and T cell proliferation, stimulates mast cell accumulation in tissues, promotes ILC survival, enhances class-switching to IgE in B cells and alters haematopoietic progenitor cell activity. Additionally, IL-9 enhances mucus production from airway epithelial cells and alters barrier function in the intestines. IL-9 is thought to contribute to asthma. The 9C1 antibody has been reported to block the bioactivity of IL-9.Specifications
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb mouse IgG2a isotype control, unknown specificity |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Mouse IL-9-OVA complex |
| Reported Applications | in vivo IL-9 neutralization |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
<2EU/mg (<0.002EU/μg) Determined by LAL gel clotting assay |
| Purity |
>95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10950648 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
Recommended Products
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Xiao, X., et al. (2015). "GITR subverts Foxp3(+) Tregs to boost Th9 immunity through regulation of histone acetylation" Nat Commun 6: 8266. PubMed
Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) is a costimulatory molecule with diverse effects on effector T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs), but the underlying mechanism remains poorly defined. Here we demonstrate that GITR ligation subverts the induction of Foxp3(+) Tregs and directs the activated CD4(+) T cells to Th9 cells. Such GITR-mediated iTreg to Th9 induction enhances anti-tumour immunity in vivo. Mechanistically, GITR upregulates the NF-kappaB family member p50, which recruits histone deacetylases to the Foxp3 locus to produce a ‘closed’ chromatin structure. Furthermore, GITR ligation also activates STAT6, and STAT6 renders Il9 locus accessible via recruitment of histone acetyltransferase p300, and together with inhibition of Foxp3, GITR induces strong Th9 responses. Thus, Th9 cells and iTregs are developmentally linked and GITR can subvert tolerogenic conditions to boost Th9 immunity.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Monteiro, M., et al. (2015). "IL-9 Expression by Invariant NKT Cells Is Not Imprinted during Thymic Development" J Immunol 195(7): 3463-3471. PubMed
Invariant NKT (iNKT) cell thymic development can lead to distinct committed effector lineages, namely NKT1, NKT2, and NKT17. However, following identification of IL-9-producing iNKT cells involved in mucosal inflammation, their development remains unaddressed. In this study, we report that although thymic iNKT cells from naive mice do not express IL-9, iNKT cell activation in the presence of TGF-beta and IL-4 induces IL-9 secretion in murine and human iNKT cells. Acquisition of IL-9 production was observed in different iNKT subsets defined by CD4, NK1.1, and neuropilin-1, indicating that distinct functional subpopulations are receptive to IL-9 polarization. Transcription factor expression kinetics suggest that regulatory mechanisms of IL-9 expression are shared by iNKT and CD4 T cells, with Irf4 and Batf deficiency deeply affecting IL-9 production. Importantly, adoptive transfer of an enriched IL-9(+) iNKT cell population leads to exacerbated allergic inflammation in the airways upon intranasal immunization with house dust mite, confirming the ability of IL-9-producing iNKT cells to mediate proinflammatory effects in vivo, as previously reported. Taken together, our data show that peripheral iNKT cells retain the capacity of shaping their function in response to environmental cues, namely TGF-beta and IL-4, adopting an IL-9-producing NKT cell phenotype able to mediate proinflammatory effects in vivo, namely granulocyte and mast cell recruitment to the lungs.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Nakatsukasa, H., et al. (2015). "The DNA-binding inhibitor Id3 regulates IL-9 production in CD4(+) T cells" Nat Immunol 16(10): 1077-1084. PubMed
The molecular mechanisms by which signaling via transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and interleukin 4 (IL-4) control the differentiation of CD4(+) IL-9-producing helper T cells (TH9 cells) remain incompletely understood. We found here that the DNA-binding inhibitor Id3 regulated TH9 differentiation, as deletion of Id3 increased IL-9 production from CD4(+) T cells. Mechanistically, TGF-beta1 and IL-4 downregulated Id3 expression, and this process required the kinase TAK1. A reduction in Id3 expression enhanced binding of the transcription factors E2A and GATA-3 to the Il9 promoter region, which promoted Il9 transcription. Notably, Id3-mediated control of TH9 differentiation regulated anti-tumor immunity in an experimental melanoma-bearing model in vivo and also in human CD4(+) T cells in vitro. Thus, our study reveals a previously unrecognized TAK1-Id3-E2A-GATA-3 pathway that regulates TH9 differentiation.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Nelson, M. H., et al. (2015). "The inducible costimulator augments Tc17 cell responses to self and tumor tissue" J Immunol 194(4): 1737-1747. PubMed
