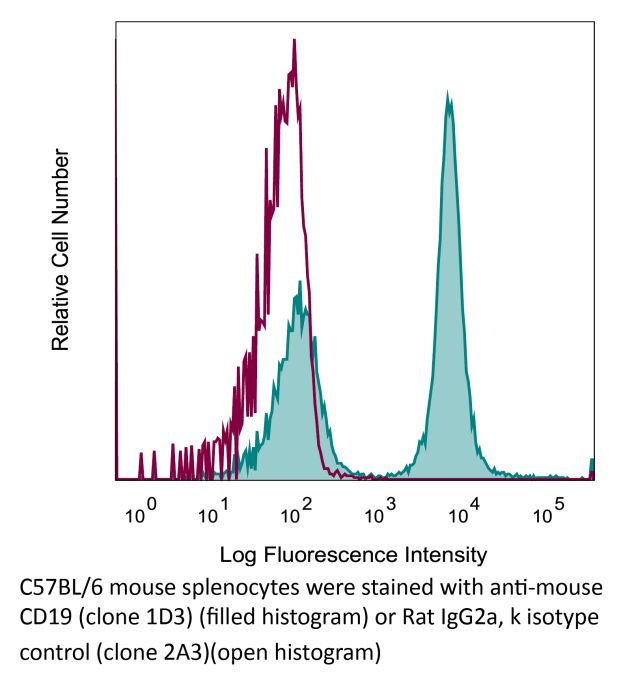
InVivoMAb anti-mouse CD19
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | InVivoMAb rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Recommended Dilution Buffer | InVivoPure pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| Conjugation | This product is unconjugated. Conjugation is available via our Antibody Conjugation Services. |
| Immunogen | K562 cells expressing the extracellular domain of mouse CD19 |
| Reported Applications |
in vivo B cell depletion in vivo CD19 neutralization in vitro B cell negative selection Flow cytometry |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
| Endotoxin |
≤1EU/mg (≤0.001EU/μg) Determined by LAL assay |
| Purity |
≥95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Sterility | 0.2 µm filtration |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G |
| RRID | AB_10949187 |
| Molecular Weight | 150 kDa |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
in vivo B cell depletion
Sawen, P., et al (2016). "Mitotic History Reveals Distinct Stem Cell Populations and Their Contributions to Hematopoiesis" Cell Rep 14(12): 2809-2818.
PubMed
Homeostasis of short-lived blood cells is dependent on rapid proliferation of immature precursors. Using a conditional histone 2B-mCherry-labeling mouse model, we characterize hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) and progenitor proliferation dynamics in steady state and following several types of induced stress. HSC proliferation following HSC transplantation into lethally irradiated mice is fundamentally different not only from native hematopoiesis but also from other stress contexts. Whereas transplantation promoted sustained, long-term proliferation of HSCs, both cytokine-induced mobilization and acute depletion of selected blood cell lineages elicited very limited recruitment of HSCs to the proliferative pool. By coupling mCherry-based analysis of proliferation history with multiplex gene expression analyses on single cells, we have found that HSCs can be stratified into four distinct subtypes. These subtypes have distinct molecular signatures and differ significantly in their reconstitution potentials, showcasing the power of tracking proliferation history when resolving functional heterogeneity of HSCs.
in vivo CD19 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Dai, M., et al (2015). "Curing mice with large tumors by locally delivering combinations of immunomodulatory antibodies" Clin Cancer Res 21(5): 1127-1138.
PubMed
PURPOSE: Immunomodulatory mAbs can treat cancer, but cures are rare except for small tumors. Our objective was to explore whether the therapeutic window increases by combining mAbs with different modes of action and injecting them into tumors. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Combinations of mAbs to CD137/PD-1/CTLA-4 or CD137/PD-1/CTLA-4/CD19 were administrated intratumorally to mice with syngeneic tumors (B16 and SW1 melanoma, TC1 lung carcinoma), including tumors with a mean surface of approximately 80 mm(2). Survival and tumor growth were assessed. Immunologic responses were evaluated using flow cytometry and qRT-PCR. RESULTS: More than 50% of tumor-bearing mice had complete regression and long-term survival after tumor injection with mAbs recognizing CD137/PD-1/CTLA-4/CD19 with similar responses in three models. Intratumoral injection was more efficacious than intraperitoneal injection in causing rejection also of untreated tumors in the same mice. The three-mAb combination could also induce regression, but was less efficacious. There were few side effects, and therapy-resistant tumors were not observed. Transplanted tumor cells rapidly caused a Th2 response with increased CD19 cells. Successful therapy shifted this response to the Th1 phenotype with decreased CD19 cells and increased numbers of long-term memory CD8 effector cells and T cells making IFNgamma and TNFalpha. CONCLUSIONS: Intratumoral injection of mAbs recognizing CD137/PD-1/CTLA-4/CD19 can eradicate established tumors and reverse a Th2 response with tumor-associated CD19 cells to Th1 immunity, whereas a combination lacking anti-CD19 is less effective. There are several human cancers for which a similar approach may provide clinical benefit.
in vivo B cell depletion
Carmi, Y., et al (2015). "Allogeneic IgG combined with dendritic cell stimuli induce antitumour T-cell immunity" Nature 521(7550): 99-104.
