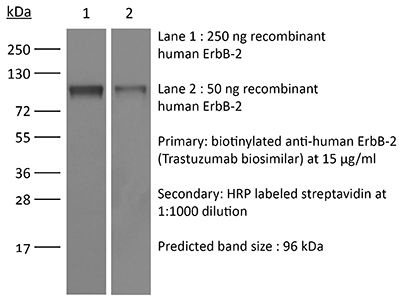
InVivoSIM anti-human HER2 (Trastuzumab Biosimilar)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Human IgG1 |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | RecombiMAb human IgG1 isotype control, anti-hen egg lysozyme |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | Human A431 cells over-expressing EGFR |
| Reported Applications |
in vitro HER2+ cell depletion (ADCC assay) Antibody-drug conjugate synthesis in vitro functional assays in vivo functional assays Flow Cytometry ELISA Immunohistochemistry Western Blot |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤0.5EU/mg (≤0.0005EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein A |
| RRID | AB_2894726 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Murine Pathogen Tests |
Ectromelia/Mousepox Virus: Negative Hantavirus: Negative K Virus: Negative Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus: Negative Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus: Negative Mouse Adenovirus: Negative Mouse Cytomegalovirus: Negative Mouse Hepatitis Virus: Negative Mouse Minute Virus: Negative Mouse Norovirus: Negative Mouse Parvovirus: Negative Mouse Rotavirus: Negative Mycoplasma Pulmonis: Negative Pneumonia Virus of Mice: Negative Polyoma Virus: Negative Reovirus Screen: Negative Sendai Virus: Negative Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis: Negative |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
Antibody-drug conjugate synthesis
Hsu YP, Nourzaie O, Tocher AE, Nerella K, Ermakov G, Jung J, Fowler A, Wu P, Ayesa U, Willingham A, Beaumont M, Ingale S (2023). "Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation Using Modified Bisected N-Glycans: Method Development and Potential toward Tun
PubMed
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have garnered worldwide attention for disease treatment, as they possess high target specificity, a long half-life, and outstanding potency to kill or modulate the functions of targets. FDA approval of multiple ADCs for cancer therapy has generated a strong desire for novel conjugation strategies with high biocompatibility and controllable bioproperties. Herein, we present a bisecting glycan-bridged conjugation strategy that enables site-specific conjugation without the need for the oligosaccharide synthesis and genetic engineering of antibodies. Application of this method is demonstrated by conjugation of anti-HER2 human and mouse IgGs with a cytotoxic drug, monomethyl auristatin E. The glycan bridge showed outstanding stability, and the resulting ADCs eliminated HER2-expressing cancer cells effectively. Moreover, our strategy preserves the feasibility of glycan structure remodeling to fine-tune the immunogenicity and pharmacokinetic properties of ADCs through glycoengineering.
in vitro HER2+ cell depletion (ADCC assay)
Lee D, Dunn ZS, Guo W, Rosenthal CJ, Penn NE, Yu Y, Zhou K, Li Z, Ma F, Li M, Song TC, Cen X, Li YR, Zhou JJ, Pellegrini M, Wang P, Yang L (2023). "Unlocking the potential of allogeneic Vδ2 T cells for ovarian cancer therapy through CD16 biomarker se
PubMed
Allogeneic Vγ9Vδ2 (Vδ2) T cells have emerged as attractive candidates for developing cancer therapy due to their established safety in allogeneic contexts and inherent tumor-fighting capabilities. Nonetheless, the limited clinical success of Vδ2 T cell-based treatments may be attributed to donor variability, short-lived persistence, and tumor immune evasion. To address these constraints, we engineer Vδ2 T cells with enhanced attributes. By employing CD16 as a donor selection biomarker, we harness Vδ2 T cells characterized by heightened cytotoxicity and potent antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) functionality. RNA sequencing analysis supports the augmented effector potential of Vδ2 T cells derived from CD16 high (CD16Hi) donors. Substantial enhancements are further achieved through CAR and IL-15 engineering methodologies. Preclinical investigations in two ovarian cancer models substantiate the effectiveness and safety of engineered CD16Hi Vδ2 T cells. These cells target tumors through multiple mechanisms, exhibit sustained in vivo persistence, and do not elicit graft-versus-host disease. These findings underscore the promise of engineered CD16Hi Vδ2 T cells as a viable therapeutic option for cancer treatment.
in vitro functional assay
Jarvi NL, Balu-Iyer SV (2023). "A mechanistic marker-based screening tool to predict clinical immunogenicity of biologics" Commun Med (Lond) 3(1):174.