The inducible costimulator (ICOS) plays a key role in the development of Th17 cells, but its role in the development and antitumor activity of IL-17-producing CD8(+) T cells (Tc17) remains unknown. We found that ICOS costimulation was important for the functional maintenance, but not differentiation, of Tc17 cells in vitro. Blocking the ICOS pathway using an antagonist mAb or by using recipient mice genetically deficient in the ICOS ligand reduced the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred Tc17 cells. Conversely, activating Tc17 cells with an ICOS agonist in vitro enhanced their capacity to eradicate melanoma and induce autoimmune vitiligo when infused into mice. However, ICOS stimulation did not augment the antitumor activity of IL-2 expanded T cells. Additional investigation revealed that ICOS stimulation not only increased IL-2Ralpha, CXCR3, and IL-23R expression on Tc17 cells, but also dampened their expression of suppressive molecule CD39. Although Tc17 cells activated with an ICOS agonist cosecreted heightened IL-17A, IL-9, and IFN-gamma, their therapeutic effectiveness was critically dependent on IFN-gamma production. Depletion of IL-17A and IL-9 had little impact on antitumor Tc17 cells activated with an ICOS agonist. Collectively, our work reveals that the ICOS pathway potentiates the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred Tc17 cells. This work has major implications for the design of vaccine, Ab and cell-based therapies for autoimmunity, infectious disease, and cancer.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Gerlach, K., et al. (2014). "TH9 cells that express the transcription factor PU.1 drive T cell-mediated colitis via IL-9 receptor signaling in intestinal epithelial cells" Nat Immunol 15(7): 676-686. PubMed
The molecular checkpoints that drive inflammatory bowel diseases are incompletely understood. Here we found more T cells expressing the transcription factor PU.1 and interleukin 9 (IL-9) in patients with ulcerative colitis. In an animal model, citrine reporter mice had more IL-9-expressing mucosal T cells in experimental oxazolone-induced colitis. IL-9 deficiency suppressed acute and chronic colitis. Mice with PU.1 deficiency in T cells were protected from colitis, whereas treatment with antibody to IL-9 suppressed colitis. Functionally, IL-9 impaired intestinal barrier function and prevented mucosal wound healing in vivo. Thus, our findings suggest that the TH9 subset of helper T cells serves an important role in driving ulcerative colitis by regulating intestinal epithelial cells and that TH9 cells represent a likely target for the treatment of chronic intestinal inflammation.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Vegran, F., et al. (2014). "The transcription factor IRF1 dictates the IL-21-dependent anticancer functions of TH9 cells" Nat Immunol 15(8): 758-766. PubMed
The TH9 subset of helper T cells was initially shown to contribute to the induction of autoimmune and allergic diseases, but subsequent evidence has suggested that these cells also exert antitumor activities. However, the molecular events that account for their effector properties are elusive. Here we found that the transcription factor IRF1 enhanced the effector function of TH9 cells and dictated their anticancer properties. Under TH9-skewing conditions, interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) induced phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT1 and subsequent expression of IRF1, which bound to the promoters of Il9 and Il21 and enhanced secretion of the cytokines IL-9 and IL-21 from TH9 cells. Furthermore, IL-1beta-induced TH9 cells exerted potent anticancer functions in an IRF1- and IL-21-dependent manner. Our findings thus identify IRF1 as a target for controlling the function of TH9 cells.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Licona-Limon, P., et al. (2013). "Th9 Cells Drive Host Immunity against Gastrointestinal Worm Infection" Immunity 39(4): 744-757. PubMed
Type 2 inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13, drive the characteristic features of immunity against parasitic worms and allergens. Whether IL-9 serves an essential role in the initiation of host-protective responses is controversial, and the importance of IL-9- versus IL-4-producing CD4(+) effector T cells in type 2 immunity is incompletely defined. Herein, we generated IL-9-deficient and IL-9-fluorescent reporter mice that demonstrated an essential role for this cytokine in the early type 2 immunity against Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Whereas T helper 9 (Th9) cells and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) were major sources of infection-induced IL-9 production, the adoptive transfer of Th9 cells, but not Th2 cells, caused rapid worm expulsion, marked basophilia, and increased mast cell numbers in Rag2-deficient hosts. Taken together, our data show a critical and nonredundant role for Th9 cells and IL-9 in host-protective type 2 immunity against parasitic worm infection.
