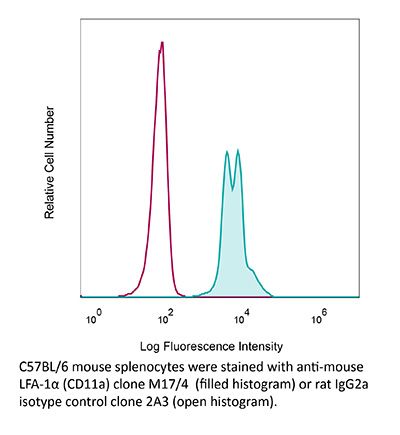
InVivoMAb anti-mouse LFA-1α (CD11a)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | C57BL/6 mouse splenic secondary cytotoxic T cells |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization Flow cytometry |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107578 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Peske, J. D., et al (2015). "Effector lymphocyte-induced lymph node-like vasculature enables naive T-cell entry into tumours and enhanced anti-tumour immunity" Nat Commun 6: 7114.
PubMed
The presence of lymph node (LN)-like vasculature in tumours, characterized by expression of peripheral node addressin and chemokine CCL21, is correlated with T-cell infiltration and positive prognosis in breast cancer and melanoma patients. However, mechanisms controlling the development of LN-like vasculature and how it might contribute to a beneficial outcome for cancer patients are unknown. Here we demonstrate that LN-like vasculature is present in murine models of melanoma and lung carcinoma. It enables infiltration by naive T cells that significantly delay tumour outgrowth after intratumoral activation. Development of this vasculature is controlled by a mechanism involving effector CD8 T cells and NK cells that secrete LTalpha3 and IFNgamma. LN-like vasculature is also associated with organized aggregates of B lymphocytes and gp38(+) fibroblasts, which resemble tertiary lymphoid organs that develop in models of chronic inflammation. These results establish LN-like vasculature as both a consequence of and key contributor to anti-tumour immunity.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Glatigny, S., et al (2015). "Integrin alpha L controls the homing of regulatory T cells during CNS autoimmunity in the absence of integrin alpha 4" Sci Rep 5: 7834.
PubMed
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS), results from an autoimmune attack of the central nervous system (CNS) by effector T helper (Th) 1 and Th17 cells. Regulatory T cells (Treg) can control effector T cells and limit the progression of CNS autoimmunity. Integrin alpha 4 (Itga4) is critical for the entry of Th1 but not Th17 cells into the CNS during EAE. Whether Itga4 controls the homing of Tregs in the CNS and whether Tregs can limit Th17-mediated EAE has, however, not been addressed. Through selective elimination of Itga4 in Foxp3-expressing cells, we show here that Tregs can suppress Th17-mediated EAE and enter into the CNS independently of Itga4. Furthermore, similarly to Th17 cells and in contrast to Th1 cells, Tregs depend on LFA-1 for their entry into the CNS in the absence of Itga4. Therefore, these data suggest that the efficacy of Itga4 neutralization on MS progression may be associated with the prevention of Th1 cells and the maintenance of Tregs migration into the CNS.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Guidotti, L. G., et al (2015). "Immunosurveillance of the liver by intravascular effector CD8(+) T cells" Cell 161(3): 486-500.
PubMed
Effector CD8(+) T cells (CD8 TE) play a key role during hepatotropic viral infections. Here, we used advanced imaging in mouse models of hepatitis B virus (HBV) pathogenesis to understand the mechanisms whereby these cells home to the liver, recognize antigens, and deploy effector functions. We show that circulating CD8 TE arrest within liver sinusoids by docking onto platelets previously adhered to sinusoidal hyaluronan via CD44. After the initial arrest, CD8 TE actively crawl along liver sinusoids and probe sub-sinusoidal hepatocytes for the presence of antigens by extending cytoplasmic protrusions through endothelial fenestrae. Hepatocellular antigen recognition triggers effector functions in a diapedesis-independent manner and is inhibited by the processes of sinusoidal defenestration and capillarization that characterize liver fibrosis. These findings reveal the dynamic behavior whereby CD8 TE control hepatotropic pathogens and suggest how liver fibrosis might reduce CD8 TE immune surveillance toward infected or transformed hepatocytes.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Zenaro, E., et al (2015). "Neutrophils promote Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline via LFA-1 integrin" Nat Med 21(8): 880-886.
