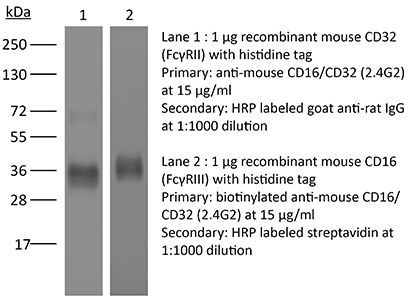
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD16/CD32
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2b, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 8.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | BALB/c mouse macrophage cell line J774 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo Fc receptor blocking Fc receptor blocking Flow cytometry Immunofluorescence |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 8.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_2736987 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Pasqual, G., et al (2018). "Monitoring T cell-dendritic cell interactions in vivo by intercellular enzymatic labelling" Nature 553(7689): 496-500.
PubMed
Interactions between different cell types are essential for multiple biological processes, including immunity, embryonic development and neuronal signalling. Although the dynamics of cell-cell interactions can be monitored in vivo by intravital microscopy, this approach does not provide any information on the receptors and ligands involved or enable the isolation of interacting cells for downstream analysis. Here we describe a complementary approach that uses bacterial sortase A-mediated cell labelling across synapses of immune cells to identify receptor-ligand interactions between cells in living mice, by generating a signal that can subsequently be detected ex vivo by flow cytometry. We call this approach for the labelling of ‘kiss-and-run’ interactions between immune cells ‘Labelling Immune Partnerships by SorTagging Intercellular Contacts’ (LIPSTIC). Using LIPSTIC, we show that interactions between dendritic cells and CD4(+) T cells during T-cell priming in vivo occur in two distinct modalities: an early, cognate stage, during which CD40-CD40L interactions occur specifically between T cells and antigen-loaded dendritic cells; and a later, non-cognate stage during which these interactions no longer require prior engagement of the T-cell receptor. Therefore, LIPSTIC enables the direct measurement of dynamic cell-cell interactions both in vitro and in vivo. Given its flexibility for use with different receptor-ligand pairs and a range of detectable labels, we expect that this approach will be of use to any field of biology requiring quantification of intercellular communication.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Pasqual, G., et al (2018). "Monitoring T cell-dendritic cell interactions in vivo by intercellular enzymatic labelling" Nature 553(7689): 496-500.
PubMed
Interactions between different cell types are essential for multiple biological processes, including immunity, embryonic development and neuronal signalling. Although the dynamics of cell-cell interactions can be monitored in vivo by intravital microscopy, this approach does not provide any information on the receptors and ligands involved or enable the isolation of interacting cells for downstream analysis. Here we describe a complementary approach that uses bacterial sortase A-mediated cell labelling across synapses of immune cells to identify receptor-ligand interactions between cells in living mice, by generating a signal that can subsequently be detected ex vivo by flow cytometry. We call this approach for the labelling of ‘kiss-and-run’ interactions between immune cells ‘Labelling Immune Partnerships by SorTagging Intercellular Contacts’ (LIPSTIC). Using LIPSTIC, we show that interactions between dendritic cells and CD4(+) T cells during T-cell priming in vivo occur in two distinct modalities: an early, cognate stage, during which CD40-CD40L interactions occur specifically between T cells and antigen-loaded dendritic cells; and a later, non-cognate stage during which these interactions no longer require prior engagement of the T-cell receptor. Therefore, LIPSTIC enables the direct measurement of dynamic cell-cell interactions both in vitro and in vivo. Given its flexibility for use with different receptor-ligand pairs and a range of detectable labels, we expect that this approach will be of use to any field of biology requiring quantification of intercellular communication.
in vivo Fc receptor blocking
Arlauckas SP, Garris CS, Kohler RH, Kitaoka M, Cuccarese MF, Yang KS, Miller MA, Carlson JC, Freeman GJ, Anthony RM, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2017). "In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 thera
PubMed
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the immune checkpoint anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (aPD-1) have demonstrated impressive benefits for the treatment of some cancers; however, these drugs are not always effective, and we still have a limited understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to their efficacy or lack thereof. We used in vivo imaging to uncover the fate and activity of aPD-1 mAbs in real time and at subcellular resolution in mice. We show that aPD-1 mAbs effectively bind PD-1+ tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells at early time points after administration. However, this engagement is transient, and aPD-1 mAbs are captured within minutes from the T cell surface by PD-1- tumor-associated macrophages. We further show that macrophage accrual of aPD-1 mAbs depends both on the drug's Fc domain glycan and on Fcγ receptors (FcγRs) expressed by host myeloid cells and extend these findings to the human setting. Finally, we demonstrate that in vivo blockade of FcγRs before aPD-1 mAb administration substantially prolongs aPD-1 mAb binding to tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and enhances immunotherapy-induced tumor regression in mice. These investigations yield insight into aPD-1 target engagement in vivo and identify specific Fc/FcγR interactions that can be modulated to improve checkpoint blockade therapy.
in vivo Fc receptor blocking
Arlauckas SP, Garris CS, Kohler RH, Kitaoka M, Cuccarese MF, Yang KS, Miller MA, Carlson JC, Freeman GJ, Anthony RM, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2017). "In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 thera
PubMed
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the immune checkpoint anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (aPD-1) have demonstrated impressive benefits for the treatment of some cancers; however, these drugs are not always effective, and we still have a limited understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to their efficacy or lack thereof. We used in vivo imaging to uncover the fate and activity of aPD-1 mAbs in real time and at subcellular resolution in mice. We show that aPD-1 mAbs effectively bind PD-1+ tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells at early time points after administration. However, this engagement is transient, and aPD-1 mAbs are captured within minutes from the T cell surface by PD-1- tumor-associated macrophages. We further show that macrophage accrual of aPD-1 mAbs depends both on the drug's Fc domain glycan and on Fcγ receptors (FcγRs) expressed by host myeloid cells and extend these findings to the human setting. Finally, we demonstrate that in vivo blockade of FcγRs before aPD-1 mAb administration substantially prolongs aPD-1 mAb binding to tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and enhances immunotherapy-induced tumor regression in mice. These investigations yield insight into aPD-1 target engagement in vivo and identify specific Fc/FcγR interactions that can be modulated to improve checkpoint blockade therapy.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Arbelaez, C. A., et al (2015). "IL-7/IL-7 Receptor Signaling Differentially Affects Effector CD4+ T Cell Subsets Involved in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis" J Immunol 195(5): 1974-1983.