in vivo IL-9 neutralization
Elyaman, W., et al. (2012). "Notch receptors and Smad3 signaling cooperate in the induction of interleukin-9-producing T cells" Immunity 36(4): 623-634. PubMed
Interleukin 9 (IL-9) is a pleiotropic cytokine that can regulate autoimmune responses by enhancing regulatory CD4(+)FoxP3(+) T regulatory (Treg) cell survival and T helper 17 (Th17) cell proliferation. Here, we analyzed the costimulatory requirements for the induction of Th9 cells, and demonstrated that Notch pathway cooperated with TGF-beta signaling to induce IL-9. Conditional ablation of Notch1 and Notch2 receptors inhibited the development of Th9 cells. Notch1 intracellular domain (NICD1) recruited Smad3, downstream of TGF-beta cytokine signaling, and together with recombining binding protein (RBP)-Jkappa bound the Il9 promoter and induced its transactivation. In experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), Jagged2 ligation regulated clinical disease in an IL-9-dependent fashion. Signaling through Jagged2 expanded Treg cells and suppressed EAE when administered before antigen immunization, but worsened EAE when administered concurrently with immunization by favoring Th17 cell expansion. We propose that Notch and Smad3 cooperate to induce IL-9 and participate in regulating the immune response.
- Cardiovascular biology,
- Immunology and Microbiology
Perivascular Fibrosis Is Mediated by a KLF10-IL-9 Signaling Axis in CD4+ T Cells.
In Circulation Research on 27 May 2022 by Zhuang, R., Chen, J., et al.
PubMed
Perivascular fibrosis, characterized by increased amount of connective tissue around vessels, is a hallmark for vascular disease. Ang II (angiotensin II) contributes to vascular disease and end-organ damage via promoting T-cell activation. Despite recent data suggesting the role of T cells in the progression of perivascular fibrosis, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood.TF (transcription factor) profiling was performed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of hypertensive patients. CD4-targeted KLF10 (Kruppel like factor 10)-deficient (Klf10fl/flCD4Cre+; [TKO]) and CD4-Cre (Klf10+/+CD4Cre+; [Cre]) control mice were subjected to Ang II infusion. End point characterization included cardiac echocardiography, aortic imaging, multiorgan histology, flow cytometry, cytokine analysis, aorta and fibroblast transcriptomic analysis, and aortic single-cell RNA-sequencing.TF profiling identified increased KLF10 expression in hypertensive human subjects and in CD4+ T cells in Ang II-treated mice. TKO mice showed enhanced perivascular fibrosis, but not interstitial fibrosis, in aorta, heart, and kidney in response to Ang II, accompanied by alterations in global longitudinal strain, arterial stiffness, and kidney function compared with Cre control mice. However, blood pressure was unchanged between the 2 groups. Mechanistically, KLF10 bound to the IL (interleukin)-9 promoter and interacted with HDAC1 (histone deacetylase 1) inhibit IL-9 transcription. Increased IL-9 in TKO mice induced fibroblast intracellular calcium mobilization, fibroblast activation, and differentiation and increased production of collagen and extracellular matrix, thereby promoting the progression of perivascular fibrosis and impairing target organ function. Remarkably, injection of anti-IL9 antibodies reversed perivascular fibrosis in Ang II-infused TKO mice and C57BL/6 mice. Single-cell RNA-sequencing revealed fibroblast heterogeneity with activated signatures associated with robust ECM (extracellular matrix) and perivascular fibrosis in Ang II-treated TKO mice.CD4+ T cell deficiency of Klf10 exacerbated perivascular fibrosis and multi-organ dysfunction in response to Ang II via upregulation of IL-9. Klf10 or IL-9 in T cells might represent novel therapeutic targets for treatment of vascular or fibrotic diseases.