PubMed
Whereas cancers grow within host tissues and evade host immunity through immune-editing and immunosuppression, tumours are rarely transmissible between individuals. Much like transplanted allogeneic organs, allogeneic tumours are reliably rejected by host T cells, even when the tumour and host share the same major histocompatibility complex alleles, the most potent determinants of transplant rejection. How such tumour-eradicating immunity is initiated remains unknown, although elucidating this process could provide the basis for inducing similar responses against naturally arising tumours. Here we find that allogeneic tumour rejection is initiated in mice by naturally occurring tumour-binding IgG antibodies, which enable dendritic cells (DCs) to internalize tumour antigens and subsequently activate tumour-reactive T cells. We exploited this mechanism to treat autologous and autochthonous tumours successfully. Either systemic administration of DCs loaded with allogeneic-IgG-coated tumour cells or intratumoral injection of allogeneic IgG in combination with DC stimuli induced potent T-cell-mediated antitumour immune responses, resulting in tumour eradication in mouse models of melanoma, pancreas, lung and breast cancer. Moreover, this strategy led to eradication of distant tumours and metastases, as well as the injected primary tumours. To assess the clinical relevance of these findings, we studied antibodies and cells from patients with lung cancer. T cells from these patients responded vigorously to autologous tumour antigens after culture with allogeneic-IgG-loaded DCs, recapitulating our findings in mice. These results reveal that tumour-binding allogeneic IgG can induce powerful antitumour immunity that can be exploited for cancer immunotherapy.
in vitro B cell negative selection
Liu, B., et al (2015). "Collaborative interactions between type 2 innate lymphoid cells and antigen-specific CD4+ Th2 cells exacerbate murine allergic airway diseases with prominent eosinophilia" J Immunol 194(8): 3583-3593.
PubMed
Type-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and the acquired CD4(+) Th2 and Th17 cells contribute to the pathogenesis of experimental asthma; however, their roles in Ag-driven exacerbation of chronic murine allergic airway diseases remain elusive. In this study, we report that repeated intranasal rechallenges with only OVA Ag were sufficient to trigger airway hyperresponsiveness, prominent eosinophilic inflammation, and significantly increased serum OVA-specific IgG1 and IgE in rested mice that previously developed murine allergic airway diseases. The recall response to repeated OVA inoculation preferentially triggered a further increase of lung OVA-specific CD4(+) Th2 cells, whereas CD4(+) Th17 and ILC2 cell numbers remained constant. Furthermore, the acquired CD4(+) Th17 cells in Stat6(-/-)/IL-17-GFP mice, or innate ILC2s in CD4(+) T cell-ablated mice, failed to mount an allergic recall response to OVA Ag. After repeated OVA rechallenge or CD4(+) T cell ablation, the increase or loss of CD4(+) Th2 cells resulted in an enhanced or reduced IL-13 production by lung ILC2s in response to IL-25 and IL-33 stimulation, respectively. In return, ILC2s enhanced Ag-mediated proliferation of cocultured CD4(+) Th2 cells and their cytokine production, and promoted eosinophilic airway inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia driven by adoptively transferred Ag-specific CD4(+) Th2 cells. Thus, these results suggest that an allergic recall response to recurring Ag exposures preferentially triggers an increase of Ag-specific CD4(+) Th2 cells, which facilitates the collaborative interactions between acquired CD4(+) Th2 cells and innate ILC2s to drive the exacerbation of a murine allergic airway diseases with an eosinophilic phenotype.
Flow Cytometry
Becker, A. M., et al (2015). "ADAM17 limits the expression of CSF1R on murine hematopoietic progenitors" Exp Hematol 43(1): 44-52 e41-43.
PubMed
All-lymphoid progenitors (ALPs) yield few myeloid cells in vivo, but readily generate such cells in vitro. The basis for this difference remains unknown. We hypothesized that ALPs limit responsiveness to in vivo concentrations of myeloid-promoting cytokines by reducing expression of the corresponding receptors, potentially through posttranscriptional mechanisms. Consistent with such a mechanism, ALPs express higher levels of CSF1R transcripts than their upstream precursors, yet show limited cell-surface protein expression of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R). All-lymphoid progenitors and other hematopoietic progenitors deficient in A disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 17 (ADAM17), display elevated cell surface CSF1R expression. ADAM17(-/-) ALPs, however, fail to yield myeloid cells upon transplantation into irradiated recipients. Moreover, ADAM17(-/-) ALPs yield fewer macrophages in vitro than control ALPs at high concentrations of macrophage colony stimulating factor. Mice with hematopoietic-specific deletion of ADAM17 have normal numbers of myeloid and lymphoid progenitors and mature cells in vivo. These data demonstrate that ADAM17 limits CSF1R protein expression on hematopoietic progenitors, but that compensatory mechanisms prevent elevated CSF1R levels from altering lymphoid progenitor potential.
in vitro B cell negative selection
Bouffi, C., et al (2015). "Transcription Factor Repertoire of Homeostatic Eosinophilopoiesis" J Immunol 195(6): 2683-2695.
