Microglia Require CD4 T Cells to Complete the Fetal-to-Adult Transition
Authors: Emanuela Pasciuto, Oliver T. Burton, Carlos P. Roca, Vasiliki Lagou,Wenson D. Rajan,Tom Theys, Renzo Mancuso, Raul Y. Tito, Lubna Kouser, Zsuzsanna Callaerts-Vegh, Alerie G. de la Fuente, Teresa Prezzemolo, Loriana G. Mascali, Aleksandra Brajic, Carly E. Whyte, Lidia Yshii, Anna Martinez-Muriana, Michelle Naughton, Andrew Young, Alena Moudra, Pierre Lemaitre, Suresh Poovathingal, Jeroen Raes, Bart De Strooper, Denise C. Fitzgerald, James Dooley,and Adrian Liston
Summary
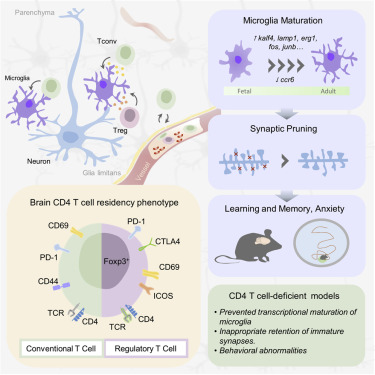
The brain is a site of relative immune privilege. Although CD4 T cells have been reported in the central nervous system, their presence in the healthy brain remains controversial, and their function remains largely unknown. We used a combination of imaging, single cell, and surgical approaches to identify a CD69+ CD4 T cell population in both the mouse and human brain, distinct from circulating CD4 T cells. The brain-resident population was derived through in situ differentiation from activated circulatory cells and was shaped by self-antigen and the peripheral microbiome. Single-cell sequencing revealed that in the absence of murine CD4 T cells, resident microglia remained suspended between the fetal and adult states. This maturation defect resulted in excess immature neuronal synapses and behavioral abnormalities. These results illuminate a role for CD4 T cells in brain development and a potential interconnected dynamic between the evolution of the immunological and neurological systems. Video AbstractReference: Pasciuto, E., Burton, O., Roca, C. et al. Microglia Require CD4 T Cells to Complete the Fetal-to-Adult Transition. Cell. 3, 182 (August 6, 2020). https://cell.com
Product Highlights:
The authors used Bio X Cell's InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD4 (clone GK1.5) and InVivoMAb anti-mouse IFNγ (clone XMG1.2) in this research study.