- Cancer Research,
- Immunology and Microbiology
IL-9 Producing Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Treg Subsets Drive Immune Escape of Tumor Cells in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 7 May 2022 by Heim, L., Yang, Z., et al.
PubMed
Although lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, the mechanisms how lung cancer cells evade the immune system remain incompletely understood. Here, we discovered IL-9-dependent signaling mechanisms that drive immune evasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We found increased IL-9 and IL-21 production by T cells in the tumoral region of the lung of patients with NSCLC, suggesting the presence of Th9 cells in the lung tumor microenvironment. Moreover, we noted IL-9 producing Tregs in NSCLC. IL-9 target cells in NSCLC consisted of IL-9R+ tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. In two murine experimental models of NSCLC, and in vitro, IL-9 prevented cell death and controlled growth of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Targeted deletion of IL-9 resulted in successful lung tumor rejection in vivo associated with an induction of IL-21 and reduction of Treg cells. Finally, anti-IL-9 antibody immunotherapy resulted in suppression of tumor development even in established experimental NSCLC and was associated with reduced IL-10 production in the lung. In conclusion, our findings indicate that IL-9 drives immune escape of lung tumor cells via effects on tumor cell survival and tumor infiltrating T cells. Thus, strategies blocking IL-9 emerge as a new approach for clinical therapy of lung cancer. Copyright © 2022 Heim, Yang, Tausche, Hohenberger, Chiriac, Koelle, Geppert, Kachler, Miksch, Graser, Friedrich, Kharwadkar, Rieker, Trufa, Sirbu, Neurath, Kaplan and Finotto.
- FC/FACS,
- Mus musculus (House mouse)
IL-9/STAT3/fatty acid oxidation-mediated lipid peroxidation contributes to Tc9 cell longevity and enhanced antitumor activity.
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 1 April 2022 by Xiao, L., Ma, X., et al.
PubMed
CD8+ T cell longevity regulated by metabolic activity plays important roles in cancer immunotherapy. Although in vitro-polarized, transferred IL-9-secreting CD8+ Tc9 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte subset 9) cells exert greater persistence and antitumor efficacy than Tc1 cells, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here, we show that tumor-infiltrating Tc9 cells display significantly lower lipid peroxidation than Tc1 cells in several mouse models, which is strongly correlated with their persistence. Using RNA-sequence and functional validation, we found that Tc9 cells exhibited unique lipid metabolic programs. Tc9 cell-derived IL-9 activated STAT3, upregulated fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial activity, and rendered Tc9 cells with reduced lipid peroxidation and resistance to tumor- or ROS-induced ferroptosis in the tumor microenvironment. IL-9 signaling deficiency, inhibiting STAT3, or fatty acid oxidation increased lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis of Tc9 cells, resulting in impaired longevity and antitumor ability. Similarly, human Tc9 cells also exhibited lower lipid peroxidation than Tc1 cells and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells expressed lower IL9 and higher lipid peroxidation- and ferroptosis-related genes than circulating CD8+ T cells in patients with melanoma. This study indicates that lipid peroxidation regulates Tc9 cell longevity and antitumor effects via the IL-9/STAT3/fatty acid oxidation pathway and regulating T cell lipid peroxidation can be used to enhance T cell-based immunotherapy in human cancer.