PubMed
IL-17-producing CD4(+) T (Th17) cells, along with IFN-gamma-expressing Th1 cells, represent two major pathogenic T cell subsets in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS). The cytokines and transcription factors involved in the development and effector functions of Th1 and Th17 cells have been largely characterized. Among them, IL-23 is essential for the generation of stable and encephalitogenic Th17 cells and for the development of EAE. The IL-7/IL-7R signaling axis participates in cell survival, and perturbation of this pathway has been associated with enhanced susceptibility to MS. A link between IL-23-driven pathogenic T cells and IL-7/IL-7R signaling has previously been proposed, but has not been formally addressed. In the current study, we showed that Th17 cells from mice with EAE express high levels of IL-7Ralpha compared with Th1 cells. Using mice that constitutively express IL-7Ralpha on T cells, we determined that sustained IL-7R expression in IL-23R-deficient mice could not drive pathogenic T cells and the development of EAE. IL-7 inhibited the differentiation of Th17 cells, but promoted IFN-gamma and GM-CSF secretion in vitro. In vivo IL-7/anti-IL-7 mAb complexes selectively expanded and enhanced the proliferation of CXCR3-expressing Th1 cells, but did not impact Th17 cells and EAE development in wild-type and IL-23R-deficient mice. Importantly, high IL-7 expression was detected in the CNS during EAE and could drive the plasticity of Th17 cells to IFN-gamma-producing T cells. Together, these data address the contribution of IL-23/IL-23R and IL-7/IL-7R signaling in Th17 and Th1 cell dynamics during CNS autoimmunity.
in vivo Fc receptor blocking
Yu, X., et al (2015). "A monoclonal antibody with anti-D-like activity in murine immune thrombocytopenia requires Fc domain function for immune thrombocytopenia ameliorative effects" Transfusion 55(6 Pt 2): 1501-1511.
PubMed
BACKGROUND: The mechanism of action of anti-D in ameliorating immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) remains unclear. The monoclonal antibody (MoAb) Ter119, which targets murine red blood cells (RBCs), has been shown to mimic the effect of anti-D in improving antibody-mediated murine ITP. The mechanism of Ter119-mediated ITP amelioration, especially the role of the antigen-binding and Fc domains, remains untested. A functional Fc domain is crucial for many therapeutic MoAb activity; therefore, the requirement of Ter119 Fc domain in ITP amelioration is investigated using outbred CD-1 mice. STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: Ter119 variants, including Ter119 F(ab’)2 fragments, deglycosylated Ter119, and afucosylated Ter119, were generated to test their effect in ameliorating antibody-induced murine ITP. In vivo inhibition of FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIIB was achieved using the Fab fragment of the FcgammaRIII/FcgammaRIIB-specific MoAb 2.4G2. RESULTS: Ter119 F(ab’)2 fragments and deglycosylated Ter119 were unable to ameliorate murine ITP or mediate phagocytosis of RBCs by RAW264.7 macrophages in vitro. Inhibition of FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIIB, as well as Ter119 defucosylation, do not affect Ter119-mediated ITP amelioration. CONCLUSION: The Fc domain of Ter119, as well as its Fc glycosylation, is required for Ter119-mediated ITP amelioration. Moreover, both Fc and Fc glycosylation are required for Ter119-mediated phagocytosis in vitro. These findings demonstrate the importance of the Fc domain in a therapeutic MoAb with anti-D-like activity.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Peske, J. D., et al (2015). "Effector lymphocyte-induced lymph node-like vasculature enables naive T-cell entry into tumours and enhanced anti-tumour immunity" Nat Commun 6: 7114.
PubMed
The presence of lymph node (LN)-like vasculature in tumours, characterized by expression of peripheral node addressin and chemokine CCL21, is correlated with T-cell infiltration and positive prognosis in breast cancer and melanoma patients. However, mechanisms controlling the development of LN-like vasculature and how it might contribute to a beneficial outcome for cancer patients are unknown. Here we demonstrate that LN-like vasculature is present in murine models of melanoma and lung carcinoma. It enables infiltration by naive T cells that significantly delay tumour outgrowth after intratumoral activation. Development of this vasculature is controlled by a mechanism involving effector CD8 T cells and NK cells that secrete LTalpha3 and IFNgamma. LN-like vasculature is also associated with organized aggregates of B lymphocytes and gp38(+) fibroblasts, which resemble tertiary lymphoid organs that develop in models of chronic inflammation. These results establish LN-like vasculature as both a consequence of and key contributor to anti-tumour immunity.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Liu, X., et al (2015). "CD47 blockade triggers T cell-mediated destruction of immunogenic tumors" Nat Med 21(10): 1209-1215.
PubMed
Macrophage phagocytosis of tumor cells mediated by CD47-specific blocking antibodies has been proposed to be the major effector mechanism in xenograft models. Here, using syngeneic immunocompetent mouse tumor models, we reveal that the therapeutic effects of CD47 blockade depend on dendritic cell but not macrophage cross-priming of T cell responses. The therapeutic effects of anti-CD47 antibody therapy were abrogated in T cell-deficient mice. In addition, the antitumor effects of CD47 blockade required expression of the cytosolic DNA sensor STING, but neither MyD88 nor TRIF, in CD11c(+) cells, suggesting that cytosolic sensing of DNA from tumor cells is enhanced by anti-CD47 treatment, further bridging the innate and adaptive responses. Notably, the timing of administration of standard chemotherapy markedly impacted the induction of antitumor T cell responses by CD47 blockade. Together, our findings indicate that CD47 blockade drives T cell-mediated elimination of immunogenic tumors.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Arbelaez, C. A., et al (2015). "IL-7/IL-7 Receptor Signaling Differentially Affects Effector CD4+ T Cell Subsets Involved in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis" J Immunol 195(5): 1974-1983.
PubMed
IL-17-producing CD4(+) T (Th17) cells, along with IFN-gamma-expressing Th1 cells, represent two major pathogenic T cell subsets in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS). The cytokines and transcription factors involved in the development and effector functions of Th1 and Th17 cells have been largely characterized. Among them, IL-23 is essential for the generation of stable and encephalitogenic Th17 cells and for the development of EAE. The IL-7/IL-7R signaling axis participates in cell survival, and perturbation of this pathway has been associated with enhanced susceptibility to MS. A link between IL-23-driven pathogenic T cells and IL-7/IL-7R signaling has previously been proposed, but has not been formally addressed. In the current study, we showed that Th17 cells from mice with EAE express high levels of IL-7Ralpha compared with Th1 cells. Using mice that constitutively express IL-7Ralpha on T cells, we determined that sustained IL-7R expression in IL-23R-deficient mice could not drive pathogenic T cells and the development of EAE. IL-7 inhibited the differentiation of Th17 cells, but promoted IFN-gamma and GM-CSF secretion in vitro. In vivo IL-7/anti-IL-7 mAb complexes selectively expanded and enhanced the proliferation of CXCR3-expressing Th1 cells, but did not impact Th17 cells and EAE development in wild-type and IL-23R-deficient mice. Importantly, high IL-7 expression was detected in the CNS during EAE and could drive the plasticity of Th17 cells to IFN-gamma-producing T cells. Together, these data address the contribution of IL-23/IL-23R and IL-7/IL-7R signaling in Th17 and Th1 cell dynamics during CNS autoimmunity.
in vivo Fc receptor blocking
Yu, X., et al (2015). "A monoclonal antibody with anti-D-like activity in murine immune thrombocytopenia requires Fc domain function for immune thrombocytopenia ameliorative effects" Transfusion 55(6 Pt 2): 1501-1511.
