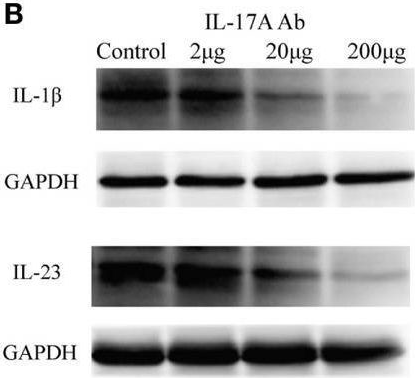
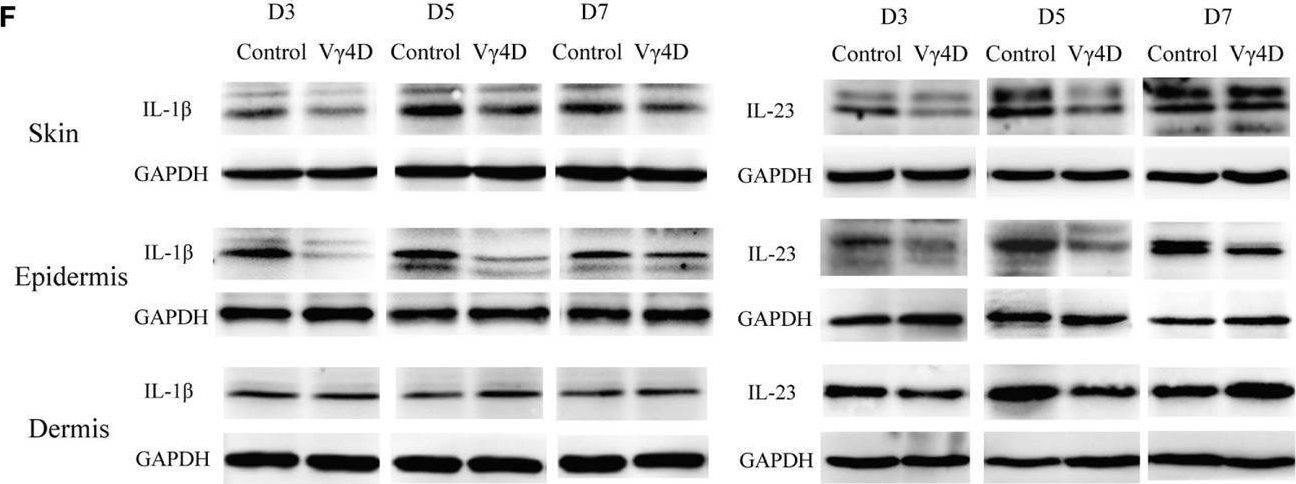
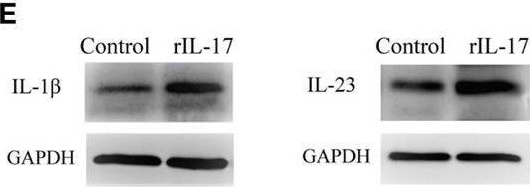
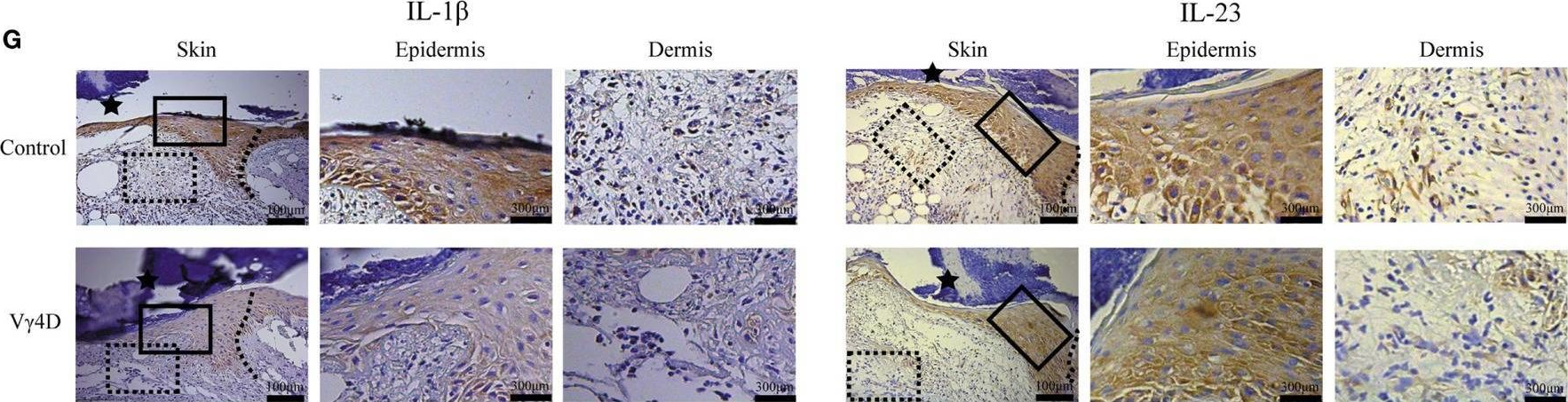
InVivoMAb anti-mouse IL-12 p40
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Recombinant mouse IL-12 p70 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization p40 affinity chromatography Immunoprecipitation ELISA Flow cytometry Western blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_1107698 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo IL-12 neutralization
Dann, S. M., et al (2018). "Giardia Infection of the Small Intestine Induces Chronic Colitis in Genetically Susceptible Hosts" J Immunol 201(2): 548-559.
PubMed
Chemokines are small chemotactic proteins that have a crucial role in leukocyte recruitment into tissue. Targeting these mediators has been suggested as a potential therapeutic option in inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis. Using quantitative RT-PCR, we found CCL7, a chemokine ligand known to interact with multiple C-C chemokine receptors, to be markedly increased in lesional psoriasis as opposed to atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, non-lesional psoriatic and normal control skin. Surprisingly, this increase in CCL7 mRNA expression exceeded that of all other chemokines investigated, and keratinocytes and dermal blood endothelial cells were identified as its likely cellular sources. In an imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mouse model, CCL7 had a profound impact on myeloid cell inflammation as well as on the upregulation of key pro-psoriatic cytokines such as CCL20, IL-12p40 and IL-17C, while its blockade led to an increase in the antipsoriatic cytokine IL-4. In humans receiving the TNF-alpha-blocker infliximab, CCL7 was downregulated in lesional psoriatic skin already within 16 hours after a single intravenous infusion. These data suggest that CCL7 acts as a driver of TNF-alpha-dependent Th1/Th17-mediated inflammation in lesional psoriatic skin.
in vivo IL-12 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Deligne, C., et al (2015). "Anti-CD20 therapy induces a memory Th1 response through the IFN-gamma/IL-12 axis and prevents protumor regulatory T-cell expansion in mice" Leukemia 29(4): 947-957.