PubMed
Inflammation is a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, and innate immune cells have been shown to contribute to disease pathogenesis. In two transgenic models of Alzheimer’s disease (5xFAD and 3xTg-AD mice), neutrophils extravasated and were present in areas with amyloid-beta (Abeta) deposits, where they released neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and IL-17. Abeta42 peptide triggered the LFA-1 integrin high-affinity state and rapid neutrophil adhesion to integrin ligands. In vivo, LFA-1 integrin controlled neutrophil extravasation into the CNS and intraparenchymal motility. In transgenic Alzheimer’s disease models, neutrophil depletion or inhibition of neutrophil trafficking via LFA-1 blockade reduced Alzheimer’s disease-like neuropathology and improved memory in mice already showing cognitive dysfunction. Temporary depletion of neutrophils for 1 month at early stages of disease led to sustained improvements in memory. Transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice lacking LFA-1 were protected from cognitive decline and had reduced gliosis. In humans with Alzheimer’s disease, neutrophils adhered to and spread inside brain venules and were present in the parenchyma, along with NETs. Our results demonstrate that neutrophils contribute to Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and cognitive impairment and suggest that the inhibition of neutrophil trafficking may be beneficial in Alzheimer’s disease.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Rabenstein, H., et al (2014). "Differential kinetics of antigen dependency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells" J Immunol 192(8): 3507-3517.
PubMed
Ag recognition via the TCR is necessary for the expansion of specific T cells that then contribute to adaptive immunity as effector and memory cells. Because CD4+ and CD8+ T cells differ in terms of their priming APCs and MHC ligands we compared their requirements of Ag persistence during their expansion phase side by side. Proliferation and effector differentiation of TCR transgenic and polyclonal mouse T cells were thus analyzed after transient and continuous TCR signals. Following equally strong stimulation, CD4+ T cell proliferation depended on prolonged Ag presence, whereas CD8+ T cells were able to divide and differentiate into effector cells despite discontinued Ag presentation. CD4+ T cell proliferation was neither affected by Th lineage or memory differentiation nor blocked by coinhibitory signals or missing inflammatory stimuli. Continued CD8+ T cell proliferation was truly independent of self-peptide/MHC-derived signals. The subset divergence was also illustrated by surprisingly broad transcriptional differences supporting a stronger propensity of CD8+ T cells to programmed expansion. These T cell data indicate an intrinsic difference between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells regarding the processing of TCR signals for proliferation. We also found that the presentation of a MHC class II-restricted peptide is more efficiently prolonged by dendritic cell activation in vivo than a class I bound one. In summary, our data demonstrate that CD4+ T cells require continuous stimulation for clonal expansion, whereas CD8+ T cells can divide following a much shorter TCR signal.
Flow Cytometry
Wang, X., et al (2014). "Integrin-mediated interactions between B cells and follicular dendritic cells influence germinal center B cell fitness" J Immunol 192(10): 4601-4609.
PubMed
Integrin-ligand interactions between germinal center (GC) B cells and Ag-presenting follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) have been suggested to play central roles during GC responses, but their in vivo requirement has not been directly tested. In this study, we show that, whereas integrins alphaLbeta2 and alpha4beta1 are highly expressed and functional on mouse GC B cells, removal of single integrins or their ligands had little effect on B cell participation in the GC response. Combined beta2 integrin deficiency and alpha4 integrin blockade also did not affect the GC response against a particulate Ag. However, the combined integrin deficiency did cause B cells to be outcompeted in splenic GC responses against a soluble protein Ag and in mesenteric lymph node GC responses against gut-derived Ags. Similar findings were made for beta2-deficient B cells in mice lacking VCAM1 on FDCs. The reduced fitness of the GC B cells did not appear to be due to decreased Ag acquisition, proliferation rates, or pAKT levels. In summary, our findings provide evidence that alphaLbeta2 and alpha4beta1 play overlapping and context-dependent roles in supporting interactions with FDCs that can augment the fitness of responding GC B cells. We also find that mouse GC B cells upregulate alphavbeta3 and adhere to vitronectin and milk-fat globule epidermal growth factor VIII protein. Integrin beta3-deficient B cells contributed in a slightly exaggerated manner to GC responses, suggesting this integrin has a regulatory function in GC B cells.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Hock, K., et al (2014). "Donor CD4 T cells trigger costimulation blockade-resistant donor bone marrow rejection through bystander activation requiring IL-6" Am J Transplant 14(9): 2011-2022.