PubMed
BACKGROUND: The mechanism of action of anti-D in ameliorating immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) remains unclear. The monoclonal antibody (MoAb) Ter119, which targets murine red blood cells (RBCs), has been shown to mimic the effect of anti-D in improving antibody-mediated murine ITP. The mechanism of Ter119-mediated ITP amelioration, especially the role of the antigen-binding and Fc domains, remains untested. A functional Fc domain is crucial for many therapeutic MoAb activity; therefore, the requirement of Ter119 Fc domain in ITP amelioration is investigated using outbred CD-1 mice. STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: Ter119 variants, including Ter119 F(ab’)2 fragments, deglycosylated Ter119, and afucosylated Ter119, were generated to test their effect in ameliorating antibody-induced murine ITP. In vivo inhibition of FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIIB was achieved using the Fab fragment of the FcgammaRIII/FcgammaRIIB-specific MoAb 2.4G2. RESULTS: Ter119 F(ab’)2 fragments and deglycosylated Ter119 were unable to ameliorate murine ITP or mediate phagocytosis of RBCs by RAW264.7 macrophages in vitro. Inhibition of FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIIB, as well as Ter119 defucosylation, do not affect Ter119-mediated ITP amelioration. CONCLUSION: The Fc domain of Ter119, as well as its Fc glycosylation, is required for Ter119-mediated ITP amelioration. Moreover, both Fc and Fc glycosylation are required for Ter119-mediated phagocytosis in vitro. These findings demonstrate the importance of the Fc domain in a therapeutic MoAb with anti-D-like activity.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Peske, J. D., et al (2015). "Effector lymphocyte-induced lymph node-like vasculature enables naive T-cell entry into tumours and enhanced anti-tumour immunity" Nat Commun 6: 7114.
PubMed
The presence of lymph node (LN)-like vasculature in tumours, characterized by expression of peripheral node addressin and chemokine CCL21, is correlated with T-cell infiltration and positive prognosis in breast cancer and melanoma patients. However, mechanisms controlling the development of LN-like vasculature and how it might contribute to a beneficial outcome for cancer patients are unknown. Here we demonstrate that LN-like vasculature is present in murine models of melanoma and lung carcinoma. It enables infiltration by naive T cells that significantly delay tumour outgrowth after intratumoral activation. Development of this vasculature is controlled by a mechanism involving effector CD8 T cells and NK cells that secrete LTalpha3 and IFNgamma. LN-like vasculature is also associated with organized aggregates of B lymphocytes and gp38(+) fibroblasts, which resemble tertiary lymphoid organs that develop in models of chronic inflammation. These results establish LN-like vasculature as both a consequence of and key contributor to anti-tumour immunity.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Liu, X., et al (2015). "CD47 blockade triggers T cell-mediated destruction of immunogenic tumors" Nat Med 21(10): 1209-1215.
PubMed
Macrophage phagocytosis of tumor cells mediated by CD47-specific blocking antibodies has been proposed to be the major effector mechanism in xenograft models. Here, using syngeneic immunocompetent mouse tumor models, we reveal that the therapeutic effects of CD47 blockade depend on dendritic cell but not macrophage cross-priming of T cell responses. The therapeutic effects of anti-CD47 antibody therapy were abrogated in T cell-deficient mice. In addition, the antitumor effects of CD47 blockade required expression of the cytosolic DNA sensor STING, but neither MyD88 nor TRIF, in CD11c(+) cells, suggesting that cytosolic sensing of DNA from tumor cells is enhanced by anti-CD47 treatment, further bridging the innate and adaptive responses. Notably, the timing of administration of standard chemotherapy markedly impacted the induction of antitumor T cell responses by CD47 blockade. Together, our findings indicate that CD47 blockade drives T cell-mediated elimination of immunogenic tumors.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Muppidi, J. R., et al (2014). "Loss of signalling via Galpha13 in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma" Nature 516(7530): 254-258.
PubMed
Germinal centre B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (GCB-DLBCL) is a common malignancy, yet the signalling pathways that are deregulated and the factors leading to its systemic dissemination are poorly defined. Work in mice showed that sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 (S1PR2), a Galpha12 and Galpha13 coupled receptor, promotes growth regulation and local confinement of germinal centre B cells. Recent deep sequencing studies of GCB-DLBCL have revealed mutations in many genes in this cancer, including in GNA13 (encoding Galpha13) and S1PR2 (refs 5,6, 7). Here we show, using in vitro and in vivo assays, that GCB-DLBCL-associated mutations occurring in S1PR2 frequently disrupt the receptor’s Akt and migration inhibitory functions. Galpha13-deficient mouse germinal centre B cells and human GCB-DLBCL cells were unable to suppress pAkt and migration in response to S1P, and Galpha13-deficient mice developed germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma. Germinal centre B cells, unlike most lymphocytes, are tightly confined in lymphoid organs and do not recirculate. Remarkably, deficiency in Galpha13, but not S1PR2, led to germinal centre B-cell dissemination into lymph and blood. GCB-DLBCL cell lines frequently carried mutations in the Galpha13 effector ARHGEF1, and Arhgef1 deficiency also led to germinal centre B-cell dissemination. The incomplete phenocopy of Galpha13- and S1PR2 deficiency led us to discover that P2RY8, an orphan receptor that is mutated in GCB-DLBCL and another germinal centre B-cell-derived malignancy, Burkitt’s lymphoma, also represses germinal centre B-cell growth and promotes confinement via Galpha13. These findings identify a Galpha13-dependent pathway that exerts dual actions in suppressing growth and blocking dissemination of germinal centre B cells that is frequently disrupted in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Leon, B., et al (2014). "FoxP3+ regulatory T cells promote influenza-specific Tfh responses by controlling IL-2 availability" Nat Commun 5: 3495.
PubMed
Here, we test the role of FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) in controlling T follicular helper (Tfh) and germinal centre (GC) B-cell responses to influenza. In contrast to the idea that Tregs suppress T-cell responses, we find that Treg depletion severely reduces the Tfh cell response to influenza virus. Furthermore, Treg depletion prevents the accumulation of influenza-specific GCs. These effects are not due to alterations in TGFbeta availability or a precursor-progeny relationship between Tregs and Tfh cells, but are instead mediated by increased availability of IL-2, which suppresses the differentiation of Tfh cells and as a consequence, compromises the GC B response. Thus, Tregs promote influenza-specific GC responses by preventing excessive IL-2 signalling, which suppresses Tfh cell differentiation.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Heesch, K., et al (2014). "The function of the chemokine receptor CXCR6 in the T cell response of mice against Listeria monocytogenes" PLoS One 9(5): e97701.