PubMed
The long-lasting clinical response by lymphoma patients to anti-CD20 therapy has been attributed to the induction of an anti-tumor adaptive immunity. We previously demonstrated that a CD4-dependent mechanism is responsible for the long-term protection of CD20(+) tumor-bearing mice by anti-CD20 treatment. Here, we compare tumor immunity in tumor-bearing animals that did or did not receive anti-CD20 treatment. Splenic CD4(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) expanded substantially in untreated mice that exhibited then a reduced survival, whereas Tregs depletion led to long-term survival of the animals, suggesting the establishment of a Treg-dependent immunosuppressive environment after tumor injection. Strikingly, anti-CD20 therapy reversed the initial expansion of Tregs, and was accompanied by a marked increase in the number of Th1 cells, with no detectable change in Th2 and Th17 cell numbers. Interleukin-12 serum level was also increased by the anti-CD20 treatment, and activated myeloid dendritic cells producing interleukin-12 could be detected in lymph nodes of treated animals, while interferon-gamma blockade strongly reduced survival. Also, CD4(+) effector memory T cells were evidenced in surviving animals, and the transfer of CD4(+) T cells induced long-term protection. Thus, anti-CD20 therapy promotes strong anti-tumor adaptive immunity, opposes Treg expansion and inhibits tumor cells from maintaining an immunosuppressive environment.
in vivo IL-12 neutralization
Brunner, P. M., et al (2015). "CCL7 contributes to the TNF-alpha-dependent inflammation of lesional psoriatic skin" Exp Dermatol 24(7): 522-528.
PubMed
Chemokines are small chemotactic proteins that have a crucial role in leukocyte recruitment into tissue. Targeting these mediators has been suggested as a potential therapeutic option in inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis. Using quantitative RT-PCR, we found CCL7, a chemokine ligand known to interact with multiple C-C chemokine receptors, to be markedly increased in lesional psoriasis as opposed to atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, non-lesional psoriatic and normal control skin. Surprisingly, this increase in CCL7 mRNA expression exceeded that of all other chemokines investigated, and keratinocytes and dermal blood endothelial cells were identified as its likely cellular sources. In an imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mouse model, CCL7 had a profound impact on myeloid cell inflammation as well as on the upregulation of key pro-psoriatic cytokines such as CCL20, IL-12p40 and IL-17C, while its blockade led to an increase in the antipsoriatic cytokine IL-4. In humans receiving the TNF-alpha-blocker infliximab, CCL7 was downregulated in lesional psoriatic skin already within 16 hours after a single intravenous infusion. These data suggest that CCL7 acts as a driver of TNF-alpha-dependent Th1/Th17-mediated inflammation in lesional psoriatic skin.
in vivo IL-12 neutralization
Villegas-Mendez, A., et al (2015). "Parasite-specific CD4+IFN-gamma+IL-10+ T cells distribute within both lymphoid and non-lymphoid compartments and are controlled systemically by IL-27 and ICOS during blood-stage malaria infection" Infect Immun. pii
PubMed
Immune-mediated pathology in IL-10 deficient mice during blood-stage malaria infection typically manifests in non-lymphoid organs, such as the liver and lung. Thus, it is critical to define the cellular sources of IL-10 in these sensitive non-lymphoid compartments during infection. Moreover, it is important to determine if IL-10 production is controlled through conserved or disparate molecular programmes in distinct anatomical locations during malaria infection, as this may enable spatiotemporal tuning of the regulatory immune response. In this study, using dual IFN-gamma-YFP and IL-10-GFP reporter mice we show that CD4+YFP+ T cells are the major source of IL-10 in both lymphoid and non-lymphoid compartments throughout the course of blood-stage P. yoelii infection. Mature splenic CD4+YFP+GFP+ T cells, which preferentially expressed high levels of CCR5, were capable of migrating to and seeding the non-lymphoid tissues, indicating that the systemically distributed host-protective cells have a common developmental history. Despite exhibiting comparable phenotypes, CD4+YFP+GFP+ T cells from the liver and lung produced significantly higher quantities of IL-10 than their splenic counterparts, showing that the CD4+YFP+GFP+ T cells exert graded functions in distinct tissue locations during infection. Unexpectedly, given the unique environmental conditions within discrete non-lymphoid and lymphoid organs, we show that IL-10 production by CD4+YFP+ T cells is controlled systemically during malaria infection through IL-27R signalling that is supported post-CD4+ T cell priming by ICOS signalling. The results in this study substantially improve our understanding of the systemic IL-10 response to malaria infection, particularly within sensitive non-lymphoid organs.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Tang, W., et al (2014). "The oncoprotein and transcriptional regulator Bcl-3 governs plasticity and pathogenicity of autoimmune T cells" Immunity 41(4): 555-566.
PubMed
Bcl-3 is an atypical member of the IkappaB family that modulates transcription in the nucleus via association with p50 (NF-kappaB1) or p52 (NF-kappaB2) homodimers. Despite evidence attesting to the overall physiologic importance of Bcl-3, little is known about its cell-specific functions or mechanisms. Here we demonstrate a T-cell-intrinsic function of Bcl-3 in autoimmunity. Bcl-3-deficient T cells failed to induce disease in T cell transfer-induced colitis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. The protection against disease correlated with a decrease in Th1 cells that produced the cytokines IFN-gamma and GM-CSF and an increase in Th17 cells. Although differentiation into Th1 cells was not impaired in the absence of Bcl-3, differentiated Th1 cells converted to less-pathogenic Th17-like cells, in part via mechanisms involving expression of the RORgammat transcription factor. Thus, Bcl-3 constrained Th1 cell plasticity and promoted pathogenicity by blocking conversion to Th17-like cells, revealing a unique type of regulation that shapes adaptive immunity.