PubMed
Bone marrow (BM) transplantation under costimulation blockade induces chimerism and tolerance. Cotransplantation of donor T cells (contained in substantial numbers in mobilized peripheral blood stem cells and donor lymphocyte infusions) together with donor BM paradoxically triggers rejection of donor BM through undefined mechanisms. Here, nonmyeloablatively irradiated C57BL/6 recipients simultaneously received donor BM (BALB/c) and donor T cells under costimulation blockade (anti-CD154 and CTLA4Ig). Donor CD4, but not CD8 cells, triggered natural killer-independent donor BM rejection which was associated with increased production of IL-6, interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) and IL-17A. BM rejection was prevented through neutralization of IL-6, but not of IFN-gamma or IL-17A. IL-6 counteracted the antiproliferative effect of anti-CD154 in vitro. Rapamycin and anti-lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 negated this effect of IL-6 in vitro and prevented BM rejection in vivo. Simultaneous cotransplantation of (BALB/cxB6)F1, recipient or irradiated donor CD4 cells, or late transfer of donor CD4 cells did not lead to BM rejection, whereas cotransplantation of third party CD4 cells did. Transferred donor CD4 cells became activated, rapidly underwent apoptosis and triggered activation and proliferation of recipient T cells. Collectively, these results provide evidence that donor T cells recognizing the recipient as allogeneic lead to the release of IL-6, which abolishes the effect of anti-CD154, triggering donor BM rejection through bystander activation.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Gerard, A., et al (2013). "Secondary T cell-T cell synaptic interactions drive the differentiation of protective CD8+ T cells" Nat Immunol 14(4): 356-363.
PubMed
Immunization results in the differentiation of CD8+ T cells, such that they acquire effector abilities and convert into a memory pool. Priming of T cells takes place via an immunological synapse formed with an antigen-presenting cell (APC). By disrupting synaptic stability at different times, we found that the differentiation of CD8+ T cells required cell interactions beyond those made with APCs. We identified a critical differentiation period that required interactions between primed T cells. We found that T cell-T cell synapses had a major role in the generation of protective CD8+ T cell memory. T cell-T cell synapses allowed T cells to polarize critical secretion of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) toward each other. Collective activation and homotypic clustering drove cytokine sharing and acted as regulatory stimuli for T cell differentiation.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Li, W., et al (2012). "Intravital 2-photon imaging of leukocyte trafficking in beating heart" J Clin Invest 122(7): 2499-2508.
PubMed
Two-photon intravital microscopy has substantially broadened our understanding of tissue- and organ-specific differences in the regulation of inflammatory responses. However, little is known about the dynamic regulation of leukocyte recruitment into inflamed heart tissue, largely due to technical difficulties inherent in imaging moving tissue. Here, we report a method for imaging beating murine hearts using intravital 2-photon microscopy. Using this method, we visualized neutrophil trafficking at baseline and during inflammation. Ischemia reperfusion injury induced by transplantation or transient coronary artery ligation led to recruitment of neutrophils to the heart, their extravasation from coronary veins, and infiltration of the myocardium where they formed large clusters. Grafting hearts containing mutant ICAM-1, a ligand important for neutrophil recruitment, reduced the crawling velocities of neutrophils within vessels, and markedly inhibited their extravasation. Similar impairment was seen with the inhibition of Mac-1, a receptor for ICAM-1. Blockade of LFA-1, another ICAM-1 receptor, prevented neutrophil adherence to endothelium and extravasation in heart grafts. As inflammatory responses in the heart are of great relevance to public health, this imaging approach holds promise for studying cardiac-specific mechanisms of leukocyte recruitment and identifying novel therapeutic targets for treating heart disease.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Rothhammer, V., et al (2011). "Th17 lymphocytes traffic to the central nervous system independently of alpha4 integrin expression during EAE" J Exp Med 208(12): 2465-2476.
PubMed
The integrin alpha4beta1 (VLA-4) is used by encephalitogenic T cells to enter the central nervous system (CNS). However, both Th1 and Th17 cells are capable of inducing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), and the molecular cues mediating the infiltration of Th1 versus Th17 cells into the CNS have not yet been defined. We investigated how blocking of alpha4 integrins affected trafficking of Th1 and Th17 cells into the CNS during EAE. Although antibody-mediated inhibition of alpha4 integrins prevented EAE when MOG(35-55)-specific Th1 cells were adoptively transferred, Th17 cells entered the brain, but not the spinal cord parenchyma, irrespective of alpha4 blockade. Accordingly, T cell-conditional alpha4-deficient mice were not resistant to actively induced EAE but showed an ataxic syndrome with predominantly supraspinal infiltrates of IL-23R(+)CCR6(+)CD4(+) T cells. The entry of alpha4-deficient Th17 cells into the CNS was abolished by blockade of LFA-1 (alphaLbeta2 integrin). Thus, Th1 cells preferentially infiltrate the spinal cord via an alpha4 integrin-mediated mechanism, whereas the entry of Th17 cells into the brain parenchyma occurs in the absence of alpha4 integrins but is dependent on the expression of alphaLbeta2. These observations have implications for the understanding of lesion localization, immunosurveillance, and drug design in multiple sclerosis.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Thomas, S. Y., et al (2011). "PLZF induces an intravascular surveillance program mediated by long-lived LFA-1-ICAM-1 interactions" J Exp Med 208(6): 1179-1188.