PubMed
The production of mature eosinophils (Eos) is a tightly orchestrated process with the aim to sustain normal Eos levels in tissues while also maintaining low numbers of these complex and sensitive cells in the blood. To identify regulators of homeostatic eosinophilopoiesis in mice, we took a global approach to identify genome-wide transcriptome and epigenome changes that occur during homeostasis at critical developmental stages, including Eos-lineage commitment and lineage maturation. Our analyses revealed a markedly greater number of transcriptome alterations associated with Eos maturation (1199 genes) than with Eos-lineage commitment (490 genes), highlighting the greater transcriptional investment necessary for differentiation. Eos-lineage-committed progenitors (EoPs) were noted to express high levels of granule proteins and contain granules with an ultrastructure distinct from that of mature resting Eos. Our analyses also delineated a 976-gene Eos-lineage transcriptome that included a repertoire of 56 transcription factors, many of which have never previously been associated with Eos. EoPs and Eos, but not granulocyte-monocyte progenitors or neutrophils, expressed Helios and Aiolos, members of the Ikaros family of transcription factors, which regulate gene expression via modulation of chromatin structure and DNA accessibility. Epigenetic studies revealed a distinct distribution of active chromatin marks between genes induced with lineage commitment and genes induced with cell maturation during Eos development. In addition, Aiolos and Helios binding sites were significantly enriched in genes expressed by EoPs and Eos with active chromatin, highlighting a potential novel role for Helios and Aiolos in regulating gene expression during Eos development.
in vivo CD19 neutralization
Flow Cytometry
Dai, M., et al (2013). "Long-lasting complete regression of established mouse tumors by counteracting Th2 inflammation" J Immunother 36(4): 248-257.
PubMed
40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.”}” data-sheets-userformat=”{“2″:14851,”3”:{“1″:0},”4”:{“1″:2,”2″:16777215},”12″:0,”14”:{“1″:2,”2″:1521491},”15″:”Roboto, sans-serif”,”16″:12}”>Mice with intraperitoneal ID8 ovarian carcinoma or subcutaneous SW1 melanoma were injected with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to CD137PD-1CTLA4 7-15 days after tumor initiation. Survival of mice with ID8 tumors tripled and >40% of mice with SW1 tumors remained healthy >150 days after last treatment and are probably cured. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4 cells and involved CD8 cells and NK cells to a less extent. The 3 mAb combination significantly decreased CD19 cells at tumor sites, increased IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha producing CD4 and CD8 T cells and mature CD86 dendritic cells (DC), and it increased the ratios of effector CD4 and CD8 T cells to CD4Foxp3 regulatory T (Treg) cells and to CD11bGr-1 myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC). This is consistent with shifting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive Th2 to an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by PCR data. Adding an anti-CD19 mAb to the 3 mAb combination in the SW1 model further increased therapeutic efficacy. Data from ongoing experiments show that intratumoral injection of a combination of mAbs to CD137PD-1CTLA4CD19 can induce complete regression and dramatically prolong survival also in the TC1 carcinoma and B16 melanoma models, suggesting that the approach has general validity.
in vivo B cell depletion
Guo, Z., et al (2013). "Combined TIM-3 blockade and CD137 activation affords the long-term protection in a murine model of ovarian cancer" J Transl Med 11: 215.