Immunoprecipitation
p40 affinity chromatography
Abdi, K., et al (2014). "Free IL-12p40 monomer is a polyfunctional adaptor for generating novel IL-12-like heterodimers extracellularly" J Immunol 192(12): 6028-6036.
PubMed
IL-12p40 partners with the p35 and p19 polypeptides to generate the heterodimeric cytokines IL-12 and IL-23, respectively. These cytokines play critical and distinct roles in host defense. The assembly of these heterodimers is thought to take place within the cell, resulting in the secretion of fully functional cytokines. Although the p40 subunit alone can also be rapidly secreted in response to inflammatory signals, its biological significance remains unclear. In this article, we show that the secreted p40 monomer can generate de novo IL-12-like activities by combining extracellularly with p35 released from other cells. Surprisingly, an unbiased proteomic analysis reveals multiple such extracellular binding partners for p40 in the serum of mice after an endotoxin challenge. We biochemically validate the binding of one of these novel partners, the CD5 Ag-like glycoprotein, to the p40 monomer. Nevertheless, the assembled p40-CD5L heterodimer does not recapitulate the biological activity of IL-12. These findings underscore the plasticity of secreted free p40 monomer, suggesting that p40 functions as an adaptor that is able to generate multiple de novo composites in combination with other locally available polypeptide partners after secretion.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Ruffell, B., et al (2014). "Macrophage IL-10 blocks CD8+ T cell-dependent responses to chemotherapy by suppressing IL-12 expression in intratumoral dendritic cells" Cancer Cell 26(5): 623-637.
PubMed
Blockade of colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) limits macrophage infiltration and improves response of mammary carcinomas to chemotherapy. Herein we identify interleukin (IL)-10 expression by macrophages as the critical mediator of this phenotype. Infiltrating macrophages were the primary source of IL-10 within tumors, and therapeutic blockade of IL-10 receptor (IL-10R) was equivalent to CSF-1 neutralization in enhancing primary tumor response to paclitaxel and carboplatin. Improved response to chemotherapy was CD8(+) T cell-dependent, but IL-10 did not directly suppress CD8(+) T cells or alter macrophage polarization. Instead, IL-10R blockade increased intratumoral dendritic cell expression of IL-12, which was necessary for improved outcomes. In human breast cancer, expression of IL12A and cytotoxic effector molecules were predictive of pathological complete response rates to paclitaxel.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Tarrio, M. L., et al (2014). "Proliferation conditions promote intrinsic changes in NK cells for an IL-10 response" J Immunol 193(1): 354-363.
PubMed
Constitutively found at high frequencies, the role for NK cell proliferation remains unclear. In this study, a shift in NK cell function from predominantly producing IFN-gamma, a cytokine with proinflammatory and antimicrobial functions, to producing the immunoregulatory cytokine IL-10 was defined during extended murine CMV infection. The response occurred at times subsequent to IL-12 production, but the NK cells elicited acquired responsiveness to IL-12 and IL-21 for IL-10 production. Because neither IL-12 nor IL-21 was required in vivo, however, additional pathways appeared to be available to promote NK cell IL-10 expression. In vitro studies with IL-2 to support proliferation and in vivo adoptive transfers into murine CMV-infected mice demonstrated that NK cell proliferation and further division enhanced the change. In contrast to the sustained open profile of the IFN-gamma gene, NK cells responding to infection acquired histone modifications in the IL-10 gene indicative of changing from a closed to an open state. The IL-10 response to IL-12 was proliferation dependent ex vivo if the NK cells had not yet expanded in vivo but independent if they had. Thus, a novel role for proliferation in supporting changing innate cell function is reported.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Yu, X., et al (2013). "A multifunctional chimeric chaperone serves as a novel immune modulator inducing therapeutic antitumor immunity" Cancer Res 73(7): 2093-2103.
PubMed
Converting the immunosuppressive tumor environment into one that is favorable to the induction of antitumor immunity is indispensable for effective cancer immunotherapy. Here, we strategically incorporate a pathogen (i.e., flagellin)-derived, NF-kappaB-stimulating “danger” signal into the large stress protein or chaperone Grp170 (HYOU1/ORP150) that was previously shown to facilitate antigen crosspresentation. This engineered chimeric molecule (i.e., Flagrp170) is capable of transporting tumor antigens and concurrently inducing functional activation of dendritic cells (DC). Intratumoral administration of adenoviruses expressing Flagrp170 induces a superior antitumor response against B16 melanoma and its distant lung metastasis compared with unmodified Grp170 and flagellin. The enhanced tumor destruction is accompanied with significantly increased tumor infiltration by CD8(+) cells as well as elevation of IFN-gamma and interleukin (IL)-12 levels in the tumor sites. In situ Ad.Flagrp170 therapy provokes systemic activation of CTLs that recognize several antigens naturally expressing in melanoma (e.g., gp100/PMEL and TRP2/DCT). The mechanistic studies using CD11c-DTR transgenic mice and Batf3-deficient mice reveal that CD8alpha(+) DCs are required for the improved T-cell crosspriming. Antibody neutralization assays show that IL-12 and IFN-gamma are essential for the Flagrp170-elicited antitumor response, which also involves CD8(+) T cells and natural killer cells. The therapeutic efficacy of Flagrp170 and its immunostimulating activity are also confirmed in mouse prostate cancer and colon carcinoma. Together, targeting the tumor microenvironment with this chimeric chaperone is highly effective in mobilizing or restoring antitumor immunity, supporting the potential therapeutic use of this novel immunomodulator in the treatment of metastatic diseases.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Chappert, P., et al (2013). "Specific gut commensal flora locally alters T cell tuning to endogenous ligands" Immunity 38(6): 1198-1210.