PubMed
Innate-like NKT cells conspicuously accumulate within the liver microvasculature of healthy mice, crawling on the luminal side of endothelial cells, but their general recirculation pattern and the mechanism of their intravascular behavior have not been elucidated. Using parabiotic mice, we demonstrated that, despite their intravascular location, most liver NKT cells failed to recirculate. Antibody blocking experiments established that they were retained locally through constitutive LFA-1-intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) 1 interactions. This unprecedented lifelong intravascular residence could be induced in conventional CD4 T cells by the sole expression of promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF), a transcription factor specifically expressed in the NKT lineage. These findings reveal the unique genetic and biochemical pathway that underlies the innate intravascular surveillance program of NKT cells.
in vivo LFA-1 neutralization
Pearl, J. I., et al (2011). "Short-term immunosuppression promotes engraftment of embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells" Cell Stem Cell 8(3): 309-317.
PubMed
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are an attractive source for tissue regeneration and repair therapies because they can be differentiated into virtually any cell type in the adult body. However, for this approach to succeed, the transplanted ESCs must survive long enough to generate a therapeutic benefit. A major obstacle facing the engraftment of ESCs is transplant rejection by the immune system. Here we show that blocking leukocyte costimulatory molecules permits ESC engraftment. We demonstrate the success of this immunosuppressive therapy for mouse ESCs, human ESCs, mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), human induced pluripotent stem cells, and more differentiated ESC/(iPSCs) derivatives. Additionally, we provide evidence describing the mechanism by which inhibition of costimulatory molecules suppresses T cell activation. This report describes a short-term immunosuppressive approach capable of inducing engraftment of transplanted ESCs and iPSCs, providing a significant improvement in our mechanistic understanding of the critical role costimulatory molecules play in leukocyte activation.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inflammation switches the chemoattractant requirements for naive lymphocyte entry into lymph nodes.
In Cell on 20 February 2025 by Chen, K. Y., De Giovanni, M., et al.
PubMed
Sustained lymphocyte migration from blood into lymph nodes (LNs) is important for immune responses. The CC-chemokine receptor-7 (CCR7) ligand CCL21 is required for LN entry but is downregulated during inflammation, and it has been unclear how recruitment is maintained. Here, we show that the oxysterol biosynthetic enzyme cholesterol-25-hydroxylase (Ch25h) is upregulated in LN high endothelial venules during viral infection. Lymphocytes become dependent on oxysterols, generated through a transcellular endothelial-fibroblast metabolic pathway, and the receptor EBI2 for inflamed LN entry. Additionally, Langerhans cells are an oxysterol source. Ch25h is also expressed in inflamed peripheral endothelium, and EBI2 mediates B cell recruitment in a tumor model. Finally, we demonstrate that LN CCL19 is critical in lymphocyte recruitment during inflammation. Thus, our work explains how naive precursor trafficking is sustained in responding LNs, identifies a role for oxysterols in cell recruitment into inflamed tissues, and establishes a logic for the CCR7 two-ligand system.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Spatial and functional targeting of intratumoral Tregs reverses CD8+ T cell exhaustion and promotes cancer immunotherapy.
In J Clin Invest on 23 May 2024 by Zhou, L., Velegraki, M., et al.
PubMed
Intratumoral Tregs are key mediators of cancer immunotherapy resistance, including anti-programmed cell death (ligand) 1 [anti-PD-(L)1] immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). The mechanisms driving Treg infiltration into the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the consequence on CD8+ T cell exhaustion remain elusive. Here, we report that heat shock protein gp96 (also known as GRP94) was indispensable for Treg tumor infiltration, primarily through the roles of gp96 in chaperoning integrins. Among various gp96-dependent integrins, we found that only LFA-1 (αL integrin), and not αV, CD103 (αE), or β7 integrin, was required for Treg tumor homing. Loss of Treg infiltration into the TME by genetic deletion of gp96/LFA-1 potently induced rejection of tumors in multiple ICB-resistant murine cancer models in a CD8+ T cell-dependent manner, without loss of self-tolerance. Moreover, gp96 deletion impeded Treg activation primarily by suppressing IL-2/STAT5 signaling, which also contributed to tumor regression. By competing for intratumoral IL-2, Tregs prevented the activation of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, drove thymocyte selection-associated high mobility group box protein (TOX) induction, and induced bona fide CD8+ T cell exhaustion. By contrast, Treg ablation led to striking CD8+ T cell activation without TOX induction, demonstrating clear uncoupling of the 2 processes. Our study reveals that the gp96/LFA-1 axis plays a fundamental role in Treg biology and suggests that Treg-specific gp96/LFA-1 targeting represents a valuable strategy for cancer immunotherapy without inflicting autoinflammatory conditions.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
KMT2D regulates activation, localization, and integrin expression by T-cells.
