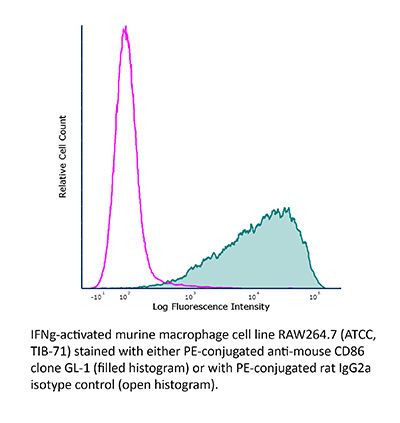
FlowMAb PE anti-mouse CD86 (B7-2)
Product Description
Specifications
| Isotype | Rat IgG2a, κ |
|---|---|
| Recommended Isotype Control(s) | FlowMAb PE rat IgG2a isotype control, anti-trinitrophenol |
| Conjugation | PE |
| Excitation Source | Yellow-Green 488 nm, 532 nm, 561 nm |
| Excitation Max | 496 nm, 566 nm |
| Emission Max | 576 nm |
| Immunogen | LPS-activated CBA/Ca mouse splenic B cells |
| Reported Applications | Flow cytometry |
| Protocol Information | It is recommended that the reagent be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. |
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/ml |
| Formulation |
PBS, pH 7.0 Contains 0.09% Sodium Azide |
| Production | Purified from cell culture supernatant in an animal-free facility |
| Purification | Protein G. Conjugated with R-phycoerythrin under optimal conditions. |
| Storage | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze. |
| Need a Custom Formulation? | See All Antibody Customization Options |
Application References
Flow Cytometry
Moser, E. K., et al. (2014). "Late engagement of CD86 after influenza virus clearance promotes recovery in a FoxP3+ regulatory T cell dependent manner" PLoS Pathog 10(8): e1004315.
PubMed
Influenza A virus (IAV) infection in the respiratory tract triggers robust innate and adaptive immune responses, resulting in both virus clearance and lung inflammation and injury. After virus clearance, resolution of ongoing inflammation and tissue repair occur during a distinct recovery period. B7 family co-stimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 have important roles in modulating T cell activity during the initiation and effector stages of the host response to IAV infection, but their potential role during recovery and resolution of inflammation is unknown. We found that antibody-mediated CD86 blockade in vivo after virus clearance led to a delay in recovery, characterized by increased numbers of lung neutrophils and inflammatory cytokines in airways and lung interstitium, but no change in conventional IAV-specific T cell responses. However, CD86 blockade led to decreased numbers of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs), and adoptive transfer of Tregs into alphaCD86 treated mice rescued the effect of the blockade, supporting a role for Tregs in promoting recovery after virus clearance. Specific depletion of Tregs late after infection mimicked the CD86 blockade phenotype, confirming a role for Tregs during recovery after virus clearance. Furthermore, we identified neutrophils as a target of Treg suppression since neutrophil depletion in Treg-depleted mice reduced excess inflammatory cytokines in the airways. These results demonstrate that Tregs, in a CD86 dependent mechanism, contribute to the resolution of disease after IAV infection, in part by suppressing neutrophil-driven cytokine release into the airways.