PubMed
BACKGROUND: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3) is known as a negative immune regulator and emerging data have implicated TIM-3 a pivotal role in suppressing antitumor immunity. The co-stimulatory receptor CD137 is transiently upregulated on T-cells following activation and increases their proliferation and survival when engaged. Although antagonistic anti-TIM-3 or agonistic anti-CD137 antibodies can promote the rejection of several murine tumors, some poorly immunogenic tumors were refractory to this treatment. In this study, we sought to evaluate whether combined TIM-3 blockade and CD137 activation would significantly improve the immunotherapy in the murine ID8 ovarian cancer model. METHODS: Mice with established ID8 tumor were intraperitoneally injected with single or combined anti-TIM-3/CD137 monoclonal antibody (mAb); mice survival was recorded, the composition and gene expression of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in these mice was analyzed by flow cytometry and quantitative RT-PCR respectively, and the function of CD8(+) cells was evaluated by ELISA and cytotoxicity assay. RESULTS: Either anti-TIM-3 or CD137 mAb alone, although effective in 3 days established tumor, was unable to prevent tumor progression in mice bearing 10 days established tumor, however, combined anti-TIM-3/CD137 mAb significantly inhibited the growth of these tumors with 60% of mice tumor free 90 days after tumor inoculation. Therapeutic efficacy was associated with a systemic immune response with memory and antigen specificity, required CD4(+) cells and CD8(+) cells. The 2 mAb combination increased CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells and decreased immunosuppressive CD4(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells and CD11b(+)Gr-1(+) myeloid suppressor cells (MDSC) at tumor sites, giving rise to significantly elevated ratios of CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells to Treg and MDSC; This is consistent with biasing local immune response towards an immunostimulatory Th1 type and is further supported by quantitative RT-PCR data showing the increased Th1-associated genes by anti-TIM-3/CD137 treatment. The increased CD8(+) T cells produced high level of IFN-gamma upon tumor antigen stimulation and displayed antigen-specific cytotoxic activity. CONCLUSIONS: To our knowledge, this is the first report investigating the effects of anti-TIM-3/CD137 combined mAb in a murine ovarian cancer model, and our results may aid the design of future trials for ovarian cancer immunotherapy.
in vitro B cell negative selection
Flow Cytometry
De Obaldia, M. E., et al (2013). "T cell development requires constraint of the myeloid regulator C/EBP-alpha by the Notch target and transcriptional repressor Hes1" Nat Immunol 14(12): 1277-1284.
PubMed
Notch signaling induces gene expression of the T cell lineage and discourages alternative fate outcomes. Hematopoietic deficiency in the Notch target Hes1 results in severe T cell lineage defects; however, the underlying mechanism is unknown. We found here that Hes1 constrained myeloid gene-expression programs in T cell progenitor cells, as deletion of the myeloid regulator C/EBP-alpha restored the development of T cells from Hes1-deficient progenitor cells. Repression of Cebpa by Hes1 required its DNA-binding and Groucho-recruitment domains. Hes1-deficient multipotent progenitor cells showed a developmental bias toward myeloid cells and dendritic cells after Notch signaling, whereas Hes1-deficient lymphoid progenitor cells required additional cytokine signaling for diversion into the myeloid lineage. Our findings establish the importance of constraining developmental programs of the myeloid lineage early in T cell development.
Flow Cytometry
Purtha, W. E., et al (2012). "Spontaneous mutation of the Dock2 gene in Irf5-/- mice complicates interpretation of type I interferon production and antibody responses" Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(15): E898-904.
PubMed
Genome-wide studies have identified associations between polymorphisms in the IFN regulatory factor-5 (Irf5) gene and a variety of human autoimmune diseases. Its functional role in disease pathogenesis, however, remains unclear, as studies in Irf5(-/-) mice have reached disparate conclusions regarding the importance of this transcription factor in type I IFN production and antibody responses. We identified a spontaneous genomic duplication and frameshift mutation in the guanine exchange factor dedicator of cytokinesis 2 (Dock2) that has arisen in at least a subset of circulating Irf5(-/-) mice and inadvertently been bred to homozygosity. Retroviral expression of DOCK2, but not IRF-5, rescued defects in plasmacytoid dendritic cell and B-cell development, and Irf5(-/-) mice lacking the mutation in Dock2 exhibited normal plasmacytoid dendritic cell and B-cell development, largely intact type I IFN responses, and relatively normal antibody responses to viral infection. Thus, confirmation of the normal Dock2 genotype in circulating Irf5(-/-) mice is warranted, and our data may partly explain conflicting results in this field.
in vivo B cell depletion
Keren, Z., et al (2011). "B-cell depletion reactivates B lymphopoiesis in the BM and rejuvenates the B lineage in aging" Blood 117(11): 3104-3112.
PubMed
Aging is associated with a decline in B-lymphopoiesis in the bone marrow and accumulation of long-lived B cells in the periphery. These changes decrease the body’s ability to mount protective antibody responses. We show here that age-related changes in the B lineage are mediated by the accumulating long-lived B cells. Thus, depletion of B cells in old mice was followed by expansion of multipotent primitive progenitors and common lymphoid progenitors, a revival of B-lymphopoiesis in the bone marrow, and generation of a rejuvenated peripheral compartment that enhanced the animal’s immune responsiveness to antigenic stimulation. Collectively, our results suggest that immunosenescence in the B-lineage is not irreversible and that depletion of the long-lived B cells in old mice rejuvenates the B-lineage and enhances immune competence.
Flow Cytometry
Purtha, W. E., et al (2011). "Memory B cells, but not long-lived plasma cells, possess antigen specificities for viral escape mutants" J Exp Med 208(13): 2599-2606.