In Front Immunol on 20 May 2024 by Potter, S. J., Zhang, L., et al.
PubMed
Individuals with Kabuki syndrome present with immunodeficiency; however, how pathogenic variants in the gene encoding the histone-modifying enzyme lysine methyltransferase 2D (KMT2D) lead to immune alterations remain poorly understood. Following up on our prior report of KMT2D-altered integrin expression in B-cells, we performed targeted analyses of KMT2D's influence on integrin expression in T-cells throughout development (thymocytes through peripheral T-cells) in murine cells with constitutive- and conditional-targeted Kmt2d deletion. Using high-throughput RNA-sequencing and flow cytometry, we reveal decreased expression (both at the transcriptional and translational levels) of a cluster of leukocyte-specific integrins, which perturb aspects of T-cell activation, maturation, adhesion/localization, and effector function. H3K4me3 ChIP-PCR suggests that these evolutionary similar integrins are under direct control of KMT2D. KMT2D loss also alters multiple downstream programming/signaling pathways, including integrin-based localization, which can influence T-cell populations. We further demonstrated that KMT2D deficiency is associated with the accumulation of murine CD8+ single-positive (SP) thymocytes and shifts in both human and murine peripheral T-cell populations, including the reduction of the CD4+ recent thymic emigrant (RTE) population. Together, these data show that the targeted loss of Kmt2d in the T-cell lineage recapitulates several distinct features of Kabuki syndrome-associated immune deficiency and implicates epigenetic mechanisms in the regulation of integrin signaling.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Three-dimensional morphologic and molecular atlases of nasal vasculature.
In Nat Cardiovasc Res on 1 May 2023 by Hong, S. P., Yang, M. J., et al.
PubMed
Understanding the function of the nasal vasculature in homeostasis and pathogenesis of common nasal diseases is important. Here we describe an extensive network of venous sinusoids (VSs) in mouse and human nasal mucosa. The endothelium of the VSs expressed Prox1 (considered to be a constitutive marker of lymphatic endothelium) and high levels of VCAM-1 and exhibited unusual cell-to-cell junctions. VSs are supported by circular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and surrounded by immune cells. The nasal mucosa also showed a rich supply of lymphatic vessels with distinctive features, such as the absence of the lymphatic marker LYVE1 and sharp-ended capillaries. In mouse models of allergic rhinitis or acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, Prox1+ VSs were regressed or compromised. However, in aged mice, the VSs lost the SMC support and were expanded and enlarged. Our findings demonstrate three-dimensional morphological and molecular heterogeneities of the nasal vasculature and offer insights into their associations with nasal inflammation, infection and aging.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Influence of circadian clocks on adaptive immunity and vaccination responses.
In Nat Commun on 30 January 2023 by Ince, L., Barnoud, C., et al.
PubMed
The adaptive immune response is under circadian control, yet, why adaptive immune reactions continue to exhibit circadian changes over long periods of time is unknown. Using a combination of experimental and mathematical modeling approaches, we show here that dendritic cells migrate from the skin to the draining lymph node in a time-of-day-dependent manner, which provides an enhanced likelihood for functional interactions with T cells. Rhythmic expression of TNF in the draining lymph node enhances BMAL1-controlled ICAM-1 expression in high endothelial venules, resulting in lymphocyte infiltration and lymph node expansion. Lymph node cellularity continues to be different for weeks after the initial time-of-day-dependent challenge, which governs the immune response to vaccinations directed against Hepatitis A virus as well as SARS-CoV-2. In this work, we present a mechanistic understanding of the time-of-day dependent development and maintenance of an adaptive immune response, providing a strategy for using time-of-day to optimize vaccination regimes.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Trogocytic-molting of T-cell microvilli controls T-cell clonal expansion
In Research Square on 15 June 2022 by Park, J., Kim, J., et al.
-
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Mechanically active integrins target lytic secretion at the immune synapse to facilitate cellular cytotoxicity.
In Nat Commun on 9 June 2022 by Wang, M. S., Hu, Y., et al.