PubMed
The chemokine receptor CXCR6 is expressed on different T cell subsets and up-regulated following T cell activation. CXCR6 has been implicated in the localization of cells to the liver due to the constitutive expression of its ligand CXCL16 on liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Here, we analyzed the role of CXCR6 in CD8+ T cell responses to infection of mice with Listeria monocytogenes. CD8+ T cells responding to listerial antigens acquired high expression levels of CXCR6. However, deficiency of mice in CXCR6 did not impair control of the L. monocytogenes infection. CXCR6-deficient mice were able to generate listeria-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses and showed accumulation of T cells in the infected liver. In transfer assays, we detected reduced accumulation of listeria-specific CXCR6-deficient CD8+ T cells in the liver at early time points post infection. Though, CXCR6 was dispensable at later time points of the CD8+ T cell response. When transferred CD8+ T cells were followed for extended time periods, we observed a decline in CXCR6-deficient CD8+ T cells. The manifestation of this cell loss depended on the tissue analyzed. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that CXCR6 is not required for the formation of a T cell response to L. monocytogenes and for the accumulation of T cells in the infected liver but CXCR6 appears to influence long-term survival and tissue distribution of activated cells.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Deng, L., et al (2014). "Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice" J Clin Invest 124(2): 687-695.
PubMed
High-dose ionizing irradiation (IR) results in direct tumor cell death and augments tumor-specific immunity, which enhances tumor control both locally and distantly. Unfortunately, local relapses often occur following IR treatment, indicating that IR-induced responses are inadequate to maintain antitumor immunity. Therapeutic blockade of the T cell negative regulator programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1, also called B7-H1) can enhance T cell effector function when PD-L1 is expressed in chronically inflamed tissues and tumors. Here, we demonstrate that PD-L1 was upregulated in the tumor microenvironment after IR. Administration of anti-PD-L1 enhanced the efficacy of IR through a cytotoxic T cell-dependent mechanism. Concomitant with IR-mediated tumor regression, we observed that IR and anti-PD-L1 synergistically reduced the local accumulation of tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which suppress T cells and alter the tumor immune microenvironment. Furthermore, activation of cytotoxic T cells with combination therapy mediated the reduction of MDSCs in tumors through the cytotoxic actions of TNF. Our data provide evidence for a close interaction between IR, T cells, and the PD-L1/PD-1 axis and establish a basis for the rational design of combination therapy with immune modulators and radiotherapy.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Deng, L., et al (2014). "Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice" J Clin Invest 124(2): 687-695.
PubMed
High-dose ionizing irradiation (IR) results in direct tumor cell death and augments tumor-specific immunity, which enhances tumor control both locally and distantly. Unfortunately, local relapses often occur following IR treatment, indicating that IR-induced responses are inadequate to maintain antitumor immunity. Therapeutic blockade of the T cell negative regulator programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1, also called B7-H1) can enhance T cell effector function when PD-L1 is expressed in chronically inflamed tissues and tumors. Here, we demonstrate that PD-L1 was upregulated in the tumor microenvironment after IR. Administration of anti-PD-L1 enhanced the efficacy of IR through a cytotoxic T cell-dependent mechanism. Concomitant with IR-mediated tumor regression, we observed that IR and anti-PD-L1 synergistically reduced the local accumulation of tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which suppress T cells and alter the tumor immune microenvironment. Furthermore, activation of cytotoxic T cells with combination therapy mediated the reduction of MDSCs in tumors through the cytotoxic actions of TNF. Our data provide evidence for a close interaction between IR, T cells, and the PD-L1/PD-1 axis and establish a basis for the rational design of combination therapy with immune modulators and radiotherapy.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Heesch, K., et al (2014). "The function of the chemokine receptor CXCR6 in the T cell response of mice against Listeria monocytogenes" PLoS One 9(5): e97701.
PubMed
The chemokine receptor CXCR6 is expressed on different T cell subsets and up-regulated following T cell activation. CXCR6 has been implicated in the localization of cells to the liver due to the constitutive expression of its ligand CXCL16 on liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Here, we analyzed the role of CXCR6 in CD8+ T cell responses to infection of mice with Listeria monocytogenes. CD8+ T cells responding to listerial antigens acquired high expression levels of CXCR6. However, deficiency of mice in CXCR6 did not impair control of the L. monocytogenes infection. CXCR6-deficient mice were able to generate listeria-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses and showed accumulation of T cells in the infected liver. In transfer assays, we detected reduced accumulation of listeria-specific CXCR6-deficient CD8+ T cells in the liver at early time points post infection. Though, CXCR6 was dispensable at later time points of the CD8+ T cell response. When transferred CD8+ T cells were followed for extended time periods, we observed a decline in CXCR6-deficient CD8+ T cells. The manifestation of this cell loss depended on the tissue analyzed. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that CXCR6 is not required for the formation of a T cell response to L. monocytogenes and for the accumulation of T cells in the infected liver but CXCR6 appears to influence long-term survival and tissue distribution of activated cells.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Leon, B., et al (2014). "FoxP3+ regulatory T cells promote influenza-specific Tfh responses by controlling IL-2 availability" Nat Commun 5: 3495.
PubMed
Here, we test the role of FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) in controlling T follicular helper (Tfh) and germinal centre (GC) B-cell responses to influenza. In contrast to the idea that Tregs suppress T-cell responses, we find that Treg depletion severely reduces the Tfh cell response to influenza virus. Furthermore, Treg depletion prevents the accumulation of influenza-specific GCs. These effects are not due to alterations in TGFbeta availability or a precursor-progeny relationship between Tregs and Tfh cells, but are instead mediated by increased availability of IL-2, which suppresses the differentiation of Tfh cells and as a consequence, compromises the GC B response. Thus, Tregs promote influenza-specific GC responses by preventing excessive IL-2 signalling, which suppresses Tfh cell differentiation.
Fc receptor blocking
Flow Cytometry
Muppidi, J. R., et al (2014). "Loss of signalling via Galpha13 in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma" Nature 516(7530): 254-258.
PubMed
Germinal centre B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (GCB-DLBCL) is a common malignancy, yet the signalling pathways that are deregulated and the factors leading to its systemic dissemination are poorly defined. Work in mice showed that sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 (S1PR2), a Galpha12 and Galpha13 coupled receptor, promotes growth regulation and local confinement of germinal centre B cells. Recent deep sequencing studies of GCB-DLBCL have revealed mutations in many genes in this cancer, including in GNA13 (encoding Galpha13) and S1PR2 (refs 5,6, 7). Here we show, using in vitro and in vivo assays, that GCB-DLBCL-associated mutations occurring in S1PR2 frequently disrupt the receptor’s Akt and migration inhibitory functions. Galpha13-deficient mouse germinal centre B cells and human GCB-DLBCL cells were unable to suppress pAkt and migration in response to S1P, and Galpha13-deficient mice developed germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma. Germinal centre B cells, unlike most lymphocytes, are tightly confined in lymphoid organs and do not recirculate. Remarkably, deficiency in Galpha13, but not S1PR2, led to germinal centre B-cell dissemination into lymph and blood. GCB-DLBCL cell lines frequently carried mutations in the Galpha13 effector ARHGEF1, and Arhgef1 deficiency also led to germinal centre B-cell dissemination. The incomplete phenocopy of Galpha13- and S1PR2 deficiency led us to discover that P2RY8, an orphan receptor that is mutated in GCB-DLBCL and another germinal centre B-cell-derived malignancy, Burkitt’s lymphoma, also represses germinal centre B-cell growth and promotes confinement via Galpha13. These findings identify a Galpha13-dependent pathway that exerts dual actions in suppressing growth and blocking dissemination of germinal centre B cells that is frequently disrupted in germinal centre B-cell-derived lymphoma.