- Cancer Research,
- Immunology and Microbiology
BFAR coordinates TGFβ signaling to modulate Th9-mediated cancer immunotherapy.
In The Journal of Experimental Medicine on 5 July 2021 by Pei, S., Huang, M., et al.
PubMed
TGFβ is essential for the generation of anti-tumor Th9 cells; on the other hand, it causes resistance against anti-tumor immunity. Despite recent progress, the underlying mechanism reconciling the double-edged effect of TGFβ signaling in Th9-mediated cancer immunotherapy remains elusive. Here, we find that TGFβ-induced down-regulation of bifunctional apoptosis regulator (BFAR) represents the key mechanism preventing the sustained activation of TGFβ signaling and thus impairing Th9 inducibility. Mechanistically, BFAR mediates K63-linked ubiquitination of TGFβR1 at K268, which is critical to activate TGFβ signaling. Thus, BFAR deficiency or K268R knock-in mutation suppresses TGFβR1 ubiquitination and Th9 differentiation, thereby inhibiting Th9-mediated cancer immunotherapy. More interestingly, BFAR-overexpressed Th9 cells exhibit promising therapeutic efficacy to curtail tumor growth and metastasis and promote the sensitivity of anti-PD-1-mediated checkpoint immunotherapy. Thus, our findings establish BFAR as a key TGFβ-regulated gene to fine-tune TGFβ signaling that causes Th9 induction insensitivity, and they highlight the translational potential of BFAR in promoting Th9-mediated cancer immunotherapy. © 2021 Pei et al.
- Cancer Research,
- Neuroscience
TBL1XR1 Mutations Drive Extranodal Lymphoma by Inducing a Pro-tumorigenic Memory Fate.
In Cell on 23 July 2020 by Venturutti, L., Teater, M., et al.
PubMed
The most aggressive B cell lymphomas frequently manifest extranodal distribution and carry somatic mutations in the poorly characterized gene TBL1XR1. Here, we show that TBL1XR1 mutations skew the humoral immune response toward generating abnormal immature memory B cells (MB), while impairing plasma cell differentiation. At the molecular level, TBL1XR1 mutants co-opt SMRT/HDAC3 repressor complexes toward binding the MB cell transcription factor (TF) BACH2 at the expense of the germinal center (GC) TF BCL6, leading to pre-memory transcriptional reprogramming and cell-fate bias. Upon antigen recall, TBL1XR1 mutant MB cells fail to differentiate into plasma cells and instead preferentially reenter new GC reactions, providing evidence for a cyclic reentry lymphomagenesis mechanism. Ultimately, TBL1XR1 alterations lead to a striking extranodal immunoblastic lymphoma phenotype that mimics the human disease. Both human and murine lymphomas feature expanded MB-like cell populations, consistent with a MB-cell origin and delineating an unforeseen pathway for malignant transformation of the immune system. Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- Immunology and Microbiology
Interleukin-9 blockage reduces early hepatic granuloma formation and fibrosis during Schistosoma japonicum infection in mice.
In Immunology on 1 December 2019 by Zhan, T., Ma, H., et al.