PubMed
Cytotoxic lymphocytes fight pathogens and cancer by forming immune synapses with infected or transformed target cells and then secreting cytotoxic perforin and granzyme into the synaptic space, with potent and specific killing achieved by this focused delivery. The mechanisms that establish the precise location of secretory events, however, remain poorly understood. Here we use single cell biophysical measurements, micropatterning, and functional assays to demonstrate that localized mechanotransduction helps define the position of secretory events within the synapse. Ligand-bound integrins, predominantly the αLβ2 isoform LFA-1, function as spatial cues to attract lytic granules containing perforin and granzyme and induce their fusion with the plasma membrane for content release. LFA-1 is subjected to pulling forces within secretory domains, and disruption of these forces via depletion of the adaptor molecule talin abrogates cytotoxicity. We thus conclude that lymphocytes employ an integrin-dependent mechanical checkpoint to enhance their cytotoxic power and fidelity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Trogocytic-molting of T-cell microvilli controls T-cell clonal expansion
In bioRxiv on 4 May 2022 by Park, J., Kim, J., et al.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Development of Tbet- and CD11c-expressing B cells in a viral infection requires T follicular helper cells outside of germinal centers.
In Immunity on 8 February 2022 by Song, W., Antao, O. Q., et al.
PubMed
Tbet+CD11c+ B cells arise during type 1 pathogen challenge, aging, and autoimmunity in mice and humans. Here, we examined the developmental requirements of this B cell subset. In acute infection, T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, but not Th1 cells, drove Tbet+CD11c+ B cell generation through proximal delivery of help. Tbet+CD11c+ B cells developed prior to germinal center (GC) formation, exhibiting phenotypic and transcriptional profiles distinct from GC B cells. Fate tracking revealed that most Tbet+CD11c+ B cells developed independently of GC entry and cell-intrinsic Bcl6 expression. Tbet+CD11c+ and GC B cells exhibited minimal repertoire overlap, indicating distinct developmental pathways. As the infection resolved, Tbet+CD11c+ B cells localized to the marginal zone where splenic retention depended on integrins LFA-1 and VLA-4, forming a competitive memory subset that contributed to antibody production and secondary GC seeding upon rechallenge. Therefore, Tbet+CD11c+ B cells comprise a GC-independent memory subset capable of rapid and robust recall responses.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
RNA sequence analysis reveals ITGAL/CD11A as a stromal regulator of murine low-grade glioma growth.
In Neuro Oncol on 5 January 2022 by de Andrade Costa, A., Chatterjee, J., et al.
PubMed
Emerging insights from numerous laboratories have revealed important roles for nonneoplastic cells in the development and progression of brain tumors. One of these nonneoplastic cellular constituents, glioma-associated microglia (GAM), represents a unique population of brain monocytes within the tumor microenvironment that have been reported to both promote and inhibit glioma proliferation. To elucidate the role of GAM in the setting of low-grade glioma (LGG), we leveraged RNA sequencing meta-analysis, genetically engineered mouse strains, and human biospecimens.
-
-
-
In vivo experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
Expeditious recruitment of circulating memory CD8 T cells to the liver facilitates control of malaria.
In Cell Rep on 2 November 2021 by Lefebvre, M. N., Surette, F. A., et al.
PubMed
Circulating memory CD8 T cell trafficking and protective capacity during liver-stage malaria infection remains undefined. We find that effector memory CD8 T cells (Tem) infiltrate the liver within 6 hours after malarial or bacterial infections and mediate pathogen clearance. Tem recruitment coincides with rapid transcriptional upregulation of inflammatory genes in Plasmodium-infected livers. Recruitment requires CD8 T cell-intrinsic LFA-1 expression and the presence of liver phagocytes. Rapid Tem liver infiltration is distinct from recruitment to other non-lymphoid tissues in that it occurs both in the absence of liver tissue resident memory "sensing-and-alarm" function and ∼42 hours earlier than in lung infection by influenza virus. These data demonstrate relevance for Tem in protection against malaria and provide generalizable mechanistic insights germane to control of liver infections.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Neuroscience
Glia limitans superficialis oxidation and breakdown promote cortical cell death after repetitive head injury.
In JCI Insight on 8 October 2021 by Mason, H. D., Johnson, A. M., et al.