PubMed
Memory B cells (MBCs) and long-lived plasma cells (LLPCs) persist after clearance of infection, yet the specific and nonredundant role MBCs play in subsequent protection is unclear. After resolution of West Nile virus infection in mice, we demonstrate that LLPCs were specific for a single dominant neutralizing epitope, such that immune serum poorly inhibited a variant virus that encoded a mutation at this critical epitope. In contrast, a large fraction of MBC produced antibody that recognized both wild-type (WT) and mutant viral epitopes. Accordingly, antibody produced by the polyclonal pool of MBC neutralized WT and variant viruses equivalently. Remarkably, we also identified MBC clones that recognized the mutant epitope better than the WT protein, despite never having been exposed to the variant virus. The ability of MBCs to respond to variant viruses in vivo was confirmed by experiments in which MBCs were adoptively transferred or depleted before secondary challenge. Our data demonstrate that class-switched MBC can respond to variants of the original pathogen that escape neutralization of antibody produced by LLPC without a requirement for accumulating additional somatic mutations.
Product Citations
-
-
Neuroscience
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Opioid-expressing B Cells Silence Tumor-infiltrating Nociceptor Neurons
In Research Square on 3 September 2025 by Talbot, S., Eichwald, T., et al.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Gene Therapy with Enterovirus 3 C Protease: A Promising Strategy for Various Solid Tumors.
In Nat Commun on 8 May 2025 by Yang, X., Li, W., et al.
PubMed
Current cancer gene therapies rely primarily on antitumor immunity, but the exploration of alternative mRNA cargoes for direct antitumor effects is crucial to expand cancer gene therapies. Here we show that lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) carrying mRNA encoding a viral 3 C protease can efficiently suppress tumors by selectively inducing tumor cell apoptosis. In various solid tumor models, intracranial injection of LNPs carrying mRNA encoding the 3 C protease (3C-LNPs) significantly inhibits tumor growth and prolongs survival in glioblastoma models. Similarly, subcutaneous injection reduces tumor volume and inhibits angiogenesis in a breast cancer model, while intravenous injection inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis and prolongs survival in hepatocellular carcinoma models. Mass spectrometry and cleavage site prediction assays identify heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1) as the main target degraded by the 3 C protease. This study suggests that viral protease mRNA could be a promising broad-spectrum antitumor therapeutic.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
Inhibitors of oncogenic Kras specifically prime CTLA4 blockade to transcriptionally reprogram Tregs and overcome resistance to suppress pancreas cancer
In bioRxiv on 4 March 2025 by Mahadevan, K. K., Maldonado, A. S., et al.
-
-
Reduction of circulating IgE and allergens by a pH-sensitive antibody with enhanced FcγRIIb binding.
In Mol Ther on 2 October 2024 by Li, N., Gong, N., et al.
PubMed
Allergen-crosslinked IgE triggers allergy by interacting with its receptor on basophils and mast cells. The anti-IgE monoclonal antibody omalizumab can alleviate allergy by competing with the receptor for IgE binding. However, along with neutralization, omalizumab also inhibits IgE degradation, which is clinically associated with high-dose and total IgE accumulation problems. In this study, we have developed an IgE-eliminating antibody on the basis of omalizumab, which has pH-dependent Fabs and an Fc with high affinity for FcγRIIb. In mice, the antibody rapidly eliminated total serum IgE to baseline levels and caused lower free IgE levels than omalizumab. At low dosages, the antibody also exhibited favorable IgE elimination effects. In addition, the antibody can degrade the corresponding allergen with the removal of IgE, addressing the allergy from its source. Introduction of the M252Y/S254T/T256E (YTE) mutation into this antibody prolongs its serum half-life without reducing potency. Thus, this engineered antibody holds a promising therapeutic option for allergy patients. Mechanistic insights are also included in this study.
-
A rationally designed CD19 monoclonal antibody-triptolide conjugate for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
In Acta Pharm Sin B on 1 October 2024 by Wang, L., Yin, H., et al.
PubMed
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F (TWHF) is a traditional Chinese medicine widely used in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with triptolide (TP) as its main active ingredient. However, its side effects also induced by TP, especially hepatotoxicity and reproductive toxicity, largely limit its application in a subset of patients. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) developed for the treatment of SLE that deplete B cells by targeting B cell-expressing antigens, such as CD19, have failed in clinical trials, partly due to their poor efficacy in consuming B cells. Here, we report the development of a rationally designed antibody‒drug conjugate (ADC), CD19 mAb-TP conjugate, to alleviate the side effects of TWHF and simultaneously improve the therapeutic efficacy of CD19 mAb. The CD19 mAb-TP conjugate, which was named ADC-TP, selectively depleted B cell subsets both in vitro and in vivo and effectively alleviated disease symptoms in mouse lupus models with enhanced therapeutic efficacy than CD19 mAb and fewer side effects than TP. Our present study proposes a CD19 mAb‒TP conjugate strategy to mitigate the toxicity of TWHF while also enhancing the therapeutical efficacy of CD19 mAbs for the treatment of SLE, providing a feasible method for improving the current agents used for treating SLE.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
Fasting reshapes tissue-specific niches to improve NK cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity.