Fc receptor blocking
Immunofluorescence
Brinkman CC, Rouhani SJ, Srinivasan N, Engelhard VH (2013). "Peripheral tissue homing receptors enable T cell entry into lymph nodes and affect the anatomical distribution of memory cells" J Immunol 191(5):2412-25.
PubMed
Peripheral tissue homing receptors enable T cells to access inflamed nonlymphoid tissues. In this study, we show that two such molecules, E-selectin ligand and α4β1 integrin, enable activated and memory T cells to enter lymph nodes (LN) as well. This affects the quantitative and qualitative distribution of these cells among regional LN beds. CD8 memory T cells in LN that express these molecules were mostly CD62L(lo) and would normally be classified as effector memory cells. However, similar to central memory cells, they expanded upon Ag re-encounter. This led to differences in the magnitude of the recall response that depended on the route of immunization. These novel cells share properties of both central and effector memory cells and reside in LN based on previously undescribed mechanisms of entry.
Fc receptor blocking
Immunofluorescence
Brinkman CC, Rouhani SJ, Srinivasan N, Engelhard VH (2013). "Peripheral tissue homing receptors enable T cell entry into lymph nodes and affect the anatomical distribution of memory cells" J Immunol 191(5):2412-25.
PubMed
Peripheral tissue homing receptors enable T cells to access inflamed nonlymphoid tissues. In this study, we show that two such molecules, E-selectin ligand and α4β1 integrin, enable activated and memory T cells to enter lymph nodes (LN) as well. This affects the quantitative and qualitative distribution of these cells among regional LN beds. CD8 memory T cells in LN that express these molecules were mostly CD62L(lo) and would normally be classified as effector memory cells. However, similar to central memory cells, they expanded upon Ag re-encounter. This led to differences in the magnitude of the recall response that depended on the route of immunization. These novel cells share properties of both central and effector memory cells and reside in LN based on previously undescribed mechanisms of entry.
Product Citations
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Cancer Research
DPEP2 suppresses metastasis via NF-κB-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and M2 polarization in p53-loss non-small cell lung cancer.
In Cancer Cell Int on 17 November 2025 by Liu, Y., Zhao, Y., et al.
PubMed
The TP53 gene (encoding the human p53 protein) is mutated in about 50% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Loss of p53 is closely related to tumor metastasis and immune regulation, contributing to malignant progression and poor prognosis. However, therapeutic strategies for p53-loss NSCLC are still relatively limited. We found that DPEP2 is a diagnostic marker and predicts better outcome and prognosis in NSCLC with mutant TP53, but not with wild-type TP53. Loss of p53 induced DPEP2 downregulation at cellular and tissue levels. Functionally, DPEP2 inhibited the invasion and migration abilities, and decreased F-actin fibers. Mechanistically, DPEP2 impeded epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via the MAP3K7-mediated NF-κB signaling. Immunological analysis suggested that low level of DPEP2 and high level of M1 macrophages led to poor prognosis, whereas patients with high level of DPEP2 and low level of M2 had the best survival. Subsequently, a co-culture system was established to verify the effect of DPEP2 on M2 macrophages. The results showed that DPEP2 inhibited M2 macrophages polarization in a NF-κB-dependent manner. In addition, we found that DPEP2 antagonized the tumor-promoting effects of M2 macrophages by depleting LTD4. In vivo experiments indicated that high DPEP2 levels resulted in fewer lung metastases and less M2 macrophage infiltration. Overall, our studies suggest that DPEP2 might be a promising therapeutic target for highly metastatic p53-loss NSCLC by inhibiting tumor metastasis and M2 macrophage capacity.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Immunology and Microbiology
ORAI1 mutation with mixed loss and gain of function properties causes immunodeficiency and HLH.
In J Hum Immun on 3 November 2025 by Noyer, L., Yeung, P. S., et al.
PubMed
Loss of function mutations of ORAI1 suppress store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) and cause an immunodeficiency disorder called Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channelopathy. Here we report an infant patient who is compound heterozygous for p.His134Pro and p.Leu194Pro mutations in ORAI1 and whose T cells have strongly reduced SOCE. Whereas the p.Leu194Pro mutant ORAI1 protein is not expressed at the plasma membrane, the p.His134Pro mutation results in a constitutively open channel that is unresponsive to activation by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1). The patient suffered from a severe form of combined immunodeficiency (CID), hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and fatal chronic cytomegalovirus infection. His immunodeficiency was characterized by an altered composition of T and NK cell compartments, impaired stimulation-induced cytokine production and signs of CD4+ T cell and NK cell activation but attenuated CD8+ T effector memory cell function. Our findings demonstrate that small constitutive SOCE through a mutant ORAI1 channel is not sufficient to provide immunity to viral infection.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
An interleukin-27-centered cytokine circuit regulates macrophage and T cell interactions in autoimmune diabetes.
In iScience on 17 October 2025 by Ciecko, A. E., Nabi, R., et al.
PubMed
In the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of autoimmune diabetes, interleukin (IL)-27 stimulates interferon γ (IFNγ) production by CD4 and CD8 T cells and is essential for disease development. Here, we tested the role of IL-27 in cellular communication. Single-cell RNA sequencing and T cell adoptive transfer showed that IL-27 intrinsically controlled the differentiation of islet-infiltrating CD4 T cells by driving them toward an IL-21+ Th1 phenotype. Consequently, IL-27 signaling in CD4 T cells was important for BATF and granzyme B expression in islet CD8 T effectors. BATF overexpression increased the diabetogenic potential of β cell autoreactive CD8 T cells lacking help from CD4 T cell-derived IL-21. Macrophages were the main source of IL-27 in the islets, whose expression correlated with T cell infiltration. IFNγ and CD40 signaling conferred by activated T cells induced macrophage IL-27 production. Collectively, our findings reveal a role for IL-27 in orchestrating interconnected positive feedback loops involving CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and macrophages in autoimmune diabetes.
-
-
Urothelial collective-gliding response acts as a toll-like receptor 4-associated defense mechanism.
In iScience on 17 October 2025 by Zhang, N., Sano, T., et al.