PubMed
Repetitive mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI) disrupt CNS barriers, the erosion of which has been linked to long-term neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions. Although much attention has been devoted to CNS vasculature following mTBI, little is known about the glia limitans superficialis - a barrier of surface-associated astrocytes that helps protect the CNS parenchyma and maintain homeostasis. Here, we identify the glia limitans superficialis as a crucial barrier surface whose breakdown after acute repeat mTBI facilitates increased cell death and recruitment of peripheral myelomonocytic cells. Using intravital microscopy, we show that brain-resident microglia fortify this structure after a single mTBI, yet they fail to do so following secondary injury, which triggers massive recruitment of myelomonocytic cells from the periphery that contribute to further destruction of the glia limitans superficialis but not cortical cell death. We demonstrate, instead, that reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated in response to repetitive head injury are largely responsible for enhanced cortical cell death, and therapeutic administration of the antioxidant glutathione markedly reduces this cell death, preserves the glia limitans, and prevents myelomonocytic cells from entering the brain parenchyma. Collectively, our findings underscore the importance of preserving the glia limitans superficialis after brain injury and offer a therapeutic means to protect this structure and the underlying cortex.
-
-
-
In vitro experiments
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Pathology
Auto-aggressive CXCR6+ CD8 T cells cause liver immune pathology in NASH.
In Nature on 1 April 2021 by Dudek, M., Pfister, D., et al.
PubMed
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a manifestation of systemic metabolic disease related to obesity, and causes liver disease and cancer1,2. The accumulation of metabolites leads to cell stress and inflammation in the liver3, but mechanistic understandings of liver damage in NASH are incomplete. Here, using a preclinical mouse model that displays key features of human NASH (hereafter, NASH mice), we found an indispensable role for T cells in liver immunopathology. We detected the hepatic accumulation of CD8 T cells with phenotypes that combined tissue residency (CXCR6) with effector (granzyme) and exhaustion (PD1) characteristics. Liver CXCR6+ CD8 T cells were characterized by low activity of the FOXO1 transcription factor, and were abundant in NASH mice and in patients with NASH. Mechanistically, IL-15 induced FOXO1 downregulation and CXCR6 upregulation, which together rendered liver-resident CXCR6+ CD8 T cells susceptible to metabolic stimuli (including acetate and extracellular ATP) and collectively triggered auto-aggression. CXCR6+ CD8 T cells from the livers of NASH mice or of patients with NASH had similar transcriptional signatures, and showed auto-aggressive killing of cells in an MHC-class-I-independent fashion after signalling through P2X7 purinergic receptors. This killing by auto-aggressive CD8 T cells fundamentally differed from that by antigen-specific cells, which mechanistically distinguishes auto-aggressive and protective T cell immunity.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Role of LFA-1 integrin in the control of a lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection.
In Virulence on 1 December 2020 by Perro, M., Iannacone, M., et al.
PubMed
Leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) is the most widely expressed member of the β2 integrin family of cell-cell adhesion molecules. Although LFA-1 is thought to regulate multiple aspects of T cell immunity, its role in the response of CD8+ T cells to viral infections remains unclear. Indeed, compelling clinical evidence shows that loss of LFA-1 function predisposes to infection in humans but animal models show limited to no susceptibility to infection. Here, we addressed this conundrum in a mouse model of infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), where CD8+ T cells are necessary and sufficient to confer protection. To this end, we followed the fate and function of wild-type and LFA-1 deficient virus-specific CD8+ T cells and assessed the effect of blocking anti-LFA-1 monoclonal antibody in the outcome of infection. Our analysis of viral clearance and T cell responses using transcriptome profiling reveals a role for LFA-1 as a gatekeeper of effector T cell survival and dysfunction that when defective can predispose to LCMV infection.
-
-
-
Cardiovascular biology
Requirements for cDC2 positioning in blood-exposed regions of the neonatal and adult spleen.
In J Exp Med on 2 November 2020 by Liu, D., Wu, J., et al.
PubMed
The marginal zone (MZ) of the spleen contains multiple cell types that are involved in mounting rapid immune responses against blood-borne pathogens, including conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) and MZ B cells. MZ B cells develop later than other B cell types and are sparse in neonatal mice. Here, we show that cDC2s are abundant in the MZ of neonatal compared with adult mice. We find that conditions associated with reduced MZ B cell numbers in adult mice cause increased cDC2 occupancy of the MZ. Treatment with the S1PR1-modulating drug, FTY720, causes cDC2 movement into the MZ through the indirect mechanism of displacing MZ B cells into follicles. Splenic cDC2s express high amounts of α4β1 and αLβ2 integrins and depend on these integrins and the adaptor Talin for their retention in blood-exposed regions of the spleen. Splenic CD4 T cell activation by particulate antigens is increased in mice with higher cDC2 density in the MZ, including in neonatal mice. Our work establishes requirements for homeostatic cDC2 positioning in the spleen and provides evidence that localization in blood-exposed regions around the white pulp augments cDC2 capture of particulate antigens. We suggest that MZ positioning of cDC2s partially compensates for the lack of MZ B cells during the neonatal period.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Pre-existing intratumoral CD8 T cells substantially contribute to control tumors following therapeutic anti-CD40 and polyI:C based vaccination
In bioRxiv on 1 September 2020 by Stevens, A. D., Bullock, T. N. J., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Neuroscience
In Vivo Chimeric Alzheimer's Disease Modeling of Apolipoprotein E4 Toxicity in Human Neurons.