In Immunity on 13 August 2024 by Delconte, R. B., Owyong, M., et al.
PubMed
Fasting is associated with improved outcomes in cancer. Here, we investigated the impact of fasting on natural killer (NK) cell anti-tumor immunity. Cyclic fasting improved immunity against solid and metastatic tumors in an NK cell-dependent manner. During fasting, NK cells underwent redistribution from peripheral tissues to the bone marrow (BM). In humans, fasting also reduced circulating NK cell numbers. NK cells in the spleen of fasted mice were metabolically rewired by elevated concentrations of fatty acids and glucocorticoids, augmenting fatty acid metabolism via increased expression of the enzyme CPT1A, and Cpt1a deletion impaired NK cell survival and function in this setting. In parallel, redistribution of NK cells to the BM during fasting required the trafficking mediators S1PR5 and CXCR4. These cells were primed by an increased pool of interleukin (IL)-12-expressing BM myeloid cells, which improved IFN-γ production. Our findings identify a link between dietary restriction and optimized innate immune responses, with the potential to enhance immunotherapy strategies.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Intranodal Injection of Immune Activator Demonstrates Antitumor Efficacy in an Adjuvant Approach.
In Vaccines (Basel) on 26 March 2024 by Josi, R., Ogrina, A., et al.
PubMed
The tumor-draining lymph nodes (tdLN) are the initial site of metastases and are the prime site for generating robust antitumor responses. In this study, we explored the efficacy of a universal immune activator (ImmAct) targeted to the tdLN. This approach can be viewed as an attempt to turn a cold, unresponsive tdLN into a hot, responsive site. The adjuvant antitumor efficacy of our novel intranodal injection was evaluated in an aggressive metastatic mammary carcinoma murine model. The cancer cells were inoculated subcutaneously in the lower quadrant of the mouse to provoke the tdLN (inguinal lymph node). The study encompasses a range of methodologies, including in vivo and in vitro assays and high-dimensional flow cytometry analysis. Our findings demonstrated that intranodal administration of ImmAct following the dissection of the primary tumor led to improved tumor-free survival and minimized weight loss. ImmAct led to both local and systemic alterations in the cellular and humoral immunity. Additionally, after ImmAct treatment, non-responders showed a higher rate of exhausted CD8+ T cells compared to responders. Indeed, our innovative approach surpassed the gold standard surgery of sentinel lymph node excision. Overall, intranodal administration of ImmAct yielded a robust antitumor immune response, offering protection against micrometastases and relapse.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Type 1 interferons and Foxo1 down-regulation play a key role in age-related T-cell exhaustion in mice.
In Nat Commun on 26 February 2024 by Durand, A., Bonilla, N., et al.
PubMed
Foxo family transcription factors are critically involved in multiple processes, such as metabolism, quiescence, cell survival and cell differentiation. Although continuous, high activity of Foxo transcription factors extends the life span of some species, the involvement of Foxo proteins in mammalian aging remains to be determined. Here, we show that Foxo1 is down-regulated with age in mouse T cells. This down-regulation of Foxo1 in T cells may contribute to the disruption of naive T-cell homeostasis with age, leading to an increase in the number of memory T cells. Foxo1 down-regulation is also associated with the up-regulation of co-inhibitory receptors by memory T cells and exhaustion in aged mice. Using adoptive transfer experiments, we show that the age-dependent down-regulation of Foxo1 in T cells is mediated by T-cell-extrinsic cues, including type 1 interferons. Taken together, our data suggest that type 1 interferon-induced Foxo1 down-regulation is likely to contribute significantly to T-cell dysfunction in aged mice.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Cancer Research
KRASG12D inhibition reprograms the microenvironment of early and advanced pancreatic cancer to promote FAS-mediated killing by CD8+ T cells.
In Cancer Cell on 11 September 2023 by Mahadevan, K. K., McAndrews, K. M., et al.
PubMed
The KRASG12D mutation is present in nearly half of pancreatic adenocarcinomas (PDAC). We investigated the effects of inhibiting the KRASG12D mutant protein with MRTX1133, a non-covalent small molecule inhibitor of KRASG12D, on early and advanced PDAC and its influence on the tumor microenvironment. Employing 16 different models of KRASG12D-driven PDAC, we demonstrate that MRTX1133 reverses early PDAC growth, increases intratumoral CD8+ effector T cells, decreases myeloid infiltration, and reprograms cancer-associated fibroblasts. MRTX1133 leads to regression of both established PanINs and advanced PDAC. Regression of advanced PDAC requires CD8+ T cells and immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) synergizes with MRTX1133 to eradicate PDAC and prolong overall survival. Mechanistically, inhibition of KRASG12D in advanced PDAC and human patient derived organoids induces FAS expression in cancer cells and facilitates CD8+ T cell-mediated death. Collectively, this study provides a rationale for a synergistic combination of MRTX1133 with ICB in clinical trials.