PubMed
Background: The efficacy and safety of therapeutic proteins are undermined by immunogenicity driven by anti-drug antibodies. Immunogenicity risk assessment is critically necessary during drug development, but current methods lack predictive power and mechanistic insight into antigen uptake and processing leading to immune response. A key mechanistic step in T-cell-dependent immune responses is the migration of mature dendritic cells to T-cell areas of lymphoid compartments, and this phenomenon is most pronounced in the immune response toward subcutaneously delivered proteins. Methods: The migratory potential of monocyte-derived dendritic cells is proposed to be a mechanistic marker for immunogenicity screening. Following exposure to therapeutic protein in vitro, dendritic cells are analyzed for changes in activation markers (CD40 and IL-12) in combination with levels of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 to represent migratory potential. Then a transwell assay captures the intensity of dendritic cell migration in the presence of a gradient of therapeutic protein and chemokine ligands. Results: Here, we show that an increased ability of the therapeutic protein to induce dendritic cell migration along a gradient of chemokine CCL21 and CXCL12 predicts higher immunogenic potential. Expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells, in combination with activation markers CD40 and IL-12, strongly correlates with clinical anti-drug antibody incidence. Conclusions: Mechanistic understanding of processes driving immunogenicity led to the development of a predictive tool for immunogenicity risk assessment of therapeutic proteins. These predictive markers could be adapted for immunogenicity screening of other biological modalities.
in vitro functional assay
in vivo functional assay
Sun W, Wang X, Wang D, Lu L, Lin H, Zhang Z, Jia Y, Nie X, Liu T, Fu W (2022). "CD40×HER2 bispecific antibody overcomes the CCL2-induced trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive gastric cancer" J Immunother Cancer 10(7):e005063.
PubMed
Background: There was much hard work to study the trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive gastric cancer (GC), but the information which would reveal this abstruse mechanism is little. In this study, we aimed to investigate the roles of tumor cell-derived CCL2 on trastuzumab resistance and overcome the resistance by treatment with the anti-CD40-scFv-linked anti-HER2 (CD40 ×HER2) bispecific antibody (bsAb). Methods: We measured the levels of CCL2 expression in HER2-positive GC tissues, and revealed biological functions of tumor cell-derived CCL2 on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and the trastuzumab resistance. Then, we developed CD40 ×HER2 bsAb, and examined the targeting roles on HER2 and CD40, to overcome the trastuzumab resistance without systemic toxicity. Results: We found the level of CCL2 expression in HER2-postive GC was correlated with infiltration of TAMs, polarization status of infiltrated TAMs, trastuzumab resistance and survival outcomes of GC patients. On exposure to CCL2, TAMs decreased the M1-like phenotype, thereby eliciting the trastuzumab resistance. CCL2 activated the transcription of ZC3H12A, which increased K63-linked deubiquitination and K48-linked auto-ubiquitination of TRAF6/3 to inactivate NF-κB signaling in TAMs. CD40 ×HER2 bsAb, which targeted the CD40 to restore the ubiquitination level of TRAF6/3, increased the M1-like phenotypic transformation of TAMs, and overcame trastuzumab resistance without immune-related adversary effects (irAEs). Conclusions: We revealed a novel mechanism of trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive GC via the CCL2-ZC3H12A-TRAF6/3 signaling axis, and presented a CD40 ×HER2 bsAb which showed great antitumor efficacy with few irAEs.
Product Citations
-
-
Cancer Research
Multi-receptor targeted therapy of breast cancer and brain metastases with a novel QUAD-drug conjugate.
In Breast Cancer Res on 27 October 2025 by Debinski, W., Fink, K. N., et al.
PubMed
Identifying treatments for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains a critical medical need. We have found that Interleukin 13 receptor alpha 2 (IL-13RA2), EphA2, EphA3 and EphB2 receptors are over-expressed collectively in majority of patients with breast cancer and its brain metastases. We are pursuing the novel idea of targeting these four tumor-associated receptors identified by us with one pharmaceutical compound. A compound, called QUAD, was designed and constructed, which binds all four targeted receptors.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Exploitable mechanisms of antibody and CAR mediated macrophage cytotoxicity.
In Nat Commun on 1 July 2025 by Liu, T., Zhang, M., et al.
PubMed
Macrophages infiltrate solid tumors and either support survival or induce cancer cell death through phagocytosis or cytotoxicity. To uncover regulators of macrophage cytotoxicity towards cancer cells, we perform two co-culture CRISPR screens using CAR-macrophages targeting different tumor associated antigens. Both identify ATG9A as an important regulator of this cytotoxic activity. In vitro and in vivo, ATG9A depletion in cancer cells sensitizes them to macrophage-mediated killing. Proteomic and lipidomic analyses reveal that ATG9A deficiency impairs the cancer cell response to macrophage-induced plasma membrane damage through defective lysosomal exocytosis, reduced ceramide production, and disrupted caveolar endocytosis. Depleting non-cytotoxic macrophages using CSF1R inhibition while preventing ATG9A-mediated tumor membrane repair enhances the anti-tumor activity of therapeutic antibodies in mice. Thus, macrophage cytotoxicity plays an important role in tumor elimination during antibody or CAR-macrophage treatment, and inhibiting tumor membrane repair via ATG9A, particularly in combination with cytotoxic macrophage enrichment through CSF1R inhibition, improves tumor-targeting macrophage efficacy.
-
-
-
Genetics
A platform to deliver single and bi-specific Cas9/guide RNA to perturb genes in vitro and in vivo.
In Mol Ther on 2 October 2024 by Li, Y. J., Chien, S. H., et al.