In Cell Rep on 28 July 2020 by Najm, R., Zalocusky, K. A., et al.
PubMed
Despite its clear impact on Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk, apolipoprotein (apo) E4's contributions to AD etiology remain poorly understood. Progress in answering this and other questions in AD research has been limited by an inability to model human-specific phenotypes in an in vivo environment. Here we transplant human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived neurons carrying normal apoE3 or pathogenic apoE4 into human apoE3 or apoE4 knockin mouse hippocampi, enabling us to disentangle the effects of apoE4 produced in human neurons and in the brain environment. Using single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq), we identify key transcriptional changes specific to human neuron subtypes in response to endogenous or exogenous apoE4. We also find that Aβ from transplanted human neurons forms plaque-like aggregates, with differences in localization and interaction with microglia depending on the transplant and host apoE genotype. These findings highlight the power of in vivo chimeric disease modeling for studying AD.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
Gasdermin-D-dependent IL-1α release from microglia promotes protective immunity during chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection.
In Nat Commun on 23 July 2020 by Batista, S. J., Still, K. M., et al.
PubMed
Microglia, resident immune cells of the CNS, are thought to defend against infections. Toxoplasma gondii is an opportunistic infection that can cause severe neurological disease. Here we report that during T. gondii infection a strong NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine transcriptional signature is overrepresented in blood-derived macrophages versus microglia. Interestingly, IL-1α is enriched in microglia and IL-1β in macrophages. We find that mice lacking IL-1R1 or IL-1α, but not IL-1β, have impaired parasite control and immune cell infiltration within the brain. Further, we show that microglia, not peripheral myeloid cells, release IL-1α ex vivo. Finally, we show that ex vivo IL-1α release is gasdermin-D dependent, and that gasdermin-D and caspase-1/11 deficient mice show deficits in brain inflammation and parasite control. These results demonstrate that microglia and macrophages are differently equipped to propagate inflammation, and that in chronic T. gondii infection, microglia can release the alarmin IL-1α, promoting neuroinflammation and parasite control.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
TRPM5 Negatively Regulates Calcium-Dependent Responses in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated B Lymphocytes.
In Cell Rep on 9 June 2020 by Sakaguchi, T., Okumura, R., et al.
PubMed
B cells produce high amounts of cytokines and immunoglobulins in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. Calcium signaling cascades are critically involved in cytokine production of T cells, and the cytosolic calcium concentration is regulated by calcium-activated monovalent cation channels (CAMs). Calcium signaling is also implicated in B cell activation; however, its involvement in the cytokine production of LPS-stimulated B cells remains less well characterized. Here, we show that the transient receptor potential melastatin 5 channel (TRPM5), which is one of the CAMs, negatively modulates calcium signaling, thereby regulating LPS-induced proliferative and inflammatory responses by B cells. LPS-stimulated B cells of Trpm5-deficient mice exhibit an increased cytosolic calcium concentration, leading to enhanced proliferation and the production of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and CXCL10. Furthermore, Trpm5-deficient mice show an exacerbation of endotoxic shock with high mortality. Our findings demonstrate the importance of TRPM5-dependent regulatory mechanisms in LPS-induced calcium signaling of splenic B cells.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Visualization of T Cell Migration in the Spleen Reveals a Network of Perivascular Pathways that Guide Entry into T Zones.
In Immunity on 19 May 2020 by Chauveau, A., Pirgova, G., et al.
PubMed
Lymphocyte homeostasis and immune surveillance require that T and B cells continuously recirculate between secondary lymphoid organs. Here, we used intravital microscopy to define lymphocyte trafficking routes within the spleen, an environment of open blood circulation and shear forces unlike other lymphoid organs. Upon release from arterioles into the red pulp sinuses, T cells latched onto perivascular stromal cells in a manner that was independent of the chemokine receptor CCR7 but sensitive to Gi protein-coupled receptor inhibitors. This latching sheltered T cells from blood flow and enabled unidirectional migration to the bridging channels and then to T zones, entry into which required CCR7. Inflammatory responses modified the chemotactic cues along the perivascular homing paths, leading to rapid block of entry. Our findings reveal a role for vascular structures in lymphocyte recirculation through the spleen, indicating the existence of separate entry and exit routes and that of a checkpoint located at the gate to the T zone.
-