-
-
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Inhalable SARS-CoV-2 vaccine for single-dose dry powder aerosol immunization
In Research Square on 8 September 2023 by Ye, T., Jiao, Z., et al.
-
-
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Immune profiling of adeno-associated virus response identifies B cell-specific targets that enable vector re-administration in mice.
In Gene Ther on 1 May 2023 by Chen, M., Kim, B., et al.
PubMed
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector-based gene therapies can be applied to a wide range of diseases. AAV expression can last for months to years, but vector re-administration may be necessary to achieve life-long treatment. Unfortunately, immune responses against these vectors are potentiated after the first administration, preventing the clinical use of repeated administration of AAVs. Reducing the immune response against AAVs while minimizing broad immunosuppression would improve gene delivery efficiency and long-term safety. In this study, we quantified the contributions of multiple immune system components of the anti-AAV response in mice. We identified B-cell-mediated immunity as a critical component preventing vector re-administration. Additionally, we found that IgG depletion alone was insufficient to enable re-administration, suggesting IgM antibodies play an important role in the immune response against AAV. Further, we found that AAV-mediated transduction is improved in µMT mice that lack functional IgM heavy chains and cannot form mature B-cells relative to wild-type mice. Combined, our results suggest that B-cells, including non-class switched B-cells, are a potential target for therapeutics enabling AAV re-administration. Our results also suggest that the µMT mice are a potentially useful experimental model for gene delivery studies since they allow repeated dosing for more efficient gene delivery from AAVs.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
GPR55 in B cells limits atherosclerosis development and regulates plasma cell maturation.
In Nat Cardiovasc Res on 1 November 2022 by Guillamat-Prats, R., Hering, D., et al.
PubMed
Dissecting the pathways regulating the adaptive immune response in atherosclerosis is of particular therapeutic interest. Here we report that the lipid G-protein coupled receptor GPR55 is highly expressed by splenic plasma cells (PC), upregulated in mouse spleens during atherogenesis and human unstable or ruptured compared to stable plaques. Gpr55-deficient mice developed larger atherosclerotic plaques with increased necrotic core size compared to their corresponding controls. Lack of GPR55 hyperactivated B cells, disturbed PC maturation and resulted in immunoglobulin (Ig)G overproduction. B cell-specific Gpr55 depletion or adoptive transfer of Gpr55-deficient B cells was sufficient to promote plaque development and elevated IgG titers. In vitro, the endogenous GPR55 ligand lysophsophatidylinositol (LPI) enhanced PC proliferation, whereas GPR55 antagonism blocked PC maturation and increased their mitochondrial content. Collectively, these discoveries provide previously undefined evidence for GPR55 in B cells as a key modulator of the adaptive immune response in atherosclerosis.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Tumor-infiltrated activated B cells suppress liver metastasis of colorectal cancers.
In Cell Rep on 30 August 2022 by Xu, Y., Wei, Z., et al.
PubMed
More than 40% of patients with late-stage colorectal cancer (CRC) develop liver metastasis (LM). Which immune cells play important roles in CRC-LM and contribute to the difference between left-sided CRC (LCC) and right-sided CRC (RCC) remain unclear. By single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), we not only find that activated B cells are significantly depleted in CRC with LM, but also find a subtype of B cells developed from activated B cells, namely immature plasma cell population alpha (iMPA), highly correlated with metastasis. Mechanistically, inhibition of the Wnt and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pathways in cancer cell promotes activated B cell migration via the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. This study reveals that B cell subpopulations in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) play a key role in CRC-LM as well as in LCC and RCC. The preventive effects of modulating B cell subpopulations in CRC may provide a rationale for subsequent drug development and CRC-LM management.
-
-
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
B Cells Are Required to Generate Optimal Anti-Melanoma Immunity in Response to Checkpoint Blockade.
In Front Immunol on 21 June 2022 by Singh, S., Roszik, J., et al.