PubMed
Differences in gut commensal flora can dramatically influence autoimmune responses, but the mechanisms behind this are still unclear. We report, in a Th1-cell-driven murine model of autoimmune arthritis, that specific gut commensals, such as segmented filamentous bacteria, have the ability to modulate the activation threshold of self-reactive T cells. In the local microenvironment of gut-associated lymphoid tissues, inflammatory cytokines elicited by the commensal flora dynamically enhanced the antigen responsiveness of T cells that were otherwise tuned down to a systemic self-antigen. Together with subtle differences in early lineage differentiation, this ultimately led to an enhanced recruitment of pathogenic Th1 cells and the development of a more severe form of autoimmune arthritis. These findings define a key role for the gut commensal flora in sustaining ongoing autoimmune responses through the local fine tuning of T-cell-receptor-proximal activation events in autoreactive T cells.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Gwyer Findlay, E., et al (2013). "IL-27 receptor signaling regulates CD4+ T cell chemotactic responses during infection" J Immunol 190(9): 4553-4561.
PubMed
IL-27 exerts pleiotropic suppressive effects on naive and effector T cell populations during infection and inflammation. Surprisingly, however, the role of IL-27 in restricting or shaping effector CD4(+) T cell chemotactic responses, as a mechanism to reduce T cell-dependent tissue inflammation, is unknown. In this study, using Plasmodium berghei NK65 as a model of a systemic, proinflammatory infection, we demonstrate that IL-27R signaling represses chemotaxis of infection-derived splenic CD4(+) T cells in response to the CCR5 ligands, CCL4 and CCL5. Consistent with these observations, CCR5 was expressed on significantly higher frequencies of splenic CD4(+) T cells from malaria-infected, IL-27R-deficient (WSX-1(-/-)) mice than from infected wild-type mice. We find that IL-27 signaling suppresses splenic CD4(+) T cell CCR5-dependent chemotactic responses during infection by restricting CCR5 expression on CD4(+) T cell subtypes, including Th1 cells, and also by controlling the overall composition of the CD4(+) T cell compartment. Diminution of the Th1 response in infected WSX-1(-/-) mice in vivo by neutralization of IL-12p40 attenuated CCR5 expression by infection-derived CD4(+) T cells and also reduced splenic CD4(+) T cell chemotaxis toward CCL4 and CCL5. These data reveal a previously unappreciated role for IL-27 in modulating CD4(+) T cell chemotactic pathways during infection, which is related to its capacity to repress Th1 effector cell development. Thus, IL-27 appears to be a key cytokine that limits the CCR5-CCL4/CCL5 axis during inflammatory settings.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Villegas-Mendez, A., et al (2013). "IL-27 receptor signalling restricts the formation of pathogenic, terminally differentiated Th1 cells during malaria infection by repressing IL-12 dependent signals" PLoS Pathog 9(4): e1003293.
PubMed
The IL-27R, WSX-1, is required to limit IFN-gamma production by effector CD4(+) T cells in a number of different inflammatory conditions but the molecular basis of WSX-1-mediated regulation of Th1 responses in vivo during infection has not been investigated in detail. In this study we demonstrate that WSX-1 signalling suppresses the development of pathogenic, terminally differentiated (KLRG-1(+)) Th1 cells during malaria infection and establishes a restrictive threshold to constrain the emergent Th1 response. Importantly, we show that WSX-1 regulates cell-intrinsic responsiveness to IL-12 and IL-2, but the fate of the effector CD4(+) T cell pool during malaria infection is controlled primarily through IL-12 dependent signals. Finally, we show that WSX-1 regulates Th1 cell terminal differentiation during malaria infection through IL-10 and Foxp3 independent mechanisms; the kinetics and magnitude of the Th1 response, and the degree of Th1 cell terminal differentiation, were comparable in WT, IL-10R1(-)/(-) and IL-10(-)/(-) mice and the numbers and phenotype of Foxp3(+) cells were largely unaltered in WSX-1(-)/(-) mice during infection. As expected, depletion of Foxp3(+) cells did not enhance Th1 cell polarisation or terminal differentiation during malaria infection. Our results significantly expand our understanding of how IL-27 regulates Th1 responses in vivo during inflammatory conditions and establishes WSX-1 as a critical and non-redundant regulator of the emergent Th1 effector response during malaria infection.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Mack, E. A., et al (2011). "Type 1 interferon induction of natural killer cell gamma interferon production for defense during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection" MBio 2(4).
PubMed
Natural killer (NK) cells are equipped to innately produce the cytokine gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) in part because they basally express high levels of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (STAT4). Type 1 interferons (IFNs) have the potential to activate STAT4 and promote IFN-gamma expression, but concurrent induction of elevated STAT1 negatively regulates access to the pathway. As a consequence, it has been difficult to detect type 1 IFN stimulation of NK cell IFN-gamma during viral infections in the presence of STAT1 and to understand the evolutionary advantage for maintaining the pathway. The studies reported here evaluated NK cell responses following infections with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) in the compartment handling the earliest events after infection, the peritoneal cavity. The production of type 1 IFNs, both IFN-alpha and IFN-beta, was shown to be early and of short duration, peaking at 30 h after challenge. NK cell IFN-gamma expression was detected with overlapping kinetics and required activating signals delivered through type 1 IFN receptors and STAT4. It took place under conditions of high STAT4 levels but preceded elevated STAT1 expression in NK cells. The IFN-gamma response reduced viral burdens. Interestingly, increases in STAT1 were delayed in NK cells compared to other peritoneal exudate cell (PEC) populations. Taken together, the studies demonstrate a novel mechanism for stimulating IFN-gamma production and elucidate a biological role for type 1 IFN access to STAT4 in NK cells.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
Prabhakara, R., et al (2011). "Suppression of the inflammatory immune response prevents the development of chronic biofilm infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Infect Immun 79(12): 5010-5018.