PubMed
Collective cell migration (CCM) is characterized by the coordinated movement of cell groups while maintaining cell-to-cell cohesion. Despite extensive research on CCM, the collective migration of mature epithelial cells over the extracellular matrix in response to external stimuli has not been reported. Using intravital imaging in mice, we identified urothelial CCM (UCCM) triggered by immunogenic substances, including bladder cancer cells (MB49) and uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). Integrin signaling inhibitors suppress UCCM, significantly enhancing MB49 tumor growth and UPEC bladder infection. UCCM initiation involves Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), we designated this TLR4-associated UCCM as the urothelial collective-gliding response (UCGR). Downstream of integrin signaling, urothelial matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-8 and MMP-9 mediate UCGR. Intravesical instillation of these factors accelerates UCCM and inhibits tumor growth and infection. UCGR may represent a TLR4-associated defense mechanism, offering potential therapeutic strategies for bladder disorders such as refractory cystitis and recurrent non-muscle invasive bladder cancer after endoscopic resection.
-
-
Cell Biology
Membrane receptors cluster phosphatidylserine to activate LC3-associated phagocytosis.
In Nat Cell Biol on 1 October 2025 by Boada-Romero, E., Guy, C. S., et al.
PubMed
LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP) represents a non-canonical function of autophagy proteins in which ATG8-family proteins (LC3 and GABARAP proteins) are lipidated onto single-membrane phagosomes as particles are engulfed by phagocytic cells. LAP plays roles in innate immunity, inflammation and anticancer responses, and is initiated following phagocytosis of particles that stimulate Toll-like receptors (TLR) and Fc receptors as well as following engulfment of dying cells. However, how this molecular process is initiated remains elusive. Here we report that receptors that engage LAP enrich phosphatidylserine (PS) in the phagosome membrane via membrane-proximal domains that are necessary and sufficient for LAP to proceed. Subsequently, PS recruits the Rubicon-containing PI3-kinase complex to initiate the enzymatic cascade leading to LAP. Manipulation of plasma membrane PS content, PS binding by Rubicon or the PS-clustering domains of receptors prevents LAP and delays phagosome maturation. Therefore, the initiation of LAP represents a novel mechanism of PS-mediated signal transduction following ligation of surface receptors.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
Axonal injury is a targetable driver of glioblastoma progression.
In Nature on 1 October 2025 by Clements, M. P., Tang, W., et al.
PubMed
Glioblastoma (GBM) is an aggressive and highly therapy-resistant brain tumour1,2. Although advanced disease has been intensely investigated, the mechanisms that underpin the earlier, likely more tractable, stages of GBM development remain poorly understood. Here we identify axonal injury as a key driver of GBM progression, which we find is induced in white matter by early tumour cells preferentially expanding in this region. Mechanistically, axonal injury promotes gliomagenesis by triggering Wallerian degeneration, a targetable active programme of axonal death3, which we show increases neuroinflammation and tumour proliferation. Inactivation of SARM1, the key enzyme activated in response to injury that mediates Wallerian degeneration4, was sufficient to break this tumour-promoting feedforward loop, leading to the development of less advanced terminal tumours and prolonged survival in mice. Thus, targeting the tumour-induced injury microenvironment may supress progression from latent to advanced disease, thereby providing a potential strategy for GBM interception and control.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
Albumin-binding dendritic siRNA improves delivery and efficacy to solid tumors in a melanoma model.
In Mol Ther Nucleic Acids on 9 September 2025 by Fakih, H. H., Tang, Q., et al.
PubMed
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutics are a new class of drugs that is rapidly expanding to tackle various diseases. Extrahepatic delivery of siRNAs, especially to the parenchyma of solid tumors, is challenging with multiple strategies being explored such as lipid nanoparticle based delivery and ligand conjugation strategies. Here, we report that an albumin-binding dendritic siRNA (D-siRNA) boosts blood circulation time following systemic administration, leading to improved delivery and silencing activity in a melanoma tumor model, in comparison to non-albumin binding lipophilic siRNAs. D-siRNAs increased the tumor-to-liver delivery ratio, including both immune and non-immune cell types within the tumor parenchyma. Using D-siRNAs to target JAK1 expression as an adjuvant to immune checkpoint inhibitors, we found that D-siRNAs was able to enhance PD1 antibody treatment and slow tumor progression of melanoma. Thus, this work demonstrates the utility of D-siRNAs as a systemically administered tumor delivery strategy, enabling the use of siRNAs as chemotherapeutic agents. Further mechanistic studies into the role of JAK1 in melanoma pathology and progression may expand this into additional targets as potential treatments.
-
-
CD138 and APRIL regulate plasma cell survival, competition, and retention in the bone marrow niche.
In Cell Rep on 26 August 2025 by Park, R., Benet, Z., et al.
PubMed
Durable serological protection is maintained through the persistence of antigen-specific plasma cells (PCs), but key factors regulating the survival of nascent PCs remain unclear. Previously, we reported that bone marrow (BM) PCs partially organize into clusters that are enriched for long-lived PCs, suggesting that clusters are survival niches. Here, we report that acute blockade of a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) and B cell activating factor (BAFF) using transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI)-Fc rapidly disrupts clusters and mobilizes BM PCs. CD138, a surface co-receptor that is abundant on PCs and binds APRIL but not BAFF, regulates PC retention in the BM and adhesion and motility on fibronectin. Cell-intrinsic CD138 levels control competition for survival between nascent CD138low PCs and mature CD138high PCs, and enhanced survival of CD138high PCs correlates with retention in clusters. Collectively, these results indicate that PC clusters are survival niches and that dynamic competition between new and pre-existing PCs regulates the survival of new PCs and the durability of antibody responses.
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Schistosoma immune evasion of NETosis is reversed by aryl hydantoin Ro 13-3978
In Research Square on 26 August 2025 by Bouchery, T., Doolan, R., et al.
-
-
Allergic Reactivity and Memory Occur Independently of Sequential Switching Through IgG1.
In Allergy on 1 August 2025 by Koenig, J. F. E., Wade-Vallance, A. K., et al.
PubMed
Allergic reactions to foods are primarily driven by allergen-binding immunoglobulin (Ig)E antibodies. IgE-expressing cells can be generated through direct switching from IgM to IgE or a sequential class switching pathway where activated B cells first switch to an intermediary isotype, most frequently IgG1, and then to IgE. It has been proposed that sequential class switch recombination is involved in augmenting the severity of allergic reactions, generating high affinity IgE, differentiation of IgE plasma cells, and in holding the memory of IgE responses. We directly tested these possibilities by comparing the allergic immunity of wild-type and IgG1-deficient (hMT) mice. We found that sequential switching through IgG1 was not required to maintain the binding capacity of IgE nor for its ability to promote degranulation and elicit anaphylaxis against bona fide food allergens. Furthermore, the absence of sequential switching modestly impacted IgE affinity and clinical reactivity against hapten antigens, suggesting that the nature of the antigen impacts the requirement for sequential switching. At a cellular level, the capacity to undergo sequential switching through IgG1 provided no competitive advantage for subsequent IgE expression among germinal center B cells or plasma cells. Furthermore, the recall of allergic immunity at memory timepoints was preserved in the absence of sequential switching through IgG1, a finding that corresponded with intact type 2 memory B cell polarization. Together, these data demonstrate that sequential switching through IgG1 is redundant in sensitization, anaphylaxis, and the persistence of allergy, ultimately revealing that IgE derived from any switching source should be targeted by novel therapeutics seeking to ameliorate allergic diseases.
