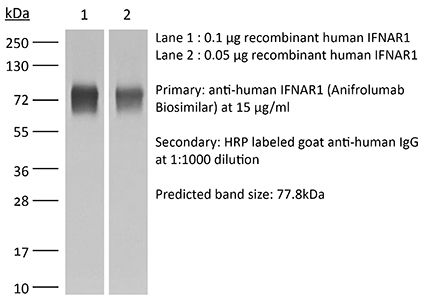
InVivoSIM anti-human IFNAR1 (Anifrolumab Biosimilar)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Human IgG1, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb human IgG1 (K214R/L234F/L235E/P331S) isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Human IFNAR1 |
| Reported Applications |
Functional assays Western blot ELISA |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inflammatory arthritis immune related adverse events represent a unique autoimmune disease entity primarily driven by T cells, but likely not autoantibodies
In medRxiv on 6 June 2025 by Zhu, X., Yu, Y., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Enhancing the Anticancer Activity of a Carcinoma-Directed Peptide-HLA-I Fusion Protein by Armoring with Mutein IFNα.
In Int J Mol Sci on 29 March 2025 by Samplonius, D. F., van Wijngarden, A. P., et al.
PubMed
Previously, we reported on the peptide-HLA-I fusion protein EpCAM-ReTARGTPR, which allows us to redirect the cytotoxic activity of pre-existing anti-CMV CD8pos T cell immunity to selectively eliminate EpCAMpos cancer cells. EpCAM-ReTARGTPR consists of the CMV pp65-derived peptide TPRVTGGGAM (TPR) fused in tandem with a soluble HLA-B*07:02/β2-microglobulin (β2M) molecule and an EpCAM-directed Fab antibody fragment. To further enhance its anticancer activity, we equipped EpCAM-ReTARGTPR with the immune-potentiating cytokine muteins IL2(H16A,F42A) and IFNαR149A, respectively. Both cytokines are engineered to have attenuated affinity for their respective cytokine receptors. Compared to EpCAM-ReTARGTPR, in vitro treatment of EpCAMpos carcinoma cell lines with EpCAM-ReTARGTPRvIL2 for 24 h increased the cytotoxic activity of PBMCs containing low levels of TPR-specific CD8pos T cells by ~15%, whereas EpCAM-ReTARGTPRIFNαR149A induced an increase of ~50%. Moreover, treatment for 120 h with EpCAM-ReTARGTPRIFNαR149A inhibited the proliferative capacity of the cancer cell lines OvCAR3 and PC3M by ~91% without compromising the viability of the TPR-specific CD8pos T cells and increased their capacity for IFNγ secretion. Importantly, EpCAM-ReTARGTPRIFNαR149A potently induced the elimination of primary EpCAMpos refractory carcinoma cells from a Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) patient. Taken together, the armoring of the carcinoma-directed peptide-HLA-I fusion protein EpCAM-ReTARGTPR with IFNαR149A potently enhanced the efficacy of pre-existing anti-CMV CD8pos T cell immunity to selectively eliminate EpCAMpos cancer cells.
-