PubMed
Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause of prosthetic implant infections, which can become chronic due to the ability of S. aureus to grow as a biofilm. Little is known about adaptive immune responses to these infections in vivo. We hypothesized that S. aureus elicits inflammatory Th1/Th17 responses, associated with biofilm formation, instead of protective Th2/Treg responses. We used an adapted mouse model of biofilm-mediated prosthetic implant infection to determine chronic infection rates, Treg cell frequencies, and local cytokine levels in Th1-biased C57BL/6 and Th2-biased BALB/c mice. All C57BL/6 mice developed chronic S. aureus implant infection at all time points tested. However, over 75% of BALB/c mice spontaneously cleared the infection without adjunctive therapy and demonstrated higher levels of Th2 cytokines and anti-inflammatory Treg cells. When chronic infection rates in mice deficient in the Th2 cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) via STAT6 mutation in a BALB/c background were assessed, the mice were unable to clear the S. aureus implant infection. Additionally, BALB/c mice depleted of Treg cells via an anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody (MAb) were also unable to clear the infection. In contrast, the C57BL/6 mice that were susceptible to infection were able to eliminate S. aureus biofilm populations on infected intramedullary pins once the Th1 and Th17 responses were diminished by MAb treatment with anti-IL-12 p40. Together, these results indicate that Th2/Treg responses are mechanisms of protection against chronic S. aureus implant infection, as opposed to Th1/Th17 responses, which may play a role in the development of chronic infection.
in vivo IL-12p40 neutralization
ELISA
Massacand, J. C., et al (2009). "Helminth products bypass the need for TSLP in Th2 immune responses by directly modulating dendritic cell function" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(33): 13968-13973.
PubMed
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is an interleukin (IL)-7-like cytokine, mainly expressed by epithelial cells, and key to the development of allergic responses. The well-documented involvement of TSLP in allergy has led to the conviction that TSLP promotes the development of inflammatory Th2 cell responses. However, we now report that the interaction of TSLP with its receptor (TSLPR) has no functional impact on the development of protective Th2 immune responses after infection with 2 helminth pathogens, Heligmosomoides polygyrus and Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Mice deficient in the TSLP binding chain of the TSLPR (TSLPR(-/-)) exhibited normal Th2 cell differentiation, protective immunity and memory responses against these two distinct rodent helminths. In contrast TSLP was found to be necessary for the development of protective Th2 responses upon infection with the helminth Trichuris muris (T. muris). TSLP inhibited IL-12p40 production in response to T. muris infection, and treatment of TSLPR(-/-) animals with neutralizing anti-IL-12p40 monoclonal antibody (mAb) was able to reverse susceptibility and attenuate IFN-gamma production. We additionally demonstrated that excretory-secretory (ES) products from H. polygyrus and N. brasiliensis, but not T. muris, were capable of directly suppressing dendritic cell (DC) production of IL-12p40, thus bypassing the need for TSLP. Taken together, our data show that the primary function of TSLP is to directly suppress IL-12 secretion, thus supporting Th2 immune responses.
Product Citations
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
IL-12/IL-23 neutralization is ineffective for alopecia areata in mice and humans.
In The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology on 1 December 2019 by Ortolan, L. S., Kim, S. R., et al.
PubMed
-
-
Macrophages orchestrate elimination of Shigella from the intestinal epithelial cell niche via TLR-induced IL-12 and IFN-γ.
In Cell Host Microbe on 10 September 2025 by Eislmayr, K. D., Nichols, C. A., et al.
PubMed
Bacteria of the genus Shigella replicate in intestinal epithelial cells and cause shigellosis, a severe diarrheal disease that resolves spontaneously in most healthy individuals. During shigellosis, neutrophils are abundantly recruited to the gut and have long been thought to be central to Shigella control and pathogenesis. However, how shigellosis resolves remains poorly understood due to the longstanding lack of a tractable and physiological animal model. Here, using our newly developed Nlrc4-/-Casp11-/- mouse model of shigellosis, we unexpectedly find no major role for neutrophils in limiting Shigella or in disease pathogenesis. Instead, we uncover an essential role for macrophages in the host control of Shigella. Macrophages respond to Shigella via Toll-like receptors (TLRs) to produce IL-12, which then induces IFN-γ, a cytokine that is essential to control Shigella replication in intestinal epithelial cells. Collectively, our findings reshape our understanding of the innate immune response to Shigella.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cardiovascular biology
Pharmacological inhibition of IL12β is effective in treating pressure overload-induced cardiac inflammation and heart failure.
In Front Immunol on 2 September 2025 by Bhattarai, U., He, X., et al.
PubMed
Emerging evidence indicates that inflammation regulates cardiac remodeling and heart failure (HF). IL12β is a subunit for proinflammatory cytokines IL12 and IL23. However, the effect of IL12β inhibition on HF development and the underlying mechanism is not understood.
-
-
FcRn-silencing of IL-12Fc prevents toxicity of local IL-12 therapy and prolongs survival in experimental glioblastoma.
In Nat Commun on 22 May 2025 by Beffinger, M. M., Schellhammer, L., et al.
PubMed
Glioblastoma remains a challenging indication for immunotherapy: the blood-brain barrier hampers accessibility for systemic treatments and the immunosuppressive microenvironment impedes immune attack. Intratumoral therapy with the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-12 (IL-12) can revert immunosuppression but leakage into the circulation causes treatment-limiting toxicity. Here we engineer an IL-12Fc fusion cytokine with reduced binding to the neonatal Fc receptor FcRn. FcRn-silenced IL-12Fc avoids FcRn-mediated brain export, thus exhibits prolonged brain retention and reduced blood levels, which prevents toxicity. In murine glioblastoma, FcRn-silenced IL-12Fc induces more durable responses with negligible systemic cytokine exposure and boosts the efficacy of radio- and chemotherapy. It triggers anti-tumor responses independently of peripheral T cell influx or lymphopenia and leads to inflammatory polarization of the tumor microenvironment in patient-derived glioblastoma explants. FcRn-silencing of IL-12Fc may unlock the full potential of IL-12 for brain cancer therapy and could be further applied to containing the activity of other therapeutics targeting neurological diseases.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Influence of MyD88 and αβ T cells on mesenteric lymph node innate lymphoid cell populations during Toxoplasma gondii infection.
In PLoS One on 29 April 2025 by Belmares-Ortega, J., Zara Issoufou Kapran, F., et al.
