Tissue-resident memory T cell reactivation by diverse antigen-presenting cells imparts distinct functional responses
Authors: Jun Siong Low, Yagmur Farsakoglu, Maria Carolina Amezcua Vesely, Esen Sefik, Joseph B. Kelly, Christian C.D. Harman, Ruaidhri Jackson, Justin A. Shyer, Xiaodong Jiang, Linda S. Cauley, Richard A. Flavell, Susan M. Kaech
Summary
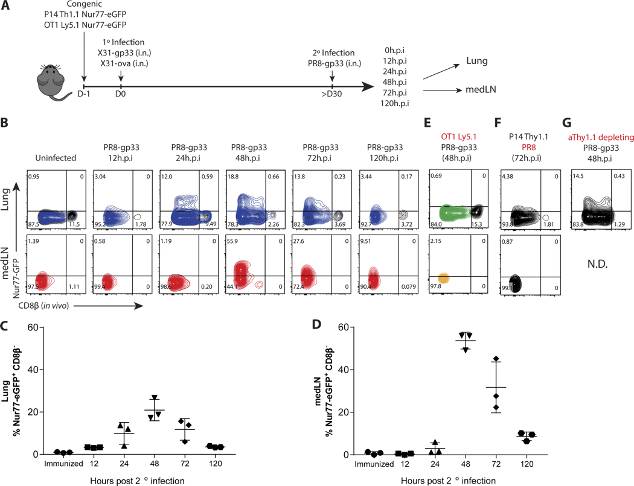
CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells (TRM cells) are poised at the portals of infection and provide long-term protective immunity. Despite their critical roles, the precise mechanics governing TRM cell reactivation in situ are unknown. Using a TCR-transgenic Nur77-GFP reporter to distinguish "antigen-specific" from "bystander" reactivation, we demonstrate that lung CD8+ TRM cells are reactivated more quickly, yet less efficiently, than their counterparts in the draining LNs (TLN cells). Global profiling of reactivated memory T cells revealed tissue-defined and temporally regulated recall response programs. Unlike the reactivation of CD8+ TLN cells, which is strictly dependent on CD11c+XCR1+ APCs, numerous antigen-presenting partners, both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic, were sufficient to reactivate lung CD8+ TRM cells, but the quality of TRM cell functional responses depended on the identity of the APCs. Together, this work uncovers fundamental differences in the activation kinetics, mechanics, and effector responses between CD8+ memory T cells in peripheral vs. lymphoid organs, revealing a novel tissue-specific paradigm for the reactivation of memory CD8+ T cells.Reference: Jun Siong Low, Yagmur Farsakoglu, Maria Carolina Amezcua Vesely, Esen Sefik, Joseph B. Kelly, Christian C.D. Harman, Ruaidhri Jackson, Justin A. Shyer, Xiaodong Jiang, Linda S. Cauley, Richard A. Flavell, Susan M. Kaech; Tissue-resident memory T cell reactivation by diverse antigen-presenting cells imparts distinct functional responses. J Exp Med 3 August 2020; 217 (8): e20192291. Retrieved from https://rupress.org/jem/
Product Highlights:
The authors used Bio X Cell's anti-mouse Ly6G/Ly6C (Gr-1) (Clone RB6-8C5) in this research study.