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
Early life high fructose impairs microglial phagocytosis and neurodevelopment.
In Nature on 1 August 2025 by Wang, Z., Lipshutz, A., et al.
PubMed
Despite the success of fructose as a low-cost food additive, epidemiological evidence suggests that high fructose consumption during pregnancy or adolescence is associated with disrupted neurodevelopment1-3. An essential step in appropriate mammalian neurodevelopment is the phagocytic elimination of newly formed neurons by microglia, the resident professional phagocyte of the central nervous system4. Whether high fructose consumption in early life affects microglial phagocytosis and whether this directly affects neurodevelopment remains unknown. Here we show that offspring born to female mice fed a high-fructose diet and neonates exposed to high fructose exhibit decreased phagocytic activity in vivo. Notably, deletion of the high-affinity fructose transporter GLUT5 (also known as SLC2A5) in neonatal microglia completely reversed microglia phagocytic dysfunction, suggesting that high fructose directly affects neonatal development by suppressing microglial phagocytosis. Mechanistically, we found that high-fructose treatment of mouse and human microglia suppresses phagocytosis capacity, which is rescued in GLUT5-deficient microglia. Additionally, we found that high fructose drives significant GLUT5-dependent fructose uptake and catabolism to fructose 6-phosphate, rewiring microglial metabolism towards a hypo-phagocytic state in part by enforcing mitochondrial localization of the enzyme hexokinase 2. Mice exposed to high fructose as neonates develop anxiety-like behaviour as adolescents-an effect that is rescued in GLUT5-deficient mice. Our findings provide a mechanistic explanation for the epidemiological observation that high-fructose exposure during early life is associated with increased prevalence of adolescent anxiety disorders.
-
-
-
Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Cancer Research
CXCL12 chemokine dimer signaling modulates acute myelogenous leukemia cell migration through altered receptor internalization.
In Sci Rep on 22 July 2025 by Drouillard, D., Halyko, M., et al.
PubMed
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a malignancy of immature myeloid blast cells with stem-like and chemoresistant cells being retained in the bone marrow through CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling. Current CXCR4 inhibitors that mobilize AML cells into the bloodstream have failed to improve patient survival, likely reflecting persistent chemokine receptor localization on target cells. Here we characterize the signaling properties of CXCL12-locked dimer (CXCL12-LD), a bioengineered variant of the naturally occurring oligomer of CXCL12. CXCL12-LD, in contrast to wild-type or locked monomer variants, was unable to induce chemotaxis in AML cells. CXCL12-LD binding to CXCR4 decreased G protein, β-arrestin, and intracellular calcium mobilization signaling pathways, and indicated the locked dimer is a partial agonist of CXCR4. Despite these partial agonist properties, CXCL12-LD increased CXCR4 internalization compared to wild-type and monomeric CXCL12. Analysis of a previously published AML transcriptomic data showed CXCR4 positive AML cells co-express genes involved in survival, proliferation, and maintenance of a blast-like state. The CXCL12-LD partial agonist effectively mobilized stem cells into the bloodstream in mice suggesting a potential role for their use in targeting CXCR4. Together, our results suggest that enhanced internalization by CXCL12-LD partial agonist can avoid pharmacodynamic tolerance and may identify new avenues to better target GPCRs.
-
-
-
Immunohistochemistry-immunofluorescence
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Secreted ISG15 induced by Chlamydia trachomatis infection exerts immunomodulatory effects on IFN-γ defense and inflammation.
In PLoS Pathog on 1 July 2025 by Guo, Y., Stulz, S. V., et al.
PubMed
Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is an immunoregulatory cytokine essential for cellular immunity against intracellular pathogens, including Chlamydia. Interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) 15, a member of the ubiquitin family, contributes to host resistance to viral and bacterial infections. ISG15 can exist either in an unconjugated form or covalently attached to host proteins through a process known as ISGylation. Here, we show that infection with Chlamydia trachomatis (Ct) induces the expression and secretion of ISG15 in human primary cells and mouse female genital tract (FGT) organoids. ISG15 secretion by genital tract epithelial cells resulted in increased IFN-γ release from natural killer (NK) cells. The production of IFN-γ by NK cells in response to ISG15 was completely abolished in NK cells lacking the interleukin-18 receptor alpha (IL-18Ra), demonstrating a co-stimulatory effect of ISG15 with IL-18 in enhancing IFN-γ release. ISG15 was secreted into the FGT and was involved in controlling bacterial load in a murine infection model. Furthermore, ISG15 reduced macrophage responsiveness to IFN-γ as an M1-polarizing signal for pro-inflammatory responses, potentially "shielding" macrophages from excessive IFN-γ. Evidence of uterine horn pathology and reduced IL-10 levels in the FGT of infected ISG15-/- mice further supports a critical dual function of ISG15 in controlling chlamydial infection and modulating the resulting inflammatory responses.
-
-
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
A non-genotoxic stem cell therapy boosts lymphopoiesis and averts age-related blood diseases in mice.
In Nat Commun on 2 June 2025 by Konturek-Ciesla, A., Zhang, Q., et al.
PubMed
Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation offers a cure for a variety of blood disorders, predominantly affecting the elderly; however, its application, especially in this demographic, is limited by treatment toxicity. In response, we employ a murine transplantation model based on low-intensity conditioning protocols using antibody-mediated HSC depletion. While aging presents a significant barrier to effective HSC engraftment, optimizing HSC doses and non-genotoxic targeting methods greatly enhance the long-term multilineage activity of the transplanted cells. We demonstrate that young HSCs, once effectively engrafted in aged hosts, improve hematopoietic output and ameliorate age-compromised lymphopoiesis. This culminated in a strategy that robustly mitigates disease progression in a genetic model of myelodysplastic syndrome. These results suggest that non-genotoxic HSC transplantation could fundamentally change the clinical management of age-associated hematological disorders, offering a prophylactic tool to delay or even prevent their onset in elderly patients.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
WNK1 mediates M-CSF-induced macropinocytosis to enforce macrophage lineage fidelity.
In Nat Commun on 28 May 2025 by Trzeciak, A., Liu, Z. L., et al.