PubMed
First encounter of Toxoplasma with the host immune system occurs within tissues of the intestine, including the intestinal mucosa and draining lymph nodes. In this study, we focused on the mesenteric lymph node compartment, the central hub of adaptive immune induction following orally acquired infection. We examined innate lymphoid cells (ILC) in mesenteric lymph nodes during Toxoplasma infection, determining the influence of MyD88 and the T lymphocyte compartment on ILC subset distribution, IFN-γ production, MHC class II expression and proliferation. Collectively, we observed an ILC1-dominated response that was impacted by both MyD88 and T lymphocytes. We also found a population of putative ILC that were negative for signature transcription factors associated with ILC1, 2 and 3 subsets. This study increases our understanding of ILC-mediated immunity during Toxoplasma infection and points to the complex interactions with which these cells engage T cell and MyD88-dependent immunity.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Macrophages orchestrate elimination ofShigellafrom the intestinal epithelial cell niche via TLR-induced IL-12 and IFN-γ
In bioRxiv on 22 January 2025 by Eislmayr, K. D., Langner, C., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Systemic IFN-I combined with topical TLR7/8 agonists promotes distant tumor suppression by c-Jun-dependent IL-12 expression in dendritic cells.
In Nat Cancer on 1 January 2025 by Sanlorenzo, M., Novoszel, P., et al.
PubMed
Dendritic cell (DC) activation by pattern recognition receptors like Toll-like-receptors (TLRs) is crucial for cancer immunotherapies. Here, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the TLR7/8 agonist imiquimod (IMQ) in treating both local tumors and distant metastases. Administered orally, IMQ activates plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) to produce systemic type I interferons (IFN-I) required for TLR7/8 upregulation in DCs and macrophages, sensitizing them to topical IMQ treatment, which is essential for therapeutic efficacy. The mechanism involves c-Jun/AP-1 mediating TLR7/8 signaling in IFN-I-primed DCs, upregulating the pDC-recruiting chemokine CCL2 and the anti-angiogenic cytokine interleukin-12, which suppresses VEGF-A production leading to tumor necrosis and regression. Combining topical and systemic IMQ or IFN-I generates a CD8+ T cell-dependent response at metastatic sites, reinforced by PD-1 blockade, leading to long-lasting memory. Analysis of cohorts of patients with melanoma demonstrates DC-specific TLR7/8 upregulation by IFN-I, supporting the translational potential of combining systemic IFN-I and topical IMQ to improve immunotherapy of topically accessible tumors.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Heightened innate immune state induced by viral vector leads to enhanced response to challenge and prolongs malaria vaccine protection.
In iScience on 20 December 2024 by Gbédandé, K., Ibitokou, S. A., et al.
PubMed
Cytomegalovirus is a promising vaccine vector; however, mechanisms promoting CD4 T cell responses to challenge, by CMV as a vector, are unknown. The ability of MCMV to prolong immunity generated by short-lived malaria vaccine was tested. MCMV provided non-specific protection to challenge with Plasmodium and increased interleukin-12 (IL-12) and CD8α+ dendritic cell (DC) numbers through prolonged MCMV-dependent interferon gamma (IFN-γ) production. This late innate response to MCMV increased IL-12 upon challenge and increased the polyclonal CD4 effector T cell response to Plasmodium, protecting in an IL-12-dependent manner. Although Plasmodium-vaccine-induced protection decayed by d200, MCMV restored protection through IFN-γ. Mechanistically, protection depended on MCMV-induced-IFN-γ increasing CD8α+ DCs and IL-12p40. MCMV expressing a Plasmodium epitope increased parasite-specific CD4 effector and effector memory T cells persisting after malaria vaccination, both phenotypes reported to protect. Overall, enhanced innate cell status, a mechanism of heterologous protection by MCMV, led to a stronger T cell response to challenge.
-
-
T lymphocyte-dependent IL-10 down-regulates a cytokine storm driven by Toxoplasma gondii GRA24.
In MBio on 13 November 2024 by Doherty, C. M., Patterson, P. R., et al.
PubMed
As a model organism in the study of immunity to infection, Toxoplasma gondii has been instrumental in establishing key principles of host anti-microbial defense and its regulation. Here, we employed an attenuated uracil auxotroph strain of Type I Toxoplasma designated OMP to further untangle the early immune response to this parasitic pathogen. Experiments using αβ T cell-deficient Tcrb-/- mice unexpectedly revealed that an intact αβ T lymphocyte compartment was essential to survive infection with OMP. Subsequent antibody depletion and knockout mouse experiments demonstrated contributions from CD4+ T cells and most predominantly CD8+ T cells in resistance. Using transgenic knockout mice, we found only a partial requirement for IFN-γ and a lack of requirement for Toll-like receptor (TLR) adaptor MyD88 in resistance. In contrast to other studies on Toxoplasma, the ability to survive OMP infection did not require IL-12p40. Surprisingly, T cell-dependent IL-10 was found to be critical for survival, and deficiency of this cytokine triggered an abnormally high systemic inflammatory response. We also found that parasite molecule GRA24, a dense granule protein that triggers TLR-independent IL-12 production, acts as a virulence factor contributing to death of OMP-infected Tcrb-/- and IL-10-/- mice. Furthermore, resistance against OMP was restored in Tcrb-/- mice via monoclonal depletion of IL-12p40, suggesting that GRA24-induced IL-12 underlies the fatal immunopathology observed. Collectively, our studies provide insight into a novel and rapidly arising T lymphocyte-dependent anti-inflammatory response to T. gondii which operates independently of MyD88 and IL-12 and that depends on the function of parasite-dense granule protein GRA24.IMPORTANCEAs a model infectious microbe and an important human pathogen, the apicomplexan Toxoplasma gondii has provided many important insights into innate and adaptive immunity to infection. We show here that a low virulence uracil auxotrophic Toxoplasma strain emerges as a virulent parasite in the absence of an intact T cell compartment. Both CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes are required for optimal protection, in line with previous findings in other models of Toxoplasma infection. Nevertheless, several novel aspects of the response were identified in our study. Protection occurs independently of IL-12 and MyD88 and only partially requires IFN-γ. This is noteworthy particularly because the cytokines IL-12 and IFN-γ have previously been regarded as essential for protective immunity to T. gondii. Instead, we identified the anti-inflammatory effects of T cell-dependent IL-10 as the critical factor enabling host survival. The parasite dense granule protein GRA24, a host-directed mitogen-activated protein kinase activator, was identified as a major virulence factor in T cell-deficient hosts. Collectively, our results provide new and unexpected insights into host resistance to Toxoplasma.