PubMed
Although CRISPR-Cas9 technology is poised to revolutionize the treatment of diseases with underlying genetic mutations, it faces some significant issues limiting clinical entry. They include low-efficiency in vivo systemic delivery and undesired off-target effects. Here, we demonstrate, by modifying Cas9 with phosphorothioate-DNA oligos (PSs), that one can efficiently deliver single and bi-specific CRISPR-Cas9/guide RNA (gRNA) dimers in vitro and in vivo with reduced off-target effects. We show that PS-Cas9/gRNA-mediated gene knockout preserves chimeric antigen receptor T cell viability and expansion in vitro and in vivo. PS-Cas9/gRNA mediates gene perturbation in patient-derived tumor organoids and mouse xenograft tumors, leading to potent tumor antitumor effects. Further, HER2 antibody-PS-Cas9/gRNA conjugate selectively perturbs targeted genes in HER2+ ovarian cancer xenografts in vivo. Moreover, we created bi-specific PS-Cas9 with two gRNAs to target two adjacent sequences of the same gene, leading to efficient targeted gene disruption ex vivo and in vivo with markedly reduced unintended gene perturbation. Thus, the cell-penetrating PS-Cas9/gRNA can achieve efficient systemic delivery and precision in gene disruption.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A mechanistic marker-based screening tool to predict clinical immunogenicity of biologics.
In Commun Med (Lond) on 8 December 2023 by Jarvi, N. L., Balu-Iyer, S. V., et al.
PubMed
The efficacy and safety of therapeutic proteins are undermined by immunogenicity driven by anti-drug antibodies. Immunogenicity risk assessment is critically necessary during drug development, but current methods lack predictive power and mechanistic insight into antigen uptake and processing leading to immune response. A key mechanistic step in T-cell-dependent immune responses is the migration of mature dendritic cells to T-cell areas of lymphoid compartments, and this phenomenon is most pronounced in the immune response toward subcutaneously delivered proteins.
-
-
-
Flow cytometry/Cell sorting
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Unlocking the potential of allogeneic Vδ2 T cells for ovarian cancer therapy through CD16 biomarker selection and CAR/IL-15 engineering.
In Nat Commun on 8 November 2023 by Lee, D., Dunn, Z. S., et al.
PubMed
Allogeneic Vγ9Vδ2 (Vδ2) T cells have emerged as attractive candidates for developing cancer therapy due to their established safety in allogeneic contexts and inherent tumor-fighting capabilities. Nonetheless, the limited clinical success of Vδ2 T cell-based treatments may be attributed to donor variability, short-lived persistence, and tumor immune evasion. To address these constraints, we engineer Vδ2 T cells with enhanced attributes. By employing CD16 as a donor selection biomarker, we harness Vδ2 T cells characterized by heightened cytotoxicity and potent antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) functionality. RNA sequencing analysis supports the augmented effector potential of Vδ2 T cells derived from CD16 high (CD16Hi) donors. Substantial enhancements are further achieved through CAR and IL-15 engineering methodologies. Preclinical investigations in two ovarian cancer models substantiate the effectiveness and safety of engineered CD16Hi Vδ2 T cells. These cells target tumors through multiple mechanisms, exhibit sustained in vivo persistence, and do not elicit graft-versus-host disease. These findings underscore the promise of engineered CD16Hi Vδ2 T cells as a viable therapeutic option for cancer treatment.
-
-
Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation Using Modified Bisected N-Glycans: Method Development and Potential toward Tunable Effector Function.
In Bioconjug Chem on 20 September 2023 by Hsu, Y. P., Nourzaie, O., et al.
PubMed
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have garnered worldwide attention for disease treatment, as they possess high target specificity, a long half-life, and outstanding potency to kill or modulate the functions of targets. FDA approval of multiple ADCs for cancer therapy has generated a strong desire for novel conjugation strategies with high biocompatibility and controllable bioproperties. Herein, we present a bisecting glycan-bridged conjugation strategy that enables site-specific conjugation without the need for the oligosaccharide synthesis and genetic engineering of antibodies. Application of this method is demonstrated by conjugation of anti-HER2 human and mouse IgGs with a cytotoxic drug, monomethyl auristatin E. The glycan bridge showed outstanding stability, and the resulting ADCs eliminated HER2-expressing cancer cells effectively. Moreover, our strategy preserves the feasibility of glycan structure remodeling to fine-tune the immunogenicity and pharmacokinetic properties of ADCs through glycoengineering.
-
-
Cancer Research
CD40×HER2 bispecific antibody overcomes the CCL2-induced trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive gastric cancer.
In J Immunother Cancer on 1 July 2022 by Sun, W., Wang, X., et al.
PubMed
There was much hard work to study the trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive gastric cancer (GC), but the information which would reveal this abstruse mechanism is little. In this study, we aimed to investigate the roles of tumor cell-derived CCL2 on trastuzumab resistance and overcome the resistance by treatment with the anti-CD40-scFv-linked anti-HER2 (CD40 ×HER2) bispecific antibody (bsAb).
-