PubMed
Hepatic fibrosis induced by schistosomes is regulated by a complex network of cytokines. T helper type 9 (Th9) cells are a new type of effector T helper cells, which mainly secrete the specific cytokine interleukin-9 (IL-9). Interleukin-9 has been shown to contribute to liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B and in a mouse model due to carbon tetrachloride. However, the role of IL-9 in schistosomiasis fibrosis remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the roles of IL-9 in schistosomiasis through in vivo and in vitro studies. The in vivo studies found that neutralization of IL-9 reduced liver granulomatous inflammation and collagen deposition around parasite eggs. The in vitro studies found that the treatment of primary hepatic stellate cells with IL-9 induced a significant increase of collagen and α-smooth-muscle actin. Moreover, we also described the dynamics and relevance of IL-9 and IL-4 in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum. We found that IL-9 might appear more quickly and at higher levels than IL-4. Hence, our findings indicated that IL-9 might play a role in regulating hepatic fibrosis in early-stage schistosomiasis and become a promising approach for regulating hepatic fibrosis caused by S. japonicum. © 2019 John Wiley Sons Ltd.
- Biochemistry and Molecular biology,
- Cell Biology
Interleukin-36 cytokines alter the intestinal microbiome and can protect against obesity and metabolic dysfunction.
In Nature Communications on 5 September 2019 by Giannoudaki, E., Hernández-Santana, Y. E., et al.
PubMed
Members of the interleukin-1 (IL-1) family are important mediators of obesity and metabolic disease and have been described to often play opposing roles. Here we report that the interleukin-36 (IL-36) subfamily can play a protective role against the development of disease. Elevated IL-36 cytokine expression is found in the serum of obese patients and negatively correlates with blood glucose levels among those presenting with type 2 diabetes. Mice lacking IL-36Ra, an IL-36 family signalling antagonist, develop less diet-induced weight gain, hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. These protective effects correlate with increased abundance of the metabolically protective bacteria Akkermansia muciniphila in the intestinal microbiome. IL-36 cytokines promote its outgrowth as well as increased colonic mucus secretion. These findings identify a protective role for IL-36 cytokines in obesity and metabolic disease, adding to the current understanding of the role the broader IL-1 family plays in regulating disease pathogenesis.
- Mus musculus (House mouse),
- Immunology and Microbiology
Neutralization of Interleukin-9 Decreasing Mast Cells Infiltration in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.
In Chinese Medical Journal on 20 April 2017 by Yin, J. J., Hu, X. Q., et al.
PubMed
Th9 cells are a newly discovered CD4+ T helper cell subtype, characterized by high interleukin (IL)-9 secretion. Growing evidences suggest that Th9 cells are involved in the pathogenic mechanism of multiple sclerosis (MS). Mast cells are multifunctional innate immune cells, which are perhaps best known for their role as dominant effector cells in allergies and asthma. Several lines of evidence point to an important role for mast cells in MS and its animal models. Simultaneously, there is dynamic "cross-talk" between Th9 and mast cells. The aim of the present study was to examine the IL-9-mast cell axis in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and determine its interaction after neutralizing anti-IL-9 antibody treatment. Female C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into three groups (n = 5 in each group): mice with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-induced EAE (EAE group), EAE mice treated with anti-IL-9 antibody (anti-IL-9 Abs group), and EAE mice treated with IgG isotype control (IgG group). EAE clinical score was evaluated. Mast cells from central nervous system (CNS) were detected by flow cytometry. The production of chemokine recruiting mast cells in the CNS was explored by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). In mice with MOG-induced EAE, the expression of IL-9 receptor (IL-9R) complexes in CNS and spleen mast cells was also explored by RT-PCR, and then was repeating validated by immunocytochemistry. In vitro, spleen cells from EAE mice were cultured with anti-IL-9 antibody, and quantity of mast cells was counted by flow cytometry after co-culture. Compared with IgG group, IL-9 blockade delayed clinical disease onset and ameliorated EAE severity (t = -2.217, P = 0.031), accompany with mast cells infiltration decreases (day 5: t = -8.005, P 0.001; day 15: t = -11.857, P 0.001; day 20: t = -5.243, P = 0.001) in anti-IL-9 Abs group. The messenger RNA expressions of C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 (t = -5.932, P = 0.003) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (t = -4.029, P = 0.004) were significantly decreased after IL-9 neutralization in anti-IL-9 Abs group, compared with IgG group. In MOG-induced EAE, the IL-9R complexes were expressed in CNS and spleen mast cells. In vitro, splenocytes cultured with anti-IL-9 antibody showed significantly lower levels of mast cells in a dose-dependent manner, compared with splenocytes cultured with anti-mouse IgG (5 μg/ml: t = -0.894, P = 0.397; 10 μg/ml: t = -3.348, P = 0.019; 20 μg/ml: t = -7.639, P 0.001). This study revealed that IL-9 neutralization reduced mast cell infiltration in CNS and ameliorated EAE, which might be relate to the interaction between IL-9 and mast cells.