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A CXCR4 partial agonist improves immunotherapy by targeting polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells and cancer-driven granulopoiesis
In bioRxiv on 11 October 2024 by Qian, J., Ma, C., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
HIF-2α-dependent induction of miR-29a restrains TH1 activity during T cell dependent colitis.
In Nat Commun on 14 September 2024 by Czopik, A. K., McNamee, E. N., et al.
PubMed
Metabolic imbalance leading to inflammatory hypoxia and stabilization of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs) is a hallmark of inflammatory bowel diseases. We hypothesize that HIF could be stabilized in CD4+ T cells during intestinal inflammation and alter the functional responses of T cells via regulation of microRNAs. Our assays reveal markedly increased T cell-intrinsic hypoxia and stabilization of HIF protein during experimental colitis. microRNA screen in primary CD4+ T cells points us towards miR-29a and our subsequent studies identify a selective role for HIF-2α in CD4-cell-intrinsic induction of miR-29a during hypoxia. Mice with T cell-intrinsic HIF-2α deletion display elevated T-bet (target of miR-29a) levels and exacerbated intestinal inflammation. Mice with miR-29a deficiency in T cells show enhanced intestinal inflammation. T cell-intrinsic overexpression of HIF-2α or delivery of miR-29a mimetic dampen TH1-driven colitis. In this work, we show a previously unrecognized function for hypoxia-dependent induction of miR-29a in attenuating TH1-mediated inflammation.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
PIKfyve, expressed by CD11c-positive cells, controls tumor immunity.
In Nat Commun on 28 June 2024 by Choi, J. E., Qiao, Y., et al.
PubMed
Cancer treatment continues to shift from utilizing traditional therapies to targeted ones, such as protein kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy. Mobilizing dendritic cells (DC) and other myeloid cells with antigen presenting and cancer cell killing capacities is an attractive but not fully exploited approach. Here, we show that PIKFYVE is a shared gene target of clinically relevant protein kinase inhibitors and high expression of this gene in DCs is associated with poor patient response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. Genetic and pharmacological studies demonstrate that PIKfyve ablation enhances the function of CD11c+ cells (predominantly dendritic cells) via selectively altering the non-canonical NF-κB pathway. Both loss of Pikfyve in CD11c+ cells and treatment with apilimod, a potent and specific PIKfyve inhibitor, restrained tumor growth, enhanced DC-dependent T cell immunity, and potentiated ICB efficacy in tumor-bearing mouse models. Furthermore, the combination of a vaccine adjuvant and apilimod reduced tumor progression in vivo. Thus, PIKfyve negatively regulates the function of CD11c+ cells, and PIKfyve inhibition has promise for cancer immunotherapy and vaccine treatment strategies.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
Synergistic effects of Smac mimetic APG-1387 with anti-PD-1 antibody are attributed to increased CD3 + NK1.1 + cell recruitment secondary to induction of cytokines from tumor cells.
In Cancer Cell Int on 24 May 2024 by Pan, W., Luo, Q., et al.
PubMed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are approved for the treatment of various tumors, but the response rate is not satisfactory in certain malignancies. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP) ubiquitin-E3 ligase activity is involved in the regulation of immune responses. APG-1387 is a novel second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (Smac) mimetic IAP inhibitor. The aim of this study was to explore the synergistic effect of APG-1387 when combined with anti-PD-1 antibody in a preclinical setting.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
PIKfyve controls dendritic cell function and tumor immunity
In bioRxiv on 2 March 2024 by Choi, J. E., Qiao, Y., et al.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
MEK inhibitors increase the mortality rate in mice with LPS-induced inflammation through IL-12-NO signaling.
In Cell Death Discov on 13 October 2023 by Hashimoto, R., Koide, H., et al.
PubMed
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an endotoxin that can cause an acute inflammatory response. Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the most important innate immune system components and is synthesized by inducible NOS (iNOS) in macrophages in response to stimulation with LPS. LPS activates the RAS-RAF-mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase (MEK)-extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling cascade in macrophages. The purpose of this study was to examine how the combination of LPS and MEK inhibitors, which have been used as anticancer agents in recent years, affects inflammation. We showed that MEK inhibitors enhanced iNOS expression and NO production in LPS-stimulated mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. A MEK inhibitor increased the mortality rate in mice with LPS-induced inflammation. The expression of the cytokine interleukin-12 (IL-12) in macrophages was enhanced by the MEK inhibitor, as shown by a cytokine array and ELISA. IL-12 enhanced iNOS expression and NO production in response to LPS. We also showed that tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) was secreted by macrophage after stimulation with LPS and that TNF-α and IL-12 synergistically induced iNOS expression and NO production. An anti-IL-12 neutralizing antibody prevented NO production and mortality in an LPS-induced inflammation mouse model in the presence of a MEK inhibitor. These results suggest that the MEK inhibitor increases the mortality rate in mice with LPS-induced inflammation through IL-12-NO signaling.
-
-
-
Western Blotting
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
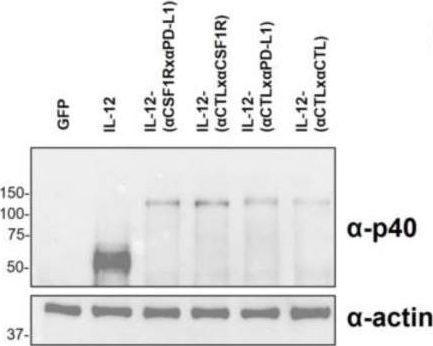
Intratumoral injection of IL-12-encoding mRNA targeted to CSFR1 and PD-L1 exerts potent anti-tumor effects without substantial systemic exposure.
In Mol Ther Nucleic Acids on 12 September 2023 by Di Trani, C. A., Cirella, A., et al.