PubMed
Immunotherapies such as checkpoint blockade therapies are known to enhance anti-melanoma CD8+ T cell immunity, but only a fraction of patients treated with these therapies achieve durable immune response and disease control. It may be that CD8+ T cells need help from other immune cells to generate effective and long-lasting anti-tumor immunity or that CD8+ T cells alone are insufficient for complete tumor regression and cure. Melanoma contains significant numbers of B cells; however, the role of B cells in anti-melanoma immunity is controversial. In this study, B16 melanoma mouse models were used to determine the role of B cells in anti-melanoma immunity. C57BL/6 mice, B cell knockout (KO) C57BL/6 mice, anti-CD19, and anti-CXCL13 antibody-treated C57BL/6 mice were used to determine treatment efficacy and generation of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in response to PD-L1 blockade alone or combination with TLR-7/8 activation. Whole transcriptome analysis was performed on the tumors from B cell depleted and WT mice, untreated or treated with anti-PD-L1. Both CD40-positive and CD40-negative B cells were isolated from tumors of TLR-7/8 agonist-treated wild-type mice and adoptively transferred into tumor-bearing B cell KO mice, which were treated with anti-PD-L1 and TLR-7/8 agonist. Therapeutic efficacy was determined in the presence of activated or inactivated B cells. Microarray analysis was performed on TLR-7/8-treated tumors to look for the B cell signatures. We found B cells were required to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of monotherapy with anti-PD-L1 antibody and combination therapy with anti-PD-L1 antibody plus TLR-7/8 agonist. However, B cells were not essential for anti-CTLA-4 antibody activity. Interestingly, CD40-positive but not CD40-negative B cells contributed to anti-melanoma immunity. In addition, melanoma patients' TCGA data showed that the presence of B cell chemokine CXCL13 and B cells together with CD8+ T cells in tumors were strongly associated with improved overall survival. Our transcriptome data suggest that the absence of B cells enhances immune checkpoints expression in the tumors microenvironment. These results revealed the importance of B cells in the generation of effective anti-melanoma immunity in response to PD-1-PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy. Our findings may facilitate the design of more effective anti-melanoma immunotherapy.
-
-
Targeted immunosuppression enhances repeated gene delivery
In Research Square on 1 March 2022 by Chen, M., Kim, B., et al.
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
GPR55 in B cells limits atherosclerosis development and regulates plasma cell maturation
In Research Square on 12 January 2022 by Guillamat-Prats, R., Hering, D., et al.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
GPR55 in B cells limits atherosclerosis development and regulates plasma cell maturation
In bioRxiv on 21 December 2021 by Guillamat-Prats, R., Hering, D., et al.
-
-
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals B cell-related molecular biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease.
In Exp Mol Med on 1 December 2021 by Xiong, L. L., Xue, L. L., et al.
PubMed
In recent years, biomarkers have been integrated into the diagnostic process and have become increasingly indispensable for obtaining knowledge of the neurodegenerative processes in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in human blood have been reported to participate in a variety of neurodegenerative activities. Here, a single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of PBMCs from 4 AD patients (2 in the early stage, 2 in the late stage) and 2 normal controls was performed to explore the differential cell subpopulations in PBMCs of AD patients. A significant decrease in B cells was detected in the blood of AD patients. Furthermore, we further examined PBMCs from 43 AD patients and 41 normal subjects by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), and combined with correlation analysis, we found that the reduction in B cells was closely correlated with the patients' Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) scores. To confirm the role of B cells in AD progression, functional experiments were performed in early-stage AD mice in which fibrous plaques were beginning to appear; the results demonstrated that B cell depletion in the early stage of AD markedly accelerated and aggravated cognitive dysfunction and augmented the Aβ burden in AD mice. Importantly, the experiments revealed 18 genes that were specifically upregulated and 7 genes that were specifically downregulated in B cells as the disease progressed, and several of these genes exhibited close correlation with AD. These findings identified possible B cell-based AD severity, which are anticipated to be conducive to the clinical identification of AD progression.
-
-
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Statins act as transient type I interferon inhibitors to enable the antitumor activity of modified vaccinia Ankara viral vectors.
In J Immunother Cancer on 1 July 2021 by Tenesaca, S., Vásquez, M., et al.
PubMed
Modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) are genetically engineered non-replicating viral vectors. Intratumoral administration of MVA induces a cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-mediated type I interferon (IFN) response and the production of high levels of the transgenes engineered into the viral genome such as tumor antigens to construct cancer vaccines. Although type I IFNs are essential for establishing CD8-mediated antitumor responses, this cytokine family may also give rise to immunosuppressive mechanisms.
-
-
-
In vitro experiments
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lactate dehydrogenase A-dependent aerobic glycolysis promotes natural killer cell anti-viral and anti-tumor function.
In Cell Rep on 1 June 2021 by Sheppard, S., Santosa, E. K., et al.
PubMed
Natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic lymphocytes capable of rapid cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion, and clonal expansion. To sustain such energetically demanding processes, NK cells must increase their metabolic capacity upon activation. However, little is known about the metabolic requirements specific to NK cells in vivo. To gain greater insight, we investigated the role of aerobic glycolysis in NK cell function and demonstrate that their glycolytic rate increases rapidly following viral infection and inflammation, prior to that of CD8+ T cells. NK cell-specific deletion of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) reveals that activated NK cells rely on this enzyme for both effector function and clonal proliferation, with the latter being shared with T cells. As a result, LDHA-deficient NK cells are defective in their anti-viral and anti-tumor protection. These findings suggest that aerobic glycolysis is a hallmark of NK cell activation that is key to their function.
-