- Immunology and Microbiology
IL-9 Expression by Invariant NKT Cells Is Not Imprinted during Thymic Development.
In The Journal of Immunology on 1 October 2015 by Monteiro, M., Agua-Doce, A., et al.
PubMed
Invariant NKT (iNKT) cell thymic development can lead to distinct committed effector lineages, namely NKT1, NKT2, and NKT17. However, following identification of IL-9-producing iNKT cells involved in mucosal inflammation, their development remains unaddressed. In this study, we report that although thymic iNKT cells from naive mice do not express IL-9, iNKT cell activation in the presence of TGF-β and IL-4 induces IL-9 secretion in murine and human iNKT cells. Acquisition of IL-9 production was observed in different iNKT subsets defined by CD4, NK1.1, and neuropilin-1, indicating that distinct functional subpopulations are receptive to IL-9 polarization. Transcription factor expression kinetics suggest that regulatory mechanisms of IL-9 expression are shared by iNKT and CD4 T cells, with Irf4 and Batf deficiency deeply affecting IL-9 production. Importantly, adoptive transfer of an enriched IL-9(+) iNKT cell population leads to exacerbated allergic inflammation in the airways upon intranasal immunization with house dust mite, confirming the ability of IL-9-producing iNKT cells to mediate proinflammatory effects in vivo, as previously reported. Taken together, our data show that peripheral iNKT cells retain the capacity of shaping their function in response to environmental cues, namely TGF-β and IL-4, adopting an IL-9-producing NKT cell phenotype able to mediate proinflammatory effects in vivo, namely granulocyte and mast cell recruitment to the lungs. Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
- Cancer Research,
- Immunology and Microbiology
The inducible costimulator augments Tc17 cell responses to self and tumor tissue.
In The Journal of Immunology on 15 February 2015 by Nelson, M. H., Kundimi, S., et al.
PubMed
The inducible costimulator (ICOS) plays a key role in the development of Th17 cells, but its role in the development and antitumor activity of IL-17-producing CD8(+) T cells (Tc17) remains unknown. We found that ICOS costimulation was important for the functional maintenance, but not differentiation, of Tc17 cells in vitro. Blocking the ICOS pathway using an antagonist mAb or by using recipient mice genetically deficient in the ICOS ligand reduced the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred Tc17 cells. Conversely, activating Tc17 cells with an ICOS agonist in vitro enhanced their capacity to eradicate melanoma and induce autoimmune vitiligo when infused into mice. However, ICOS stimulation did not augment the antitumor activity of IL-2 expanded T cells. Additional investigation revealed that ICOS stimulation not only increased IL-2Rα, CXCR3, and IL-23R expression on Tc17 cells, but also dampened their expression of suppressive molecule CD39. Although Tc17 cells activated with an ICOS agonist cosecreted heightened IL-17A, IL-9, and IFN-γ, their therapeutic effectiveness was critically dependent on IFN-γ production. Depletion of IL-17A and IL-9 had little impact on antitumor Tc17 cells activated with an ICOS agonist. Collectively, our work reveals that the ICOS pathway potentiates the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred Tc17 cells. This work has major implications for the design of vaccine, Ab and cell-based therapies for autoimmunity, infectious disease, and cancer. Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.