PubMed
IL-12 is a potent cytokine for cancer immunotherapy. However, its systemic delivery as a recombinant protein has shown unacceptable toxicity in the clinic. Currently, the intratumoral injection of IL-12-encoding mRNA or DNA to avoid such side effects is being evaluated in clinical trials. In this study, we aimed to improve this strategy by further favoring IL-12 tethering to the tumor. We generated in vitro transcribed mRNAs encoding murine single-chain IL-12 fused to diabodies binding to CSF1R and/or PD-L1. These targeted molecules are expressed in the tumor microenvironment, especially on myeloid cells. The binding capacity of chimeric constructs and the bioactivity of IL-12 were demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Doses as low as 0.5 μg IL-12-encoding mRNA achieved potent antitumor effects in subcutaneously injected B16-OVA and MC38 tumors. Treatment delivery was associated with increases in IL-12p70 and IFN-γ levels in circulation. Fusion of IL-12 to the diabodies exerted comparable efficacy against bilateral tumor models. However, it achieved tethering to myeloid cells infiltrating the tumor, resulting in nearly undetectable systemic levels of IL-12 and IFN-γ. Overall, tethering IL-12 to intratumoral myeloid cells in the mRNA-transferred tumors achieves similar efficacy while reducing the dangerous systemic bioavailability of IL-12.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
pH Dependence of a GPR4 Selective Antagonist Hampers Its Therapeutic Potential.
In J Pharmacol Exp Ther on 1 July 2023 by Stalewski, J., Shih, A. Y., et al.
PubMed
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by chronic mucosal inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and is associated with extracellular acidification of mucosal tissue. Several extracellular pH-sensing receptors, including G protein-coupled receptor 4 (GPR4), play an important role in the regulation of inflammatory and immune responses, and GPR4 deficiency has been shown to be protective in IBD animal models. To confirm the therapeutic potential of GPR4 antagonism in IBD, we tested Compound 13, a selective GPR4 antagonist, in the interleukin 10-/- mouse model of colitis. Despite good exposures and albeit there was a trend toward improvement for a few readouts, Compound 13 treatment did not improve colitis in this model, and there were no signs of target engagement. Interestingly, Compound 13 behaved as an "orthosteric" antagonist, i.e., its potency was pH dependent and mostly inactive at pH levels lower than 6.8 with preferential binding to the inactive conformation of GPR4. Mutagenesis studies confirmed Compound 13 likely binds to the conserved orthosteric binding site in G protein-coupled receptors, where a histidine sits in GPR4 likely preventing Compound 13 binding when protonated in acidic conditions. While the exact mucosal pH in the human disease and relevant IBD mice models is unknown, it is well established that the degree of acidosis is positively correlated with the degree of inflammation, suggesting Compound 13 is not an ideal tool to study the role of GPR4 in moderate to severe inflammatory conditions. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Compound 13, a reported selective GPR4 antagonist, has been widely used to assess the therapeutic potential of GPR4, a pH-sensing receptor, for numerous indications. Its pH dependence and mechanism of inhibition identified in this study clearly highlights the limitations of this chemotype for target validation.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
XCR1+ DCs are critical for T cell-mediated immunotherapy of chronic viral infections.
In Cell Rep on 28 February 2023 by Domenjo-Vila, E., Casella, V., et al.
PubMed
The contribution of cross-presenting XCR1+ dendritic cells (DCs) and SIRPα+ DCs in maintaining T cell function during exhaustion and immunotherapeutic interventions of chronic infections remains poorly characterized. Using the mouse model of chronic LCMV infection, we found that XCR1+ DCs are more resistant to infection and highly activated compared with SIRPα+ DCs. Exploiting XCR1+ DCs via Flt3L-mediated expansion or XCR1-targeted vaccination notably reinvigorates CD8+ T cells and improves virus control. Upon PD-L1 blockade, XCR1+ DCs are not required for the proliferative burst of progenitor exhausted CD8+ T (TPEX) cells but are indispensable to sustain the functionality of exhausted CD8+ T (TEX) cells. Combining anti-PD-L1 therapy with increased frequency of XCR1+ DCs improves functionality of TPEX and TEX subsets, while increase of SIRPα+ DCs dampened their proliferation. Together, this demonstrates that XCR1+ DCs are crucial for the success of checkpoint inhibitor-based therapies through differential activation of exhausted CD8+ T cell subsets.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Sterile liver injury induces a protective tissue-resident cDC1-ILC1 circuit through cDC1-intrinsic cGAS-STING-dependent IL-12 production.
In Cell Rep on 28 February 2023 by Hildreth, A. D., Padilla, E. T., et al.
PubMed
Tissue-resident immune cells are critical to the initiation and potentiation of inflammation. However, the tissue-protective cellular communication networks initiated by resident immunity during sterile inflammation are not well understood. Using single-cell transcriptomic analysis, we show the liver-resident cell connectome and signalome during acute liver injury. These analyses identify Il12b as a central regulator of liver injury-associated changes in gene expression. Interleukin (IL)-12 produced by conventional type 1 dendritic cells (cDC1s) is required for protection during acute injury through activation of interferon (IFN)-γ production by liver-resident type 1 innate lymphoid cells (ILC1s). Using a targeted in vivo CRISPR-Cas9 screen of innate immune sensing pathways, we find that cDC1-intrinsic cGAS-STING signaling acts upstream of IL-12 production to initiate early protective immune responses. Our study identifies the core communication hubs initiated by tissue-resident innate immune cells during sterile inflammation in vivo and implicates cDC1-derived IL-12 as an important regulator of this process.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
T-cell activation Rho GTPase-activating protein maintains intestinal homeostasis by regulating intestinal T helper cells differentiation through the gut microbiota.
In Front Microbiol on 28 January 2023 by He, R., Chen, J., et al.
PubMed
Common variants of the T-cell activation Rho GTPase-activating protein (TAGAP) are associated with the susceptibility to human inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs); however, the underlying mechanisms are still unknown. Here, we show that TAGAP deficiency or TAGAP expression downregulation caused by TAGAP gene polymorphism leads to decreased production of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), such as reg3g, which subsequently causes dysregulation of the gut microbiota, which includes Akkermansia muciniphila and Bacteroides acidifaciens strains. These two strains can polarize T helper cell differentiation in the gut, and aggravate systemic disease associated with the dextran sodium sulfate-induced (DSS) disease's phenotype in mice. More importantly, we demonstrated that recombinant reg3g protein or anti-p40 monoclonal antibody exerted therapeutic effects for the treatment of DSS-induced colitis in wild-type and TAGAP-deficient mice, suggesting that they are potential medicines for human IBD treatment, and they may also have a therapeutic effect for the patients who carry the common variant of TAGAP rs212388.
-