PubMed
Tissue-resident macrophages (TRM) are critical for mammalian organismal development and homeostasis. Here we report that with-no-lysine 1 (WNK1) controls myeloid progenitor fate, with Csf1riCre-mediated Wnk1 deletion in mice (WNK1-deficient mice) resulting in loss of TRMs and causing perinatal mortality. Mechanistically, absence of WNK1 or inhibition of WNK kinase activity disrupts macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)-stimulated macropinocytosis, thereby blocking mouse and human progenitor and monocyte differentiation into macrophages and skewing progenitor differentiation into neutrophils. Treatment with PMA rescues macropinocytosis but not macrophage differentiation of WNK-inhibited progenitors, implicating that M-CSF-stimulated, macropinocytosis-induced activation of WNK1 is required for macrophage differentiation. Finally, M-CSF-stimulated macropinocytosis triggers WNK1 nuclear translocation and concomitant increased protein expression of interferon regulatory factor (IRF)8, whereas inhibition of macropinocytosis or WNK kinase activity suppresses IRF8 expression. Our results thus suggest that WNK1 and downstream IRF8-regulated genes are important for M-CSF/macropinocytosis-mediated regulation of myeloid cell lineage commitment during TRM development and homeostasis.
-
-
Tracking Oral Nanoparticle Uptake in Mouse Gastrointestinal Tract by Fluorescent Labeling and t-SNE Flow Cytometry.
In Bio Protoc on 20 May 2025 by Mow, R. J., Kuczma, M. P., et al.
PubMed
The growing demand for advanced analytical techniques to explore complex cellular targets of nanotherapeutics has driven the development of innovative methodologies. This protocol presents a refined approach for fluorescent labeling and flow cytometric analysis of colonic cells following oral lipid nanoparticle (LNP) treatment, focusing on LNP uptake in colonic cell subpopulations in a DSS-induced colitis mouse model. By integrating optimized fluorochrome selection and gating strategies with advanced t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) analysis, this method enables precise identification and multidimensional visualization of LNP-targeted epithelial and macrophage populations under the complex conditions of inflamed colon tissue. Building on our previous studies demonstrating the effectiveness of nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery, this approach highlights the utility of flow cytometry for assessing uptake efficiency and cellular targeting. Unlike conventional protocols, it incorporates t-SNE for enhanced multidimensional analysis, allowing for the detection of subtle cellular patterns and the delineation of intricate clusters. By addressing gaps in traditional methodologies, this protocol provides a robust and reproducible framework for investigating in vivo cellular targets and optimizing drug delivery strategies for nanomedicines. Key features • This protocol is optimized for investigating nanoparticle uptake in inflamed colonic tissues from DSS-induced colitis models. • This protocol integrates flow cytometry with t-SNE for high-dimensional data analysis, enabling detailed characterization of cellular populations.
-
Mutant prion protein enhances NMDA receptor activity, activates PKC, and triggers rapid excitotoxicity in mice.
In J Clin Invest on 15 May 2025 by Lin, J., Callender, J. A., et al.
PubMed
Neuronal hyperexcitability precedes synapse loss in certain neurodegenerative diseases, yet the synaptic membrane interactions and downstream signaling events remain unclear. The disordered amino terminus of the prion protein (PrPC) has been implicated in aberrant signaling in prion and Alzheimer's disease. To disrupt neuronal interactions and signaling linked to the amino terminus, we CRISPR-engineered a knockin mouse expressing mutant PrPC (G92N), generating an N-linked glycosylation site between 2 functional motifs. Mice developed seizures and necrosis of hippocampal pyramidal neurons, similar to prion-infected mice and consistent with excitotoxicity. Phosphoproteomics analysis revealed phosphorylated glutamate receptors and calcium-sensitive kinases, including protein kinase C (PKC). Additionally, 92N-PrPC-expressing neurons showed persistent calcium influx as well as dendritic beading, which was rescued by an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist. Finally, survival of Prnp92N mice was prolonged by blocking active NMDAR channels. We propose that dysregulated PrPC-NMDAR-induced signaling can trigger an excitatory-inhibitory imbalance, spongiform degeneration, and neurotoxicity and that calcium dysregulation is central to PrPC-linked neurodegeneration.
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
GRP78 Nanobody-Directed Immunotoxin Activates Innate Immunity Through STING Pathway to Synergize Tumor Immunotherapy.
In Adv Sci (Weinh) on 1 May 2025 by Wang, H., Zhou, R., et al.
PubMed
The lack of targetable antigens poses a significant challenge in developing effective cancer-targeted therapies. Cell surface translocation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperones, such as glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), during malignancy, drug resistance, and ER stress induced by therapies, offers a promising pan-cancer target. To target GRP78, nanobody C5, identified from a phage library and exhibiting high affinity for human and mouse GRP78, is utilized to develop the Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE) immunotoxin C5-PE38. C5-PE38 induced ER stress, apoptosis and immunogenic cell death in targeted cells and showed antitumor efficacy against colorectal cancer and melanoma models without obvious toxicity. Mechanistically, transcriptome profiling showed that C5-PE38 reshaped the tumor immune microenvironment with enhanced innate and adaptive immune response and response to interferon beta. Moreover, C5-PE38-induced cell death could trans-activate STING pathway in dendritic cells and macrophages, promoting CD8+ T cell infiltration. It also sensitizes both primary and metastatic melanomas to anti-PD1 therapy, partly through STING activation. Overall, this study unveils a feasible GRP78 nanobody-directed therapy strategy for single or combinatorial cancer intervention. This work finds that C5-PE38-induced cell death stimulates STING-dependent cytosolic DNA release to promote antitumor immunity, a mechanism not previously reported for PE38, providing valuable insights for its clinical use.
-
-
CDH17-targeting CAR-NK cells synergize with CD47 blockade for potent suppression of gastrointestinal cancers.
In Acta Pharm Sin B on 1 May 2025 by Zheng, L., Ding, Y., et al.
PubMed
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancers are a leading cause of cancer morbidity and mortality worldwide. Despite advances in treatment, cancer relapse remains a significant challenge, necessitating novel therapeutic strategies. In this study, we engineered nanobody-based chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) natural killer (NK) cells targeting cadherin 17 (CDH17) for the treatment of GI tumors. In addition, to enhance the efficacy of CAR-NK cells, we also incorporated CV1, a CD47-SIRPα axis inhibitor, to evaluate the anti-tumor effect of this combination. We found that CDH17-CAR-NK cells effectively eliminated GI cancers cells in a CDH17-dependent manner. CDH17-CAR-NK cells also exhibit potent in vivo anti-tumor effects in cancer cell-derived xenograft and patient-derived xenograft mouse models. Additionally, the anti-tumor activity of CDH17-CAR-NK cells is synergistically enhanced by CD47-signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) axis inhibitor CV1, likely through augmented macrophages activation and an increase in M1-phenotype macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Collectively, our findings suggest that CDH17-targeting CAR-NK cells are a promising strategy for GI cancers. The combination of CDH17-CAR-NK cells with CV1 emerges as a potential combinatorial approach to overcome the limitations of CAR-NK therapy. Further investigations are warranted to speed up the clinical translation of these findings.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Purinergic adipocyte-macrophage crosstalk promotes degeneration of thermogenic brown adipose tissue
In Research Square on 17 April 2025 by Heeren, J., Jaeckstein, M. Y., et al.
-